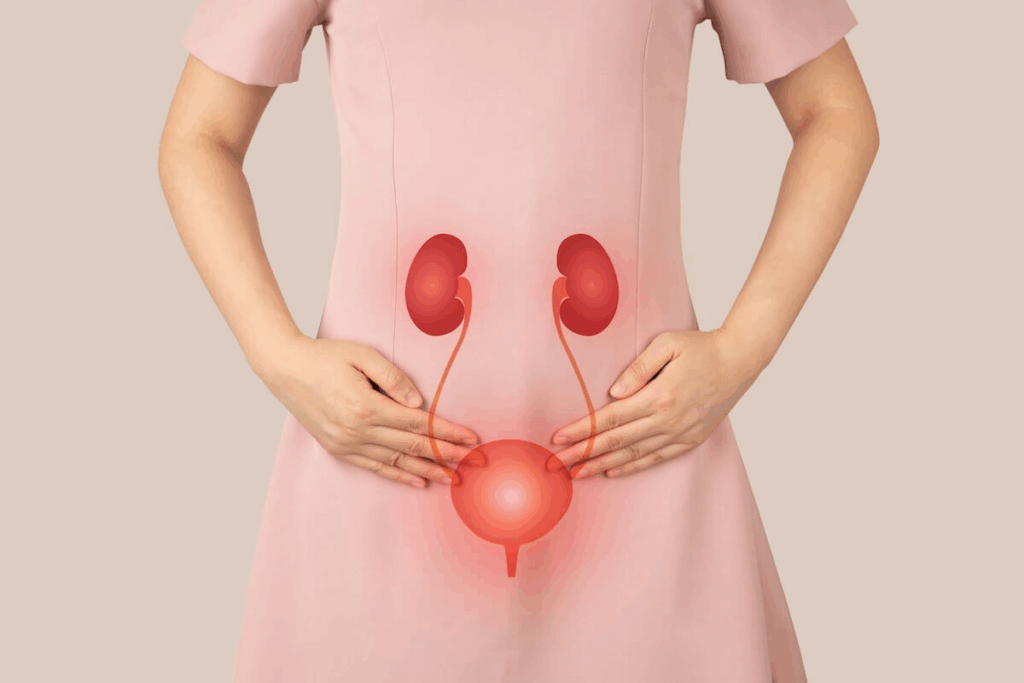
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) affect millions worldwide. It’s important to know what happens if you ignore them. While some UTIs might go away on their own, ignoring symptoms can cause serious health problems. What happens if you leave a UTI untreated? Learn about the progression from a simple bladder infection to a serious kidney infection (pyelonephritis).
Leaving a UTI untreated can lead to serious issues, like sepsis and permanent kidney damage. At Liv Hospital, we stress the need for quick medical check-ups and proper treatments to avoid these problems.
It’s key to understand the dangers of untreated UTIs to keep yourself healthy. In this article, we’ll look at the health risks and complications from ignoring UTI symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- UTIs can lead to severe health complications if left untreated.
- Ignoring UTI symptoms can result in life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
- Prompt medical attention is key to prevent long-term damage.
- Evidence-based treatment protocols can effectively manage UTIs.
- Understanding the risks of untreated UTIs is vital for maintaining health.
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)
The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. It can get infected by bacteria, known as Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs). Most UTIs happen in the lower urinary tract, like the bladder and urethra.
Common Causes of UTIs
UTIs are mainly caused by bacteria. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the top cause, responsible for 80-90% of cases. Other bacteria, like Staphylococcus saprophyticus, can also cause UTIs but less often. Risks include being female, being sexually active, using certain birth control, and having urinary tract issues.
Typical Symptoms of a UTI
Symptoms of a UTI can vary. They include a strong urge to urinate and a burning feeling while doing so. You might also pass small amounts of urine often or notice it looks cloudy or smells bad. Women might also feel pelvic pain.
Prevalence and Statistics
UTIs are a big health issue, causing about 8.1 million doctor visits each year in the U.S. They affect many people, but women get them more often than men. Knowing about UTIs and getting help quickly is key to avoiding serious problems.
How Long Does a UTI Typically Last?

The time a UTI lasts can change a lot, depending on treatment. Without treatment, UTIs can last for weeks and even get worse. But, with the right antibiotics, symptoms can go away in a few days.
Duration of Treated UTIs
When treated quickly with antibiotics, most UTIs start to get better in 48 hours. Symptoms like burning when you pee and needing to pee a lot usually get better. It’s key to finish all the antibiotics to make sure the infection is gone.
Here’s what you can expect with treated UTIs:
- Symptoms start to get better in 2-3 days after starting antibiotics.
- Most people feel much better in 5 days.
- It’s important to finish the antibiotic treatment (usually 7-14 days) for full recovery.
Timeline of Untreated Infections
Untreated UTIs can be unpredictable. Without antibiotics, the infection can:
- Last for weeks or even longer.
- Get worse and cause more severe symptoms.
- Spread to the kidneys, which is serious and needs more treatment.
About 3 percent of untreated UTIs can turn into kidney infections. These are serious and need more treatment. If symptoms don’t get better or get worse, you should see a doctor.
In summary, treated UTIs usually get better in a few days to a week. But, untreated infections can last longer and cause serious problems. Knowing how important quick treatment is can help manage symptoms and avoid long-term issues.
Can UTIs Resolve Without Treatment?
Some UTIs might go away without treatment, but waiting can be risky. Urinary Tract Infections are common and affect millions. Knowing if they can heal on their own is key to managing them well.
Self-Resolving UTIs: Fact or Fiction?
Studies show that 25% to 50% of mild UTIs can clear up without antibiotics. But, waiting for a UTI to heal on its own is not without danger. Whether it resolves depends on the infection’s severity and the person’s health.
Factors Influencing Natural Resolution
- The severity of the UTI: Mild infections are more likely to resolve on their own.
- Overall health of the individual: Healthy individuals with robust immune systems are more likely to clear the infection naturally.
- Presence of underlying health conditions: Conditions such as diabetes or kidney disease can complicate UTIs and reduce the likelihood of natural resolution.
Risks of Waiting It Out
Waiting for a UTI to heal on its own might seem like a good option. But, there are serious risks. Untreated UTIs can cause kidney damage and, in rare cases, sepsis. These complications highlight the need to see a doctor if symptoms don’t improve or get worse.
To understand the risks better, let’s look at the data on treated vs. untreated UTIs:
Outcome | Treated UTIs | Untreated UTIs |
Resolution Rate | 90-100% | 25-50% |
Complication Rate | <5% | 20-30% |
Recurrence Rate | 10-20% | 30-50% |
In summary, while some UTIs might heal without treatment, the dangers of waiting are real. It’s important for those with UTI symptoms to talk to a healthcare professional. They can help decide the best treatment plan.
What Happens if You Leave a UTI Untreated: Initial Consequences
Not treating a UTI can make symptoms worse and increase the risk of more problems. At first, symptoms might seem okay. But they can get much worse if not treated.
Worsening Symptoms
UTI symptoms include burning during urination, frequent urges to urinate, and pelvic pain. If not treated, these symptoms can get worse. The burning feeling can get stronger, and you might need to pee more often.
Spreading Infection
Not treating a UTI can let it spread to other parts of the urinary tract. This can lead to serious conditions. The infection can move up to the kidneys and ureters, causing pyelonephritis.
Impact on Daily Life and Functionality
Untreated UTIs can really disrupt your daily life. The need to pee a lot and the pain can make simple tasks hard. This can affect your work, social life, and overall happiness.
It’s important to treat UTIs quickly to avoid these problems. Knowing what can happen if you don’t treat a UTI can help you decide to see a doctor.
Progression to Upper Urinary Tract Infection
Upper urinary tract infections happen when bacteria from a UTI reach the kidneys. This can cause permanent damage. It often occurs if the first infection isn’t treated quickly or well.
From Cystitis to Pyelonephritis
Cystitis, an infection of the bladder, can move up to the kidneys and become pyelonephritis. This happens when bacteria, like E. coli, travel up the urinary tract. If not treated, pyelonephritis can cause serious problems, like kidney damage and scarring.
A study in the Journal of Urology says, “Pyelonephritis is a serious infection that needs quick treatment to avoid long-term kidney damage.”
“The timely diagnosis and treatment of pyelonephritis are key to prevent complications and lower the chance of more infections.”
Symptoms of Kidney Infection
Kidney infection symptoms are often worse than those of a lower UTI. They can include:
- Fever and chills
- Back or flank pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Frequent urination
- Blood in the urine
These signs mean the infection has moved up to the upper urinary tract. It needs immediate medical care.
Timeline of Infection Progression
The time it takes for a lower UTI to turn into an upper urinary tract infection varies. It depends on the bacteria type and the person’s health.
Timeframe | Possible Symptoms and Progression |
0-3 days | Initial UTI symptoms such as dysuria and frequency |
3-7 days | Possible progression to upper urinary tract infection with symptoms like flank pain and fever |
7+ days | Increased risk of complications, including kidney damage if left untreated |
Prompt treatment is key to stop UTIs from turning into upper urinary tract infections.
Serious Complications of Untreated UTIs
Untreated urinary tract infections (UTIs) can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening complications. We will explore the risks and consequences of not treating UTIs promptly and effectively.
Permanent Kidney Damage and Scarring
Untreated UTIs can cause permanent kidney damage and scarring. When a UTI spreads to the kidneys, it can lead to pyelonephritis. This condition can cause scarring and irreversible damage if not treated promptly. This damage can impair kidney function and increase the risk of future kidney problems.
The risk of kidney damage is higher for individuals with pre-existing kidney issues or those who are prone to recurrent UTIs. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Sepsis and Systemic Infection
Another severe complication of untreated UTIs is the risk of developing sepsis. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that occurs when the infection spreads to the bloodstream. It can cause widespread inflammation and organ failure, making it a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
UTIs are among the common causes of sepsis, which is a concern for older adults or individuals with compromised immune systems. Recognizing the signs of sepsis, such as fever, rapid heart rate, and confusion, is critical for prompt intervention.
Rare but Serious Complications
In addition to kidney damage and sepsis, untreated UTIs can lead to other rare but serious complications. These may include kidney abscesses, permanent kidney failure, and pregnancy complications in expectant mothers. While these outcomes are less common, they underscore the importance of treating UTIs promptly and effectively.
Complication | Description | Risk Factors |
Permanent Kidney Damage | Scarring and irreversible damage to kidney tissue | Recurrent UTIs, delayed treatment |
Sepsis | Life-threatening condition caused by infection in the bloodstream | Older adults, compromised immune systems |
Kidney Abscess | A pocket of pus in the kidney tissue | Untreated UTIs, underlying health conditions |
Understanding the complications of untreated UTIs highlights the importance of seeking medical care if symptoms persist or worsen. Prompt treatment can prevent long-term damage and reduce the risk of serious health consequences.
UTIs in Different Populations
UTIs are a big health issue that hits different groups in different ways. We need to tailor how we find and treat them. Knowing these differences helps us manage and prevent UTIs better.
Women and UTIs
Women get UTIs more often because their urethra is shorter. This makes it easier for bacteria to get into the bladder. Recurrent UTIs are common in women, with some getting them often. Things like sex, pregnancy, and menopause can make UTIs more likely.
- Hormonal changes during menopause can increase UTI risk.
- Sexual activity can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract.
- Pregnancy increases the risk due to physiological changes.
Men and UTIs
UTIs are less common in men but can be more serious. They often mean there’s something wrong like an enlarged prostate. Escherichia coli is the main cause, but other germs can also cause them.
- UTIs in men are often associated with underlying conditions.
- Symptoms can be more severe and include fever and flank pain.
- Diagnosis may involve additional testing to identify underlying causes.
Elderly Patients
UTIs in older adults can be tricky to spot because they often don’t show typical symptoms. Catheter-associated UTIs are a big worry in this group, mainly in care settings.
- Non-specific symptoms can delay diagnosis.
- Catheter use increases the risk of UTIs.
- Antibiotic resistance is more common in this population.
Children and UTIs
UTIs in kids can lead to serious problems if not treated right away. Vesicoureteral reflux is a big risk factor. Doctors often use imaging to check for any problems.
- Prompt diagnosis is key to avoid lasting damage.
- Imaging studies are often used to assess for abnormalities.
- Antibiotic prophylaxis may be recommended for recurrent UTIs.
In conclusion, UTIs affect different groups in unique ways. We need to tailor our approach to diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Understanding these differences is essential for effective care.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a UTI
Knowing when to get medical help for a UTI is key to avoiding bigger problems. UTIs can get worse fast if not treated, leading to serious health issues. We’ll talk about the signs that mean you need to see a doctor right away and how UTIs are diagnosed.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Care
Some symptoms mean your UTI is serious and needs quick medical help. These include:
- High Fever: A fever over 101°F (38.3°C) might mean the infection has reached your kidneys.
- Severe Pain: Pain in your lower back, abdomen, or pelvis could be a sign of a serious infection.
- Signs of Sepsis: Feeling cold, having a fast heart rate, or being confused could mean sepsis, a dangerous condition.
- Blood in Urine: Seeing blood in your urine is a sign you need to see a doctor.
- Vomiting and Nausea: If you keep vomiting and can’t keep fluids down, it can lead to dehydration and make things worse.
Diagnostic Process for UTIs
Diagnosing a UTI involves several tests to find out if you have an infection and what bacteria are causing it. The steps usually include:
Diagnostic Test | Description | Purpose |
Urinalysis | Testing a urine sample for bacteria, blood, or other problems. | To confirm if you have an infection. |
Urine Culture | Growing bacteria from a urine sample to find out what kind it is. | To choose the right antibiotics. |
Imaging Tests | Using ultrasound or CT scans to look at your urinary tract. | To see if there are any structural problems or complications. |
Cystoscopy | Putting a scope into your bladder to see inside. | To find any issues in your bladder. |
Knowing when to get medical help and how UTIs are diagnosed helps you take care of your health. If you think you have a UTI, see a doctor quickly to avoid bigger problems.
Treatment Options for UTIs
Effective treatment for urinary tract infections (UTIs) is key to avoid complications and ease symptoms. The right treatment can greatly help manage UTIs and prevent them from coming back. We will look at the different treatment options, including medical treatments and home remedies.
Antibiotic Treatments
Antibiotics are the main treatment for UTIs. They target and kill the bacteria causing the infection. The type of antibiotic used depends on the bacteria and how severe the infection is.
Common antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin. It’s important to finish all antibiotics as directed. This ensures the infection is fully cleared and helps prevent it from coming back.
Pain Management
Managing pain is a big part of UTI treatment. Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help ease the discomfort. Sometimes, doctors may prescribe special medications to help with symptoms. Applying a heating pad to the lower abdomen can also provide relief.
Home Remedies as Complementary Approaches
While antibiotics are the main treatment, some home remedies can help too. They can make symptoms easier to manage.
Drinking lots of water helps flush out bacteria from the urinary tract. Cranberry juice is also often suggested, though its effectiveness can vary. Avoiding things like caffeine and spicy foods can also help reduce discomfort.
Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
Antibiotics | Target and eliminate bacteria causing UTIs | Effective in clearing infections, preventing recurrence |
Pain Management | Relieve discomfort associated with UTIs | Reduces pain, improves quality of life |
Home Remedies | Complementary approaches to alleviate symptoms | Supports medical treatment, may prevent future UTIs |
Knowing the treatment options for UTIs helps individuals manage their condition better. It’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to find the best treatment plan.
Conclusion
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common health issue. They can lead to severe complications if not treated. In this article, we discussed the causes, symptoms, and risks of UTIs, along with treatment options.
Treating UTIs quickly is key to prevent long-term damage and ensure a fast recovery. Untreated UTIs can worsen symptoms, spread infection, and even lead to life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
In summary, understanding UTIs and treating them is vital for good health. Recognizing warning signs and seeking medical help when needed helps avoid risks from untreated UTIs.
As we’ve highlighted, treating UTIs is very important. Taking a proactive approach to treatment reduces the risk of complications and improves overall health.
FAQ
Can a UTI resolve on its own without treatment?
Some UTIs might clear up by themselves. But, it’s not safe to wait for this to happen. Untreated UTIs can cause serious problems.
How long does a UTI typically last if left untreated?
The time an untreated UTI lasts can vary. But, symptoms often get worse. The infection can also spread to other parts of the urinary system.
What happens if you leave a UTI untreated?
Untreated UTIs can get worse. The infection might spread. This can lead to serious issues like kidney damage and sepsis.
Can UTIs cause long-term damage if left untreated?
Yes, untreated UTIs can harm the kidneys and other urinary system parts. They can also cause systemic infections.
Will a bladder infection go away by itself?
Some bladder infections might clear up by themselves. But, it’s important to see a doctor to avoid complications.
How long can you have a UTI before it causes serious complications?
The time it takes for a UTI to cause serious problems varies. It’s key to get medical help quickly to avoid lasting damage.
What are the risks of waiting for a UTI to resolve on its own?
Waiting for a UTI to clear up can make symptoms worse. It can also spread the infection and lead to serious issues.
Can a urinary tract infection go away on its own without antibiotics?
Some UTIs might clear up without antibiotics. But, antibiotics are usually needed to fully treat the infection and prevent complications.
How long does it take to treat a UTI?
Treating a UTI’s time depends on the infection’s severity and treatment’s success. Most UTIs can be treated with antibiotics in a short time.
What are the warning signs that a UTI requires immediate medical attention?
Signs that a UTI needs immediate care include severe symptoms. These include intense pain, fever, and vomiting. Also, look out for signs of kidney infection or sepsis.
References
NIH MedlinePlus. (2024, May 22). Crystals in urine. https://medlineplus.gov/lab-tests/crystals-in-urine/


































