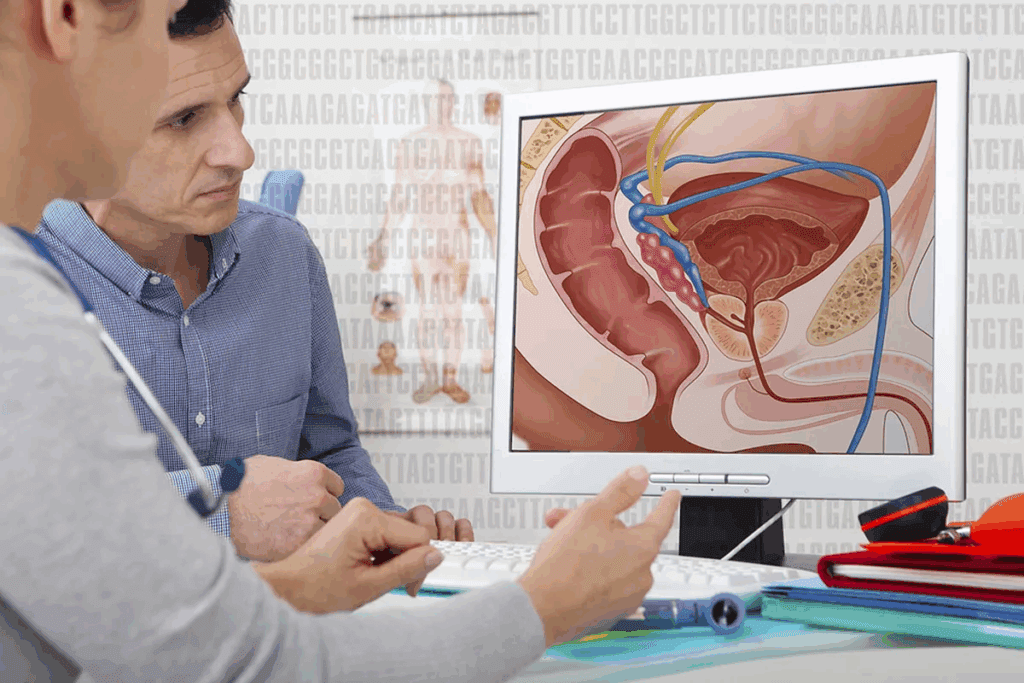
Enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is a common issue for men as they get older. It happens when the prostate gland grows too big. This can cause problems with urination.How to find the best enlarged prostate doctor for BPH treatment? Use our guide to choose a urologist specializing in your needs.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact reason for an enlarged prostate isn’t known. But, it’s thought to be linked to hormonal changes that come with aging. Family history and lifestyle might also influence it.
Symptoms
Symptoms of an enlarged prostate include trouble starting to urinate and a weak urine flow. Men may also find themselves needing to urinate more often. These issues can really affect a man’s life quality.
Treatment Options
Treatment for an enlarged prostate varies. It can start with simple changes like diet and exercise. There are also medicines like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors to help symptoms.
What Causes an Enlarged Prostate?
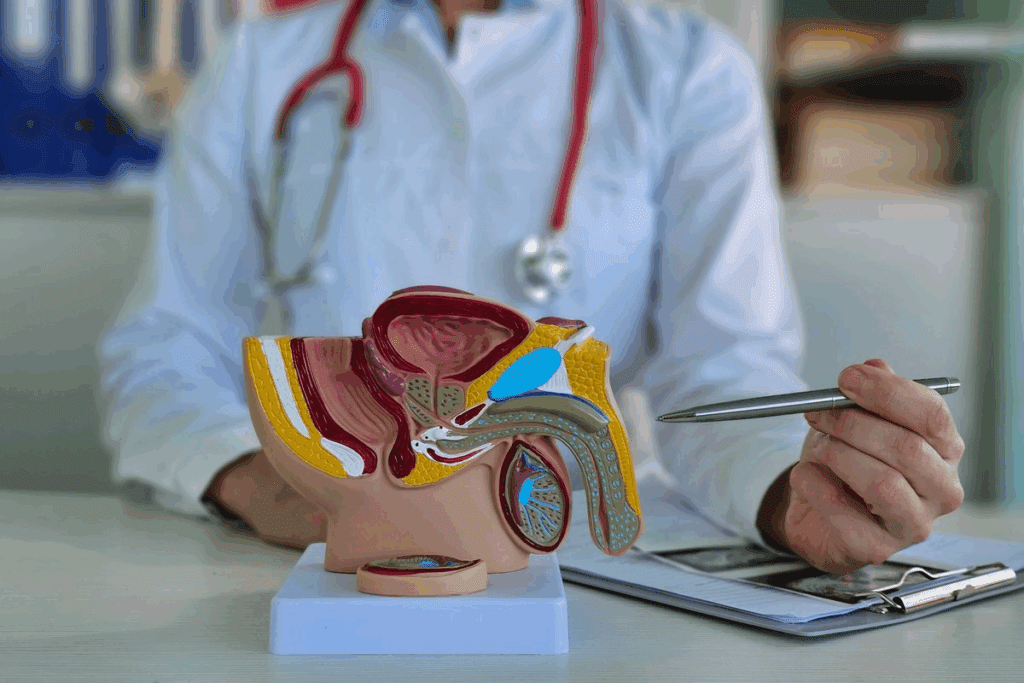
An enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is common in older men. It’s caused by age and hormonal changes.
Men over 50 are more likely to get an enlarged prostate. Hormonal shifts, like testosterone turning into DHT, also contribute to BPH.
Knowing what causes an enlarged prostate helps in managing it. It also helps in reducing its symptoms.
Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
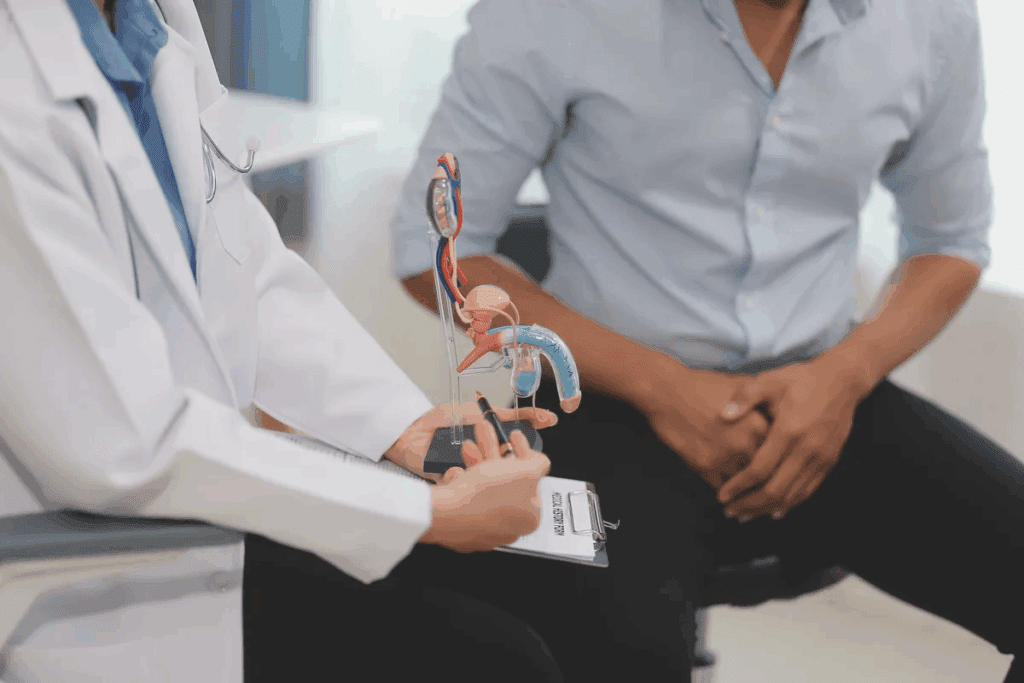
An enlarged prostate can cause many urinary and other symptoms. These symptoms can really affect a man’s life. They can change how he urinates, making daily tasks harder.
Some common symptoms are frequent urination, weak or interrupted urine flow, and difficulty starting urination. Men might also feel pain while urinating or a feeling of incomplete bladder emptying. These symptoms can get worse if not treated.
Complications of Untreated Enlarged Prostate
Not treating an enlarged prostate can lead to serious problems. These can include urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder stones, and bladder damage.
It can also cause acute urinary retention, where a man can’t urinate. This is a serious issue that needs quick medical help. Also, there’s a higher risk of prostate cancer, even though an enlarged prostate isn’t cancer itself.
Knowing these risks shows why it’s key to see a doctor if symptoms don’t go away. Early treatment can help a lot and lower the chance of these problems.
Diagnosing Enlarged Prostate
To diagnose an enlarged prostate, doctors use several steps. They start by looking at the patient’s medical history and symptoms. This helps them find any risk factors or past health issues that might be linked to the problem.
A digital rectal examination (DRE) is a key part of this process. In a DRE, a doctor checks the prostate gland by inserting a finger into the rectum. This helps find out if the prostate is too big or has any other issues.
Doctors also do blood tests like the Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test. This test checks the PSA levels in the blood. High levels can mean an enlarged prostate or even cancer. While it’s not a sure sign on its own, it’s very helpful when used with other tests.
Imaging tests might also be suggested to look closer at the prostate. Ultrasound is often used for this. It gives clear pictures of the prostate, helping doctors see its size and any problems.
The table below shows the main ways doctors diagnose an enlarged prostate:
| Diagnostic Approach | Description | Purpose |
| Medical History | Evaluation of symptoms and previous medical conditions | Identify risk factors and relevant conditions |
| Digital Rectal Examination (DRE) | Physical examination to assess prostate size and texture | Identify abnormalities or enlargement |
| PSA Testing | Blood test to measure Prostate-Specific Antigen levels | Assess for possible prostate issues, including cancer |
| Ultrasound | Imaging test to check prostate size and find any issues | Give detailed images for diagnosis and assessment |
By using these methods together, doctors can accurately find out if a prostate is enlarged. Then, they can create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
Managing an enlarged prostate means knowing your treatment choices. These range from simple watchful waiting to more complex surgeries. We’ll dive into each option to guide you in making the right health decisions.
For many, the first step is regular check-ups to monitor the condition. This is often advised for those with mild symptoms or when the condition doesn’t affect daily life much.
When symptoms worsen, medications can help. Doctors often prescribe alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Alpha-blockers relax muscles in the prostate and bladder neck, easing urination. 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors shrink the prostate by blocking DHT, a hormone that promotes prostate growth.
Lifestyle changes are also key in managing symptoms. Eating less caffeine and alcohol and more fruits and veggies can help. Regular exercise and stress-reducing activities like meditation or yoga also support prostate health.
In severe cases, surgery might be needed. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is a common surgery to remove excess tissue. Other options include laser surgery and open prostatectomy, though these are less common.
Knowing the various treatment options is vital for managing an enlarged prostate. By working with your healthcare provider, you can find the best treatment for your specific situation.
Lifestyle Changes for Managing Enlarged Prostate
Making lifestyle changes is key to managing enlarged prostate symptoms. Simple changes in daily life can help ease symptoms and improve your overall well-being.
Eating a diet full of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help. These foods are packed with antioxidants, fiber, and nutrients that boost health. Try to eat a variety of colorful fruits and veggies to get the most benefits.
Regular physical activity is also vital. Exercise can improve your health, lessen symptoms, and make you feel better. Walking, cycling, or swimming are great choices.
Stress management is another important part of managing enlarged prostate. Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help. Chronic stress can make prostate issues worse, so managing stress is key.
| Lifestyle Change | Benefit |
| Diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains | Alleviates symptoms, supports overall health |
| Regular physical activity | Improves overall health, reduces symptoms |
| Stress management techniques | Reduces symptoms, enhances well-being |
By making these lifestyle changes, you can actively manage your enlarged prostate symptoms. Always talk to a healthcare provider before starting any new lifestyle changes or treatments.
Medications for Enlarged Prostate
Treating an enlarged prostate requires lifestyle changes and medicines. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are key medicines used.
Alpha-Blockers
Alpha-blockers help relax the prostate and bladder muscles. This makes it easier to pee. They quickly ease symptoms like a weak urine flow.
5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors
These medicines shrink the prostate gland. They help reduce symptoms over time. They work best for men with bigger prostates.
Knowing about these treatments helps people make better choices for their health.
Surgical Options for Enlarged Prostate
There are several surgical options for an enlarged prostate. These include transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), open prostatectomy, and laser surgery. These methods aim to ease symptoms like urinary retention and boost quality of life.
The right surgery depends on how severe the condition is and the patient’s health. Each option has its own benefits and considerations.
Alternative Therapies for Enlarged Prostate
Men with enlarged prostate may find alternative therapies helpful. Saw palmetto is one option that has been studied. It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional before trying new supplements.
Understanding Prostate Health and Enlarged Prostate
Prostate health is key for men’s well-being. Keeping the prostate healthy can greatly improve life quality. Issues with the prostate can be minor or serious, like prostate cancer.
It’s important for men to know about prostate health. They should be aware of symptoms and treatment options. This is even more critical as men get older.
Causes and Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
It’s important to know about enlarged prostate causes and symptoms. As men get older, their prostate gland can grow. This can lead to urinary issues.
The exact reason for an enlarged prostate, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), is not known. But, several things can make it happen. Age is a big factor, with BPH being rare in men under 40 but common with age.
Other risk factors include:
- Family history: Men with a family history of BPH are more likely to develop the condition.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk.
- Diabetes: Men with diabetes are at higher risk.
- Lack of physical activity: Sedentary lifestyle may contribute to the development of BPH.
Symptoms of an enlarged prostate can vary but often include:
- Weak or interrupted urine flow.
- Frequent urination, specially at night.
- Difficulty starting urination.
- Dribbling of urine.
Spotting these symptoms early can help get medical help sooner. This can lower the risk of serious problems.
We suggest talking to a healthcare professional. They can give a proper diagnosis and a treatment plan that fits your needs.
Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
Managing an enlarged prostate needs a full plan. This includes lifestyle changes, medicines, and sometimes surgery. We make sure each treatment fits the person best, aiming for the best results.
Managing Enlarged Prostate through Lifestyle
Changing your lifestyle can help a lot. Drinking less water at night, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and doing pelvic floor exercises can make a big difference. It’s best to talk to a doctor to create a plan that works for you.
Medications for Symptom Relief
There are many medicines to help with enlarged prostate. Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help relax the prostate and shrink it. We help find the right medicine for you, making sure it works well and has few side effects.
FAQ
What are the common causes of an enlarged prostate?
A diet full of fat, not enough exercise, and being overweight can lead to an enlarged prostate. This condition is also known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
How is an enlarged prostate diagnosed?
We use several tests to diagnose an enlarged prostate. These include blood tests like PSA testing and imaging tests like ultrasound. These help us check the prostate gland.
What are the treatment options for an enlarged prostate?
We offer many treatment options. These include making lifestyle changes, like eating right and exercising. We also have medications and surgeries, like Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), to remove extra tissue.
Can lifestyle changes help manage enlarged prostate symptoms?
Yes, making lifestyle changes can help. This includes changing your diet, exercising, and managing stress. Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can also help.
What is the role of stress management in managing enlarged prostate?
Stress management is important. Techniques like meditation or deep breathing can help reduce symptoms of an enlarged prostate.
Are there alternative therapies available for enlarged prostate?
Yes, we offer alternative therapies as part of a treatment plan. They help manage an enlarged prostate.
How can I check if I have an enlarged prostate?
For a proper diagnosis, see a healthcare professional. They will do a physical exam, ask about your medical history, and run tests. This will tell if you have an enlarged prostate gland or BPH.
What is the difference between an enlarged prostate and prostate cancer?
An enlarged prostate, or BPH, is not cancerous. It’s a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate. Prostate cancer is different and more serious.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How to Find the Right Doctor for Enlarged. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9005727/)




































