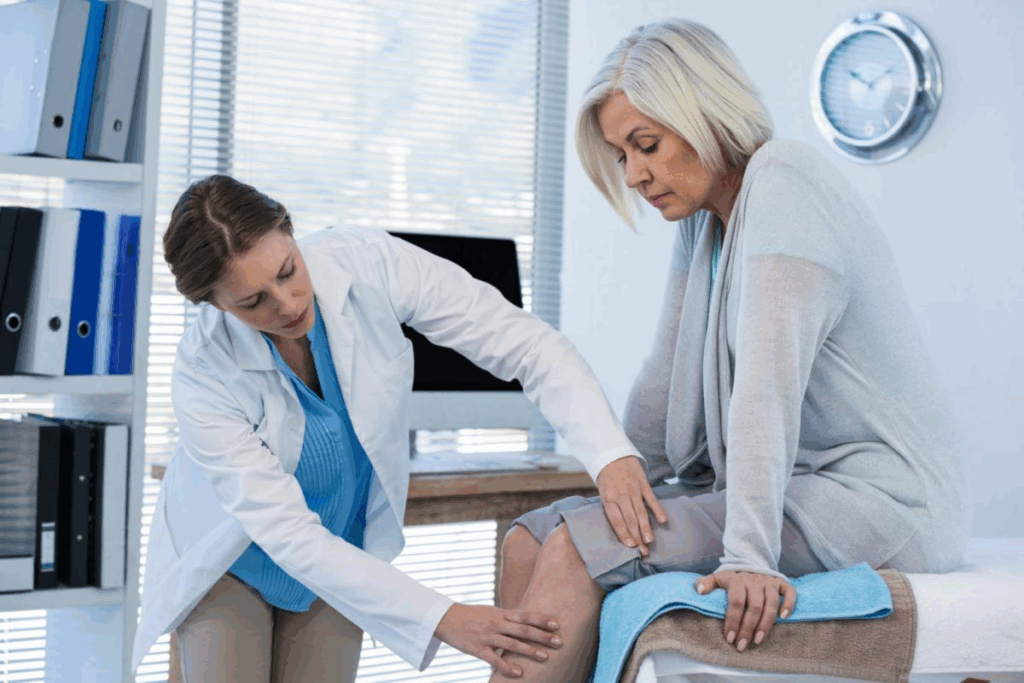
Knee pain can come from many things, like minor sprains or serious health issues. It’s common for people to wonder if their knee pain is serious or not. Knowing when to get help quickly is very important.
Recognizing the signs of a knee pain emergency is key. Some knee pain can be treated with rest and care at home. But if there’s trauma or certain symptoms, you need to see a doctor right away. We’re here to help you know when knee pain is an emergency, so you get the care you need fast.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the severity of knee pain is key to knowing if you need emergency care.
- Certain symptoms with knee pain might mean a serious problem.
- Getting medical help quickly can greatly improve your knee pain situation.
- Not all knee pain needs immediate doctor visits, but knowing when is important.
- Spotting emergency signs early can prevent serious damage later.
Understanding the Difference Between Urgent and Non-Urgent Knee Pain
Knee pain can be caused by many things, some of which need quick medical help. We’ll look at the differences between urgent and non-urgent knee pain. This will help you know when to get medical help.
Common Non-Emergency Knee Pain Causes
Non-emergency knee pain often comes from overuse, minor strains, or conditions like osteoarthritis. Common causes include repetitive strain injuries, tendonitis, and mild ligament sprains. These can usually be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), and over-the-counter pain relievers.
But it’s important to tell the difference between mild and severe conditions. If your pain doesn’t go away or gets worse, see a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
Red Flags That Indicate a Potential Emergency
Certain symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. Red flags include severe pain, swelling, or bruising around the knee, not being able to bear weight on the affected leg, and visible deformity. These signs could mean serious injuries like fractures, dislocations, or severe ligament tears.
- Severe pain or swelling
- Inability to bear weight
- Visible deformity
- Instability or buckling of the knee
The Importance of Timely Medical Intervention
Timely medical intervention is crucial for avoiding long-term damage and ensuring effective healing. Waiting too long can lead to chronic pain, limited mobility, or more injury. If you’re unsure about your knee pain or see any red flag symptoms, seek medical care.
By knowing the causes of knee pain and recognizing emergency signs, you can take the right steps towards recovery. This helps keep your knees healthy.
Sudden Severe Knee Injury: When to Seek Immediate Care

When a knee injury happens, knowing how bad it is and what caused it is key. Injuries can come from sports, falls, or direct hits to the knee.
Traumatic Injuries Requiring Emergency Attention
Some knee injuries need help right away. These include breaks, dislocations, and severe sprains or tears. These can really hurt your knee’s function and might cause lasting problems if not treated fast.
Fractures in the kneecap, shinbone, or thigh bone are emergencies. They can move out of place or hurt nerves. Knee dislocations are also serious because they can cut off blood to the lower leg.
The Role of Mechanism of Injury in Assessment
The way an injury happens helps doctors figure out how bad it is. Big traumas, like car crashes or big falls, usually mean more serious injuries.
Knowing how an injury happened helps doctors guess what might be wrong. For example, a hit to the knee might mean a break or bruise. A twist could mean a sprain or tear.
Post-Injury Warning Signs
After a knee injury, some signs mean you need to see a doctor right away. Look out for a lot of pain, not being able to stand, swelling, or feeling unstable.
- Severe pain that limits mobility or is unbearable
- Visible deformity or abnormal alignment of the knee
- Significant swelling or bruising around the knee
- Instability or feeling of the knee “giving way”
- Open wounds or signs of infection
Seeing these signs and getting medical help fast is important. It helps avoid more damage and helps you heal better.
Inability to Bear Weight on the Affected Leg
Not being able to put weight on a leg because of knee pain is a big sign that needs quick doctor help. This problem can come from many things, like sudden injuries, serious infections, or long-term inflammation.
Differentiating Between Pain-Related Avoidance and True Inability
It’s key to tell the difference between not wanting to put weight on a leg because of pain and not being able to do so. Pain-related avoidance means someone can technically put weight on but doesn’t because of pain. On the other hand, true inability means there’s a real problem that stops you from putting weight on, no matter how much pain you can handle.
- Pain-related avoidance usually means there’s a lot of pain or discomfort.
- True inability might show a more serious problem, like a break, dislocation, or bad ligament injury.
Associated Symptoms That Increase Concern
Some symptoms can make you worry more if you can’t put weight on your leg. These include:
- Severe pain that doesn’t get better with rest or medicine.
- Swelling or bruising around the knee, which might mean there’s an injury inside.
- Instability or feeling like the knee might collapse.
- Deformity or the leg looks off in some way.
Timeline Considerations for Weight-Bearing Issues
When you first can’t put weight on your leg is very important. If it happened suddenly, it might be an acute injury. If it happened slowly, it could be a long-term problem. Knowing this helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
Not being able to put weight on your leg can be really scary. Our medical team is here to help with kindness and care. We want to help you feel better and fix the problem that’s causing your trouble.
Visible Deformity and Extensive Bruising
Visible deformity and extensive bruising are key signs of knee injuries that need quick medical help. These signs often point to serious trauma or conditions. If not treated fast, they can cause lasting damage.
Recognizing Abnormal Knee Alignment
Abnormal knee alignment is a big worry after a knee injury. Visible deformity can show as an odd shape or position of the knee. This might mean a dislocation, fracture, or severe ligament sprain.
We need to check the knee closely to see if it’s out of place. This can affect how stable and functional the leg is.
Spotting abnormal knee alignment means looking closely and comparing it to the other knee. Any big difference in shape, angle, or position is a red flag. Doctors use this to figure out how fast they need to act.
Significance of Rapid or Delayed Bruising
Bruising around the knee can happen right after an injury or later. Rapid bruising often means a lot of internal bleeding. Delayed bruising might mean a milder injury. But, how fast and how much bruising shows can tell us a lot about the injury.
The amount and spread of bruising can show how bad the injury is. A lot of bruising might mean deeper damage, like to muscles, tendons, or bones.
Distinguishing Between Surface and Deep Tissue Damage
Telling surface and deep tissue damage apart is key for the right treatment. Surface injuries are easy to see, with cuts or bruises. But deep tissue damage can be hidden, with little to no outside signs.
We use checks, patient history, and scans to tell the difference. Deep tissue damage often needs more serious treatment, like surgery, to fix and prevent future problems.
Joint Dislocation and Instability Emergencies
It’s important to know when a joint dislocation is an emergency. This is because it can lead to serious injuries if not treated right away. A joint dislocation happens when the bones in a joint move out of place. This can cause instability and harm to the surrounding tissues.
Patella Dislocation Signs and Symptoms
Patella dislocation occurs when the kneecap moves out of its usual spot. Signs and symptoms include:
- Pain and tenderness around the kneecap
- Visible deformity or abnormal positioning of the kneecap
- Inability to straighten the knee
- Instability or feeling of the knee giving way
Complete Knee Dislocation as a Medical Emergency
A complete knee dislocation is a serious injury. It happens when the shinbone is completely out of place from the thigh bone. This is a medical emergency because it can harm nerves and blood vessels. Immediate symptoms include:
- Severe pain and swelling
- Deformity and instability
- Numbness or tingling due to nerve damage
- Coldness or paleness of the foot due to compromised blood flow
Neurovascular Complications of Dislocations
Neurovascular complications are a big worry with joint dislocations, like knee dislocations. The popliteal artery can be injured, which can cause serious problems. Key neurovascular complications include:
- Arterial injury leading to limb ischemia
- Nerve damage causing sensory or motor deficits
- Compartment syndrome due to swelling and increased pressure within the limb compartments
It’s very important to treat these problems quickly. This helps avoid long-term damage and helps the limb work better again.
Fractures and Serious Structural Damage
Timely medical intervention is crucial for avoiding long-term damage and ensuring effective healing.
Patella, Tibia, and Femur Fracture Symptoms
Fractures in the patella, tibia, or femur show up differently. Common signs include:
- Severe pain that gets worse with movement
- Swelling and bruising around the knee
- Can’t straighten or bear weight on the leg
- Visible deformity or abnormal alignment
Instability or a feeling that the knee is going to give way
Seek medical help right away if you notice these symptoms. Quick action can greatly improve recovery chances.
Stress Fractures vs. Acute Breaks
It’s important to tell stress fractures from acute breaks. Stress fractures are small cracks from too much stress or overuse, common in athletes. Acute breaks are more serious, caused by a single event.
Both need a doctor’s check-up, but treatment can differ. Stress fractures might just need rest and rehab. Acute breaks might need surgery to fix the bone.
Growth Plate Injuries in Pediatric Patients
Knee injuries in kids can affect growth plates. These are cartilage areas that help bones grow. Damage here can affect bone growth long-term.
Symptoms include pain, swelling, and trouble moving. Getting a diagnosis and treatment early is vital. It helps avoid growth problems or deformity. Treatment is based on the child’s age and injury severity.
Ligament and Tendon Tears Requiring Urgent Care
When ligaments or tendons in the knee are torn, it’s vital to get medical help fast. This is to avoid more damage. Tears in these areas can really hurt your knee’s function and how well you can move.
Complete ACL Tear Emergency Indicators
A complete tear of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) is a serious injury. It often needs urgent care. Signs of a complete ACL tear include:
- A loud “pop” or snap at the time of injury
- Severe pain and inability to continue the activity
- Instability or feeling of the knee “giving way”
- Swelling within a few hours after injury
Multiple Ligament Injuries and Knee Stability
Multiple ligament injuries can make the knee unstable. This is due to severe trauma. It may also affect other areas around the knee.
Key consequences include:
- Increased risk of further injury due to knee instability
- Difficulty in diagnosing and treating individual ligament injuries
- Potential for long-term knee dysfunction if not properly addressed
Quadriceps and Patellar Tendon Ruptures
Quadriceps and patellar tendon ruptures are serious injuries. They can greatly affect knee function. A rupture happens when the tendon is completely torn, often needing surgery.
Symptoms include:
- Suddenly, severe pain in the front of the knee
- Inability to straighten the knee or bear weight
- A gap or indentation above or below the kneecap
- Bruising and swelling around the knee
Infection and Inflammatory Emergencies
It’s important to know the signs of knee infection and inflammatory emergencies. These can turn serious fast if not treated right away.
Septic Arthritis Warning Signs
Septic arthritis is very dangerous and needs quick medical help. Look out for these signs:
- Severe knee pain and swelling
- Redness and warmth around the knee
- Fever and chills
- Limited range of motion
- General feeling of illness
If you see these symptoms, get medical help fast. Septic arthritis can cause permanent damage if not treated in 24 to 48 hours.
Post-Surgical Infection Red Flags
After knee surgery, some pain and swelling are okay. But watch out for these signs of infection:
- Increasing pain or swelling
- Redness or warmth around the surgical site
- Pus or discharge from the wound
- Fever or chills
- A general feeling of being unwell
Spotting these signs early is key to managing the infection and avoiding serious problems.
Prosthetic Joint Infection Emergencies
People with prosthetic knee joints face a big risk of infection. Look out for these signs:
- Persistent pain or stiffness
- Swelling or redness around the prosthetic joint
- Fever or chills
- Instability or looseness of the prosthetic
Prosthetic joint infections need urgent medical care and might need surgery to fix.
Vascular Complications: Blood Clots and Circulation Issues
Vascular problems linked to knee pain can be deadly and need quick medical help. These issues include blood clots and circulation problems. They can come from or get worse because of knee injuries or conditions.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Symptoms
Deep Vein Thrombosis is when a blood clot forms in deep veins, often in the legs. Signs of DVT include swelling, pain, or tenderness in the leg. The skin may also be warm or red.
It’s key to spot these signs early. DVT can turn deadly if the clot moves to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
Key symptoms to watch for:
- Swelling in one leg (rarely both)
- Pain or tenderness not caused by an injury
- Red or discolored skin on the leg
- A feeling of warmth in the affected leg
Compartment Syndrome as a Surgical Emergency
Compartment syndrome is a serious issue. It happens when muscle compartment pressure gets too high. This can occur after a severe injury or fracture around the knee.
Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, and tightness in the affected limb. Sometimes, there’s numbness or weakness. It’s a surgical emergency that needs quick action to avoid permanent damage.
“Compartment syndrome is a true orthopedic emergency. Prompt recognition and treatment are critical to avoid long-term problems.” – Orthopedic Specialist
Popliteal Artery Occlusion Signs
The popliteal artery runs through the knee. If it gets blocked, it can cut off blood flow to the lower leg. Signs include severe pain, pale skin, and numbness or tingling.
It’s vital to get medical help right away. This is to restore blood flow and prevent tissue death.
| Condition | Symptoms | Urgency |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | Swelling, pain, warmth, redness | High |
| Compartment Syndrome | Severe pain, swelling, tightness, numbness | Critical (Surgical Emergency) |
| Popliteal Artery Occlusion | Severe pain, pallor, pulselessness, poikilothermia, paresthesias, paralysis | Critical (Immediate Attention) |
We stress the need to spot these vascular problems early. Quick diagnosis and treatment can greatly improve outcomes and prevent serious issues.
Systemic Conditions Presenting as Knee Emergencies
Certain systemic conditions can show up as sudden knee problems. These need quick medical help to avoid lasting damage.
Severe Gout and Pseudogout Attacks
Gout and pseudogout cause sudden, severe pain and swelling in the knee. Severe gout attacks can be caused by diet, genetics, and health issues. Pseudogout, or calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD), is similar but caused by calcium crystals.
During an attack, the knee may turn red, warm, swollen, and very painful. It’s hard to move. Doctors often need to take out the joint fluid to diagnose and treat these conditions.
| Condition | Common Triggers | Diagnostic Method | Treatment Approach |
| Gout | Diet, Genetics, Kidney Disease | Joint Fluid Analysis | NSAIDs, Colchicine, Steroids |
| Pseudogout | Trauma, Surgery, Metabolic Disorders | Joint Fluid Analysis, Imaging | NSAIDs, Steroids, Joint Aspiration |
Rheumatoid and Autoimmune Crisis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other autoimmune diseases can cause knee emergencies. RA is a chronic inflammatory disorder that affects more than just the knees, causing pain, stiffness, and swelling.
An autoimmune crisis in the knee may show severe inflammation, instability, or even infection. It’s important to quickly figure out if it’s a flare-up or something more serious.
- Recognizing the signs of a rheumatoid flare-up
- Understanding the risk of infections in immunocompromised patients
- Managing pain and inflammation effectively
Malignancy-Related Emergencies
Knee pain can sometimes be due to cancer, either in the bone or soft tissues. Bone tumors or soft tissue sarcomas can cause knee pain or swelling.
Malignancy-related emergencies can include pathological fractures, spinal cord compression, or hypercalcemia. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to better outcomes.
It’s important to understand how systemic conditions can lead to knee emergencies. Recognizing the signs early helps healthcare providers act fast. This can prevent complications and improve patient care.
Special Populations and Risk Factors
Knee pain emergencies need different approaches for different people. Kids and the elderly have special needs. We must tailor care to meet these needs.
Pediatric Knee Emergency Considerations
When kids have knee pain, we must think about their age and growth. Pediatric patients need careful checks to distinguish normal growth from emergencies. Their bones are growing, so they need a special way of being treated.
Elderly Patients and Fall-Related Emergencies
Older people are more likely to have emergencies from falls. Fall prevention is key for them. They might also get serious injuries like fractures that need quick doctor visits.
High-Risk Groups for Complications
Some groups face more risks from knee problems. This includes people with diabetes, vascular disease, and those on blood thinners. Spotting these risks early helps manage their care better. It’s important to know these risks to help them the most.
| Risk Group | Characteristics | Potential Complications |
| Pediatric Patients | Developing bones, growth plates | Growth disturbances, fractures |
| Elderly Patients | Osteoporosis, decreased mobility, and comorbidities | Increased risk of fractures, falls, and slow healing |
| Patients with Diabetes | Neuropathy, vascular disease | Wound healing issues, infections |
Emergency Department Evaluation and Procedures
Visiting the emergency department for knee pain can be stressful. Knowing what to expect can help. We aim to provide a thorough and caring evaluation to find out why you’re in pain.
What to Expect During Assessment
When you arrive, our triage team will quickly check your condition. They will ask about your medical history, including when your pain started and how long it’s lasted. They will also do a physical exam to look for swelling or other signs of injury.
They might check how well you can move your knee and how much weight you can put on it. We know this can be uncomfortable. We’ll try to make you as comfortable as we can.
Common Diagnostic Tests for Knee Emergencies
To find out what’s causing your pain, we might use several tests. These include:
- X-rays to look for breaks or misalignments.
- Ultrasound to check for soft tissue damage or fluid in the knee.
- CT scans for detailed views of the knee, useful for complex injuries.
- MRI to see injuries to ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
- Blood tests to check for infections or inflammation.
These tests help us understand your knee condition. They guide us to the best treatment for you.
Initial Treatment Approaches
After we figure out what’s wrong, we’ll talk about your treatment options. This might include pain meds and rest, or more urgent steps like draining an infected joint.
If surgery isn’t needed right away, we’ll plan for your ongoing care. This might include follow-up visits, physical therapy, or more tests. We aim to give you the best care for your condition, helping you recover quickly.
We’re here to explain things clearly, offer caring support, and address your concerns. Our team is committed to providing top-notch treatment for your knee pain.
At-Home Management While Awaiting Medical Care
Managing knee pain at home before seeing a doctor involves a few steps. First, you need to apply first aid, position correctly, and manage pain. These steps can’t replace a doctor’s care but can help ease symptoms and prevent more harm.
Appropriate First Aid Measures
The RICE principle (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) is a good first aid for knee injuries. Rest the knee to avoid more strain. Use ice to lessen pain and swelling. Apply compression bandages to the knee and keep it elevated above heart level.
Positioning and Immobilization Techniques
Proper positioning and immobilization can greatly reduce discomfort. Keeping the knee straight or slightly bent can help with pain, depending on the injury. Using a knee brace or splint can also prevent further injury. This is helpful for suspected fractures or severe ligament sprains.
Pain Management Strategies
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help with knee pain. But, it’s important to follow the dosage and talk to a healthcare provider before taking any medication. This is even more important if you have other health conditions or are taking other medications.
Conclusion
Knowing when knee pain is an emergency is key to avoiding long-term damage. This article has covered when knee pain needs immediate care. This includes sudden severe injuries and systemic conditions that affect the knee.
It’s important to recognize signs of a knee emergency. These include not being able to bear weight, visible deformities, or joint dislocations. We also talked about red flags like severe pain, swelling, or instability. These signs mean you need to see a doctor right away.
We’ve summarized the main points to stress the need for medical help with knee pain. Getting help quickly can greatly improve treatment results. It helps avoid complications and ensures a better recovery.
If you’re unsure about your knee pain, it’s safer to get medical help. Our discussion shows how important it is to be informed and proactive about knee health. This way, you can get the right care for any knee emergency.
FAQ
What are the emergency signs of knee pain that require immediate medical attention?
Look out for sudden severe pain and not being able to bear weight. Also, visible deformity, a lot of bruising, and joint dislocation are red flags. Fractures, ligament and tendon tears, and signs of infection like redness and swelling are urgent. So are vascular issues like deep vein thrombosis.
How can I differentiate between minor and serious knee pain?
Serious pain starts suddenly and is very intense. It’s often accompanied by swelling, redness, warmth, or fever. If you can’t put weight on it or see a deformity, it’s serious.
What are the common causes of non-emergency knee pain?
Overuse injuries, minor sprains, osteoarthritis, bursitis, and tendinitis are common. These can be treated with rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Over-the-counter pain meds can also help.
When should I seek immediate care for a knee injury?
Get help right away for traumatic injuries, severe pain, or if you can’t bear weight. Also, if you see a deformity, signs of infection, or vascular problems.
How is a knee injury assessed in the emergency department?
Doctors will do a physical exam and might use X-rays or an MRI. Blood tests may also be done to check for infection or inflammation.
What are the signs of a prosthetic joint infection?
Look for increasing pain, redness, swelling, warmth around the joint, fever, and sometimes drainage or loosening of the prosthetic.
Can knee pain be a sign of a systemic condition?
Yes, it can be linked to severe gout, pseudogout, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune diseases, or malignancies.
How do I manage knee pain at home while awaiting medical care?
Use rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE). Over-the-counter pain relievers can help. Immobilizing the knee can also reduce pain and swelling.
Are there specific considerations for pediatric knee emergencies?
Yes, kids need special care, like avoiding growth plate injuries. Any trauma or sudden pain in children should be checked quickly.
What are the risks associated with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the leg?
DVT can cause serious problems, like pulmonary embolism, which is deadly. Symptoms include leg pain, swelling, redness, and warmth.
How can I prevent knee injuries during sports or physical activities?
Prevent injuries with proper warm-up and cool-down, using protective gear, staying in shape, and safe techniques.
What are the emergency signs of a ligament or tendon tear in the knee?
Watch for a sudden “pop” or snap, severe pain, instability, and trouble straightening or bearing weight on the knee.
When is knee pain considered a medical emergency in elderly patients?
In older adults, knee pain is urgent if it’s after a fall, very severe, or if you can’t bear weight. Also, signs of infection are serious.
References
- Gompels, B. (2024). Just the facts: Assessing and managing soft tissue knee injuries. Emergency Medicine Practice, 26(8), 1-10. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11557647/



































