Mandibular cancer is a serious head and neck cancer that affects the lower jawbone. It’s a type of jaw cancer that can have serious effects if not caught early.
At Liv Hospital, we know how important early detection and care are. Oral cancer, including mandibular cancer, happens when mouth cells mutate. This often starts in the thin cells lining the lips and mouth.
It’s key to spot jaw tumor symptoms early. Look out for persistent lumps, trouble swallowing, and pain in the ear and jaw. Our patient-focused care uses the latest imaging and team care to help patients the most.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding mandibular cancer and its symptoms is vital for early detection.
- Jaw tumor symptoms include persistent lumps and difficulty swallowing.
- Liv Hospital offers complete care for mandibular cancer patients.
- Early diagnosis greatly improves treatment results.
- Our method includes top-notch imaging and team care.
Understanding Mandibular Cancer
Mandibular cancer is a type of jaw tumor that affects the lower jawbone. It’s important to know about it for early detection and treatment. We’ll look at what the mandible is, its anatomy, and the different jaw cancers to understand this condition better.
Definition and Anatomy of the Mandible
The mandible, or lower jawbone, is key to our facial structure. It’s the biggest and strongest bone in the face. It helps us chew, speak, and keep our face shape. About 66% of jaw tumors happen in this area. Knowing the mandible’s anatomy is key for treating mandibular cancer.
Oral cancer can happen in the mouth and throat. It can appear on the tongue, mouth lining, gums, under the tongue, at the tongue’s base, and in the throat’s back. The mouth’s complex anatomy means jaw cancer can show up in many ways. It’s important to know the specifics of mandibular cancer.
Types of Jaw Cancer
Jaw cancer can be different based on where it starts. The most common is squamous cell carcinoma, from the mouth and throat lining. Odontogenic tumors start from tooth development tissues. These can be benign or cancerous and only happen in the jaw.
Other jaw cancers include salivary gland tumors and cancers that spread to the jaw. Knowing the types of jaw cancer helps doctors choose the right treatment and predict outcomes.
Prevalence and Epidemiology
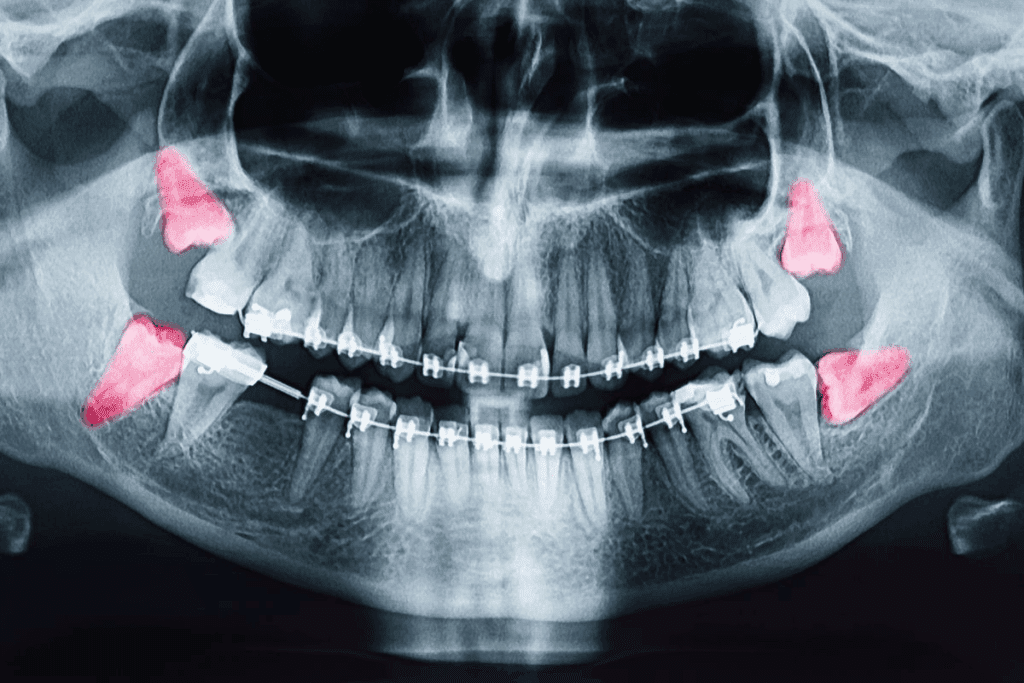
The study of jaw tumors shows us how common they are and where they happen. Knowing this helps us find out who is at risk. It also helps us improve how we diagnose and treat jaw cancer.
Incidence Rates of Jaw Tumors
Jaw tumors, both benign and malignant, occur at different rates around the world. Oral cancer, which includes jaw cancers, is a big part of all cancers globally. The rate of jaw cancer changes based on where you are, your age, and if you’re a man or woman.
Most oral cancers happen in people over 40, and men get them more often than women. Using tobacco and alcohol greatly increases the risk of getting oral cancer, including jaw cancer.
Demographic | Incidence Rate | Relative Risk |
Men over 40 | Higher | 2x compared to women |
Tobacco users | Significantly higher | Associated with increased risk |
Alcohol consumers | Higher | Synergistic effect with tobacco |
Distribution in the Mandible vs. Maxilla
Jaw tumors can occur in the mandible (lower jaw) or maxilla (upper jaw). Some tumors prefer one over the other. The mandible often gets more jaw cancers.
Knowing where jaw tumors happen helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. We’ll look at more details in the next sections. This will give us a full picture of jaw cancer.
Common Types of Mandibular Cancer
It’s important to know about the different types of mandibular cancer. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat the cancer better. Mandibular cancer includes various cancers that differ in their cause, behavior, and effect on patients.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common oral cancer. It mostly happens in the mouth but can also affect the jaw. Squamous cell carcinoma of the mandible is very aggressive and needs quick treatment. It starts from squamous cells, which are thin, flat cells lining the mouth and jaw.
To diagnose squamous cell carcinoma, doctors use clinical exams, imaging, and biopsies. Treatment often includes surgery, radiation, or both, depending on the tumor’s size and stage.
Odontogenic Tumors
Odontogenic tumors come from tooth development tissues. Most are benign, but some can be dangerous. Ameloblastoma is a common tumor that can damage the jaw if not treated.
Doctors usually remove these tumors surgically. Sometimes, they need to remove more tissue to get rid of the tumor completely. It’s important to check for any signs of the tumor coming back.
Other Malignancies of the Jaw
Other cancers can also affect the mandible. These include osteosarcoma, a rare bone cancer, and metastatic tumors that spread to the jaw from other places.
Doctors use CT scans and MRI to diagnose these cancers. They then take a biopsy to confirm the cancer type. Treatment plans are made based on the cancer type, stage, and location.
Knowing the exact type of mandibular cancer is key to choosing the right treatment. This helps improve patient outcomes.
Recognizing Jaw Tumor Symptoms
Spotting jaw tumor symptoms early can greatly help in treating mandibular cancer. We’ll look at common signs and symptoms. This will help patients and caregivers know when to get medical help.
Early Warning Signs
Jaw tumors can show different symptoms, some of which might seem small but are serious. Look out for white or red patches in the mouth, sores that don’t heal, and unusual bleeding. You might also feel numbness or pain in your mouth or jaw.
A lump or swelling in your jaw or mouth that doesn’t go away is another sign. Watching for changes in your mouth and jaw is key. Early detection can greatly improve treatment.
Advanced Symptoms
As jaw tumors grow, symptoms can get worse and more painful. Look out for ear and jaw pain on one side, trouble swallowing, and voice changes. You might also see facial swelling and asymmetry, which can be upsetting.
Advanced tumors can also cause loose teeth and changes in how you chew and speak. These signs mean you need to see a doctor right away.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you’re experiencing any of these symptoms, get medical help fast. These signs can mean different things, but a doctor’s check-up is needed to find out why.
See a specialist if symptoms keep coming back or get worse. Early treatment can greatly improve outcomes for mandibular cancer patients.
Visible Signs of Mandibular Cancer
Spotting the signs of jaw cancer early can really help. Mandibular cancer shows itself in different ways. These signs are key for catching it early.
Lumps and Masses in the Jaw
Lumps or masses in the jaw are a common sign. These can be painless or hurt. They might grow, making it hard to chew or swallow.
Not every lump is cancer. But, any odd growth in the jaw needs a doctor’s check.
White or Red Patches in the Mouth
White or red patches in the mouth are another sign. These patches, called leukoplakia or erythroplakia, might be early signs of cancer. They could be precancerous or cancerous.
Visible Sign | Description | Potential Implication |
Lumps/Masses | Unusual growth or swelling in the jaw | Potential cancerous growth affecting jaw function |
White/Red Patches | Appearance of white or red patches in the mouth | Possible precancerous or cancerous lesions |
Physical Symptoms and Discomfort
Bone cancer in the jaw bone can cause significant discomfort. It affects daily activities. Understanding these symptoms is key to knowing about jawline cancer and the patient’s health.
Ear and Jaw Pain on One Side
Ear and jaw pain on one side is a common symptom of mandibular cancer. This pain can be constant and might be confused with TMJ disorder. But, if it’s related to jawline cancer, getting a medical check-up is important.
- Pain that radiates to the ear or temple area
- Difficulty in opening the mouth wide
- Clicking or tenderness in the jaw
Difficulty Swallowing
As the tumor grows, swallowing can become hard, known as dysphagia. This symptom can harm a patient’s nutrition and health. It shows the cancer is getting worse and needs quick medical help.
- Feeling of something being stuck in the throat
- Pain while swallowing
- Coughing or choking during meals
Facial Swelling and Asymmetry
Facial swelling and asymmetry can happen due to mandibular cancer. The tumor can make the face swell or show a noticeable lump.
These symptoms can be upsetting and harm a patient’s self-esteem and life quality. It’s important for those with these symptoms to see a doctor for the right diagnosis and treatment.
Dental Manifestations of Jaw Cancer
Jaw cancer can affect dental health in many ways. It can cause various dental problems. These issues can greatly impact a person’s life.
Loose Teeth and Dental Issues
Loose teeth are a key sign of jaw cancer. The tumor can damage the bone and tissue around the teeth. This can make teeth fall out or become loose.
Other dental problems include:
- Tooth mobility without apparent cause
- Unexplained changes in the fit of dentures
- Pain or discomfort in the teeth or gums
These symptoms are worrying and need immediate dental care. Dentists should watch for jaw cancer signs in such cases.
Changes in Bite and Jaw Alignment
Jaw cancer can also change how teeth fit together. The tumor can shift the jaw’s alignment. This makes chewing and speaking hard.
Common signs include:
- Difficulty in closing the mouth properly
- Changes in the way dentures fit
- Pain or clicking in the jaw joint
At first, these changes might be small. But they can grow as the disease gets worse. Patients should see a doctor if they notice these signs.
Regular dental visits are vital. They help catch jaw cancer early. Dentists often spot jaw cancer signs during routine checks.
Risk Factors for Developing Mandibular Cancer
Knowing the risk factors for mandibular cancer is key to preventing and catching it early. Several things can make someone more likely to get this condition.
Tobacco and Alcohol Use
Tobacco is a big risk for mandibular cancer. This includes smoking, using e-cigarettes, chewing tobacco, and snuff. Tobacco has harmful chemicals that can cause cancer in jaw tissues. Avoiding all tobacco products is a big step in lowering mandibular cancer risk.
Drinking a lot of alcohol is also a risk factor. When you add alcohol to tobacco use, the risk goes up even more. Alcohol and tobacco together can greatly increase the risk of oral cancers, including mandibular cancer.
Betel Nut Chewing
Betel nut chewing is common in some cultures and is a risk for mandibular cancer. The areca nut in betel quid has harmful compounds that can damage jaw cells and lead to cancer. People who chew betel nut should know the risks and watch their oral health closely.
Age and Other Demographic Factors
Age is a big factor, with risk going up after 55. Other factors might also play a part, but their impact can differ. Knowing these risk factors can help in catching and preventing mandibular cancer early.
The main risk factors for mandibular cancer are:
- Tobacco use in any form
- Heavy alcohol consumption
- Betel nut chewing
- Being over 55 years old
By understanding and tackling these risk factors, people can lower their chance of getting mandibular cancer. Regular health checks and a healthy lifestyle are also important for prevention and early detection.
Diagnostic Procedures for Jaw Cancer
Diagnosing jaw cancer is a detailed process. It starts with a thorough check-up, followed by advanced imaging and a biopsy. This process helps find the best treatment.
Initial Examination and Screening
The first step is a detailed check-up. Our team looks at your medical history and does a physical exam. They search for signs of jaw cancer.
They check the mouth, lips, tongue, cheeks, and throat for any unusual signs. If they find something odd, they’ll do more tests.
Imaging Tests
Next, we use imaging tests to see more about the tumor. These tests include:
- X-rays: To see the jaw bones and find any problems.
- CT (Computed Tomography) scans: Give detailed images of the jaw and tissues around it.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): Show detailed images of soft tissues and the tumor’s size.
- PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scans: Check the tumor’s activity and if it has spread.
These tests help us understand the cancer’s stage and plan treatment.
Biopsy and Pathological Confirmation
A biopsy is the key to diagnosing jaw cancer. It involves taking a tissue sample from the tumor. There are different types of biopsies, like:
- Incisional biopsy: Takes a part of the tumor for study.
- Excisional biopsy: Removes the whole tumor or area of concern.
Our pathologists then study the sample. They confirm if it’s cancer and what type. This info is key for treatment planning.
The table below shows the steps to diagnose jaw cancer:
Diagnostic Procedure | Purpose |
Initial Examination | To find signs and symptoms of jaw cancer |
Imaging Tests (X-rays, CT, MRI, PET) | To see the tumor and its size |
Biopsy | To confirm cancer and its type |
Treatment Options for Mandibular Cancer
Treating mandibular cancer often requires a mix of treatments. The main goal is to remove the tumor and restore function and looks. Surgery, like a mandibulectomy, is usually the key treatment. It involves removing part of the jaw.
After surgery, radiation therapy might be needed to kill any cancer cells left behind. Sometimes, chemotherapy is used too, either alone or with radiation. The treatment plan depends on the cancer’s stage, type, and the patient’s health.
We create a treatment plan that fits each patient’s needs. By using advanced medical treatments and support services, we help patients deal with mandibular cancer. Our goal is to improve their quality of life.
FAQ
What is mandibular cancer, and how does it differ from other types of jaw cancer?
Mandibular cancer is a type of jaw cancer that affects the lower jawbone, or mandible. It is different from other jaw cancers, like those in the upper jawbone, or maxilla.
What are the common symptoms of mandibular cancer?
Symptoms of mandibular cancer include a lump in the jaw and pain in the ear and jaw. You might also have trouble swallowing, facial swelling, and loose teeth. White or red patches in the mouth are also signs.
What are the risk factors for developing mandibular cancer?
Risk factors include tobacco and alcohol use, betel nut chewing, and age. Knowing these can help spot who’s at higher risk.
How is mandibular cancer diagnosed?
First, there’s an examination and screening. Then, imaging tests like X-rays or CT scans are used. A biopsy confirms if there are cancer cells.
What are the treatment options for mandibular cancer?
Treatments include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. The choice depends on the cancer’s stage, type, and the patient’s health.
Can jawbone cancer be treated successfully?
Yes, jawbone cancer, including mandibular cancer, can be treated if caught early. Success depends on the cancer’s stage and the treatment’s effectiveness.
What is the difference between a cancerous jaw tumor and a benign jaw tumor?
A cancerous jaw tumor is malignant and can spread. A benign jaw tumor is non-cancerous and doesn’t spread.
Are there any specific dental issues associated with jaw cancer?
Yes, jaw cancer can cause dental problems like loose teeth and changes in bite. These symptoms might indicate jaw cancer.
How common is mandibular cancer compared to other types of jaw cancer?
Mandibular cancer is more common than other jaw cancers. The mandible is more often affected than the maxilla.
Can ear and jaw pain on one side be a symptom of cancer?
Yes, ear and jaw pain on one side can be a sign of mandibular cancer. It’s important to see a healthcare professional for a proper check-up.
References
World Health Organization. (2025). What Is Mandibular Cancer Jaw Tumor Symptoms Explained. Retrieved from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/oral-health




































