At Liv Hospital, we know how vital early detection is for treating bladder cancer well. As a top international healthcare place, we use the latest medical ways to care for our patients. We use ultrasound as a non-invasive way to find problems.
Can ultrasound detect bladder cancer? Find out how sonography is used as a screening and diagnostic tool for bladder tumors.
Every year, thousands get bladder cancer. Men over 55 are at the highest risk. Finding it early is key to better treatment results. We see ultrasound as a great first step for those with symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Ultrasound is a non-invasive imaging technique used to detect bladder abnormalities.
- Early detection is key to improving treatment outcomes for bladder cancer patients.
- Men over 55 are most at risk of developing bladder cancer.
- Liv Hospital utilizes advanced medical protocols for patient-centered care.
- Ultrasound is a safe, radiation-free diagnostic option.
Understanding Bladder Cancer: An Overview
Understanding bladder cancer is key to fighting it. We need to know its symptoms, risk factors, and why early detection is so important. Bladder cancer starts in the bladder’s lining, where cells grow out of control and form tumors. Let’s dive into the basics of bladder cancer to grasp this condition fully.
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer happens when cells in the bladder lining grow abnormally and form tumors. There are three main types: urothelial carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and adenocarcinoma. Urothelial carcinoma is the most common, making up about 90% of cases. Knowing the type helps doctors choose the best treatment.
Common Symptoms and Risk Factors
Spotting symptoms and risk factors early can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Blood in the urine (hematuria)
- Frequent urination
- Pelvic pain or discomfort
- Urinary urgency
Risk factors that may up your chance of getting bladder cancer include:
- Smoking
- Exposure to certain chemicals (e.g., in dye, rubber, and paint industries)
- Age (risk increases after 55)
- Family history of bladder cancer
- Chronic bladder irritation or infection
Knowing these risk factors helps you take steps to prevent it and seek help if symptoms show up.
Importance of Early Detection
Finding bladder cancer early can greatly improve treatment success. Early detection means less aggressive treatments like surgery or chemotherapy. Regular check-ups and screenings for those at high risk can catch it early. We stress the need to watch for symptoms and risk factors to catch it early.
The Diagnostic Journey for Bladder Cancer
Diagnosing bladder cancer involves several steps. It starts with initial tests, then imaging studies, and a detailed medical check-up. Knowing this process helps patients and their families understand what to expect.
First Signs That Prompt Medical Attention
Seeing blood in the urine, or other unusual symptoms, can be a warning sign. These symptoms include frequent need to urinate or pain while doing so. It’s important not to ignore these signs.
Spotting these signs early is key. It can lead to a quicker diagnosis and better treatment options.
Initial Tests and Examinations
When symptoms suggest bladder cancer, doctors start with a detailed medical history and physical exam. This helps identify risk factors and plan the next steps.
- A detailed medical history to identify risk factors and previous exposures
- A physical examination to check for any abnormalities
- Urine analysis to check for blood or other abnormalities in the urine
The Role of Imaging in Diagnosis
Imaging tests are vital in diagnosing bladder cancer. They help doctors see the bladder and surrounding areas. This helps find tumors and understand how far the disease has spread.
| Imaging Test | Description | Role in Bladder Cancer Diagnosis |
| Ultrasound | Uses sound waves to create images of the bladder | Helps identify tumors and assess bladder wall thickness |
| CT Scan | Uses X-rays to create detailed cross-sectional images | Provides information on the size, location, and extent of tumors |
A leading oncologist says, “Imaging tests are essential in diagnosing and staging bladder cancer. They give vital information for treatment planning.”
“The choice of imaging modality depends on various factors, including the patient’s condition, the suspected extent of disease, and the availability of resources.”
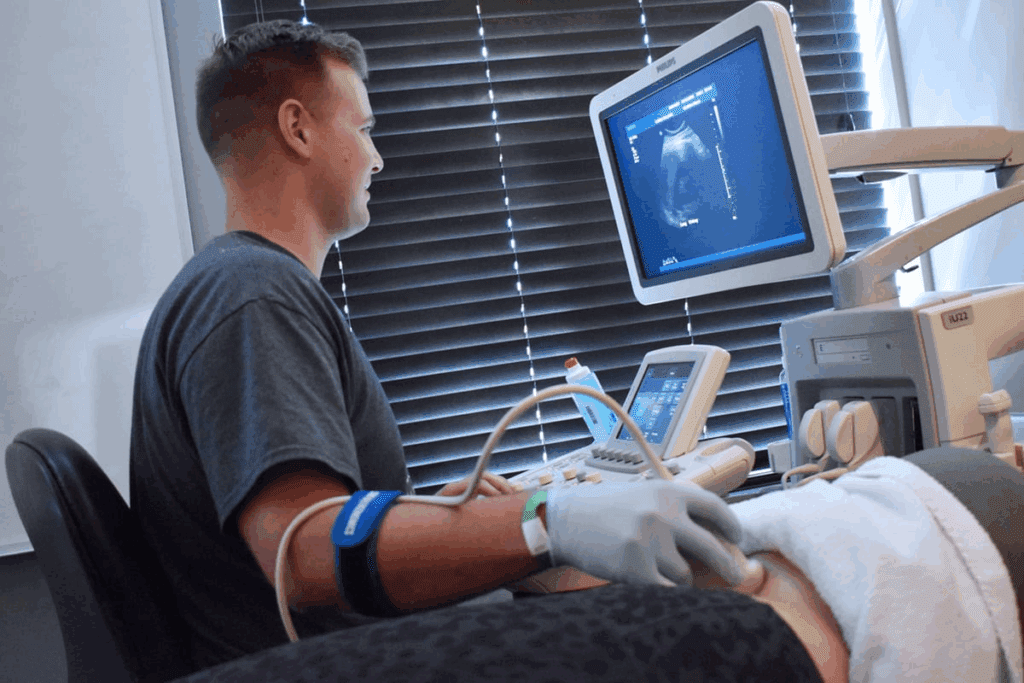
Bladder Cancer Ultrasound: How It Works
Diagnosing bladder cancer often uses ultrasound technology. It gives clear images of the bladder and nearby tissues. This tool is key for spotting problems and planning treatment.
The Science Behind Ultrasound Technology
Ultrasound technology sends high-frequency sound waves to create detailed images. It’s used to see tumors in the bladder, measure their size, and check how they affect the bladder’s function.
A device called a transducer sends sound waves that bounce off the bladder. These waves then return to the transducer, showing an image on the ultrasound machine. Doctors then look at this image to find any issues.
Types of Ultrasound Used for Bladder Examination
There are different types of ultrasound for bladder checks:
- Transabdominal ultrasound: This is the most common, where the transducer is on the abdomen.
- Transrectal ultrasound: This involves putting the transducer into the rectum for a closer look at the bladder.
What Happens During the Procedure
For a bladder ultrasound, patients need a full bladder. The transducer is placed on the abdomen or in the rectum, depending on the ultrasound type.
The procedure is usually painless and takes about 30 minutes to an hour.
| Ultrasound Type | Description | Duration |
| Transabdominal | Transducer placed on the abdomen | 30-45 minutes |
| Transrectal | Transducer inserted into the rectum | 30-60 minutes |
Can Ultrasound Detect Bladder Cancer Effectively?
Ultrasound is a key tool in finding bladder cancer. It has its strengths and weaknesses. Thanks to new tech, it’s now a big help in finding bladder cancer.
Accuracy Rates and Sensitivity
How well ultrasound finds bladder cancer matters a lot. It’s good at spotting big tumors or changes in the bladder wall. But, it’s not as good with small or flat tumors.
Accuracy rates change based on the tumor’s size, location, and the ultrasound expert. It’s not perfect but is useful because it’s safe and cheap.
What Ultrasound Can and Cannot Show
Ultrasound can show tumors in the bladder, their size, and how they affect the bladder wall. But, it can’t always tell if a tumor is cancer or not. It also can’t find very small tumors.
Ultrasound can’t give all the details about a tumor’s stage or type. Doctors might need to use other tests like cystoscopy or biopsy to confirm what ultrasound finds.
Research and Clinical Evidence
Many studies have looked at ultrasound’s role in finding bladder cancer. The evidence shows ultrasound is useful, but not the best way to diagnose bladder cancer. It’s good for first checks or keeping an eye on the cancer.
Research shows ultrasound works better when used with other tests. This mix can make diagnosis more accurate and help patients better.
Limitations of Ultrasound in Cancer Detection
Ultrasound has its downsides in finding cancer. It depends on the person doing the test, can be hard to see some parts of the bladder, and misses small or flat tumors.
Knowing these limits is key for doctors to decide when to use ultrasound. It shows we need a full plan for diagnosing bladder cancer, including more tests.
Identifying Bladder Abnormalities on Ultrasound
Ultrasound is key in finding bladder cancer. It looks at images to spot oddities. This method is non-invasive and shows real-time pictures.
What Cancer Looks Like on Ultrasound Images
Cancer on ultrasound might show as odd growths or thick bladder walls. These signs could mean bladder cancer. But, we need more checks to be sure.
“The look of bladder cancer on ultrasound can change,” says a top urology expert. “It often shows as a mass or odd shape in the bladder wall.” This shows how important it is to understand ultrasound images well.
Distinguishing Between Cancerous and Non-cancerous Findings
Telling cancer from non-cancer on ultrasound is hard. Things like bladder stones or inflammation can look like cancer. We look at the ultrasound images closely, along with the patient’s history and symptoms, to guess right.
- Size and shape of the lesion
- Location within the bladder
- Presence of blood flow within the lesion (using Doppler ultrasound)
By looking at these things, we can guess better and avoid mistakes.
Common Challenges in Interpretation
Reading ultrasound images can be tricky. We often struggle to tell cancer from non-cancer. Also, image quality can be a problem.
To get better, we keep learning about new ultrasound tech. We also work on our skills. This helps us find bladder cancer more accurately and care for our patients better.
CT Scans for Bladder Cancer Detection
CT scans are key in finding bladder cancer. They give detailed pictures of the bladder and nearby tissues. We’ll look at how CT scans help diagnose bladder cancer, their success, and what to expect during the test.
Will Bladder Cancer Show Up on a CT Scan?
Yes, CT scans can spot bladder cancer. They show the bladder’s structure well. CT scans are great for finding tumors and seeing how far cancer has spread. The scan’s success depends on the tumor’s size and where it is.
How CT Scans Work for Bladder Imaging
CT scans use X-rays to make detailed pictures of the bladder and nearby areas. The patient lies on a table that moves through a CT scanner. It takes X-ray images from different angles. These images are then put together to show the bladder’s details.
CT scans are very helpful in finding bladder cancer and planning treatment. The test is usually quick and doesn’t hurt. Some people might need to hold their breath for a bit.
What a Mass in Bladder on CT Scan Might Indicate
A mass in the bladder on a CT scan might mean there’s a tumor. But not all masses are cancer. A final diagnosis needs more tests, like a biopsy.
- A mass in the bladder wall could be invasive bladder cancer.
- Some masses are not cancer, like benign tumors or cysts.
- More tests are needed to know what the mass is.
Preparing for a CT Scan
Getting ready for a CT scan involves a few steps. Patients might need to:
- Take off any metal objects or jewelry that could get in the way.
- Wear loose clothes, like a hospital gown.
- Follow specific rules about eating and drinking before the scan.
- Tell their doctor about any allergies or health issues.
It’s important to follow these steps to get clear images. Patients should also talk to their doctor about any worries or questions before the test.
Comparing Imaging Methods: Ultrasound vs. CT vs. Other Techniques
Imaging is key in finding bladder cancer. Techniques like ultrasound and CT scans are often used. But how do they stack up? We’ll look at the different ways to find bladder cancer, their good points, and what makes one better than another.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Method
Ultrasound is safe because it doesn’t use radiation. It’s a non-invasive way to look inside the body. But, it might miss small tumors or those in tricky spots.
CT scans give clearer pictures and can spot tiny tumors. But, they use radiation, which is a big deal for patients, even more so for those needing many scans.
Comparison of Imaging Methods:
| Imaging Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, no radiation | Limited by tumor size and location |
| CT Scans | Detailed images, detects small tumors | Involves radiation exposure |
| MRI | High-resolution images, no radiation | Higher cost, less accessible |
Radiation Exposure Considerations
When picking an imaging method, radiation is a big worry. CT scans use more radiation than X-rays. It’s important for patients to talk to their doctors about these risks.
Cost and Accessibility Factors
Cost and how easy it is to get imaging vary a lot. Ultrasound is cheaper and easier to get than CT or MRI. But, the right choice depends on the situation and what’s needed for a good look.
When Doctors Choose One Method Over Another
Doctors think about many things when picking an imaging method. They look at the patient’s health, the tumor’s size and where it is, and how detailed they need the images. They pick the best method to get the right info while keeping risks and costs low.
Additional Diagnostic Methods for Bladder Cancer
There are many ways to find and treat bladder cancer, beyond just looking at images. These methods help doctors understand the disease better. This way, they can make the best treatment plans for patients.
Cystoscopy: The Gold Standard
Cystoscopy is the top way to find bladder cancer. It uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera to look inside the bladder. Doctors can take biopsy samples from any areas that look suspicious.
This method is great because it lets doctors see the bladder up close. They can also take tissue samples for tests. This helps confirm if there’s cancer and how far it has spread.
Urine Cytology and Biomarker Tests
Urine cytology checks urine for cancer cells. It’s not as good as cystoscopy but is useful for finding high-grade tumors. Biomarker tests look for proteins or genes linked to bladder cancer. They help doctors diagnose and keep an eye on the disease.
- Urine cytology is easy and can be done often.
- Biomarker tests might find cancer early and keep track of it.
- These tests work well with cystoscopy and imaging.
MRI and Other Advanced Imaging
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is also key in finding and understanding bladder cancer. It shows detailed pictures of the bladder and nearby areas. This helps doctors see how big the tumor is and how far it has spread. Other advanced images might be used too.
Combining Methods for Accurate Diagnosis
Doctors often use more than one method to make sure they have the right diagnosis. For example, they might use cystoscopy with CT or MRI scans. They might also use urine tests or biomarker tests for more info.
- Cystoscopy lets doctors see inside and take biopsies.
- Scans show how big the tumor is and where it is.
- Urine tests are a gentle way to find cancer cells or markers.
By mixing these methods, doctors get a full picture of bladder cancer. This helps them decide the best treatment for each patient.
Advancements in Bladder Cancer Detection Technology
Medical technology is getting better at finding and treating bladder cancer. These changes help patients and make the disease easier to handle.
New Ultrasound Techniques Improving Accuracy
Ultrasound tech has gotten a lot better at spotting bladder cancer. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) shows tumors more clearly. It uses special agents to highlight blood flow and tumor growth.
Three-dimensional (3D) ultrasound also helps a lot. It gives a detailed look at the bladder and its contents. This is great for figuring out how big a tumor is and planning surgery.
Enhanced CT Imaging Protocols
CT scans are key for diagnosing bladder cancer. New CT imaging methods make pictures clearer and use less radiation. Dual-energy CT is one such method that helps spot tumors and stones better.
CT urography also improves. It shows the urinary tract in detail. This helps find tumors and other issues more accurately.
Artificial Intelligence in Image Interpretation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing how we read medical images. AI can look at lots of data fast and find patterns humans might miss. It helps spot bladder cancer on scans, making diagnoses more accurate.
AI does more than just detect cancer. It can also guess how a tumor will behave and how it will react to treatment.
Future Directions in Non-invasive Diagnostics
The future of finding bladder cancer is non-invasive. Liquid biopsies are being looked at to find cancer markers in urine or blood. This could be a safe way to check how the disease is progressing and if treatments are working.
As tech keeps getting better, we’ll see even more ways to find and treat bladder cancer. This will lead to earlier diagnoses and better treatment plans.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About Bladder Cancer Screening
Early detection and accurate diagnosis are key to treating bladder cancer effectively. We’ve looked at how ultrasound and CT scans help find bladder problems. These tools are important for spotting issues early.
Choosing the right screening method is critical. Knowing the strengths and weaknesses of each test helps patients make better decisions. This way, they can pick the best option for their health.
It’s essential to talk to doctors about screening options. They can suggest the best tests based on your risk and medical history. This approach ensures you get the right care on time, leading to better results.
FAQ
Can ultrasound detect bladder cancer?
Yes, ultrasound can detect bladder cancer. It’s a non-invasive method that spots bladder abnormalities, like tumors.
How accurate is ultrasound in detecting bladder cancer?
Ultrasound’s accuracy in finding bladder cancer varies. It depends on the tumor’s size, location, and the operator’s skill. It’s useful for initial checks and monitoring.
Will bladder cancer show up on a CT scan?
Yes, bladder cancer can be seen on a CT scan. CT scans use X-rays and computer tech to show detailed images of the bladder and nearby tissues. They help find tumors and see how big they are.
What does a mass in the bladder on a CT scan indicate?
A mass in the bladder on a CT scan might mean a tumor. It could be benign or cancerous. More tests, like cystoscopy and biopsy, are needed to figure it out.
Can a CT scan show bladder cancer effectively?
Yes, CT scans are good at finding bladder cancer. They work best when used with other tests. They give important info about the cancer’s size, location, and if it has spread.
What is the role of ultrasound in bladder cancer diagnosis?
Ultrasound helps in the early stages of bladder cancer diagnosis. It’s non-invasive and quick. It spots bladder issues and guides further tests.
Are there any limitations to using ultrasound for bladder cancer detection?
Yes, ultrasound has its limits for bladder cancer detection. It might miss small tumors. It can also be hard to tell if a lesion is cancerous or not.
How does CT scan compare to ultrasound for bladder cancer detection?
CT scans and ultrasound have different uses. CT scans give detailed images and check cancer spread. Ultrasound is non-invasive and doesn’t use radiation.
What other diagnostic methods are used for bladder cancer?
Other methods for bladder cancer include cystoscopy, urine cytology, biomarker tests, and MRI. These tests can be used alone or together for a correct diagnosis.
How is bladder cancer diagnosed?
Bladder cancer is diagnosed with imaging tests like ultrasound and CT scans, and invasive procedures like cystoscopy and biopsy. The choice of tests depends on the case and doctor’s judgment.
Can bladder cancer be detected with a CT scan without contrast?
A CT scan without contrast can give some info. But, using a contrast agent is usually better for seeing bladder tumors and their size.
Is ultrasound or CT scan better for detecting bladder cancer?
Choosing between ultrasound and CT scan for bladder cancer depends on many factors. These include the situation, patient’s health, and the tumor’s characteristics.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). Can Ultrasound Detect Bladder Cancer What You Need.

































