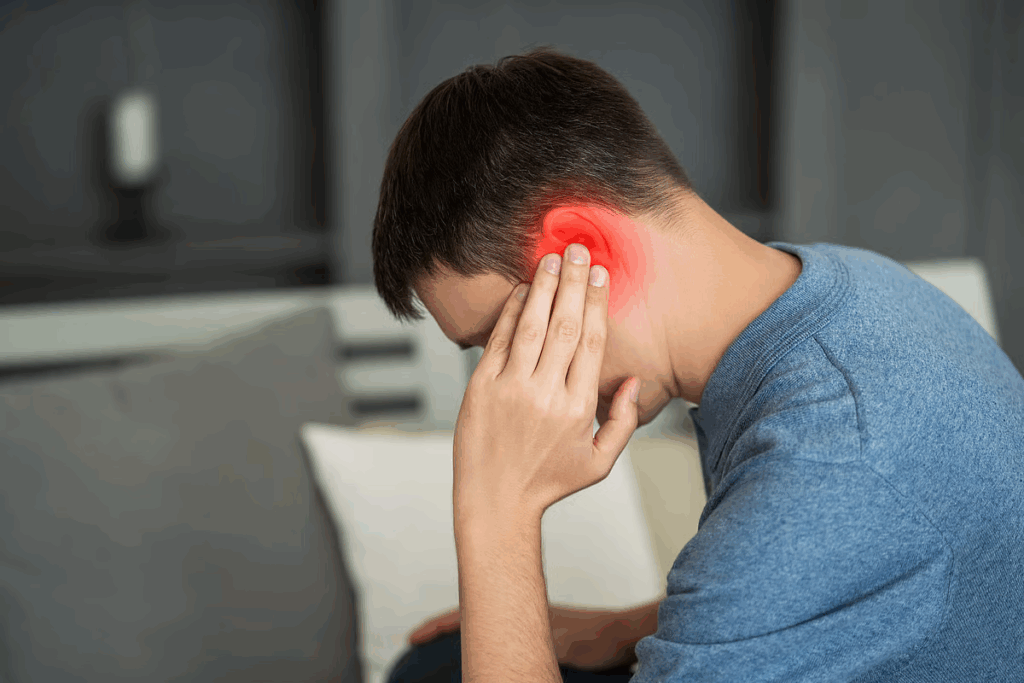
Occipital lymph nodes are at the base of the skull. They help fight off infections. If they swell, it might mean you have an infection or illness.
At Liv Hospital, we understand the concern when you find a tender lump at the base of your skull. Our team is here to help. We aim to diagnose and treat swollen occipital lymph nodes well.
Key Takeaways
- Swollen occipital lymph nodes can result from infections or illnesses.
- Understanding the causes is essential for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers comprehensive care for international patients.
- Our multidisciplinary team is dedicated to your health and well-being.
- Seeking medical attention is key if swelling persists or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Understanding Occipital Lymph Nodes
Occipital lymph nodes are near the base of the skull. They help filter out harmful substances. These nodes are key to our body’s defense against infections.
Location and Anatomy
The occipital lymph nodes are at the back of the head, near the occipital bone. They are small and not usually felt unless they swell. The head and neck have over 300 lymph nodes, with the occipital nodes being important but less talked about.
These nodes are designed to drain and filter lymph from the scalp, neck, and head. Knowing where they are helps us understand why they swell with certain conditions.
Function in the Immune System
The main job of occipital lymph nodes is to filter lymph fluid. They trap pathogens and harmful substances. They also have immune cells like lymphocytes to fight infections.
When an infection hits the scalp, head, or neck, these nodes swell. They work hard to fight off the invaders.
The role of occipital lymph nodes in our immune system is vital. They are a first line of defense against scalp, head, and neck infections. Their ability to filter lymph and start immune responses is essential for our health.
| Function | Description |
| Filtering Lymph Fluid | Trapping pathogens and harmful substances |
| Immune Response | Containing lymphocytes to fight infections |
| Drainage | Draining lymph from the scalp, neck, and head |
Understanding the location, anatomy, and function of occipital lymph nodes is key. It shows their importance in our immune system. Their swelling can signal health issues.
The Lymphatic System’s Role in Health

The lymphatic system is key to our health, fighting off infections. It’s a big part of our immune system. It filters out bad stuff and helps move white blood cells around the body.
How Lymph Nodes Filter Harmful Substances
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures found all over the body. They’re in the head and neck too. These nodes act as filters, catching pathogens like bacteria and viruses.
When lymph nodes find these pathogens, they spring into action. They start an immune response to fight off the infection.
At the back of the head, occipital lymph nodes get swollen. This happens when they’re filtering out bad stuff from the scalp, neck, and head. Swelling means they’re working hard to keep us safe from infection.
Distribution of Lymph Nodes in the Head and Neck
Lymph nodes are all over the head and neck. Each group covers different areas. The occipital lymph nodes focus on the back of the scalp.
Other groups, like the cervical lymph nodes, cover more ground. They’re split into superficial and deep nodes. These nodes drain a big area of the head and neck.
Knowing where lymph nodes are helps doctors figure out what’s wrong. By finding out which nodes are swollen, they can often find the source of the problem.
Common Causes of Inflamed Lymph Nodes on Back of Head
It’s important to know why lymph nodes on the back of the head get swollen. This can happen for many reasons, like infections or skin problems.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections often cause swollen lymph nodes on the back of the head. For example, impetigo, a contagious skin infection, can make lymph nodes swell. Here are some bacterial infections that can cause this:
- Impetigo: A contagious skin infection that causes red sores and crusting.
- Folliculitis: Inflammation of the hair follicles, often due to bacterial infection.
- Erysipelas: A bacterial infection that affects the upper layer of the skin.
Viral Infections
Viral infections are another big reason for swollen lymph nodes on the back of the head. Viruses like rubella and herpes simplex can make lymph nodes swell. Here are some viral infections to know:
| Viral Infection | Characteristics |
| Rubella | A viral infection causing a red rash, fever, and swollen lymph nodes. |
| Herpes Simplex | A viral infection leading to painful sores and possible lymph node swelling. |
| Mononucleosis | An infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, leading to fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. |
Scalp Conditions
Scalp conditions can also make the occipital lymph nodes swell. For example, psoriasis and head lice infestations can cause this. Here are some scalp conditions to be aware of:
- Psoriasis: An autoimmune condition causing red, scaly patches on the scalp.
- Head Lice Infestation: An infestation by tiny insects that live on the human scalp, causing itching and possible lymph node swelling.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: A skin condition causing scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff.
We’ve looked at why lymph nodes on the back of the head get swollen. This includes bacterial and viral infections, as well as scalp conditions. Knowing these causes helps find the right treatment.
Unilateral vs. Bilateral Occipital Lymph Node Swelling
Swollen occipital lymph nodes can be on one side or both. This is important for figuring out the cause. Knowing if it’s one-sided or both-sided helps doctors diagnose better.
Right Side Occipital Lymph Node Swelling
A swollen right side occipital lymph node usually means a problem in that area. Common reasons include:
- Infections in the scalp
- Dermatological conditions such as eczema or psoriasis
- Localized abscesses or infected wounds
This swelling might be due to a viral or bacterial infection. It’s key to watch for symptoms like pain, redness, or fever.
Swelling on Both Sides
Swelling on both sides usually points to a bigger issue. This could be:
- Systemic infections like mononucleosis or HIV
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis
- Generalized skin conditions affecting the scalp
When both sides swell, a detailed medical check-up is needed. A doctor should perform tests to find the cause.
Understanding unilateral and bilateral swelling helps in diagnosing and treating. Whether it’s one side or both, it shows the body is reacting to something that needs attention.
Less Common Causes of Occipital Lymph Node Swelling
Occipital lymph nodes can swell due to several rare medical conditions. These include autoimmune diseases and certain cancers. It’s important to look at these causes to get the right diagnosis and treatment.
Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune disorders happen when the body attacks its own tissues. Conditions like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis can make lymph nodes swell. This includes those in the occipital area.
“Autoimmune diseases can manifest in various ways, including the swelling of lymph nodes. It’s essential to consider these conditions in the differential diagnosis of occipital lymph node swelling.”
Medical Expert, Rheumatologist
To diagnose these conditions, doctors use a detailed approach. This includes clinical exams and lab tests to find the underlying disease.
Tuberculosis and Other Rare Infections
Tuberculosis (TB) is a rare but possible cause of swollen occipital lymph nodes. It’s more common in areas with high TB rates. Other rare infections can also cause lymph node swelling.
| Infection | Characteristics | Diagnostic Approach |
| Tuberculosis | Chronic infection, often with systemic symptoms | TB skin test, sputum analysis, imaging |
| Toxoplasmosis | Parasitic infection, often asymptomatic | Serological tests, PCR |
Malignancies and Cancer
Cancers like lymphoma and melanoma can also cause swollen lymph nodes. These conditions need quick diagnosis and treatment.
Lymphoma, a cancer of the lymphatic system, can show up as swollen lymph nodes. Melanoma, a skin cancer, can spread to lymph nodes, including those in the occipital area.
It’s key for healthcare providers to know about these rare causes. This helps them make accurate diagnoses and plan effective treatments.
Symptoms Associated with Swollen Occipital Lymph Nodes
Knowing the symptoms of swollen occipital lymph nodes is important. These nodes can be tender and painful. They may also have other symptoms depending on the cause.
Physical Characteristics of Swollen Nodes
Swollen occipital lymph nodes can feel different. They might be tender, painful, or just bigger. Their size can range from a small pea to a large marble or even bigger.
Healthcare professionals look at these nodes closely. They check their size, tenderness, texture, and how they move. This helps them understand the problem.
Accompanying Symptoms to Watch For
Swollen lymph nodes can come with other symptoms. These symptoms can give clues about what’s causing the nodes to swell. Some common symptoms include:
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
| Fever | Infection or inflammatory process |
| Night Sweats | Possible lymphoma or other chronic infection |
| Unexplained Weight Loss | Potential malignancy or chronic disease |
| Sore Throat | Upper respiratory infection |
| Skin Lesions or Rashes on the Scalp | Skin conditions or infections affecting the scalp |
It’s important to notice these symptoms. They help figure out why the lymph nodes are swollen. If you see any of these symptoms, see a doctor right away.
Diagnosis of Swollen Lymph Nodes at the Base of Skull
Diagnosing swollen lymph nodes at the back of the head is a detailed process. We start by looking closely at the cause. This helps us figure out what’s going on.
Physical Examination
First, we do a physical check. We look at the size, tenderness, and feel of the nodes. We also check the area around them for signs of infection or swelling.
Laboratory Tests
Lab tests are key to finding out why the lymph nodes are swollen. We might do:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) to check for infection or inflammation signs
- Blood cultures to find bacterial infections
- Serological tests to spot viral infections
Imaging Studies
Imaging helps us see the lymph nodes and the tissues around them. We might use:
- Ultrasound to look at the lymph node shape
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans to see how much the nodes are involved
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to check the soft tissues
Biopsy Procedures
At times, a biopsy is needed to find the cause. We might do a fine-needle aspiration biopsy or an excisional biopsy. This gets tissue samples for further study.
Diagnosing swollen lymph nodes at the base of the skull involves several steps. These include physical checks, lab tests, imaging, and biopsies. The tests we choose depend on the patient’s symptoms and medical history.
| Diagnostic Test | Purpose |
| Physical Examination | Assess lymph node size, tenderness, and consistency |
| Laboratory Tests | Identify infection, inflammation, or malignancy |
| Imaging Studies | Visualize lymph nodes and surrounding tissues |
| Biopsy Procedures | Obtain tissue samples for histopathological examination |
Treatment Options and Prevention Strategies
It’s important to know how to treat and prevent swollen occipital lymph nodes. The right treatment depends on finding and fixing the cause of the swelling.
Addressing the Underlying Cause
The first step is to find out why the lymph nodes are swollen. Treatment for swollen lymph nodes changes based on the cause. This could be a bacterial or viral infection, a scalp issue, or another health problem.
If it’s a bacterial infection, antibiotics might be needed. For a viral infection, the focus is on managing symptoms and boosting the immune system.
Medication Options for Symptom Relief
There are many medication options to help with swollen lymph nodes. Over-the-counter pain relievers can ease discomfort and reduce swelling.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can help with pain and swelling.
- For severe infections, antibiotics or antifungal meds might be needed.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Medical treatment isn’t the only way to handle swollen lymph nodes. Home remedies and self-care strategies can also help. These include:
- Using warm compresses to ease discomfort.
- Keeping clean to avoid infections.
- Resting well to support the immune system.
Prevention of Recurrent Swelling
To stop swollen lymph nodes from coming back, it’s key to address the causes and keep healthy. This means:
- Keeping the scalp clean to prevent infections.
- Managing stress with relaxation techniques.
- Getting vaccinated to avoid infections that can cause swelling.
By using these treatment and prevention strategies, you can manage swollen occipital lymph nodes well. This helps prevent them from coming back.
When to See a Doctor About Lymph Nodes in Back of Head
Lymph node swelling can be alarming. Knowing when to see a doctor is important. Swollen lymph nodes at the back of the head might mean you have an underlying condition.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Look out for these signs: persistent swelling, pain or tenderness in the lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, or unexplained weight loss. These signs could indicate a serious underlying condition that needs prompt medical evaluation.
If you have trouble swallowing or breathing, get medical help right away. These symptoms can mean a serious problem with your lymph nodes or nearby areas.
What to Expect During Your Doctor’s Visit
At your doctor’s visit, expect a detailed check-up. The doctor will look at the swollen lymph nodes, check for other symptoms, and might order tests or imaging studies to find out why they’re swollen.
A detailed medical history is key. Be ready to talk about your symptoms, medical history, and any recent infections or illnesses.
- A physical examination of the swollen lymph nodes
- Laboratory tests, such as blood tests or biopsies
- Imaging studies, like ultrasound or CT scans
It’s important to find out why your lymph nodes are swollen. By getting medical help when needed, you can get a quick diagnosis and treatment.
Conclusion
It’s important to know why occipital lymph nodes swell. These nodes are at the back of the head. They help fight off harmful substances.
Swollen lymph nodes can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or cancer. It’s key to notice symptoms like pain, tenderness, and fever. These signs mean you should see a doctor.
To find out why lymph nodes swell, doctors do exams, tests, and sometimes biopsies. Treatment depends on the cause. It might include medicine or home remedies.
We stress the need to understand swollen lymph nodes and their health impact. If swelling doesn’t go away or gets worse, see a doctor. This helps avoid serious problems.
FAQ
Where are the occipital lymph nodes located?
The occipital lymph nodes are found at the skull’s base, in the head’s back. They help filter out harmful substances from the scalp, neck, and head.
What causes swollen occipital lymph nodes?
Swollen occipital lymph nodes can result from infections, scalp issues like psoriasis, head lice, autoimmune diseases, or cancer.
Are swollen occipital lymph nodes a sign of cancer?
Swollen lymph nodes can hint at cancer, like lymphoma or melanoma. But, they’re often due to infections or other non-cancerous issues. A doctor’s diagnosis is key to find out why.
What are the symptoms associated with swollen occipital lymph nodes?
Symptoms include swelling or tenderness at the skull’s base, pain, and possibly fever, fatigue, or scalp skin lesions.
How are swollen occipital lymph nodes diagnosed?
Diagnosis includes a physical check-up, lab tests, imaging studies, and sometimes biopsies to figure out the cause.
What are the treatment options for swollen occipital lymph nodes?
Treatment varies based on the cause. It might include treating the infection, medication, home remedies, and self-care to manage swelling and prevent it from coming back.
When should I see a doctor about swollen lymph nodes in the back of my head?
See a doctor if swelling, pain, or tenderness persists or worsens, or if you have fever, fatigue, or unexplained weight loss.
Can swollen occipital lymph nodes be prevented?
While prevention isn’t always possible, good hygiene, avoiding head lice, and managing health conditions can lower the risk of swollen lymph nodes.
Are there lymph nodes on the head?
Yes, there are lymph nodes in the head and neck area, including the occipital lymph nodes at the skull’s base.
What does it mean if I have swollen lymph nodes on one side of the back of my head?
Swelling on one side might mean a localized infection or issue. It’s important to see a healthcare professional to find out why.
References
National Health Service (NHS). (2025). Why Are Lymph Nodes on Back of Head. Retrieved from
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/swollen-lymph-nodes/




































