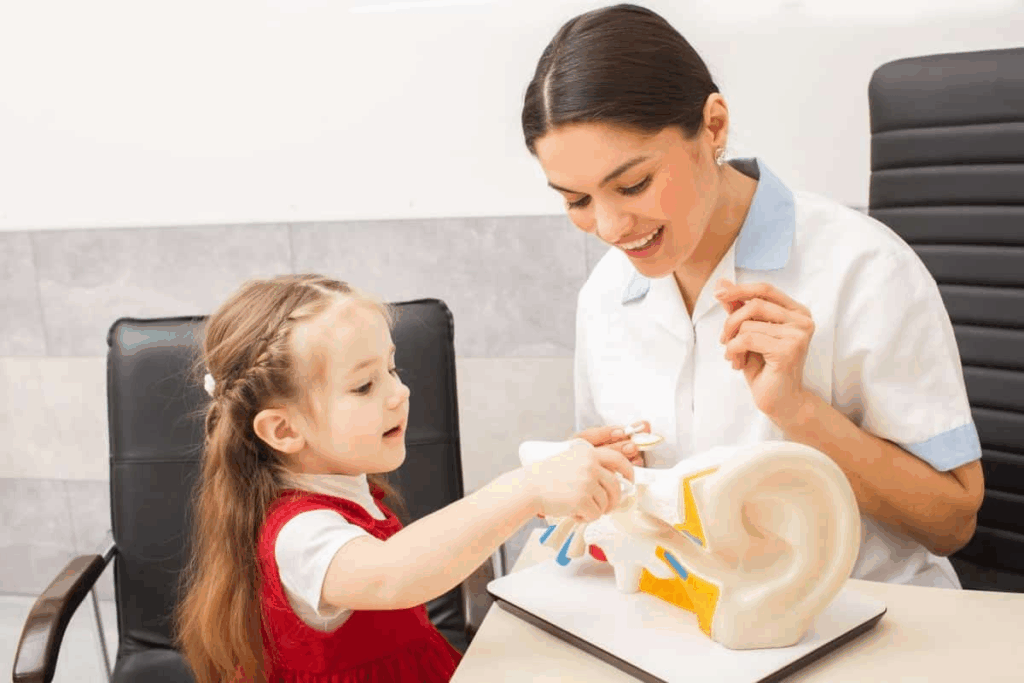
If you’re feeling ear pain, nausea, vomiting, and headaches, you might have an inner ear problem. This needs to be checked by a doctor.
Inner ear infections, like labyrinthitis or otitis interna, can make you feel sick. They affect your balance and hearing.
At Liv Hospital, our team knows that inner ear infections can cause more than just ear pain. They can lead to a range of symptoms.
Will an ear infection cause vomiting and headaches? Learn the link, particularly with inner ear inflammation and associated vertigo.
Key Takeaways
- Inner ear infections can cause vomiting and headaches due to their impact on balance and hearing.
- Nausea and vomiting are significant symptoms of inner ear infections.
- The inner ear plays a critical role in controlling balance and equilibrium.
- Infections affecting the inner ear can lead to a range of symptoms beyond ear pain.
- Medical attention is necessary to address inner ear infections and related symptoms.
Understanding Ear Infections and Their Symptoms
It’s important to know about the different ear infections to spot their symptoms early. There are three main types: outer, middle, and inner ear infections. Each has its own signs and needs special care.
Types of Ear Infections: Outer, Middle, and Inner
Ear infections can hit different parts of the ear. Otitis externa, or outer ear infection, is in the outer ear canal. Otitis media, or middle ear infection, is behind the eardrum. Labyrinthitis, an inner ear infection, messes with balance and hearing.
Type of Ear Infection | Common Name | Affected Area |
Otitis Externa | Outer Ear Infection | Outer ear canal |
Otitis Media | Middle Ear Infection | Behind the eardrum |
Labyrinthitis | Inner Ear Infection | Inner ear |
Common Symptoms Across Different Ear Infections
Ear infections share some common signs. Pain and discomfort are common in all types. Other symptoms include fever, hearing loss, and feeling like the ear is full.
In some cases, ear infections can cause vertigo or dizziness, mainly if the inner ear is affected.
How Symptoms Vary in Children vs. Adults
Ear infection symptoms can differ in children and adults. Kids might seem irritable, have a fever, and pull at their ears. Adults tend to describe their pain and discomfort more clearly.
Ear infections are a big health issue that needs quick and right treatment. Knowing about the types of ear infections and their symptoms helps us manage them better and avoid serious problems.
The Connection Between Ear Infections and Balance
The inner ear plays a key role in our balance. It houses the vestibular system, which keeps us steady and oriented.
How the Inner Ear Controls Balance and Spatial Orientation
The vestibular system is in the inner ear. It has three semicircular canals and otolith organs. These are filled with fluid and have sensory hair cells.
These cells detect movement and changes in head position. When we move, the fluid in the canals lags. This bends the hair cells, sending signals to the brain.
The brain uses these signals to understand our position and movement. This helps us stay balanced and oriented. This process is vital for everyday activities, like walking or dancing.
The Vestibular System and Its Functions
The vestibular system is key for balance and spatial awareness. It works with the visual system and proprioception to keep us balanced. It detects linear and rotational movements, helping the brain adjust our balance.
When it’s working right, we move easily and stay balanced. But, if it’s disrupted, we might feel vertigo, dizziness, or nausea.
When Infection Disrupts Normal Balance Mechanisms
Ear infections, mainly those in the inner ear, can harm the vestibular system. Infection can cause inflammation and damage to the inner ear’s structures. This can lead to problems with balance and equilibrium.
This can cause symptoms like vertigo or dizziness. It can also lead to nausea or vomiting. These symptoms can make it hard to stand or walk.
It’s important to understand how ear infections affect balance. This helps doctors treat both the infection and its impact on balance effectively.
Will an Ear Infection Cause Vomiting?
Understanding if an ear infection can cause vomiting needs a closer look. Ear infections, mainly those in the inner ear, can cause symptoms beyond ear pain and fever.
The Physiological Mechanism Behind Infection-Related Nausea
The inner ear is key for balance and equilibrium. An infection here can mess with the vestibular system. This can lead to vertigo, nausea, and vomiting.
The vestibular system helps us stay balanced. When it’s affected, the brain gets confused signals. This can make us feel like we’re spinning, leading to vertigo.
Vertigo and Its Direct Connection to Vomiting
Vertigo makes you feel like you or things around you are spinning. It’s closely tied to vomiting with ear infections. When the vestibular system is off, it can make us feel really off-balance. This can cause nausea and vomiting.
Why Some Ear Infections Cause Vomiting While Others Don’t
Not every ear infection makes you vomit. It depends on the infection’s type and how bad it is. Outer or middle ear infections are less likely to make you vomit than inner ear ones.
Type of Ear Infection | Likelihood of Vomiting | Common Symptoms |
Outer Ear Infection | Low | Ear pain, itching, discharge |
Middle Ear Infection | Moderate | Ear pain, fever, hearing loss |
Inner Ear Infection | High | Vertigo, nausea, vomiting, hearing loss |
The table shows that inner ear infections are more likely to cause vomiting. This is because they directly affect the vestibular system.
In conclusion, not all ear infections make you vomit. But, inner ear infections are more likely to do so. This is because they mess with the vestibular system and cause vertigo.
How Ear Infections Lead to Headaches
Ear infections and headaches are connected in many ways. This includes pressure, inflammation, and nerve irritation. These changes can cause headache pain.
Pressure Build-up and Pain Pathways in the Ear
Fluid buildup and pressure changes in the ear can start pain pathways. This pressure can spread to the head, causing headaches. The eustachian tube helps control ear pressure. If it’s blocked by infection, it can make the ear feel full and lead to headaches.
Inflammation and Trigeminal Nerve Involvement
Inflammation from an ear infection can bother nearby nerves, like the trigeminal nerve. This nerve is important for headache pain. When it’s irritated, it can send pain signals to the brain, causing headaches.
“The trigeminal nerve is a key player in headache generation, and its interaction with inflammatory processes in ear infections can lead to significant pain.”
Medical Expert, ENT Specialist
Referred Pain Patterns from Ear to Different Parts of the Head
Ear infections can cause pain in different head areas. This is because the nerves in the ear also cover other parts of the head and neck. For example, ear pain can feel like it’s coming from the temple or the back of the head.
Referred Pain Location | Possible Cause |
Temple Area | Trigeminal nerve irritation |
Back of the Head | Greater occipital nerve involvement |
Behind the Eye | Referral from trigeminal nerve branches |
Knowing how ear infections cause headaches is key to treating them. Doctors can help by treating the infection and managing symptoms. This can relieve the complex pain patterns caused by ear infections.
Inner Ear Infections: Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuritis
The inner ear is very delicate. Infections like labyrinthitis and vestibular neuritis can mess with its balance. These problems affect the labyrinth and the vestibular nerve, which helps the brain understand balance.
Viral vs. Bacterial Causes of Inner Ear Inflammation
Labyrinthitis often comes from viruses, like those causing colds or flu. Bacterial labyrinthitis is rarer but can happen, usually with a middle ear infection. Vestibular neuritis is usually from a viral infection that irritates the vestibular nerve.
Knowing if it’s a virus or bacteria is key. Viruses don’t need antibiotics, but bacteria do.
Distinguishing Symptoms of Labyrinthitis
Labyrinthitis symptoms include vertigo, hearing loss, tinnitus, and nausea. The vertigo can be so bad it makes it hard to stand or walk. Some people might also see their eyes move on their own.
The symptoms can be different for everyone. Sometimes, it goes away in a few weeks. Other times, it lasts longer and needs ongoing care.
Risk Factors and Possible Complications
Some people are more likely to get inner ear infections. This includes having a viral infection, being stressed, or having a history of respiratory infections.
Complications can be serious. They include permanent hearing loss, ongoing balance issues, and rare cases of meningitis. Seeing a doctor quickly is important to avoid these problems.
Ear Infections in Different Age Groups
Ear infections can affect people of all ages, but the reasons and symptoms vary. We’ll look at how ear infections differ by age. This includes why these differences happen.
Why Children Are More Susceptible to Ear Infections
Children often get ear infections, like middle ear infections, because of their immune systems and Eustachian tubes. The Eustachian tube is shorter and more horizontal in kids. This makes it easier for germs to get into the middle ear. Also, kids’ immune systems are not as strong yet, making them more likely to get sick.
How Symptoms Present Differently in Children
Ear infection symptoms in kids can be hard to spot. They might seem irritable, have a fever, or pull at their ears. Young kids can’t tell us how they feel, so they might act differently or have trouble sleeping. It’s important for parents to watch for these signs and get help if they think their child has an ear infection.
Older kids can usually tell us about their ear pain or hearing problems. This makes it easier to figure out if they have an ear infection.
Ear Infections in Adults: Causes and Concerns
Ear infections do happen in adults, but not as often as in kids. They can be caused by colds, allergies, or other health issues. Smoking and being around smoke can also raise the risk of getting an ear infection.
Comparison of Ear Infection Characteristics Across Age Groups
Characteristic | Children | Adults |
Common Type of Infection | Middle ear infections | Outer or middle ear infections |
Primary Cause | Eustachian tube anatomy and developing immune system | Respiratory infections, allergies, or anatomical issues |
Symptom Presentation | Non-specific (irritability, fever, ear pulling) | More specific (ear pain, hearing loss) |
Knowing these differences helps us diagnose and treat ear infections better. This improves health outcomes for both kids and adults.
Diagnosing Ear Infections with Vomiting and Headache Symptoms
Healthcare professionals use many ways to find out if you have an ear infection. They look at your symptoms, do physical checks, and sometimes use imaging. This helps them know what’s causing your pain and other symptoms.
Physical Examination Procedures
First, doctors do a physical check. They use an otoscope to look into your ear. They look for signs like redness or fluid. This tells them how bad the infection is.
They might also do a hearing test. This is important if the infection has caused hearing loss. It helps them understand the extent of the damage.
Diagnostic Tests and Imaging Techniques
Tests are key to confirming an ear infection. They might do a tympanometry test. This checks how well your eardrum moves. Sometimes, they use CT or MRI scans to look for other problems.
Audiometry is another test. It checks your hearing levels. This is helpful for diagnosing inner ear infections or seeing how a middle ear infection affects your hearing.
Differential Diagnosis: Conditions with Similar Symptoms
It’s important to rule out other possible causes. Doctors think about things like migraines or sinus infections. They do this to make sure they find the right cause of your symptoms.
Condition | Symptoms | Diagnostic Tests |
Ear Infection | Ear pain, fever, vomiting, headaches | Otoscopy, tympanometry, audiometry |
Migraine | Severe headaches, nausea, vomiting | Clinical evaluation, MRI or CT scans |
Sinus Infection | Facial pain, nasal congestion, headaches | Imaging studies (CT or MRI), nasal endoscopy |
By looking at physical checks, test results, and other possibilities, doctors can find the right diagnosis. Then, they can start the right treatment.
Treatment Options and Home Remedies
Dealing with ear infections requires a mix of medical care and home remedies. We’ll look at how to manage ear infections. This includes medicines and self-care steps.
Medical Treatments: Antibiotics, Antivirals, and Anti-inflammatories
The right treatment for an ear infection depends on the cause and how bad it is. Antibiotics fight bacterial infections. Antiviral medications tackle viral ones. Anti-inflammatory drugs help with swelling and pain.
“Antibiotics work well against bacterial infections, but we must use them wisely to prevent resistance,” says an otolaryngology expert.
- Amoxicillin is a common antibiotic for ear infections.
- Antiviral drugs like acyclovir are for viral infections.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen ease pain and swelling.
Managing Nausea, Vomiting, and Vertigo Symptoms
It’s important to manage symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and vertigo. Vestibular suppressants help with vertigo. Antiemetic medications control nausea and vomiting.
Resting in a quiet, dark place can help with vertigo. Also, avoiding sudden movements helps prevent making symptoms worse.
Effective Headache Relief Strategies
There are ways to handle headaches from ear infections. Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen work well. A warm compress on the ear can also help.
“A warm compress can ease ear pain and headaches,” says a healthcare expert.
Home Remedies and Self-Care Approaches
Home remedies can also help with ear infection symptoms. Sleeping with your head elevated can reduce ear pressure. Using ear drops or olive oil can soothe the ear.
Always talk to a healthcare professional before trying new remedies. This is important if symptoms don’t get better or get worse.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get medical help can save lives. Ear infections are common but can be serious if not treated right. It’s important to know when to go to the doctor to avoid long-term problems.
Warning Signs That Require Immediate Care
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Severe ear pain that doesn’t go away with over-the-counter meds.
- High fever, over 102°F (39°C), which might mean a serious infection.
- Discharge or fluid leakage from the ear, which could mean a ruptured eardrum.
- Hearing loss or big changes in hearing.
- Dizziness or vertigo that’s bad or lasts a long time.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology says if you or your child has these symptoms, get medical help fast.
Emergency Symptoms in Children and Adults
Some symptoms are the same for everyone, but kids are more at risk because of their immune systems and smaller Eustachian tubes. For kids, watch for:
- Irritability or fussiness, with fever or ear pulling.
- Difficulty sleeping or loss of appetite, which can mean ear pain.
- Mastoiditis, a rare but serious infection of the bone behind the ear.
For adults, look out for severe headache, confusion, or facial paralysis with an ear infection. These are signs to see a doctor right away.
“Prompt medical attention is key to avoiding complications from ear infections. If you’re not sure about your symptoms, it’s better to be safe than sorry.”
What to Expect During Your Doctor’s Visit
At your doctor’s visit for an ear infection, you’ll get a full check-up. This includes:
- Talking about your medical history to understand your symptoms and past infections.
- A physical check of your ear with an otoscope to look for infection or damage.
- Possible hearing tests if there’s worry about hearing loss.
- Talking about treatment options, like antibiotics, pain relief, or other steps based on the infection’s severity and cause.
Knowing what to expect at your doctor’s visit can make you feel better. It helps you talk about your symptoms and treatment options clearly.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into how ear infections, vomiting, and headaches are linked. The inner ear plays a big role in keeping us balanced and oriented. When ear infections hit the inner ear, they can make us feel sick and hurt our head.
It’s important to know how ear infections and their symptoms are connected. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. By spotting the signs early, people can get help fast. This can stop more problems and make them feel better.
In the end, treating ear infections right is key. It involves doctor’s care and taking care of yourself. This way, you can get better and avoid getting sick again.
FAQ
Can an ear infection cause vomiting?
Yes, an ear infection, mainly an inner ear infection, can make you vomit. This happens because the infection messes with the vestibular system. This can cause vertigo and nausea.
Can an earache cause headaches?
Yes, an earache can lead to headaches. This is because of the pressure and pain in the ear. Inflammation and the trigeminal nerve also play a role.
Will an ear infection make you nauseous?
Yes, an ear infection can make you feel nauseous. This is more likely if the infection is in the inner ear. It can mess with your balance and cause vertigo.
Can ear infections cause nausea and headaches?
Yes, ear infections can make you feel both nauseous and have headaches. This is because the infection affects the inner ear. It messes with the vestibular system and pain pathways.
Do ear infections cause headaches?
Yes, ear infections can lead to headaches. This is due to the pressure, inflammation, and nerve involvement. These can cause pain in different parts of the head.
Can an ear infection cause you to vomit?
Yes, an ear infection can make you vomit. This is more likely if it causes severe vertigo. It can also disrupt your balance, making it hard to stay steady.
Can ear infections cause vomiting in children?
Yes, ear infections can make children vomit. This is because their balance and vestibular systems are not fully developed. They are more likely to be affected by inner ear infections.
How do ear infections affect balance?
Ear infections, mainly those in the inner ear, can mess with the vestibular system. This can lead to balance problems, vertigo, and symptoms like nausea and vomiting.
What are the symptoms of an inner ear infection?
Symptoms of an inner ear infection include vertigo, nausea, vomiting, and balance problems. You might also experience hearing loss and ear pain, depending on the severity.
When should I seek medical attention for an ear infection?
You should see a doctor if you have severe symptoms. This includes intense ear pain, high fever, vomiting, or trouble balancing. Also, seek help if symptoms don’t get better or get worse over time.
References
MedlinePlus. (n.d.). Tonsillectomy – adult. Retrieved fromhttps://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/002930.htm



































