recurrent ear infections in adultsRecurrent ear infections are a big worry for adults. They often mean there’s something deeper going on that needs special care. Unlike kids, adults can get middle ear infections that keep coming back. This can lead to fluid buildup and even hearing loss if not treated recurrent ear infections in adults.
At Liv Hospital, we know how hard it is to treat ear infections in adults. We do a full check-up and specialized treatment to find and fix the real problem. Adults with recurring ear infections face special challenges, like bacteria that antibiotics can’t kill.
We aim to help by understanding why these infections happen, how to spot them, and how to treat them. Our goal is to give top-notch care and support to patients from around the world who need advanced medical help.
Key Takeaways
- Recurrent ear infections in adults require a detailed check-up and special treatment.
- Not treating ear infections can cause serious problems like hearing loss.
- Liv Hospital offers top medical treatments for ear infections.
- Bacteria that hide in biofilms can resist common antibiotics.
- Knowing the reasons and signs is key to treating ear infections well.
Understanding Ear Infections in the Adult Population
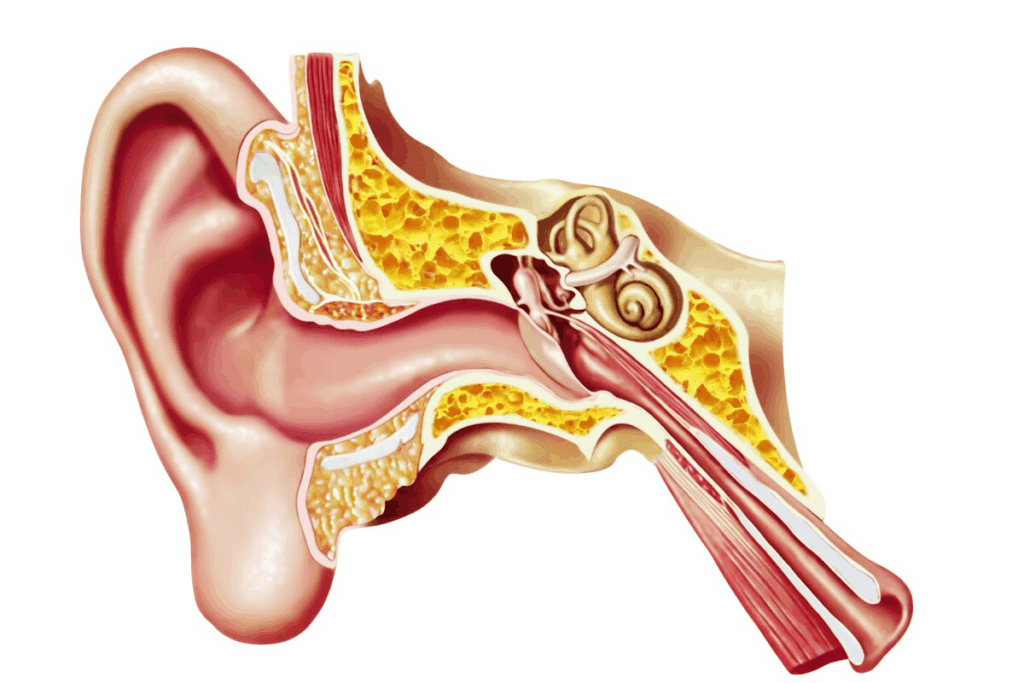
Ear infections in adults are important to understand. They can show health problems that need to be fixed. Unlike kids, adults get ear infections less often but they can mean serious health issues.
Definition and Types of Ear Infections
Ear infections, also called otitis media, are when the middle ear gets inflamed or infected. There are different kinds, like acute otitis media, otitis media with effusion, and chronic otitis media. Acute otitis media happens suddenly, with fever and ear pain.
Otitis media with effusion is when fluid builds up in the middle ear without infection signs. Chronic otitis media is when infections keep coming back, leading to bigger problems.
Ear infections in adults are sorted by how long they last and if there’s fluid or infection. Knowing this helps doctors figure out the best treatment.
Why Adults Get Ear Infections
Adults get ear infections from swimming, colds, injuries, or allergies. “The Eustachian tube, which controls ear pressure, can get blocked,” says Medical Expert, an ENT specialist.
Many things can make the Eustachian tube not work right. This includes being born with certain ear shapes, allergies, or colds. When it doesn’t work, fluid and infection can build up in the middle ear.
Differences Between Adult and Childhood Infections
Ear infections are more common in kids because their Eustachian tubes and immune systems are not fully grown. But adults get ear infections for different reasons. They might have other health problems or ear shapes that make them more likely to get infections.
Adults with allergies or sinus infections are more likely to get ear infections. Also, things like a crooked septum or nasal polyps can raise the risk. It’s important to treat adult ear infections differently because they often have deeper causes.
While kids might grow out of ear infections, adults need more detailed treatment. “Knowing the differences helps doctors treat ear infections in adults better,” say health experts.
Causes of Recurrent Ear Infections in Adults
Recurrent ear infections in adults come from many sources. These include bacteria, viruses, and environmental factors. Knowing what causes them helps us find better ways to treat them.
Bacterial and Viral Pathogens
Bacteria and viruses are big players in ear infections. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis are common bacteria. Viruses like respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and influenza virus also play a part.
These pathogens can keep coming back because they’re good at avoiding our immune system. We’ll look into how they cause recurrent ear infections.
Biofilm Formation and Antibiotic Resistance
Biofilms are another big problem in ear infections. Biofilms are groups of microorganisms stuck together in a protective layer. This layer makes it hard for antibiotics to reach the bacteria.
Research shows that biofilms help ear infections stick around. We’ll talk about how biofilms make antibiotics less effective and what it means for treatment.
Anatomical and Environmental Factors
Other factors like anatomy and environment also matter. Allergies, upper respiratory infections, water exposure, smoking, and ear trauma can raise the risk of ear infections. Knowing these can help prevent them from coming back.
We’ll look at how these factors lead to recurrent ear infections. We’ll also talk about ways to reduce their impact.
Recognizing the Symptoms and Stages of Ear Infections
Ear infections show up in different ways. Knowing the signs early is important for treatment. Adults should watch for common signs of an ear infection to get medical help fast.
Early Warning Signs
The first signs of an ear infection are often small but important. You might feel pain or discomfort in your ear. You might also feel like your ear is full or have mild hearing loss. These early warning signs are key to catching the problem early.
- Ear pain or discomfort
- Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear
- Mild hearing loss
Progressive Symptoms
As the infection gets worse, symptoms can get more serious. You might see fluid coming out of your ear, hear less clearly, or feel dizzy. Spotting these progressive symptoms helps you understand how bad the infection is.
- Fluid discharge from the ear
- Increased hearing loss
- Dizziness or balance issues
Fever and Other Systemic Symptoms
Ear infections can also cause body-wide symptoms like fever, headache, and tiredness. These signs mean your body is fighting off the infection and might need medical help.
Systemic Symptoms | Description |
Fever | Elevated body temperature indicating infection |
Headache | Pain or discomfort in the head or neck |
Fatigue | Feeling tired or lacking energy |
Knowing these symptoms and stages helps adults get the right medical care. This ensures they get treated well and avoid bigger problems.
Diagnosing Chronic Otitis Media
To find out if someone has chronic otitis media, doctors use a detailed plan. They look at the patient’s past health, do a careful check-up, and use special tests.
Medical History Assessment
Looking at the patient’s past health is key. We start by asking about their symptoms, like ear pain and hearing loss. We also ask about past ear infections and allergies. This helps us understand what might be causing the problem.
Physical Examination Techniques
Checking the ears is important. We use an otoscope to see inside the ear. This helps us find out if there’s an infection or damage. We might also use a pneumatic otoscopy to check how well the eardrum moves.
Advanced Diagnostic Testing
Special tests are needed to confirm the diagnosis. Tympanometry helps us see how the eardrum moves. Audiometry and imaging studies, like CT scans, help us understand hearing loss and any other issues.
Diagnosing chronic otitis media involves these steps. By looking at the patient’s history, doing physical exams, and using special tests, we can find out what’s wrong and treat it.
- Key Diagnostic Steps:
- Medical history assessment to identify symptoms and risk factors
- Physical examination using otoscopy and pneumatic otoscopy
- Advanced diagnostic testing, including tympanometry and audiometry
By using this detailed approach, we make sure patients get the right diagnosis and treatment for chronic otitis media.
Medical Treatment Approaches for Adult Ear Infections
Adult ear infections need a special treatment plan. This plan helps manage symptoms and prevent serious problems. We will look at the different medical treatments available. We focus on the best ways to fight ear infections in adults.
Antibiotic Selection and Duration
Antibiotics are key in treating bacterial ear infections. The choice of antibiotics depends on the bacteria causing the infection and the patient’s health history. Amoxicillin is often the first choice because it works well against common bacteria. But, if there’s a chance of resistance or recent antibiotic use, doctors might choose azithromycin or ceftriaxone.
Antibiotic treatment usually lasts 7 to 10 days. This depends on how severe the infection is and how well the patient responds to treatment. It’s important to finish all antibiotics as directed. This ensures the infection is fully treated and helps prevent antibiotic resistance.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Anti-inflammatory drugs are also important in treating ear infections. They help reduce swelling and pain. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen are common over-the-counter options. They help manage ear pain and lower fever.
In severe cases, doctors might prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. But, this is usually for very swollen cases or when inflammation is severe.
Proper Application of Ear Drops
Ear drops can deliver medication directly to the ear. It’s important to apply them correctly to ensure they work well. To apply ear drops, tilt your head, pull your ear back and up, and put in the drops. Keep your head tilted for a few minutes to let the drops work.
Treatment Option | Description | Benefits |
Antibiotics | Kill bacteria causing infection | Effective against bacterial infections, reduces risk of complications |
Anti-inflammatory Medications | Reduce inflammation and pain | Alleviates symptoms, improves patient comfort |
Ear Drops | Deliver medication directly to the ear | Targeted treatment, reduces systemic side effects |
Managing Otitis Media with Effusion in Adults
Managing otitis media with effusion in adults involves monitoring and specific treatments. This condition causes fluid to build up in the middle ear. It can lead to hearing loss and discomfort if not treated.
Understanding Middle Ear Fluid Accumulation
Middle ear effusion happens when fluid builds up behind the eardrum. It can be caused by Eustachian tube problems, allergies, colds, or sinus infections. Knowing the cause is key to managing it well.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Allergies
- Upper respiratory infections
- Sinus infections
Monitoring Approaches
Monitoring otitis media with effusion means regular visits to a healthcare provider. They check how the condition is doing and if treatments are working. This may include:
- Regular hearing tests to monitor any changes in hearing
- Tympanometry to assess the movement of the eardrum and the condition of the middle ear
- Imaging studies in some cases to rule out other conditions
Treatment Strategies for Persistent Effusion
Treatment for otitis media with effusion in adults depends on how severe and long-lasting it is. Strategies may include:
Treatment | Description |
Nasal Decongestants | Medications to reduce nasal congestion and promote Eustachian tube function |
Autoinflation Devices | Devices that help open the Eustachian tube by increasing nasal pressure |
Myringotomy | A surgical procedure to drain the fluid from the middle ear |
Managing otitis media with effusion in adults needs a detailed plan. This includes monitoring and the right treatments. By understanding the condition and its causes, healthcare providers can improve outcomes and quality of life.
Surgical Interventions for Serious Ear Infections
When ear infections are severe or keep coming back, surgery might be the best option. Surgery can seem scary, but it often greatly improves life for those with serious ear infections.
Tympanostomy Tubes (Ear Tubes)
Tympanostomy tubes, or ear tubes, are small tubes put into the eardrum. They help drain fluid and keep the middle ear ventilated. This is often suggested for those with frequent ear infections or fluid buildup.
The tubes help in several ways:
- They reduce the number and severity of ear infections.
- They improve hearing by removing fluid from the middle ear.
- They lower the chance of eardrum damage from chronic infection or fluid.
Putting in ear tubes is usually done as an outpatient procedure, under general anesthesia. The tubes usually come out on their own in 6 to 12 months. Sometimes, a second procedure is needed to remove them.
Mastoidectomy Procedures
A mastoidectomy removes infected mastoid bone cells. It’s needed when an ear infection spreads to the mastoid bone, causing mastoiditis. The main goals are:
- To remove infected tissue and prevent further problems.
- To drain abscesses or infected fluid collections.
- To keep the facial nerve and other structures safe.
Mastoidectomy procedures can be simple or complex, depending on the infection and the patient’s health. The choice depends on how bad the infection is and the patient’s overall health.
Tympanoplasty and Reconstruction Options
Tympanoplasty repairs the eardrum and sometimes the middle ear bones. It’s needed when ear infections damage these structures. The goal is to:
- Fix hearing by repairing or replacing damaged parts.
- Make the eardrum stronger to prevent future infections.
- Improve ear function overall.
The details of the tympanoplasty depend on the damage. Surgeons might use grafts for the eardrum or prosthetics for the ossicles. The aim is to fix hearing and prevent future problems.
Choosing surgery is a big decision. But for many with serious ear infections, it’s a way to better ear health and a better life.
Effective Home Remedies and Self-Care Strategies
Several home remedies can help with ear infection discomfort. These self-care strategies support recovery and ease symptoms.
Pain Management Techniques
Managing pain is key when dealing with ear infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help. Always check with a healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Pain Relief Options:
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol)
- Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin)
Warm Compress Application
Using a warm compress on the affected ear can ease pain. Soak a clean cloth in warm water, wring it out, and apply it for a few minutes. Repeat this several times a day as needed.
Natural Supportive Therapies
Natural therapies can help manage symptoms alongside medical treatment. These include:
- Garlic oil drops
- Olive oil drops
- Steam inhalation
A table summarizing these natural therapies is provided below:
Therapy | Description | Potential Benefits |
Garlic Oil Drops | Using garlic oil in ear drops | Antibacterial properties |
Olive Oil Drops | Applying olive oil to the ear | Soothes the ear canal |
Steam Inhalation | Inhaling steam to loosen mucus | Relieves congestion |
While these remedies and strategies can offer relief, it’s vital to see a healthcare provider. They ensure the infection is fully treated and address any complications.
How Long Do Ear Infections Last and Recovery Timeline
People often wonder how long ear infections last and when they can get better. Knowing how long ear infections usually last and when you might start feeling better can help. It also helps spot any problems early on.
Typical Duration of Acute Infections
Ear infections usually go away in a few days to a week. How long it takes can depend on several things. These include the type of infection, how well treatment works, and your overall health.
Acute otitis media, a common ear infection, usually gets better in 7-10 days with antibiotics. But, some infections might take longer. In some cases, symptoms can last for weeks.
Signs That an Ear Infection Is Healing
When an ear infection starts to heal, you might notice a few things. These include:
- Less ear pain and discomfort
- Better hearing
- A lower fever
- Less fluid coming out of the ear
It’s important to watch for these signs and talk to a doctor if you have any worries.
When to Worry About Slow Recovery
Most ear infections get better in a week or two. But, some might take longer. If your symptoms don’t get better or get worse, you should see a doctor. Signs of a slow recovery or possible complications include:
Symptom | Potential Complication |
Persistent ear pain | Mastoiditis or other secondary infections |
Hearing loss | Damage to the eardrum or middle ear |
Fever above 102°F (39°C) | Severe infection or sepsis |
If you have any of these symptoms, it’s important to talk to a doctor. They can help figure out what to do next.
Preventing Recurrent Ear Infections
To avoid the discomfort and complications of recurrent ear infections, adopting preventive measures is key. Preventing these infections requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes lifestyle changes, environmental controls, and immune system support.
Lifestyle Modifications
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of recurrent ear infections. These include:
- Avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke, as it can irritate the Eustachian tube and increase the risk of infection.
- Maintaining good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, to reduce the transmission of pathogens.
- Avoiding close contact with individuals who have colds or other respiratory infections.
Environmental Controls
Modifying your environment can also play a key role in preventing recurrent ear infections. Consider the following:
- Using a humidifier to maintain an optimal indoor humidity level, which can help prevent the drying out of the Eustachian tube.
- Avoiding allergens and irritants that can trigger allergic reactions, which may increase the risk of ear infections.
We can also use an air purifier to remove allergens and bacteria from the air, creating a cleaner environment.
Immune System Support Strategies
Supporting your immune system is vital in preventing recurrent ear infections. This can be achieved through:
- Nutritional interventions, such as consuming a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Regular exercise to boost overall immune function.
- Adequate sleep to help your immune system recover and fight off infections.
Also, certain supplements like vitamin C, zinc, and probiotics may help support immune function. But, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplements to your regimen.
Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
Lifestyle Modifications | Avoiding secondhand smoke, maintaining good hygiene, avoiding close contact with infected individuals | Reduces risk of ear infections, promotes overall health |
Environmental Controls | Using humidifiers, avoiding allergens and irritants | Prevents Eustachian tube dysfunction, reduces allergy-related complications |
Immune System Support | Nutritional interventions, regular exercise, adequate sleep | Boosts immune function, helps fight off infections |
By implementing these strategies, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing recurrent ear infections. It’s about creating a plan that addresses lifestyle, environmental factors, and immune system health.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help is key to treating ear infections well. Some ear infections might get better on their own. But, others can cause serious problems if not treated.
Red Flag Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe pain that doesn’t get better with over-the-counter pain meds
- High fever over 102°F (39°C)
- Discharge or fluid from the ear
- Hearing loss or changes in hearing
- Dizziness or loss of balance
If you have any of these symptoms, get medical help fast.
Complications of Untreated Infections
Not treating ear infections can cause serious problems. These include:
Complication | Description |
Mastoiditis | An infection of the mastoid bone in the skull, which can be life-threatening |
Chronic Otitis Media | Recurring or persistent infection of the middle ear |
Hearing Loss | Permanent damage to hearing due to prolonged infection |
Facial Paralysis | In rare cases, infection can spread to the facial nerve, causing paralysis |
These complications show why you should see a doctor if symptoms don’t get better or get worse.
Follow-up Care Guidelines
After treating an ear infection, follow-up care is vital. Here’s what to do:
- Make sure to see your doctor for a follow-up as they suggest.
- Watch your symptoms and tell your doctor about any changes or worries.
- Finish all antibiotics if you’re given some.
- Stay away from things that might make symptoms worse, like smoke or allergens.
By following these steps, you can make sure you fully recover and avoid complications.
Conclusion
Managing and preventing ear infections needs a full plan. Knowing the causes, signs, and treatments helps a lot. This way, people can handle their infections better and stop them from coming back.
We talked about different ways to treat ear infections. This includes choosing the right antibiotics and using anti-inflammatory drugs. We also mentioned surgery options like putting in tympanostomy tubes. Plus, home remedies and self-care can help with pain and healing.
It’s not just about treating the infection. It’s also about stopping it from coming back. Making lifestyle changes, controlling the environment, and boosting the immune system are key. These steps help keep ears healthy and prevent infections.
By following our advice, people can take charge of their ear health. We want to give them the tools and knowledge to handle ear infections well. This way, they can avoid future problems.
FAQ
How long does it take for an ear infection to go away?
The time it takes for an ear infection to heal depends on its type and how bad it is. Acute infections usually get better in a few days to a week with the right treatment. Chronic infections might need more treatment and can last longer.
What is otitis media with effusion in adults?
Otitis media with effusion is when fluid builds up in the middle ear without an infection. It can cause hearing loss and discomfort in adults. Treatment might include watching it, medication, or surgery.
How is middle ear effusion treated in adults?
Treatment for middle ear effusion in adults can be watching it, using nasal decongestants, antihistamines, or surgery. The choice depends on the cause and how bad the symptoms are.
What are the stages of an ear infection?
Ear infections go through stages like the start of symptoms, the peak, and getting better. Knowing these stages helps in knowing when to see a doctor.
How can I tell if my ear infection is getting better?
Signs it’s getting better include less ear pain, better hearing, and lower fever. If symptoms get worse or don’t get better, you need to see a doctor.
Can adults get ear infections?
Yes, adults can get ear infections, though they’re more common in kids. Adults might get them due to Eustachian tube problems, allergies, or other issues.
What are the signs of an ear infection in adults?
Signs in adults include ear pain, hearing loss, and feeling like the ear is full. A fever and discharge are also signs. Seeing a doctor early is key.
How long does otitis media last?
Otitis media’s length varies. Acute cases usually last a few days to a week. Chronic cases can last longer, depending on treatment and individual factors.
Why do adults get ear infections?
Adults get ear infections from bacteria or viruses, Eustachian tube issues, allergies, colds, or body shape problems. Knowing why helps in preventing and treating them.
What are the symptoms of a serious ear infection?
Serious symptoms include severe pain, high fever, and discharge. Hearing loss, dizziness, or facial weakness are also signs. Seeing a doctor right away is important.
How can I prevent recurrent ear infections?
To prevent them, avoid smoking and secondhand smoke, manage allergies, and keep hygiene up. Stay vaccinated and consider immune support and environmental changes.
When should I seek medical attention for an ear infection?
See a doctor for severe pain, high fever, discharge, hearing loss, or dizziness. If symptoms get worse or don’t improve, get help fast. Early treatment is key.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2025). How to Treat Recurrent Ear Infections in Adults. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23536557/




































