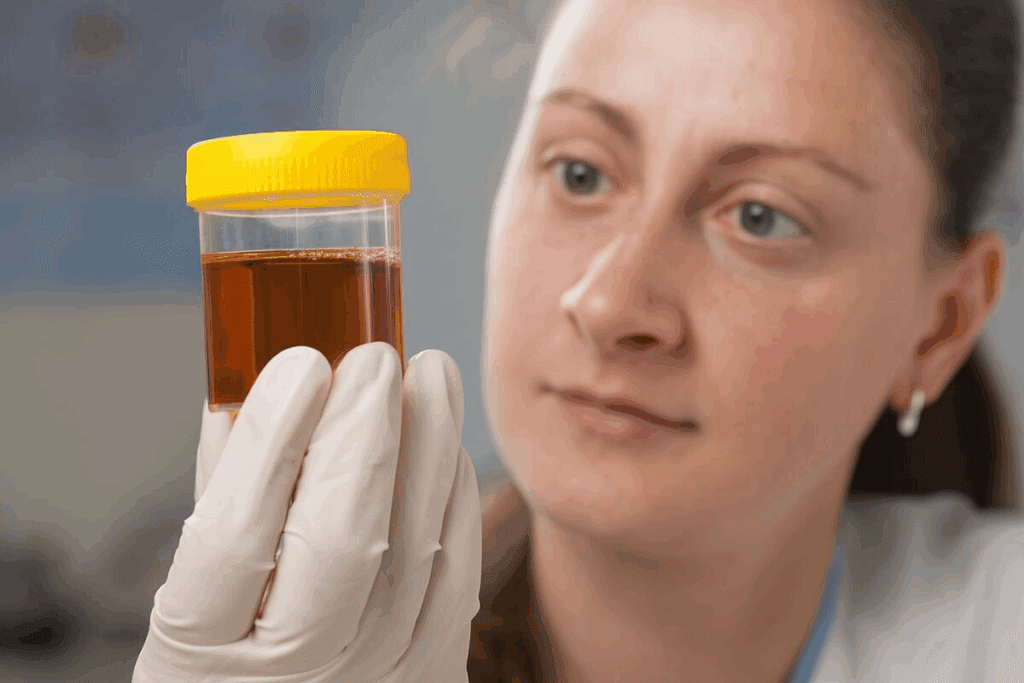
Hematuria, or blood in the urine, is a big health worry for millions of women. It shows up as either gross hematuria, where urine looks different, or microscopic hematuria, where blood is only seen under a microscope blood in urine female.
At Liv Hospital, finding blood in urine is scary. But, it usually means you have a treatable problem, not a serious disease. Doctors say blood in the urine can mean infection, kidney stones, or other issues.
Key Takeaways
- Hematuria is a common condition affecting women worldwide.
- It can be either gross or microscopic.
- Seeking medical attention is key for the right diagnosis.
- Liv Hospital offers detailed checks and caring treatment.
- Early diagnosis can lead to effective treatment and peace of mind.
Understanding Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Hematuria is when blood shows up in your urine. It can be seen with the naked eye or only under a microscope. We’ll look at the different kinds and what they mean.
Definition and Types of Hematuria
There are two main types: gross and microscopic hematuria. Gross hematuria makes the urine look red or brown. Microscopic hematuria means tiny blood cells are found in the urine, even if it looks clear.
- Gross hematuria usually means a serious problem and is easy to spot.
- Microscopic hematuria is harder to see but needs a doctor’s check-up to find out why.
Prevalence and Statistics
Studies show that microscopic hematuria affects 2% to 31% of people. This wide range shows how different studies and populations can be.
| Type of Hematuria | Prevalence | Common Causes |
| Gross Hematuria | Less common than microscopic hematuria | Bladder or kidney stones, infections, trauma |
| Microscopic Hematuria | 2% to 31% of the general population | Infections, kidney disease, bladder or kidney stones |
Knowing about hematuria’s types and how common they are is key. It helps both patients and doctors figure out what’s going on and how to treat it.
Common Causes of Blood in Urine Female

Hematuria, or blood in urine, can have many causes in females. These range from infections to serious conditions. Knowing these causes is key for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Overview of Primary Causes
The main reasons for hematuria in females fall into a few main categories. Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a big cause. They can cause inflammation and bleeding in the urinary tract. About 40% to 60% of women get UTIs at some point, making them a big factor in hematuria.
Other causes include kidney stones, which can bleed as they move, and endometriosis. This is when tissue like the uterus lining grows outside the uterus and can affect the urinary system.
- Urinary tract infections
- Kidney stones
- Endometriosis
- Gynecological conditions
Risk Factors for Developing Hematuria
There are several risk factors for hematuria in women. These include:
- Age: The risk of conditions like kidney stones or cancers goes up with age.
- Sexual activity: Being sexually active increases the risk of UTIs, a common cause of hematuria.
- Family history: Having a family history of kidney disease or stones raises your risk.
- Medical conditions: Conditions like diabetes or hypertension can harm the kidneys and increase hematuria risk.
Knowing these risk factors and main causes helps in early detection and management of hematuria. If you notice symptoms, seeing a healthcare professional is vital for the right evaluation and treatment.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are a common cause of blood in the urine for women. They can really affect your quality of life if not treated right. UTIs happen when bacteria get into the urinary tract and cause an infection.
This infection can lead to symptoms like blood in the urine. It’s important to know about UTIs and their symptoms.
Causes and Mechanisms
UTIs cause blood in the urine because of inflammation and irritation in the urinary tract. Bacteria in the urinary tract cause an infection. This infection can lead to inflammation and bleeding.
The blood in the urine can be tiny or big enough to see. It depends on how bad the infection is.
Key factors that contribute to UTI-related hematuria include:
- Infection severity
- Location of the infection within the urinary tract
- Individual’s overall health and immune response
Symptoms Associated with UTI-Related Bleeding
Women with UTI-related bleeding might also have other symptoms. These include:
- Dysuria (painful urination)
- Frequent urination
- Urgent need to urinate
- Lower abdominal pain
If you think you have a UTI, you should see a doctor right away. Quick treatment can help with symptoms and prevent worse problems.
Prevalence and Statistics
UTIs are a big health issue for women. Studies show UTIs are more common in women than men. This is mainly because of differences in anatomy.
| Age Group | Prevalence of UTIs |
| 18-24 years | High |
| 25-44 years | Moderate to High |
| 45-64 years | Moderate |
| 65+ years | Moderate to Low |
If a UTI is found, doctors usually start with antibiotics. Antibiotics are very effective in treating UTIs. It’s key for women to know about UTI risks and symptoms to get medical help fast.
Kidney and Bladder Stones
It’s important to understand how kidney and bladder stones can cause blood in urine. These stones are a big health issue, leading to over 500,000 emergency room visits each year in the U.S.
Formation and Types of Urinary Stones
Urinary stones form when urine’s mineral balance is off, causing minerals to crystallize. They can be made of different materials like calcium oxalate, uric acid, and cystine. Dehydration, diet, and genetics play a role in their formation.
The main types of urinary stones are:
- Calcium Stones: The most common, linked to too much calcium in urine.
- Uric Acid Stones: More common in men, but women with gout can also get them.
- Cystine Stones: Rare, found in people with a genetic disorder that makes cystine leak into urine.
- Struvite Stones: Usually linked to urinary tract infections (UTIs).
How Stones Cause Bleeding
Stones can damage the bladder or kidney lining by scraping against it. This damage can cause blood vessels to leak, leading to bleeding.
Symptoms Beyond Hematuria
Kidney and bladder stones can cause more than just blood in urine. They can also lead to:
- Severe Pain: Often described as one of the most intense pains, felt in the flank or lower abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting: May happen, mainly if the pain is severe or there’s an infection.
- Frequent Urination: Stones can irritate the bladder, causing a strong urge to urinate.
- Difficulty Urinating: In some cases, stones can block urine flow, making it hard to urinate.
It’s key to recognize these symptoms early. Untreated stones can lead to serious issues like infection or kidney damage.
Gynecological Causes of Blood in Urine
Many gynecological conditions can cause blood in urine. Hematuria is often linked to urinary tract issues. But, it’s important to think about gynecological factors, too, for female patients. We’ll look at some key gynecological causes and how they might lead to blood in urine.
Endometriosis and Adenomyosis
Endometriosis affects over 11% of women in the U.S. It’s when tissue like the uterus lining grows outside the uterus. This can cause pelvic pain and sometimes blood in urine. Adenomyosis, where this tissue grows into the uterus wall, can also lead to heavy bleeding and blood in urine.
Key points about endometriosis and adenomyosis:
- Endometriosis can cause inflammation and scarring that might affect the urinary tract.
- Adenomyosis is associated with heavy menstrual bleeding, which can sometimes be confused with hematuria.
- Both conditions are linked to hormonal changes and can have significant impacts on quality of life.
Menstruation-Related Bleeding
Menstruation is a normal part of female health. But, it can sometimes be mistaken for blood in urine. It’s important to understand the timing and characteristics of the bleeding to figure out its cause.
Factors to consider:
- The timing of the bleeding in relation to the menstrual cycle.
- The presence of other symptoms such as pain or urinary frequency.
- The appearance and quantity of the blood.
Distinguishing Vaginal from Urinary Bleeding
It’s key to tell vaginal bleeding from urinary bleeding. Vaginal bleeding can happen for many gynecological reasons, like menstruation. It might look like hematuria. A detailed medical check is needed to find out where the bleeding is coming from.
To find out why there’s blood in urine, doctors might do tests like urinalysis and imaging studies. They might also do gynecological exams. Knowing the cause is important for the right treatment.
Kidney Diseases and Conditions
Kidney diseases are a big reason for blood in the urine in women. They affect the urinary system in many ways. We’ll look at the kidney diseases and conditions that cause blood in the urine. Understanding their impact and the need for proper diagnosis is key.
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease that inflames the glomeruli. These are the kidneys’ filtering units. This condition can cause blood in the urine because of the damage to the kidneys.
Symptoms and Causes: Symptoms include blood in the urine, too much protein in the urine, and high blood pressure. Causes can be infections or autoimmune diseases.
Polycystic Kidney Disease
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder. It causes many cysts to grow in the kidneys. These cysts can damage the kidneys and make them not work right, leading to blood in the urine.
Key Features: PKD is marked by many cysts of different sizes. These cysts can cause problems like kidney stones, cyst infections, and kidney failure.
Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis, or bladder pain syndrome, causes bladder pressure and pain. It can also cause pelvic pain. Symptoms can get worse with certain foods and drinks.
Diagnostic Approaches: To diagnose interstitial cystitis, other conditions that could cause similar symptoms are ruled out. Treatment aims to manage symptoms.
| Kidney Condition | Primary Symptoms | Potential Complications |
| Glomerulonephritis | Hematuria, Proteinuria, Hypertension | Kidney Failure, Cardiovascular Disease |
| Polycystic Kidney Disease | Cysts in Kidneys, Hematuria, Pain | Kidney Failure, Cyst Infections, Kidney Stones |
| Interstitial Cystitis | Bladder Pain, Urgency, Frequency | Reduced Bladder Capacity, Pelvic Pain |
Medications and Blood in Urine
Certain medications can lead to hematuria, which is blood in the urine. It’s important for patients to know this, as it helps in finding the cause of hematuria.
Many medications can cause blood in the urine. This can happen as a side effect or because of how the medication works. Knowing this helps in diagnosing and treating hematuria.
Common Medications That Cause Hematuria
Several types of medications have been linked to hematuria. These include:
- Antibiotics: Some antibiotics, like penicillins and cephalosporins, can cause blood in the urine.
- Cyclophosphamide: This chemotherapy drug can lead to hemorrhagic cystitis, causing blood in the urine.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Taking NSAIDs for a long time or in high doses can raise the risk of blood in the urine.
These medications can cause blood in the urine in different ways. They might irritate the bladder or affect how the body clots blood.
Blood Thinners and Anticoagulants
Blood thinners and anticoagulants can also lead to hematuria. These drugs prevent blood clots or break them up.
They are key in stopping and treating blood clots. But, they can also increase the risk of bleeding, including blood in the urine. Common ones include warfarin, apixaban, and rivaroxaban.
People taking these drugs should watch for signs of blood in the urine. Their doctor might need to adjust their medication to lower this risk.
It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand how medications can cause hematuria. This helps manage side effects and find the true cause of blood in the urine.
Cancer as a Cause of Hematuria
Blood in urine can be scary, and sometimes it means cancer. Cancers of the bladder and kidney are big worries when we talk about hematuria.
Bladder Cancer Risk Factors and Symptoms
Bladder cancer is a common disease that affects the bladder. Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, exposure to chemicals, and radiation therapy. Symptoms include blood in urine, painful urination, and needing to urinate often.
Kidney Cancer and Hematuria
Kidney cancer, or renal cell carcinoma, can also cause blood in urine. Risk factors for kidney cancer include smoking, being overweight, and genetic conditions. Blood in urine is often the first sign, along with pain in the side and a noticeable mass.
Importance of Early Detection
Finding cancer early is key to better treatment. Knowing the signs of bladder and kidney cancer, like blood in urine, is vital. We stress the need to be aware of these symptoms for early diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
To diagnose hematuria, doctors need to look at your medical history, do a physical exam, and run tests. This helps find out why you have blood in your urine. Then, they can plan the best treatment.
Initial Assessment and Tests
When you see a doctor with hematuria, they start by asking about your health history. They also do a physical exam to find any signs of the problem.
Tests are key to figuring out why you have hematuria. These might include:
- Urinalysis to check for infection, stones, or other abnormalities
- Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to visualize the urinary tract
- Cystoscopy to examine the inside of the bladder and urethra
- Blood tests to assess kidney function and check for other conditions
Treatment Approaches for Different Causes
Treatment for hematuria depends on what’s causing it. For example, if it’s a urinary tract infection, you’ll need antibiotics. If it’s kidney stones, you might need pain meds, lots of water, and sometimes surgery.
For serious issues like kidney disease or cancer, treatment might include:
- Medications to manage symptoms and slow disease progression
- Surgical procedures to remove tumors or repair damaged tissues
- Lifestyle modifications to reduce risk factors and improve overall health
Prevention Strategies
To prevent hematuria, you need to tackle its causes. For many women, this means keeping the urinary tract clean and drinking plenty of water. Others might need to manage chronic conditions.
Some ways to prevent hematuria include:
- Staying well-hydrated to dilute urine and reduce the risk of stone formation
- Maintaining good urinary tract hygiene
- Managing chronic conditions through lifestyle changes and medication
- Avoiding certain medications that can cause hematuria
By knowing why hematuria happens and using these prevention tips, women can lower their risk. This helps keep their urinary system healthy.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Attention
It’s important for women to know when to see a doctor if they have blood in their urine. Hematuria can mean different things, from simple infections to serious diseases like cancer.
If you notice blood in your urine, get a doctor to check it out. Quick action is key. This way, you can find out what’s causing it and get the right treatment.
Women with hematuria should talk to a healthcare professional right away. Don’t wait if you see blood in your urine. Getting medical help quickly is the best way to get the care you need.
FAQ
What does blood in the urine indicate for a woman?
Blood in the urine, or hematuria, can mean many things. It could be a sign of infections, kidney stones, or even cancer. It’s important to see a doctor to find out why.
Why would a female pee blood?
Blood in urine can happen for many reasons. It might be due to infections, stones, endometriosis, or some medicines. We can figure out why and find the right treatment.
What causes blood in the urine for a female?
Blood in urine can come from infections, stones, endometriosis, or kidney diseases. We’ll talk about these reasons and help you understand your situation.
What are the risk factors for developing hematuria?
Certain things can increase your risk of hematuria. These include past infections, stones, some medicines, and diseases like kidney problems or cancer. We can look at your specific risks.
Can menstruation cause blood in the urine?
Menstruation itself doesn’t cause urine blood. But, vaginal bleeding can sometimes mix with urine. We’ll help you tell the difference.
How is hematuria diagnosed?
Doctors use several steps to diagnose hematuria. This includes looking at your medical history, doing a physical exam, and tests like ultrasound or CT scans. We’ll guide you through this process and suggest the right tests.
What are the treatment options for hematuria?
Treatment for hematuria varies based on the cause. It could be antibiotics for infections, surgery for stones or cancer, or other options. We’ll find the best treatment for you.
Can certain medications cause blood in the urine?
Yes, some medicines, like blood thinners, can lead to hematuria. We’ll check your medicines and explain how they might affect you.
Is blood in the urine a sign of cancer?
Blood in urine can be a sign of cancer, like bladder or kidney cancer. But, it’s not the only reason. We’ll find out why you have it and give you a proper diagnosis.
How can I prevent hematuria?
To prevent hematuria, stay hydrated, keep good hygiene, and manage health conditions. We can give you advice to lower your risk.
When should I seek medical attention for blood in my urine?
If you see blood in your urine, see a doctor right away. This is important if you also have pain, fever, or trouble urinating. We’re here to help you figure out what’s going on and get the right treatment.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information.. What Causes Blood in Urine for Females Hematuria. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK534213/)



































