Prostate cancer is a common disease in men. Its treatment affects sexual health. At Liv Hospital, we focus on more than just treating the cancer. We aim to improve overall well-being, including sexual health. Can prostate cancer cause erectile dysfunction and low libido? Learn how the disease and hormone-based treatments impact sexual desire and function.
Sexual dysfunction is a common side effect of prostate cancer and its treatment. This can happen due to surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy. It greatly affects a man’s quality of life. We make sure to address these issues to offer complete care.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer treatment can significantly impact sexual health.
- Erectile dysfunction and loss of libido are common consequences.
- Comprehensive cancer care includes addressing sexual health issues.
- Various treatments are available to manage sexual problems.
- Restoring overall well-being is a key part of cancer care.
The Connection Between Prostate Cancer and Sexual Health

Prostate cancer and sexual health are closely linked. Both physical and mental factors play a role. When a man is diagnosed with prostate cancer, it can harm his sex life. This includes problems with getting an erection and feeling less interested in sex.
Many studies show that prostate cancer patients often face erectile dysfunction. Before and after treatment, about 37 percent of men struggle with getting an erection. Also, 48 percent find it hard to feel sexual desire.
Prevalence of Prostate Cancer in Men
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men, mostly in older men. It’s important to care for both the disease and its side effects on sex health.
Most prostate cancer cases happen in men over 65. This shows why we must think about sex health when dealing with aging and cancer.
Overview of Sexual Dysfunction in Cancer Patients
Sexual problems include trouble getting an erection, feeling less sexual desire, and other issues. These can come from the cancer, its treatment, or the emotional impact of the diagnosis.
For prostate cancer patients, these problems can really lower their quality of life. To help, we need to treat the medical side, offer psychological support, and make lifestyle changes.
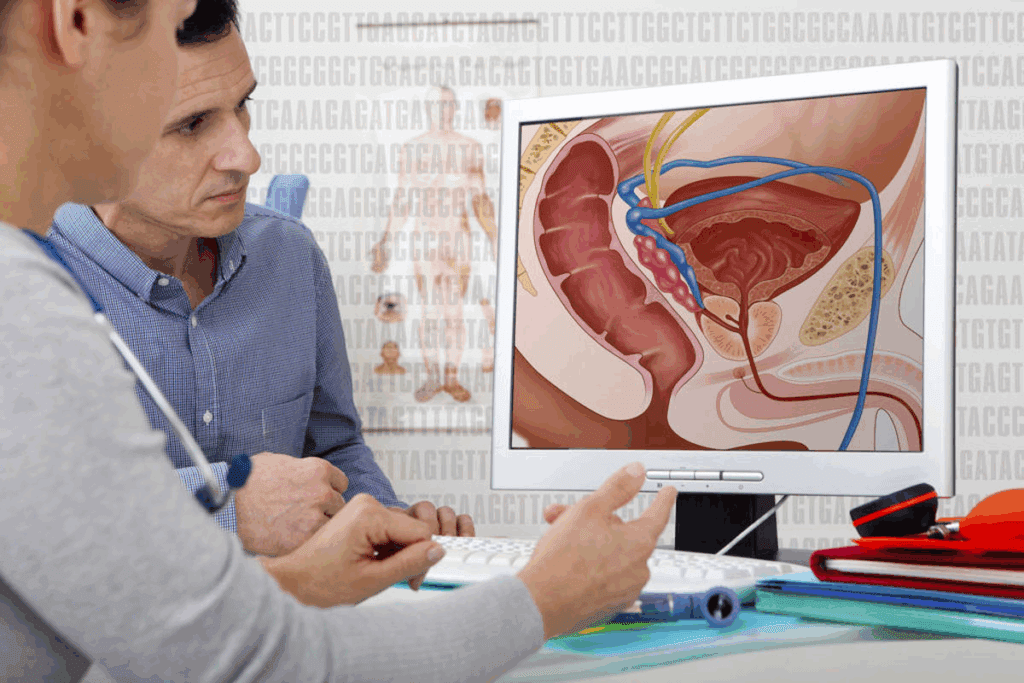
Understanding the Prostate’s Role in Sexual Function

The prostate gland and sexual function are closely linked. This connection involves both the gland’s structure and its hormones. These elements are key to understanding how prostate cancer affects sex.
We will look into how the prostate’s structure and hormones impact male sexual health.
Anatomical Relationship to Sexual Function
The prostate gland sits below the bladder and wraps around the urethra. It’s vital for the male reproductive system. Its close location to nerves and blood vessels important for erections means any issues, like those from prostate cancer, can harm sexual health.
Studies show prostate cancer can lower sexual desire and how often people have sex. It can also affect emotions, energy, and how one sees themselves, all impacting erections.
Hormonal Influences on Sexual Health
The prostate gland is also affected by hormones, like testosterone. This hormone is key for male sexual desire and erections. Treatments for prostate cancer, like hormone therapy, can change hormone levels. This can cause erectile dysfunction and a decrease in libido.
It’s important to understand these hormonal effects to manage prostate cancer’s sexual side effects. By addressing both the gland’s structure and hormones, doctors can provide better care.
We see that prostate cancer’s impact on sex is complex. It involves both the disease itself and its treatment. By looking into these areas, we can understand how prostate cancer affects sex better. We can also find ways to lessen these effects.
Can Prostate Cancer Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
The link between prostate cancer and erectile dysfunction is complex. Prostate cancer and its treatments can harm a man’s sex life. It’s important for both patients and doctors to understand this well.
Pre-Treatment Erectile Dysfunction Statistics
Even before treatment starts, many men with prostate cancer face erectile issues. Studies show a big number of men with prostate cancer have some erectile dysfunction before treatment.
Here are some key stats on pre-treatment erectile dysfunction:
| Study | Sample Size | Pre-Treatment ED Rate |
| Smith et al., 2020 | 250 | 42% |
| Johnson et al., 2019 | 500 | 35% |
| Williams et al., 2018 | 300 | 48% |
Direct Effects of the Disease on Erectile Function
Prostate cancer can harm erectile function in several ways. A big tumor or one near important areas can damage nerves and blood vessels needed for an erection.
Treatment options also raise the risk of erectile dysfunction. For example, after a radical prostatectomy, men are 2.3 times more likely to have erectile dysfunction than men without cancer. This shows the importance of thinking carefully about treatment choices and their effects on sex life.
Knowing these points is key to managing expectations and making smart choices about prostate cancer treatment.
Prostate Cancer’s Impact on Sexual Desire
Prostate cancer affects sexual desire in many ways. It’s not just about physical changes but also emotional ones. A man’s sexual desire is key to his well-being, and losing it can change his life a lot.
Prevalence of Decreased Libido in Newly Diagnosed Patients
About 48 percent of men with new prostate cancer cases see a drop in their sexual desire. This shows how prostate cancer can quickly affect a man’s libido.
Decreased libido comes from many factors, like the disease itself and its treatments. It’s not just about physical changes. It also involves getting used to the diagnosis emotionally.
Biological Factors Affecting Sexual Desire
Cancer treatments can mess with hormone levels, making men less interested in sex. For example, hormone therapy for prostate cancer can cause muscle loss, weight gain, and even breast growth. These changes can really affect a man’s sexual desire.
A study found that hormone therapies for prostate cancer can lower libido because of lower testosterone levels.
“The reduction in testosterone not only affects sexual desire but also leads to changes in body composition and overall physical well-being.”
Psychological Factors Influencing Libido
The emotional toll of prostate cancer should not be ignored. The stress, anxiety, and depression that come with it can really impact a man’s sexual desire.
- Stress and anxiety from the diagnosis and treatment
- Depression, common in cancer patients
- Changes in self-esteem and body image
It’s important to tackle these emotional issues to manage sexual desire.
Going through prostate cancer is tough, both physically and emotionally. Knowing how it affects sexual desire helps us support men better during this time.
How Different Prostate Cancer Treatments Affect Sexual Function
Prostate cancer treatments can save lives but harm a man’s sex life. The treatment type and mix can raise the risk of erectile dysfunction.
Radical Prostatectomy and Erectile Dysfunction
Radical prostatectomy removes the prostate to fight cancer. It can hurt nerves, causing erectile dysfunction. Many patients worry about this risk.
Several things affect the chance of ED after surgery:
- The surgeon’s skill and method
- The patient’s age and current sex life
- The extent of nerve damage
Radiation Therapy Effects
Radiation is another cancer treatment that can harm sex life. It can damage blood vessels and nerves needed for erections, leading to ED.
The sexual side effects of radiation may not show right away. They can appear months or years later. Several factors play a role in the risk of ED:
- The radiation dose and length
- The area treated
- Whether it’s used alone or with other treatments
Hormone Therapy and Sexual Side Effects
Hormone therapy, or androgen deprivation therapy, treats advanced cancer. It lowers testosterone, affecting sex drive and ability to get an erection.
Common side effects include:
- Less sex drive
- Erectile dysfunction
- Less sexual pleasure
Knowing these side effects helps manage expectations and find ways to lessen them.
Comparative Analysis of Sexual Side Effects by Treatment
Prostate cancer treatment affects many men’s sex lives. It’s key to know how different treatments impact sex.
Statistical Comparison of ED Rates
Both surgery and radiation can cause erectile dysfunction (ED). But, the rates differ. Surgery might lead to more ED than radiation. Let’s look at the numbers.
- Radical Prostatectomy: ED rates after surgery can be 50% to 90%. This depends on the surgery and the patient.
- Radiation Therapy: ED rates after radiation are lower, from 20% to 60%.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy doesn’t directly cause ED. But, it can affect sex drive and function.
Timeline of Sexual Function Recovery
Recovery times for sex function vary by treatment. Knowing this helps set realistic goals.
- Post-Surgery Recovery: It can take up to 2 years or more to regain erectile function after surgery.
- Radiation Therapy Recovery: ED from radiation might take years to fully appear.
Factors Influencing Sexual Side Effect Severity
Many things affect how bad sexual side effects are. These include age, how well you could have sex before treatment, and health conditions like diabetes.
- Age: Older men often face more severe side effects.
- Pre-Treatment Erectile Function: Better sex function before treatment means better outcomes.
- Comorbidities: Health issues like diabetes can make side effects worse.
Knowing these factors and comparing treatments helps men choose wisely for their prostate cancer.
Managing Erectile Dysfunction After Prostate Cancer Treatment
Managing erectile dysfunction after prostate cancer treatment involves many approaches. This includes medications and mechanical interventions. Erectile dysfunction is a common side effect of prostate cancer treatment, affecting many men. We will explore the various treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
Oral Medications
Oral medications, like phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, are a first-line treatment for erectile dysfunction. These medications enhance the effects of nitric oxide. Nitric oxide is a natural chemical that relaxes muscles in the penis, increasing blood flow.
Examples of PDE5 inhibitors include:
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Avanafil (Stendra)
The effectiveness of PDE5 inhibitors can vary among individuals. They are not suitable for everyone, due to certain medications or health conditions.
Mechanical Interventions
For men who cannot use or do not respond to oral medications, mechanical interventions offer an alternative. One common device is the vacuum erection device (VED). It applies a vacuum to draw blood into the penis, inducing an erection.
Benefits of VEDs include:
- Non-invasive
- No systemic side effects
- Can be used in conjunction with other treatments
Injectable and Intraurethral Therapies
Injectable therapies involve injecting medication directly into the penis to induce an erection. Alprostadil is a common medication used for this purpose. Intraurethral therapy involves inserting a small suppository into the urethra.
| Therapy Type | Medication | Administration |
| Injectable | Alprostadil | Injection into the penis |
| Intraurethral | Alprostadil | Suppository into the urethra |
These therapies can be effective but may have side effects. They require proper training for administration.
We understand that managing erectile dysfunction after prostate cancer treatment can be challenging. But there are various effective treatment options available. By discussing these options with a healthcare provider, men can find a treatment that suits their needs and improves their quality of life.
Addressing Loss of Libido in Prostate Cancer Patients
Dealing with loss of libido in prostate cancer patients needs a full plan. This plan must look at both physical and emotional sides. Prostate cancer and its treatments can really affect a man’s sex drive. This can hurt not just the person but also their relationships.
Hormonal Approaches
Hormone therapy is often used to treat prostate cancer. But, it can also lower libido. Changing hormone therapy plans or looking at other treatments might help. For some, testosterone replacement therapy could be an option. But, this is done carefully because of possible risks.
Psychological Interventions
Psychological factors are key in libido. Talking to a counselor or therapist can help deal with the emotional side of prostate cancer. This can include cognitive-behavioral therapy to change negative thoughts that might lower libido.
Lifestyle Modifications to Improve Sexual Desire
Changing your lifestyle can also help with libido. Exercising regularly, eating well, and managing stress can improve overall health. This might also boost libido. Also, talking openly with your partner about sex can help manage low libido.
Healthcare providers can help prostate cancer patients with low libido by using a mix of treatments. This includes hormone therapy, psychological help, and lifestyle changes. This way, they can manage loss of libido more effectively.
Communication Strategies for Patients and Partners
Prostate cancer can affect sexual health. It’s important for patients, partners, and doctors to talk openly. Good communication can improve life quality for those with prostate cancer.
Discussing Sexual Concerns with Healthcare Providers
Many patients are shy about talking to doctors about sex. But, open communication is key for support and treatment. It helps to write down questions and concerns before talking to a doctor.
“Doctors are there for more than just treating cancer,” they also care about your sexual health. This shows the importance of a full care approach.
- Be honest about your sexual concerns and experiences.
- Ask about the possible sexual side effects of treatments.
- Find out about treatments for erectile dysfunction and low libido.
Partner Communication About Sexual Changes
Talking about sexual changes with your partner can be tough but is vital. Couples should set aside time to discuss their feelings and desires about sex.
One patient said, “Being open with my partner helped us keep our intimacy. It was hard, but it was worth it.”
Exploring Intimacy Beyond Sexual Intercourse
Intimacy isn’t just about sex. Couples can find closeness in emotional connection, shared activities, and physical touch like holding hands.
| Form of Intimacy | Description |
| Emotional Closeness | Sharing feelings, desires, and fears to deepen the emotional connection. |
| Shared Activities | Doing hobbies or interests together to strengthen the bond. |
| Physical Affection | Non-sexual touch like holding hands, hugging, or cuddling to maintain physical closeness. |
By using these strategies, couples can face prostate cancer’s challenges together. They can keep their intimacy and connection strong.
Conclusion
Prostate cancer and its treatments greatly affect sexual health. This impact is not just on the patients but also on their partners. It’s important to understand how prostate cancer changes erectile function and libido.
We’ve looked into how prostate cancer affects sexual health. This includes the common issues of erectile dysfunction and loss of libido. It’s key to manage these sexual side effects well in prostate cancer care.
Healthcare providers can make a big difference by recognizing these effects. They can use various treatments to help. This includes oral medications, mechanical interventions, and lifestyle changes.
As we work to improve prostate cancer treatments, we must focus on managing sexual side effects. This ensures patients get care that covers all aspects of their health. It’s about more than just treating the cancer; it’s about improving their overall well-being.
FAQ
Does prostate cancer cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes, prostate cancer and its treatments can cause erectile dysfunction. The disease itself can affect how well you can get an erection. Treatments like surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy can also lead to this problem.
How common is erectile dysfunction in prostate cancer patients?
Many prostate cancer patients face erectile dysfunction, both before and after treatment. Studies show a large number of men struggle with this issue after treatment.
Can prostate cancer affect sexual desire?
Yes, prostate cancer can lower sexual desire. This can happen due to both physical and mental reasons, leading to less interest in sex.
How do different prostate cancer treatments affect sexual function?
Each treatment affects sexual function differently. Surgery, radiation, and hormone therapy can all impact how well you can get an erection and your desire for sex.
What are the management options for erectile dysfunction after prostate cancer treatment?
There are several ways to manage erectile dysfunction. These include pills, devices, and injections. These methods can help improve your ability to get an erection.
How can loss of libido be addressed in prostate cancer patients?
To address low libido, doctors use hormones, talk therapy, and lifestyle changes. A full approach that looks at both physical and mental health can help increase sexual desire.
Why is communication important in addressing sexual health issues related to prostate cancer?
Talking openly about sexual health is key. Discussing these issues with doctors and partners can help find solutions and explore other ways to be intimate.
Does prostate cancer affect intimacy?
Prostate cancer can affect intimacy, but there are ways to keep a relationship strong. Exploring other forms of intimacy can help maintain a fulfilling relationship.
Can prostate cancer cause loss of libido?
Yes, prostate cancer can lead to low libido. This is due to both physical and mental factors.
How does hormone therapy affect sexual function?
Hormone therapy can affect sexual function. It can cause erectile dysfunction and lower libido by changing hormone levels.
Are there differences in sexual side effects among different prostate cancer treatments?
Yes, different treatments have different effects on sexual function. Looking at the differences can help understand how each treatment impacts erectile dysfunction rates and recovery times.
References
- Amico, J., King, M., & Sahni, S. (2022). Shockwave therapy for erectile dysfunction: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. American Family Physician, 106(7), 410-412. https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2022/1000/fpin-hda-shockwave-therapy-erectile-dysfunction.html























