Mouth cancer is a serious disease that affects many people worldwide. Yes, mouth cancer can be fatal. Knowing about its prognosis is key for making good choices. At Liv Hospital, we offer the latest medical care and insights to those affected.
Can you die from mouth cancer? Learn about the survival rates and the critical importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
The survival rate for oral cancer depends on when it’s found. 68% of people with oral cancer survive for 5 years after being diagnosed. It’s important to know about survival rates, prognosis, and treatment outcomes for patients, families, and doctors.
Key Takeaways
- Oral cancer can be fatal if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
- The 5-year survival rate for oral cancer is around 68%.
- Early detection and proper treatment significantly improve prognosis.
- Liv Hospital provides multidisciplinary specialist care for oral cancer patients.
- Understanding survival rates and prognosis is key for making informed decisions.
Understanding Mouth Cancer: The Basics
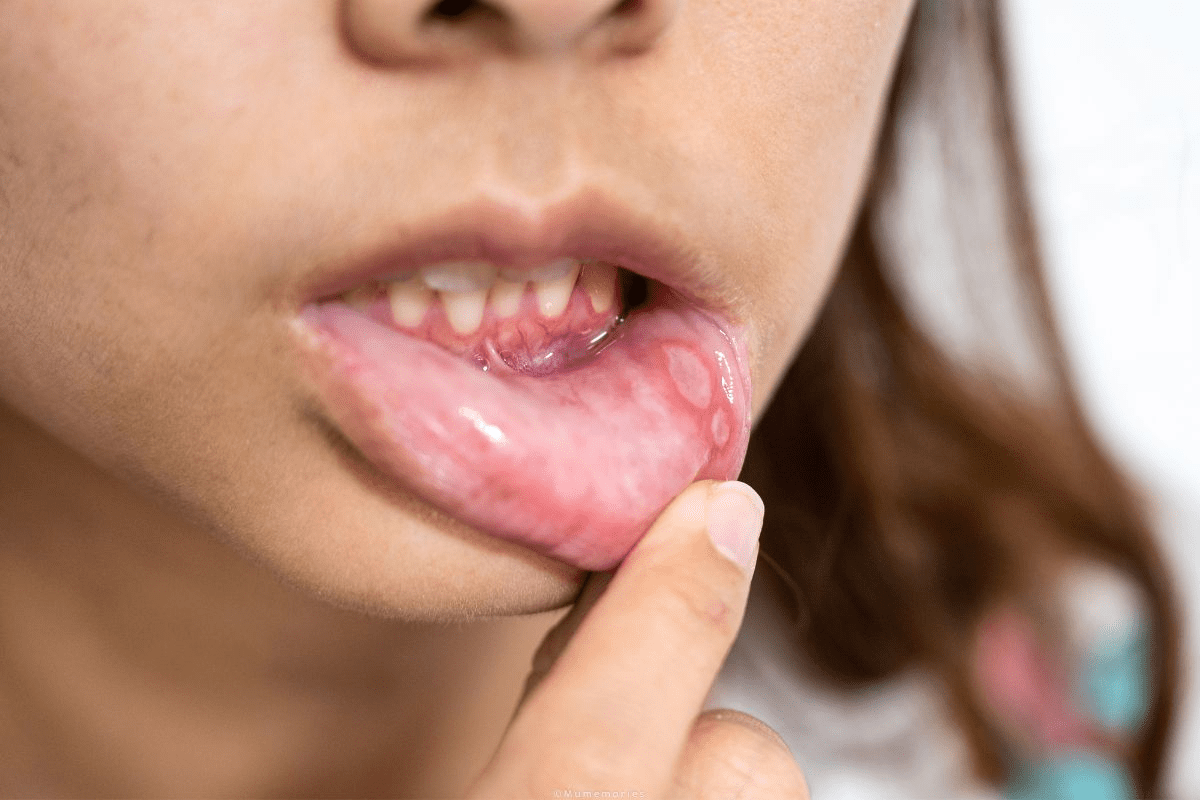

Knowing the basics of mouth cancer is key for early detection and treatment. Mouth cancer, also called oral cancer, includes many types of cancers in the mouth area.
What Is Mouth Cancer?
Mouth cancer affects the tissues in the mouth, like the lips, tongue, and gums. It happens when abnormal cells grow out of control. Oral cancer can be aggressive and needs quick medical care.
Common Types of Oral Cancers
There are several types of oral cancers, with the most common being:
- Squamous cell carcinoma, which makes up most oral cancer cases.
- Verrucous carcinoma, a rare type that usually affects the gums or inside of the cheek.
- Minor salivary gland tumors, which can be cancerous and happen in the mouth’s tissues.
Knowing the specific type of oral cancer is key for the right treatment.
Anatomical Sites Affected
Mouth cancer can hit different parts of the mouth, including:
- The lips, which can get cancer from too much sun.
- The tongue, a common spot for oral cancers, often on the sides or underside.
- The gums, where cancer can grow in the tissues around the teeth.
- The floor of the mouth, an area at risk because of its blood flow.
Knowing where in the mouth the cancer is helps tailor treatment to each person’s needs.
Can You Die From Mouth Cancer? The Hard Truth
Mouth cancer can be deadly if caught too late. We must face this truth to grasp the disease’s gravity.
Mortality Statistics in the United States
In the U.S., over 12,250 people die from oral cancer each year. That’s about 1 person every hour. These mortality statistics show how serious mouth cancer is in the country.
The high death rate from mouth cancer often comes from late diagnosis. We must stress the need for early detection to save lives.
Global Mortality Rates
Worldwide, mouth cancer’s death rates are just as scary. The World Health Organization says it’s among the top 15 cancers globally. Rates vary by region.
Regional differences in death rates are due to tobacco, alcohol, and HPV infection rates. Knowing these helps us create better prevention plans.
Comparing Mouth Cancer to Other Cancer Types
Mouth cancer’s death rate is notable when compared to other cancers. The 5-year survival rate for oral cancer is about 66%. This is lower than cancers like breast or prostate.
But, early detection can greatly increase survival chances. We must spread the word about mouth cancer risks and symptoms to help catch it early.
Survival Rates by Stage
The stage at diagnosis greatly affects mouth cancer survival rates. Knowing these rates helps patients understand their chances and make treatment choices.
Localized Survival Rates
Early detection is key. If caught early, the 5-year survival rate is 83.7%. But, if it spreads, the rate drops to 38.5%.
Stage 1 and 2 Survival Rates
Stage 1 mouth cancer has a high survival rate, often over 80%. Stage 2 is a bit more advanced but also has a good prognosis, with a rate above 60-70%. Early treatment greatly improves survival chances.
Stage 3 Survival Rates
At Stage 3, the cancer may be larger or in nearby lymph nodes. The 5-year survival rate is usually 40-50%. Treatment often includes surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy.
Stage 4 Survival Rates
Stage 4 is the most advanced stage. The 5-year survival rate is about 20-30%. Yet, with new treatments, some patients can live well.
How These Numbers Are Calculated
Survival rates come from cancer registries. They track patient outcomes over time. The 5-year survival rate shows the percentage of patients alive 5 years after diagnosis.
These rates are averages and don’t predict individual outcomes. Many factors, like treatment response and health, affect a patient’s prognosis.
Factors That Influence Mouth Cancer Prognosis
The outlook for mouth cancer depends on many things. These include age, overall health, and lifestyle. Knowing these factors helps both patients and doctors make better treatment choices.
Age and Overall Health
Age is a big factor in survival rates for oral cancer. Younger people usually do better with treatment. A person’s overall health is also key. Those with fewer health problems tend to do better.
For example, people with diabetes or heart disease might face more challenges during treatment.
Age Group | 5-Year Survival Rate |
Under 45 | 63% |
45-54 | 55% |
55-64 | 48% |
65 and older | 42% |
Cancer Location and Type
The location and type of mouth cancer matter a lot. Cancers in some areas, like the tongue, might have different outcomes. The type of cancer, like squamous cell carcinoma, also affects treatment and survival.
Treatment Response
How well a patient responds to treatment is very important. Those who do well with treatment usually have better chances. The cancer’s genetics and the patient’s health can affect this response.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices, like smoking and drinking, greatly impact mouth cancer prognosis. Using these substances during and after treatment can lead to worse outcomes. Quitting or reducing their use can improve survival chances.
Understanding these factors helps patients and doctors create effective treatment plans. This can lead to better outcomes for those with mouth cancer.
Why Early Detection Is Critical
Early detection is key in fighting mouth cancer. It greatly boosts survival chances. When caught early, treatments work better, and survival rates soar.
Survival Rate Differences Between Early and Late Detection
The survival gap between early and late mouth cancer detection is huge. Early diagnosis of oral cancer leads to much higher 5-year survival rates. Patients with early-stage mouth cancer have a much better chance of living five years compared to those diagnosed later.
Stage at Diagnosis | 5-Year Survival Rate |
Localized (Early Stage) | 80-90% |
Regional (Spread to nearby lymph nodes) | 40-50% |
Distant (Metastasized to other parts of the body) | 20-30% |
This table shows the big survival rate difference by diagnosis stage. Early detection clearly leads to a better outcome.
Common Reasons for Delayed Diagnosis
Many mouth cancers are diagnosed late. Reasons include not knowing the symptoms, fear of dental visits, and thinking symptoms are minor.
- Lack of awareness about oral cancer symptoms
- Fear of visiting the dentist or doctor
- Misdiagnosis of symptoms as minor issues
Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Knowing mouth cancer signs is vital for early detection. Look out for persistent sores, lumps, or thickening, and trouble swallowing or chewing. If you notice these, see a doctor right away.
Early detection saves lives. Being alert to mouth cancer signs and getting medical help early can greatly improve survival and quality of life.
Treatment Options and Their Impact on Survival
Patients with mouth cancer need to know about treatment options. The right treatment can greatly affect survival rates. We’ll look at surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy for mouth cancer.
Surgery
Surgery is often the first choice for mouth cancer, mainly for early stages. It aims to remove the tumor and some healthy tissue. This ensures all cancer cells are gone. Reconstructive surgery helps restore the mouth’s shape and function after surgery.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy rays. It can be used alone or with surgery and chemotherapy. There are two types: external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and brachytherapy. EBRT comes from outside the body, while brachytherapy places radioactive material near the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It’s often used with radiation therapy for advanced mouth cancers. Chemotherapy can be given before or after surgery to target remaining cancer cells.
Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy are newer treatments for mouth cancer. Targeted therapy uses drugs that target cancer cells, sparing normal cells. Immunotherapy boosts the immune system to fight cancer. These treatments offer hope for advanced or recurrent cases.
Treatment Option | Description | Impact on Survival |
Surgery | Removal of tumor and surrounding tissue | Highly effective for early-stage disease |
Radiation Therapy | High-energy rays to kill cancer cells | Can be curative or palliative |
Chemotherapy | Drugs to kill cancer cells | Often used in combination with other treatments |
Targeted Therapy | Drugs targeting specific cancer cells | Promising for advanced or recurrent disease |
Immunotherapy | Boosting immune system to fight cancer | Emerging as a promising treatment |
In conclusion, mouth cancer treatments are varied and improving. Knowing these options and their survival impact is key for patients and doctors to make the best care choices.
Life After Diagnosis: What to Expect
Getting a mouth cancer diagnosis can change your life. Knowing what to expect can help your recovery. Many oral cancer survivors live normal lives, even after treatment.
Short-term Recovery Challenges
The first few weeks after treatment can be tough. You might feel pain, swelling, and have trouble eating or speaking. These symptoms usually go away with time and the right care.
It’s important to follow your doctor’s advice for aftercare. This helps avoid problems and makes recovery easier.
- Manage pain effectively with prescribed medication
- Maintain a soft diet to ease eating difficulties
- Stay hydrated to support overall health
Long-term Quality of Life Considerations
As you get better, thinking about your long-term quality of life is key. Some people might find it hard to eat, speak, or swallow. Speech and language therapy can help with these issues.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found that
“Rehabilitation interventions can significantly improve the quality of life for patients with head and neck cancer.”
Psychological Impact
A mouth cancer diagnosis can deeply affect your mind. You might feel anxiety, depression, and fear. It’s vital to have access to counseling and support groups to deal with these feelings.
Functional Changes and Adaptations
Treatment can lead to functional changes, like changes in speech or eating. Using adaptive strategies and devices can help. For example, speech therapy can improve how you communicate, and changing your diet can make eating easier.
Knowing what to expect can help you face the challenges after a mouth cancer diagnosis. With the right support, many patients can live well and do their usual activities again.
Recurrence Risks and Secondary Cancers
Mouth cancer survivors worry about recurrence and secondary cancers. Knowing these risks is key to managing long-term survival.
Monitoring for Recurrence
Regular visits to healthcare providers are vital for watching for recurrence. These visits include physical checks, imaging tests, and sometimes biopsies to spot cancer coming back.
Key components of monitoring for recurrence include:
- Regular physical examinations
- Imaging tests (e.g., CT scans, MRI)
- Biopsies when necessary
- Patient self-examination education
Field Cancerization and Second Primary Tumors
Field cancerization means the whole area exposed to harmful substances can get cancer. This is why some patients get second tumors in the same area.
The risk factors for field cancerization include:
- Tobacco use
- Alcohol consumption
- HPV infection
- Previous radiation exposure
Improving Long-term Outcomes
Improving long-term results needs a few steps. These include making lifestyle changes, sticking to follow-up plans, and sometimes taking preventive steps.
Strategy | Description | Benefit |
Lifestyle Changes | Quitting tobacco, reducing alcohol consumption | Reduces risk of recurrence and second primary tumors |
Adherence to Follow-up | Regular check-ups and screenings | Early detection of recurrence or new cancers |
Preventive Measures | HPV vaccination, chemoprevention | Reduces risk of certain types of mouth cancer |
By understanding and tackling recurrence and secondary cancer risks, mouth cancer survivors can better their long-term health and life quality.
Prevention Strategies That Save Lives
Reducing mouth cancer starts with prevention. Knowing and using these strategies can lower your risk. This can help prevent a serious disease.
Tobacco and Alcohol Cessation
Tobacco and alcohol are big risks for mouth cancer. Stopping these habits can greatly lower your risk. Here’s what we suggest:
- Get help to quit tobacco and alcohol
- Try nicotine replacement therapy or other aids
- Join support groups for help and motivation
HPV Vaccination
HPV is linked to some mouth cancers. HPV vaccination can lower your risk. We recommend:
- Talk to your doctor about the HPV vaccine
- Learn about the vaccine’s benefits and risks
- Get vaccinated before you’re exposed to HPV
Regular Dental Check-ups
Dental check-ups are key for early mouth cancer detection. We suggest:
- Go to your dentist every six months for a full check
- Tell your dentist about any risks or symptoms
- Have regular oral cancer screenings during dental visits
Self-examination Techniques
Knowing your mouth through self-examination can catch problems early. We recommend:
- Check your mouth often for unusual changes or symptoms
- Use a mirror and good light to look at all parts of your mouth
- See a healthcare professional if you find anything odd
Adding these prevention steps to your life can lower your mouth cancer risk. Remember, prevention is the best way to save lives.
Living With Uncertainty: Coping Strategies
Dealing with mouth cancer treatment and beyond needs good coping strategies. A mouth cancer diagnosis is more than a medical issue. It’s also an emotional and psychological journey.
Support Groups and Resources
Connecting with others who face similar challenges is very helpful. Support groups offer a safe place to share feelings and experiences. Look for both online and in-person groups to find what suits you best.
There are many resources for patients and their families. These include counseling, educational materials, and financial help. Reaching out for help shows strength, not weakness.
Communication With Healthcare Providers
Talking openly with your healthcare team is key to managing uncertainty. We suggest being honest about your worries, asking questions, and clarifying any care details you’re unsure about.
Having a good relationship with your healthcare providers can ease anxiety. It ensures you get the right care for your needs.
Managing Anxiety About Prognosis
Feeling anxious about mouth cancer prognosis is normal. Focus on what you can control, like following your treatment plan and living healthily.
Mindfulness, like meditation and deep breathing, can help with anxiety. Seeking help from mental health professionals is also a good idea for dealing with emotional effects of cancer.
Planning for Different Outcomes
It’s important to stay positive but also plan for different outcomes. Talk about advance care planning with your healthcare team and loved ones.
Knowing your care options and making informed choices can reduce uncertainty. It ensures your wishes are respected.
Conclusion
Knowing about mouth cancer survival rates is key for patients and their families. We’ve looked at how survival changes based on cancer stage, health, and treatment.
Early detection and the right treatment boost mouth cancer survival chances. Being aware of signs and taking steps to prevent it can lower risk.
Mouth cancer survival rates vary a lot based on when it’s found. Early detection means a better chance of survival. So, it’s important to watch for symptoms and see a doctor if they don’t go away.
By being aware, catching it early, and getting the right treatment, we can help mouth cancer patients. We need to keep supporting research and education to fight this disease.
FAQ
Can you die from mouth cancer?
Yes, mouth cancer can be fatal if not caught early. The survival rate depends on the cancer’s stage at diagnosis.
How deadly is mouth cancer?
Mouth cancer is serious and can be deadly, mainly if caught late. But, early detection and treatment can boost survival chances.
What are the survival rates for mouth cancer by stage?
Survival rates for mouth cancer vary by stage. Early-stage cancer has a better survival rate than late-stage cancer.
Is mouth cancer fatal?
Mouth cancer can be fatal. Survival depends on the stage at diagnosis, overall health, and treatment response.
Can you survive oral cancer?
Yes, many survive oral cancer, mainly if caught and treated early. Quick medical attention and following treatment plans are key.
What is the life expectancy of mouth cancer?
Life expectancy for mouth cancer patients varies. It depends on the stage at diagnosis and other factors. Early-stage diagnosis generally offers a better prognosis.
How long can you live with cancer of the mouth?
Living time with mouth cancer varies. It depends on the stage, health, and treatment response. Proper treatment can help manage the disease and improve life quality.
What are the factors that influence mouth cancer prognosis?
Several factors affect mouth cancer prognosis. These include age, health, cancer location and type, treatment response, and lifestyle.
Why is early detection critical for mouth cancer?
Early detection is key because it boosts survival rates. Early-stage cancer is more treatable, increasing survival chances.
What are the treatment options for mouth cancer?
Treatments for mouth cancer include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. Treatment choice depends on cancer stage, location, and patient health.
Can mouth cancer be prevented?
Not all mouth cancer can be prevented, but risks can be lowered. Strategies include quitting tobacco and alcohol, HPV vaccination, dental check-ups, and self-examination.
What is the prognosis for stage 3 oral cancer?
Stage 3 oral cancer prognosis varies. It depends on health and treatment response. Generally, stage 3 has a lower survival rate than early stages.
What is the 4th stage mouth cancer survival rate?
Stage 4 mouth cancer survival rates are lower. Yet, with proper treatment, some patients can manage the disease and improve their life quality.
How can I cope with a mouth cancer diagnosis?
Coping with mouth cancer involves seeking support from healthcare, support groups, and loved ones. Managing anxiety, planning for outcomes, and staying positive also helps.
Is oropharyngeal cancer deadly?
Oropharyngeal cancer can be deadly if not treated early. But, with the right treatment and care, many patients can manage the disease and improve their survival chances
.
References
Government Health Resource. (2025). Can You Die From Mouth Cancer Survival Rates. Retrieved from https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/oralcav.html



































