
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be scary, even more so without pain or during non-menstrual periods.
Seeing blood in your urine can be alarming. It’s important to know why it happens. There are two types: gross hematuria, which you can see, and microscopic hematuria, which only tests can find blood in urine female no pain no period.
Blood in your urine can mean many things, like infections or kidney stones. At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tests and care to find out why it’s happening.
Key Takeaways
- Hematuria refers to the presence of blood in the urine, which can be visible or detectable only through lab tests.
- The condition can occur without pain or during non-menstrual periods.
- Hematuria can be a sign of various underlying health issues.
- Comprehensive assessment is key to finding the cause.
- Liv Hospital offers advanced diagnostic protocols and patient-centered care for hematuria.
Understanding Hematuria: Blood in Urine Explained
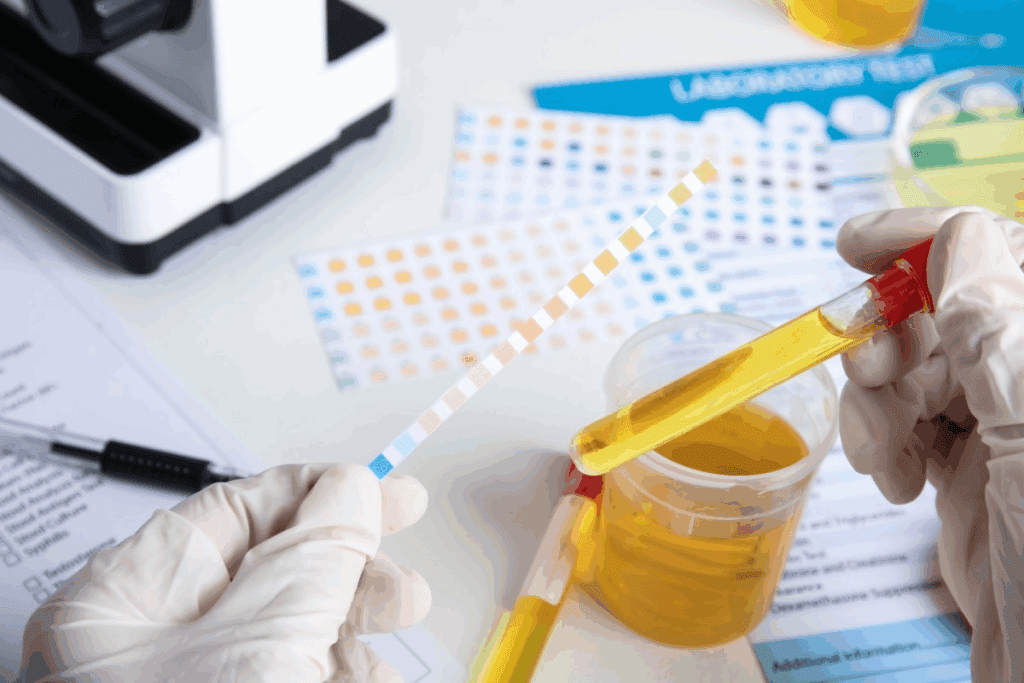
Blood in urine, known as hematuria, can worry people. It often points to health problems. Hematuria shows up in different ways and can signal issues with the urinary system.
What Is Hematuria?
Hematuria means blood in the urine. It’s split into visible and invisible types. Hematuria is a symptom, not a diagnosis. Doctors need to check it out to find the cause.
Gross vs. Microscopic Hematuria
Hematuria comes in two forms: gross and microscopic. Gross hematuria is when you can see blood in your urine. Microscopic hematuria needs a lab test to find, as it’s not visible.
Gross hematuria is scary because you can see it. Microscopic hematuria is found in routine tests. Both need a doctor’s check-up to find the reason.
Prevalence and Demographics
About 2 percent to 31 percent of people have microscopic hematuria. It’s more common than you might think. The chance of having hematuria changes with age, gender, and other factors. Knowing this helps doctors understand who might get it.
Hematuria affects people of all ages, but some groups are at higher risk. Young women often get it from urinary tract infections. Older men might get it from bladder cancer.
Blood in Urine Female No Pain No Period: Common Causes

Blood in urine can worry women, even if it’s not during their period or painful. Knowing the possible reasons is key to finding the right treatment.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
UTIs are a common reason for blood in urine in women. Bacteria in the urinary tract cause inflammation and bleeding. Symptoms include frequent urination, a burning feeling, and cloudy or smelly urine. Some women might not show any signs.
Kidney Stones and Crystallization
Kidney stones are hard mineral deposits in the kidneys. They can cause blood in urine, even without pain. Risk factors include dehydration, certain diets, and family history.
Bladder or Kidney Infections
Infections in the bladder or kidneys can also cause blood in urine. These infections are usually from bacteria and may cause fever, chills, and pain. Antibiotics are often needed to treat these infections.
Exercise-Induced Hematuria
Strenuous exercise can lead to blood in urine, often in activities like running or jumping. The exact reason is unclear, but it’s thought to be due to minor trauma from the impact.
| Cause | Common Symptoms | Typical Treatment |
| Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Frequent urination, burning sensation, cloudy urine | Antibiotics |
| Kidney Stones | Pain, hematuria, nausea | Hydration, pain management, possible surgery |
| Bladder or Kidney Infections | Fever, chills, abdominal or back pain | Antibiotics |
| Exercise-Induced Hematuria | Often asymptomatic, hematuria | Reducing exercise intensity, hydration |
Urological Conditions Leading to Painless Hematuria
Blood in urine without pain can signal several urological problems. Painless hematuria, or blood in urine without pain, can stem from various issues. It’s important to know these conditions for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Bladder Polyps and Tumors
Bladder polyps and tumors are growths in the bladder. Some are benign, but others can be cancerous. These can cause bleeding, leading to hematuria. Early detection is critical for effective treatment. Tests like cystoscopy and imaging studies help identify these growths.
Kidney Disease and Glomerulonephritis
Kidney disease includes many conditions that affect kidney function. Glomerulonephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys’ filtering units. Both can cause hematuria. Chronic kidney disease can progress silently, making regular check-ups important for early detection.
Urethral Disorders and Strictures
Urethral disorders, including strictures or narrowing of the urethra, can cause urinary symptoms and hematuria. These can result from injury, infection, or inflammation. Proper diagnosis through imaging and endoscopic procedures is necessary to determine the extent of the condition.
Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis, also known as bladder pain syndrome, causes bladder pressure and pain. Sometimes, it presents with painless hematuria. The exact cause is unknown, but it’s believed to involve defects in the bladder lining, immune system dysfunction, and nerve damage.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Diagnostic Approaches |
| Bladder Polyps/Tumors | Hematuria, urinary frequency | Cystoscopy, Imaging studies |
| Kidney Disease/Glomerulonephritis | Hematuria, proteinuria, edema | Urinalysis, Kidney biopsy |
| Urethral Disorders/Strictures | Urinary obstruction, hematuria | Urethroscopy, Imaging studies |
| Interstitial Cystitis | Bladder pain, urinary urgency | Symptom assessment, Cystoscopy |
Distinguishing Between Period Blood and Urinary Bleeding
It’s important for women to know the difference between menstrual and urinary bleeding. Many women get confused, which can delay finding and treating health problems.
Blood in Urine Before Period Starts
Blood in urine before your period can be scary. It’s key to figure out if it’s from your urinary tract or menstrual cycle. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) or kidney stones might look like menstrual bleeding.
Many things can cause blood in urine before your period. Hormonal changes and physical issues are some examples. We’ll look into these more.
Blood in Urine After Menstruation
Blood in urine after your period can also be confusing. It’s important to find out where the bleeding is coming from. Gynecological issues like endometriosis can sometimes look like urinary bleeding.
We’ll talk about what might cause blood in urine after your period. And how to tell it apart from menstrual bleeding.
Identifying the Source of Bleeding
Finding where the bleeding is coming from is key for the right treatment. A doctor will do tests like urinalysis and imaging studies. These help figure out if it’s from your urinary tract or reproductive system.
| Characteristics | Menstrual Bleeding | Urinary Bleeding |
| Timing | Occurs at the regular menstrual cycle | Can occur at any time, unrelated to menstrual cycle |
| Color | Varies from bright red to dark brown | Typically bright red or cola-colored |
| Associated Symptoms | Cramps, bloating, mood swings | Dysuria, frequency, urgency |
Gynecological Conditions Mimicking Hematuria
Some gynecological issues can look like urinary bleeding. This makes it hard to find the real cause. Problems like endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and cervical lesions can cause bleeding that looks like urine.
We’ll dive deeper into these conditions. And how to tell them apart from true urinary bleeding.
Systemic Conditions That Can Cause Hematuria
Blood in urine, or hematuria, can signal several health issues. These problems can affect different parts of the body. They might show up as hematuria.
Blood Disorders and Clotting Issues
Blood disorders can mess up blood clotting, leading to hematuria. Hemophilia and thrombocytopenia are examples. They cause bleeding in the urinary tract, showing up as blood in the urine. Also, some medicines can make bleeding more likely.
- Hemophilia A and B: Genetic disorders that make it hard for the body to clot blood, needed to stop bleeding.
- Thrombocytopenia: A condition with low platelet count, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Autoimmune Diseases Affecting the Urinary System
Autoimmune diseases happen when the body attacks its own tissues. Some can harm the urinary system, causing hematuria. For example, IgA nephropathy affects the kidneys and can lead to blood in the urine.
- IgA Nephropathy: Involves IgA antibodies in the kidneys, causing inflammation and kidney problems.
- Lupus Nephritis: A kidney issue from systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an autoimmune disease affecting many organs.
Medications and Supplements That Discolor Urine
Some medicines and supplements can make urine look discolored or bloody. Rifampin, an antibiotic, and laxatives are examples. It’s key to tell true hematuria from color changes caused by drugs.
Genetic and Hereditary Factors
Genetics can also cause hematuria. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) and Alport syndrome are hereditary. They can lead to hematuria and other symptoms.
- Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD): Involves many cysts in the kidneys, harming their function.
- Alport Syndrome: A genetic disorder affecting type IV collagen, causing kidney disease, hearing loss, and eye problems.
Diagnostic Process for Blood in Urine
Diagnosing blood in urine needs a detailed approach. This includes many tests and a full medical history. Finding out why you have blood in your urine is key to treating it right.
Initial Assessment and Medical History
We start by asking about your symptoms and medical history. We also look at your lifestyle. This helps us figure out the best tests to run.
Urinalysis and Laboratory Tests
Urinalysis is a big part of finding out what’s wrong. We check for blood, protein, and other issues. Tests like urine culture and blood tests help find infections and check kidney function.
- Urine culture to check for infections
- Blood tests to assess kidney function and detect other abnormalities
- Urine cytology to check for cancer cells
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT, and MRI
Imaging studies help us see inside the urinary tract. We might use:
- Ultrasound to examine the kidneys and bladder
- CT scans to provide detailed images of the urinary tract
- MRI to assess the kidneys and urinary tract without radiation
Specialized Urological Procedures: Cystoscopy and Biopsy
Sometimes, we need special tests to find the cause of blood in urine. Cystoscopy lets us see inside the bladder. Biopsy takes a tissue sample for more checks.
These tests help find problems like bladder cancer, stones, or other issues in the urinary tract.
Treatment Approaches for Hematuria
Dealing with hematuria starts with finding the root cause. Once we know why there’s blood in the urine, we can pick the best treatment.
Treating Underlying Causes
Fixing the cause is key to managing hematuria well. This might mean treating infections, handling kidney stones, or tackling diseases of the bladder or kidneys.
For example, if a UTI is causing the problem, antibiotics are used to fight the infection. If kidney stones are the issue, we might use pain meds, lots of water, and sometimes surgery to remove or break up the stones.
Medication Options for Various Conditions
Medicine is a big part of treating hematuria. Antibiotics are used for infections, and other meds help with symptoms or diseases like kidney or bladder problems.
We might give pain meds for kidney stone or infection pain. Some meds help prevent certain stones from forming.
Surgical Interventions When Necessary
Surgery is sometimes needed to fix the cause of hematuria. This could be to take out stones, fix urinary tract issues, or remove tumors.
Surgery is considered when other treatments don’t work. For example, a cystoscopy might be done to look inside the bladder and urethra, allowing for the removal of growths.
Follow-up Care and Monitoring
Aftercare is vital for managing hematuria. It lets us check if the treatment is working and make changes if needed. Regular check-ups and tests help keep an eye on the condition and adjust the treatment plan.
Following up as recommended is important for the best results. This might include regular urinalyses, imaging, or other tests to keep an eye on the condition and tweak the treatment plan if necessary.
| Treatment Approach | Condition | Description |
| Antibiotics | Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) | Clearing bacterial infections |
| Hydration and Pain Management | Kidney Stones | Managing symptoms and facilitating stone passage |
| Surgical Intervention | Bladder or Kidney Stones, Tumors | Removing or breaking up stones, removing tumors |
Potential Complications of Untreated Hematuria
Blood in urine can lead to serious problems if not treated. It can harm the urinary system and overall health. We will look at these complications and their effects.
Progression of Underlying Conditions
Untreated hematuria can make health issues worse. For example, urinary tract infections can spread to the kidneys. This can cause pyelonephritis or even sepsis.
Kidney Function Deterioration
Untreated conditions like glomerulonephritis or kidney stones can damage kidneys. This can lead to chronic kidney disease or kidney failure. In severe cases, dialysis or a kidney transplant may be needed.
Anemia and Blood Loss Concerns
Long-term hematuria can cause a lot of blood loss. This can lead to anemia. Anemia makes you feel tired, weak, and short of breath, affecting your daily life.
Psychological Impact of Chronic Symptoms
Living with chronic hematuria can be very stressful. It can cause anxiety, stress, and depression. The constant presence of blood in urine can greatly impact your mental health and quality of life.
| Complication | Description | Potential Consequences |
| Progression of Underlying Conditions | Untreated causes of hematuria can worsen. | Severe infections, organ damage. |
| Kidney Function Deterioration | Kidney function declines due to untreated conditions. | Chronic kidney disease, kidney failure. |
| Anemia and Blood Loss | Significant blood loss leads to anemia. | Fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath. |
| Psychological Impact | Chronic symptoms cause mental health issues. | Anxiety, stress, depression. |
When to Seek Medical Attention for Blood in Urine
If you see blood in your urine, it’s important to know when to get help. Blood in the urine, or hematuria, can mean different things. Some of these things need quick medical care.
Emergency Warning Signs
Some symptoms with blood in urine need you to go to the emergency room right away. These include:
- Severe pain in the abdomen or back
- Heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop
- Fever and chills
- Difficulty urinating
- Blood clots in the urine
If you see any of these, get to the hospital fast.
Symptoms That Shouldn’t Be Ignored
Other symptoms with blood in urine also need a doctor’s visit. These include:
| Symptom | Possible Indication |
| Frequent urination | Urinary tract infection or bladder issue |
| Painful urination | Infection or irritation in the urinary tract |
| Abdominal or pelvic pain | Possible kidney stone or other obstruction |
These signs can mean you have a problem that needs a doctor’s check-up.
Questions to Ask Your Healthcare Provider
When you see your doctor, having questions ready can help you understand your situation. Ask things like:
- What are the possible causes of my hematuria?
- What tests are needed to diagnose the underlying cause?
- What treatment options are available?
- Are there any lifestyle changes I should make?
Asking these questions helps you take an active role in your care.
What to Expect During Your Medical Visit
Your doctor will likely ask about your medical history and do a physical check. They might also do tests like urinalysis and imaging studies to find out why you have blood in your urine.
Being ready for your visit by writing down your symptoms and questions can make things easier.
Conclusion: Managing and Understanding Blood in Urine
It’s key to understand hematuria to manage it well. We’ve looked at what blood in urine means, why it happens, and how to find out. Knowing the types of hematuria helps us find the cause of the blood.
Handling hematuria needs a full plan. This includes finding the cause, treating it, and keeping an eye on it. We talked about how to find the source of the bleeding. This could be from infections, stones, or other issues.
We also talked about the need for a detailed check-up. This includes tests like urinalysis and imaging. Working with doctors helps get a correct diagnosis and a good treatment plan. If symptoms don’t go away, seeing a doctor is important.
Understanding and managing hematuria can make life better. We urge people to be involved in their care. Working with doctors helps address any worries or questions.
FAQ
What is hematuria and what are its types?
Hematuria is when blood shows up in your urine. It’s divided into two types. Gross hematuria means you can see the blood with your eyes. Microscopic hematuria is when you can only see it under a microscope.
Can hematuria occur without pain or during menstrual periods?
Yes, hematuria can happen without pain or during your period. Sometimes, women might not feel any pain but experience it. Other times, it might be linked to their menstrual cycle.
What are the common causes of hematuria in females with no pain or period involvement?
Common causes include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, and bladder or kidney infections. Exercise-induced hematuria is another reason.
How can I distinguish between period blood and urinary bleeding?
It’s hard to tell period blood from urinary bleeding. But, it’s key to figure out where the bleeding is coming from. Gynecological issues can sometimes look like hematuria, so getting a proper diagnosis is important.
What are the systemic conditions that can cause hematuria?
Systemic conditions like blood disorders, autoimmune diseases, and genetic factors can cause hematuria. Some medicines and supplements can also make your urine look like blood.
What is the diagnostic process for hematuria?
Diagnosing hematuria starts with an initial check-up and urinalysis. Then, imaging studies like ultrasound, CT, or MRI might be done. Special urological procedures like cystoscopy and biopsy are also used.
How is hematuria treated?
Treatment for hematuria depends on the cause. It might involve treating the underlying issue, using medicine, surgery, or ongoing care and monitoring.
What are the possible complications of untreated hematuria?
Untreated hematuria can lead to serious issues. These include worsening of the underlying condition, kidney damage, anemia, and psychological effects.
When should I seek medical attention for blood in urine?
You should see a doctor for blood in urine if you have severe pain, heavy bleeding, or trouble urinating. Also, if you keep getting hematuria, you should get checked out.
What can I expect during my medical visit for hematuria?
At your visit, your doctor will do a physical exam and take your medical history. They’ll also order tests to find out why you have hematuria. Be ready to ask questions and share your symptoms and worries.
Can occult blood in urine be related to menstrual periods?
Occult blood in urine means you can’t see the blood with your eyes. While menstrual blood might get into your urine, it’s not the main cause. You need a proper diagnosis to know why.
Is blood in urine a normal occurrence during or after menstruation?
Blood in urine isn’t normal during or after your period. Even if some women might get hematuria during their cycle, it’s important to see a doctor. They can check for any other health issues.
References
Government Health Resource. (2025). Why Am I Bleeding in My Urine Without. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/hematuria-blood-urine























