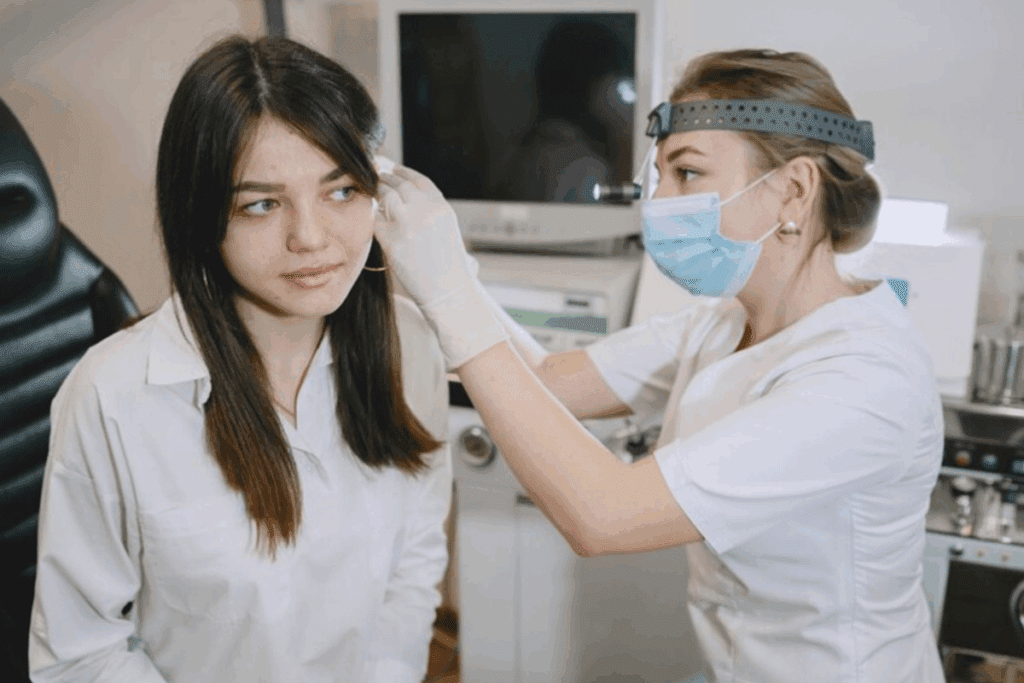
Feeling vomiting or nausea with an ear infection is more common than you might think. At Liv Hospital, we know that ear infections can cause symptoms beyond just ear pain. Sometimes, the infection can upset the inner ear’s delicate balance system, leading to symptoms like vomiting and nausea.
We understand that nausea and vomiting can be really tough to deal with. It’s key to tackle these symptoms fully. Our team at Liv Hospital is committed to giving you the best care for ear infections and their related issues.
Would an ear infection cause vomiting? Yes, especially inner ear infections where severe dizziness and vertigo often trigger nausea and vomiting.
Key Takeaways
- Ear infections can lead to a range of symptoms, including pain, fever, vomiting, and nausea.
- The inner ear’s balance system can be affected by the infection, causing distressing symptoms.
- Comprehensive care is essential to address all symptoms and ensure rest.
- Liv Hospital provides trusted, patient-centered expertise in diagnosing and managing ear infections.
- Associated complications can be managed with proper care and attention.
The Relationship Between Ear Infections and Digestive Symptoms
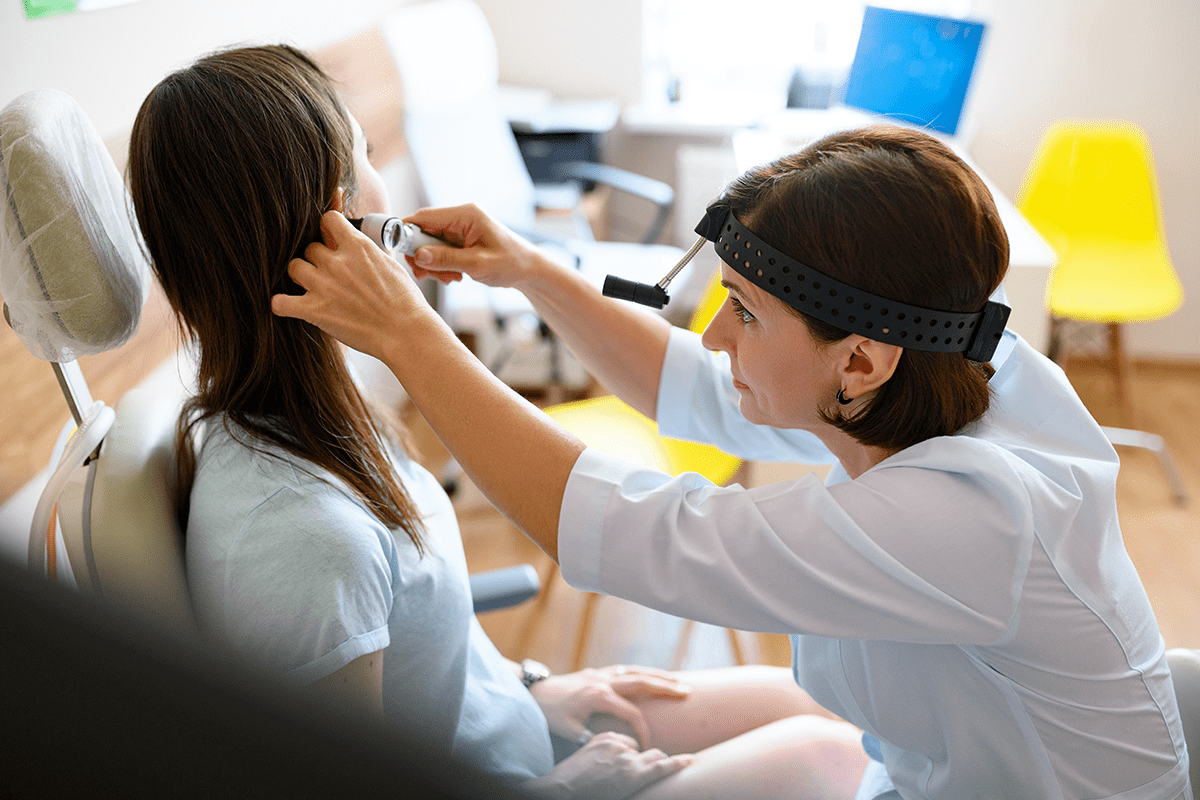
Understanding ear infections and digestive issues is key. Ear infections can affect different parts of the ear. This leads to various symptoms and complications.
Overview of Ear Infection Types
Ear infections are divided into outer, middle, and inner ear types. Outer ear infections happen in the outer ear canal. They are often caused by bacteria or fungi.
Middle ear infections affect the middle ear. They are usually caused by bacteria or viruses. Inner ear infections impact the inner ear. They can cause balance problems and hearing loss.
Each ear infection has its own symptoms. Outer ear infections cause pain, itching, and redness. Middle ear infections lead to ear pain, fever, and hearing issues. Inner ear infections can cause vertigo, nausea, and vomiting.
Primary Symptoms Beyond Ear Pain
Ear infections can cause more than just ear pain. They can also lead to digestive problems. For example, inner ear infections can cause vertigo. This can make you feel like you’re spinning and can lead to nausea and vomiting.
The connection between the inner ear and digestion is linked to balance. The discomfort from ear infections can also cause stress. This stress can make digestive problems worse in some people.
How the Ear and Digestive System Are Connected
The ear and digestive system might seem unrelated, but they’re linked through complex neural pathways. This link explains why ear infections can cause nausea and vomiting.
Anatomy of the Inner Ear and Vestibular System
The inner ear has the vestibular system, key for balance and equilibrium. It has three semicircular canals and otolith organs filled with fluid and sensory hair cells. These cells detect movement and head position changes, sending signals to the brain.
The inner ear anatomy is detailed, with the vestibular system near the cochlea for hearing. This close relationship means ear infections can affect balance and hearing.
Neural Pathways Between Ear and Stomach
The ear and digestive system are connected through neural pathways. The vestibular system sends signals to the brain, influencing the digestive system. Disruptions, like ear infections, can cause nausea and vomiting.
The neural pathways are complex, involving brain parts for balance, vomiting, and more. The vagus nerve, which connects to the stomach, is key in this connection.
Understanding these connections helps us see how ear infections can cause nausea and vomiting. By looking at the neural pathways between the ear and stomach, we can understand these symptoms better.
Would an Ear Infection Cause Vomiting? The Scientific Evidence
Studies have shown that ear infections can lead to vomiting. This happens because of problems with balance and inflammation. The inner ear is key for balance. An infection can mess with this, causing nausea and vomiting.
Research on Vestibular Disruption
Vestibular disruption is a big reason for vomiting in ear infection cases. The inner ear’s balance system gets affected by infection. This leads to balance problems, vertigo, and vomiting.
“The vestibular system plays a critical role in balance and spatial awareness. An ear infection can severely disrupt this, causing vertigo and vomiting.”
A study in the Journal of Vestibular Research found that inner ear infections cause severe balance problems. These include vertigo and vomiting. It shows how important the vestibular system is in these symptoms.
Inflammation and Pressure Effects
Inflammation and pressure changes in the ear also play a part in vomiting. An ear infection causes inflammation. This increases pressure in the inner ear, making balance problems worse.
Mechanism | Effect on the Body |
Vestibular Disruption | Disturbances in balance, vertigo, nausea, and vomiting |
Inflammation | Increased pressure within the inner ear, exacerbating vestibular symptoms |
Pressure Effects | Further disruption of vestibular function, contributing to nausea and vomiting |
The science backs up the idea that ear infections can cause vomiting. This is due to vestibular problems and inflammation. Knowing these causes helps in finding better treatments.
Inner Ear Infections and Balance Disorders
The inner ear is key for balance. Infections here can really mess things up. Conditions like labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis can cause balance problems, vertigo, and other symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis
Labyrinthitis is when the inner ear’s labyrinth gets inflamed. It affects balance and hearing. Vestibular neuritis is when the vestibular nerve, which sends balance info to the brain, gets inflamed. Both can happen from viruses or bacteria.
These infections mess with the inner ear’s function. This leads to vertigo, dizziness, and imbalance. Symptoms can be very severe and really affect a person’s life.
How Vertigo Triggers Nausea
Vertigo makes you feel like you’re spinning or the world is spinning. It’s a common sign of inner ear infections. This feeling can confuse your body and brain.
This confusion can upset your balance system. It can make you feel sick and might make you throw up. The brain tries to fix the problem by making you vomit.
It’s important to know how inner ear infections and balance disorders are linked. This helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. Here’s a quick look at labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis:
Condition | Primary Symptoms | Causes |
Labyrinthitis | Vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus | Viral or bacterial infection |
Vestibular Neuritis | Vertigo, dizziness, imbalance | Viral infection |
Knowing the symptoms and causes helps doctors create good treatment plans. This can help manage these conditions and reduce symptoms.
Middle and Outer Ear Infections and Their Systemic Effects
Ear infections can affect more than just your ears. Middle and outer ear infections can cause problems in your stomach too. We’ll look at how these infections, like acute otitis media, can cause symptoms beyond the ear.
Acute Otitis Media and Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Acute otitis media is a common middle ear infection. It causes ear pain and fever. But it can also cause gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the back of the throat. It plays a big role in how infections spread. This can affect your stomach.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction and Referred Symptoms
Eustachian tube dysfunction is a big problem in ear infections. When the tube doesn’t work right, it can cause pressure in the middle ear. This can lead to acute otitis media.
- The dysfunction can cause a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
- It can lead to hearing difficulties or ear pain.
- In some cases, it may result in gastrointestinal symptoms due to the referred pain or discomfort.
Understanding the Eustachian tube’s role in ear infections is key. By fixing the tube, doctors can help with ear and stomach problems.
Can an Ear Infection Cause Headaches?
Many people worry about the link between ear infections and headaches. Ear infections can cause headaches because of the inflammation and pressure changes they bring.
Mechanisms Behind Ear Infection-Related Headaches
Ear infections can lead to headaches in a few ways. The inflammation from an ear infection can cause pain that feels like it’s in the head. Also, the pressure changes in the ear can affect nearby areas, leading to headaches.
Inflammation and Pain Referral: The inflammation from an ear infection can release pain-producing chemicals. These chemicals can make pain receptors active, causing the feeling of a headache.
Types and Locations of Associated Head Pain
The type and location of head pain from ear infections can differ. Some people might feel a dull ache on one side of their head. Others might have a headache that feels more general.
- Unilateral Headaches: Often, the headache is on one side, matching the ear infection.
- Temporal or Frontal Pain: Pain can be in the temporal or frontal areas, showing the pain from the ear.
It’s important to understand how ear infections and headaches are connected. Knowing how ear infections cause headaches helps doctors give better care. They can target their treatment to help patients feel better.
Ear Infections Across Different Age Groups
Ear infections can happen to anyone, but they show up differently in kids, adults, and the elderly. We’ll look at how ear infections appear in each group. We’ll also talk about the special challenges each age faces.
Children and Ear Infections: Why They’re More Vulnerable
Children get ear infections more often because their immune systems are not fully grown. Their Eustachian tubes are shorter and more open, making it easier for germs to get in. Ear infections in kids often show as fever, crankiness, and ear pulling. It’s important to catch and treat these infections early to avoid serious problems.
- Common symptoms in children include ear pain, fever, and hearing loss.
- Recurring ear infections can cause delays in development and speech problems.
- Acting fast is key to avoiding long-term effects.
Adult Ear Infections: Presentation Differences
While ear infections are more common in kids, adults can get them too. Adults might feel ear pain, hearing loss, and ringing in the ears. But they usually don’t have fever or widespread symptoms. Adult ear infections can be caused by colds, allergies, or problems with the Eustachian tube. Knowing these differences helps us treat them right.
- Adult symptoms can start slowly.
- Underlying health issues can make diagnosis harder.
- Treatment might focus on fixing the cause and easing symptoms.
Elderly Patients: Special Considerations
When it comes to ear infections, the elderly need extra care. As people get older, their immune system weakens and they might have other health issues. Elderly people can face serious problems like hearing loss or balance problems. We need to keep these things in mind to help them properly.
- Older adults might not show symptoms in the usual way, making it harder to diagnose.
- Other health problems can affect treatment and results.
- It’s important to watch them closely to prevent and handle serious issues.
Diagnosing Ear Infections When Nausea and Vomiting Are Present
Ear infections with nausea and vomiting need a detailed diagnosis. Finding out if someone has an ear infection can be tricky. This is because many symptoms can happen, like feeling sick and throwing up. We must look at both the ear infection and other symptoms to get a correct diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation Techniques
To check a patient with ear infection and nausea or vomiting, we use several methods. Otoscopy lets us see the ear canal and eardrum for signs of infection. We look for redness, swelling, or holes in the eardrum.
Tympanometry is another tool. It checks how well the eardrum and bones move by changing air pressure in the ear. This test can show if there’s fluid or tube problems in the middle ear, which might cause symptoms.
It’s also important to ask about symptoms. We want to know when they started, how long they last, and how bad they are. We ask about other symptoms too, like dizziness, hearing loss, or ear pain. This helps us understand how serious the infection is and how it affects the patient’s health.
Diagnostic Technique | Purpose | Relevance to Nausea and Vomiting |
Otoscopy | Examine ear canal and tympanic membrane | Identifies infection or damage that could contribute to symptoms |
Tympanometry | Assess tympanic membrane mobility and middle ear function | Helps diagnose conditions like Eustachian tube dysfunction that may cause nausea and vomiting |
Symptom Assessment | Evaluate the patient’s symptoms comprehensively | Provides insight into the severity and impact of nausea and vomiting |
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When diagnosing ear infections with nausea and vomiting, we must think about other possible causes. Conditions like labyrinthitis, vestibular neuritis, or stomach problems could have similar symptoms.
“The diagnosis of ear infections requires a careful consideration of the patient’s symptoms and clinical findings to differentiate it from other conditions that may cause nausea and vomiting.” –
Medical Guidelines for Ear Infections
We also look at the patient’s past health, including any ear infections, allergies, or other conditions. A full check-up helps us give the right diagnosis and treatment.
In summary, diagnosing ear infections with nausea and vomiting needs a mix of clinical methods and thinking about other possible causes. By using these approaches, we make sure patients get the right care for their condition.
Treatment Approaches for Ear Infections with Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Ear infections with stomach problems need a full treatment plan. We must treat the infection and the symptoms to help the patient feel better and avoid more problems.
Antibiotic Therapy and When It’s Necessary
Antibiotics are key for bacterial ear infections. We use them when the infection is caused by bacteria. The right antibiotic depends on the infection’s severity, the patient’s age, and any allergies.
Key considerations for antibiotic therapy include:
- Selecting an appropriate antibiotic based on the suspected or confirmed pathogen
- Ensuring the dosage and duration are adequate for the specific infection
- Monitoring for possible side effects and adjusting treatment as needed
Managing Nausea and Vomiting Symptoms
It’s important to manage nausea and vomiting to avoid dehydration. We use antiemetic medications to help. Also, staying hydrated and resting are key for recovery.
Strategies for managing nausea include:
- Administering antiemetic medication as needed
- Encouraging fluid intake to prevent dehydration
- Recommending rest to alleviate discomfort and support recovery
Pain Relief Strategies
Managing pain is a big part of treating ear infections. We use pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Sometimes, we also suggest topical pain relief.
Effective pain relief strategies include:
- Using over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen
- Applying topical pain relief drops, if appropriate
- Encouraging patients to avoid lying on the affected ear to reduce discomfort
By treating both the ear infection and stomach symptoms, we offer complete care. This improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Preventing Ear Infections and Associated Complications
Ear infections can be prevented by changing risk factors, getting vaccinations, and making lifestyle changes. Knowing what causes ear infections helps us avoid them. This can also lower the chance of vomiting and nausea.
Risk Factor Modification
Changing risk factors is key to preventing ear infections. Important risk factors include:
- Exposure to tobacco smoke: Staying away from secondhand smoke can lower ear infection risk.
- Attendance at daycare centers: Kids in daycare face more germs, raising their ear infection risk.
- Feeding practices: Bottle-feeding in a lying down position can increase ear infection risk.
- Anatomical issues: Conditions like cleft palate can make ear infections more likely.
By tackling these risk factors, we can cut down ear infection chances.
Vaccination and Preventive Medications
Vaccines are essential in fighting ear infections. The pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) and influenza vaccine are key in lowering ear infection rates.
Preventive meds might also be suggested. For example, antibiotics could be given to those who often get ear infections.
Lifestyle and Environmental Adjustments
Changing our lifestyle and environment can also prevent ear infections. These include:
- Maintaining good hygiene: Washing hands often can stop the spread of ear infection-causing germs.
- Avoiding allergens: Controlling allergies can help prevent ear infections.
- Breastfeeding: Exclusive breastfeeding for at least six months can offer protection against ear infections.
By taking these steps, we can greatly reduce our risk of ear infections and their complications.
Conclusion
It’s important to understand how ear infections can cause vomiting and nausea. This knowledge helps in diagnosing and treating these issues. We’ve looked into how ear infections affect the digestive system.
Ear infections can be very uncomfortable. When they cause vomiting and nausea, it’s key to act fast. This is to avoid dehydration and other serious problems.
Knowing that ear infections can lead to vomiting and nausea helps a lot. It means people can get help quickly. This is vital for managing these symptoms effectively.
We stress the need for a complete care plan for ear infections. This includes treating both the ear and the stomach symptoms. A holistic approach is best for managing these conditions.
FAQ
Can an ear infection cause vomiting?
Yes, an ear infection can make you vomit. This is more likely if it’s an inner ear infection. It can mess with your balance and make you feel sick to your stomach.
How does an ear infection cause nausea and vomiting?
The inner ear is linked to your stomach through nerves. When the inner ear gets upset, it can throw off your balance. This can make you feel queasy and want to vomit.
Can a middle ear infection cause gastrointestinal symptoms?
Yes, middle ear infections can upset your stomach. They can make you feel nauseous and want to vomit. This happens because of problems with the Eustachian tube and how your body reacts to the infection.
Are ear infections more likely to cause vomiting in children?
Kids are more prone to ear infections and vomiting. Their balance systems are not fully developed. This makes them more likely to get inner ear infections and feel sick.
Can an ear infection cause headaches?
Yes, ear infections can give you headaches. The swelling and pressure in your ear can send pain to your head. This can make you feel really uncomfortable.
How are ear infections diagnosed when nausea and vomiting are present?
Doctors use several ways to figure out if you have an ear infection. They look at your ear and check how you’re feeling. They also make sure it’s not something else causing your symptoms.
What are the treatment approaches for ear infections with gastrointestinal symptoms?
To treat ear infections, doctors might give you antibiotics. They also help manage your nausea and vomiting. They might use pain relievers to make you feel better.
Can ear infections be prevented?
Yes, you can lower your chances of getting an ear infection. You can get vaccinated and make some lifestyle changes. This can help keep your ears healthy.
Do ear infections cause nausea?
Yes, ear infections can make you feel nauseous. This is more common with inner ear infections. They can mess with your balance and make you feel sick.
Can an earache cause headaches?
Yes, an earache can lead to headaches. The pain from your ear can travel to your head. This can be really painful and uncomfortable.
Will an ear infection make you nauseous?
Yes, an ear infection can make you feel nauseous. This is true for inner ear infections. They can affect your balance and make you feel sick to your stomach.
Can an ear infection cause throwing up?
Yes, an ear infection can make you throw up. This is more likely if the inner ear is affected. It can cause severe balance problems and make you feel really sick.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Sore Throat. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/community/for-patients/sore-throat.html




































