Last Updated on November 25, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
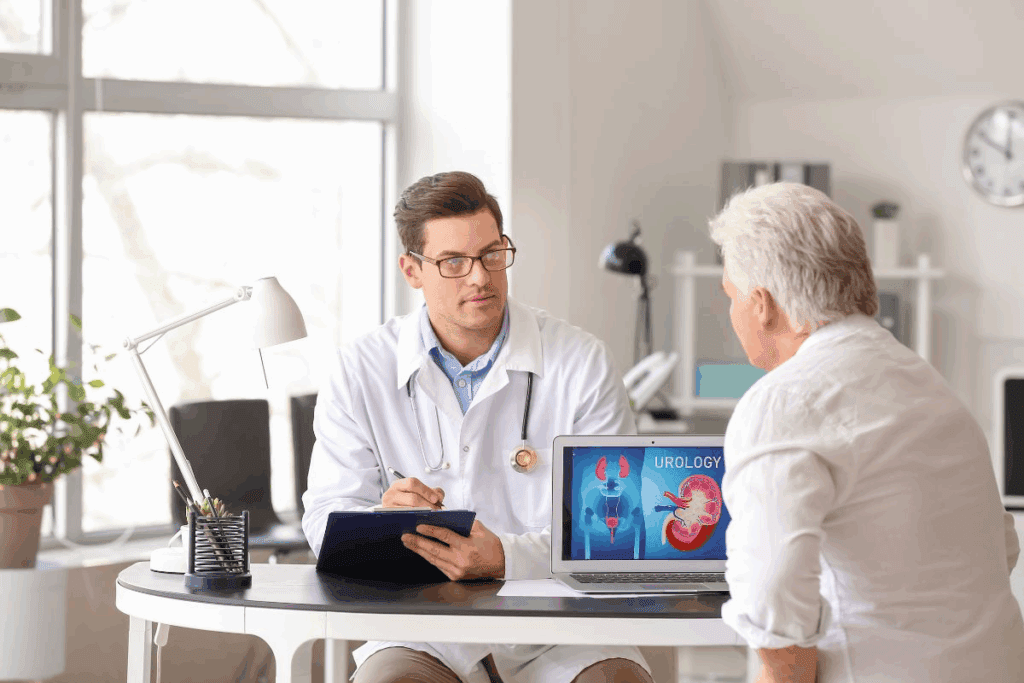

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia, or BPH, is a common issue in older men. It happens when the prostate gland gets bigger. To diagnose BPH, doctors do a detailed medical check-up.
How is a BPH diagnostic performed by a urologist? Learn about the key tests, common symptoms, and prevention strategies for BPH.
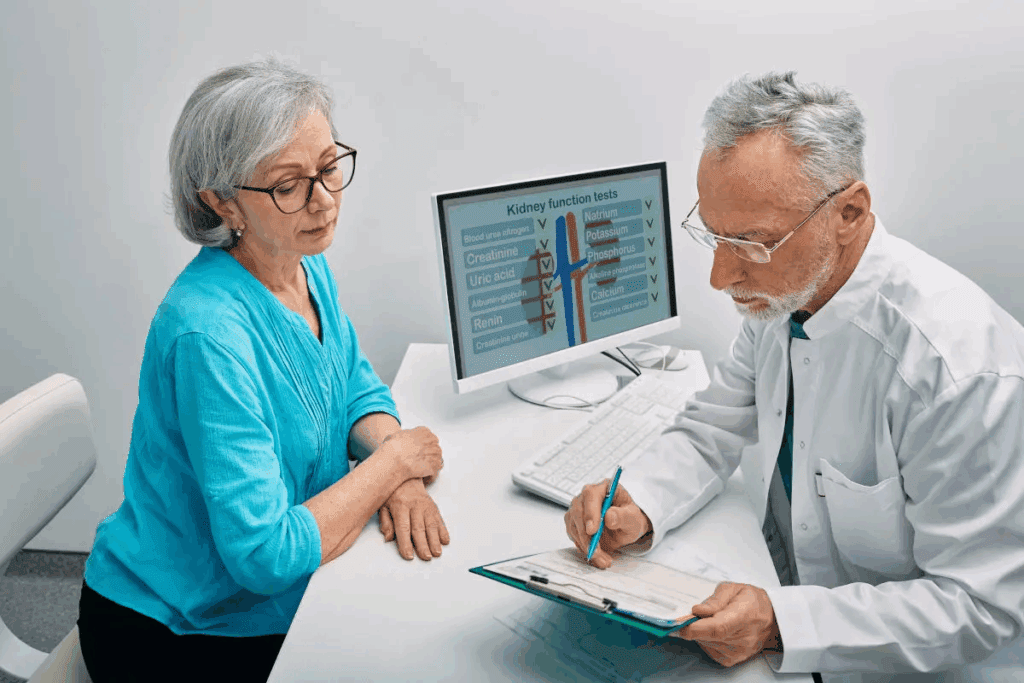

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue for men as they get older. The exact reason for BPH isn’t fully known. But, several factors are known to help it grow.
Age is a big risk factor, with BPH becoming more common after 40. Hormonal changes, like testosterone turning into DHT, also play a big part.
Family history is another key factor. Men with a family history of BPH are more likely to get it too.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Age | Increases with age, specially after 40 |
| Family History | Men with a family history are more likely to develop BPH |
| Hormonal Changes | Conversion of testosterone to DHT contributes to BPH development |
Knowing these risk factors helps in spotting and managing BPH early.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue for men as they get older. It’s important to know the signs early on. Symptoms include weak urine flow, needing to urinate often, waking up to use the bathroom, and trouble starting to urinate.
If you notice any of these signs, see a doctor right away. They can help figure out what’s going on and find the right treatment. Catching it early can make a big difference in how you feel.
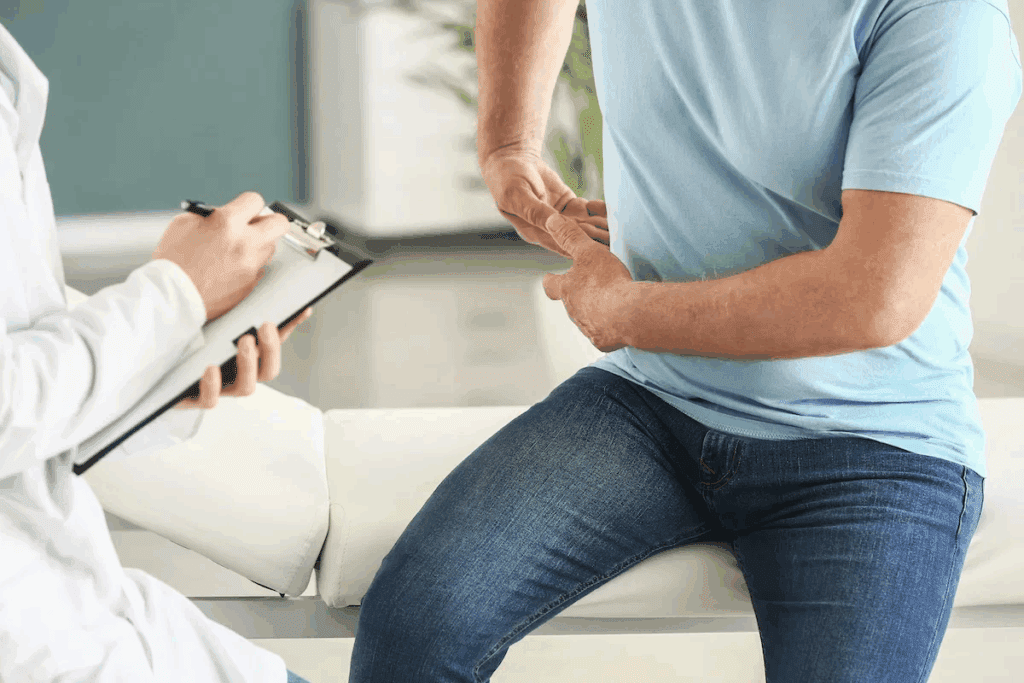

Diagnosing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) involves several tests. These help find out if someone has BPH and how bad it is. The process includes a detailed medical history, a physical check-up, and various tests.
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical exam. The doctor will ask about symptoms like how often you need to pee, how urgent it is, and if your urine flow is weak. This helps them understand your situation better.
There are several tests to confirm BPH. These include:
By looking at the results of these tests, doctors can accurately diagnose BPH. They can then create a treatment plan that fits the person’s needs.
It’s important to know the different ways to treat BPH. The right choice depends on how bad your symptoms are, your overall health, and what you prefer.
For those with mild symptoms, watchful waiting might be suggested. This means keeping an eye on your symptoms and only getting treatment if they get worse. Regular visits to your doctor are key to catching any changes early.
Medications are a common treatment. There are two main kinds: alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. Alpha-blockers help relax the muscles in your prostate and bladder neck, making it easier to pee. 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors help shrink your prostate over time.
Changing your lifestyle can also help manage BPH symptoms. This includes eating differently, like drinking less water before bed. Also, try to avoid things that can irritate your bladder, like caffeine and alcohol.
Being proactive about your BPH means learning about these treatment options. Talk to your doctor to figure out the best plan for you.
Making a few simple changes can help with Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). Eating a balanced diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains is key. This can help manage the condition.
Eating foods high in antioxidants, like berries, is good. Try to eat a variety of fruits and vegetables.
Regular exercise, like brisk walking or cycling, can help. Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise each day.
Too much stress can make symptoms worse. Try stress-reducing activities like meditation or deep breathing.
By making these simple changes, you can manage your condition better. This can improve your quality of life.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common issue for men as they get older. Luckily, there are many medicines to help manage its symptoms.
Alpha-blockers relax the muscles in the prostate and bladder neck. This makes it easier to pee. Alfuzosin and tamsulosin are examples.
5-alpha-reductase inhibitors shrink the prostate gland. This can improve urine flow. Finasteride and dutasteride are common ones.
For severe symptoms, doctors might prescribe a mix of alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. This combo can be more effective.
While most BPH medicines are safe, they can have side effects. Common ones include dizziness, feeling lightheaded, and a decrease in libido. Always talk to a healthcare provider about possible side effects.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) makes the prostate gland grow bigger. This can lead to urinary problems in men. If other treatments don’t work, surgery might be needed.
There are several ways to treat BPH with surgery. These include Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP), Transurethral Incision of the Prostate (TUIP), and Open Prostatectomy.
TURP: This is a common surgery for BPH. It removes prostate tissue blocking urine flow. The surgery is done under general or spinal anesthesia.
TUIP: This is less invasive than TURP. It makes small cuts in the prostate to ease pressure on the urethra.
Open Prostatectomy: This is more invasive, used for bigger prostates. It involves an incision in the lower abdomen to reach the prostate.
Each surgery has its own benefits and risks. The right choice depends on the symptoms, prostate size, and the patient’s health.
There are other ways to manage Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) apart from traditional treatments.
Eating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can be helpful.
Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can ease symptoms.
Herbal supplements like saw palmetto might help with BPH symptoms.
Managing Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) needs a mix of diet changes, lifestyle tweaks, and knowing when to see a doctor. These steps can help improve life quality and lessen BPH symptoms.
Eating a diet full of fruits, veggies, and whole grains can help with BPH symptoms. Some foods and nutrients are good for the prostate.
Healthy lifestyle choices are key in handling BPH. Regular exercise, keeping a healthy weight, and not smoking can lessen symptoms.
Knowing about BPH and making smart lifestyle choices can help manage it. This improves overall health and well-being.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) can cause several problems if not treated properly. It’s important to know these issues to manage the condition well.
Urinary retention is a big problem with BPH. When the prostate gets bigger, it blocks the urethra. This makes it hard to pee.
BPH raises the chance of UTIs. This is because the bladder doesn’t empty fully. Bacteria can then grow.
Long-term blockage from BPH can harm the bladder. This can lead to worse urinary issues.
Untreated BPH can damage the kidneys. This happens because urine pressure builds up.
Seeing a doctor is key if symptoms get worse. Early treatment can stop these problems and make life better.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a condition that can be managed well. Knowing the causes and symptoms is important. Getting the right treatment can greatly improve your life.
Getting an early diagnosis and managing BPH well is essential. We suggest you take charge of your health. Talk to your doctor and learn about BPH and its treatments.
With your doctor’s help, you can face BPH’s challenges. This way, you can keep your health and well-being at their best.
BPH is when the prostate gland gets bigger. This can lead to urinary problems in men.
Symptoms include weak urine flow and needing to urinate often. You might also wake up a lot at night to go to the bathroom. Other signs are trouble starting or stopping urination and feeling like you can’t empty your bladder fully.
Doctors use a mix of medical history, physical exams, and tests. These include a digital rectal exam, PSA test, and urodynamic tests.
Options include watching it, taking medications, or surgery. Surgical choices are TURP or open prostatectomy.
There’s no sure way to stop BPH. But, a healthy lifestyle can lower your risk.
Untreated BPH can cause urinary retention and damage to the bladder and kidneys.
BPH can really affect a man’s life. It can disrupt daily activities, sleep, and overall well-being.
Yes, there are alternatives like diet changes and stress management. Herbal supplements like saw palmetto are also options. But, always talk to a doctor first.
Yes, medications like alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors can help with BPH symptoms.
If you have symptoms like weak urine flow or needing to urinate often, see a doctor. They can help figure out what’s going on and treat it.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How Is BPH Diagnosed in Urology Understanding Tests. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK558920/
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!