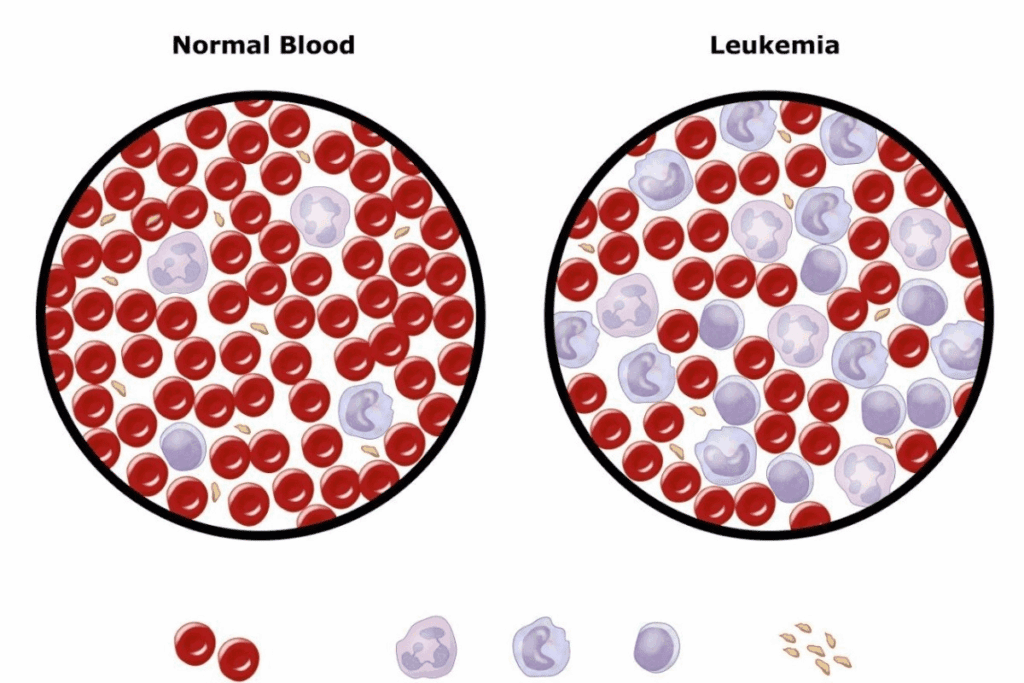
Leukemia spots appearance is a blood cancer that affects the bone marrow. Early detection is key for a good treatment. The American Cancer Society says leukemia is a common cancer in the U.S.
Spotting leukemia early is important. Signs include feeling very tired, losing weight, and getting sick often. Knowing these signs can help get a leukemia diagnosis and start the right leukemia treatment.
Key Takeaways
- Early detection of leukemia is vital for effective treatment.
- Common leukemia symptoms include fatigue and weight loss.
- Understanding leukemia causes can help in prevention.
- There are different leukemia types, each needing specific treatment.
- Timely leukemia diagnosis leads to better treatment outcomes.
Understanding Leukemia: A Blood Cancer Overview

Leukemia is a blood cancer that affects millions globally. It’s important to know about its types and effects. This cancer makes white blood cells grow abnormally, which is key for fighting off infections.
This abnormal growth can lead to health problems. It happens because cancer cells take over the bone marrow, leaving less room for healthy cells.
What Happens in the Body During Leukemia
In leukemia, the bone marrow makes bad white blood cells. These cells don’t work right and build up in the bone marrow. This blocks the production of normal blood cells.
People with leukemia might feel tired, get sick easily, and have bleeding problems. This is because they don’t have enough healthy blood cells.
Common Types of Leukemia
Leukemia comes in several types, like Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL), and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). Each type is different and affects people in various ways.
For example, AML is more common in adults and grows fast. CLL, on the other hand, is seen in older adults and grows slowly.
Early Warning Signs of Leukemia

It’s important to know the early signs of leukemia for early treatment. Leukemia is a blood and bone marrow cancer. Its symptoms can look like other illnesses, so staying alert to health issues is key.
Systemic Symptoms
Systemic symptoms affect the whole body. In leukemia, you might feel fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections. Feeling extremely tired is common because leukemia cells take over, reducing oxygen to tissues.
Weight loss happens because the body’s metabolism speeds up to fight the disease. Frequent infections occur because leukemia reduces normal white blood cells, which fight off infections.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you have symptoms like fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or recurring infections, see a doctor. Also, watch for easy bruising, pale skin, and swollen lymph nodes.
A doctor will do tests like blood tests and bone marrow biopsies to find the cause. Early diagnosis is vital for effective treatment. A medical expert says,
“Early detection and treatment of leukemia can significantly improve patient outcomes.”
Leukemia Spots Appearance: Skin Manifestations Explained
Leukemia can show itself through skin signs like petechiae and bruising. It affects blood cells and platelets, leading to skin changes. Knowing these signs is key for early detection.
Petechiae: Tiny Red or Purple Spots
Petechiae are small, red or purple spots on the skin. They happen when blood vessels break and bleed a bit. In leukemia, they show up because of low platelet counts.
“Petechiae are a hallmark sign of bleeding disorders, including leukemia.” They look like small dots and are flat. They can be found on legs, arms, and buttocks.
Bruising and Ecchymosis
Bruising and ecchymosis are also signs of leukemia. Bruising happens when bigger blood vessels get damaged. Ecchymosis are bigger patches of bruising on the body.
In leukemia, even small bumps can cause bruising. It’s important to see a doctor if you get bruises or petechiae without reason.
Distinguishing Leukemia Spots from Other Skin Conditions
It’s important to tell leukemia spots from other skin issues. Petechiae and bruising can mean different things. A doctor needs to check and test to find out why.
“Accurate diagnosis requires a thorough check-up, including blood tests and bone marrow exams.”
Doctors can make better choices with knowledge of leukemia spots. This helps in deciding what tests and treatments are needed.
Why Skin Changes Occur in Leukemia
Leukemia can cause many skin changes. These changes happen because leukemia affects the body’s blood cells and skin.
Low Platelet Counts and Bleeding
Low platelet counts, or thrombocytopenia, are a big reason for skin changes in leukemia. Platelets help blood clot. Without enough, bleeding under the skin can happen, leading to:
- Petechiae: small, pinpoint spots that are red or purple
- Ecchymosis: larger areas of bruising
- Purpura: purple patches on the skin
These symptoms happen because the body can’t stop bleeding without enough platelets. Low platelet counts are a common complication in leukemia patients, making them more prone to bruising and bleeding.
Leukemia Cells in the Skin
Leukemia cells in the skin also cause changes. This is known as leukemia cutis. It can show up as:
- Skin lesions or nodules
- Rashes or plaques
- Red or purple discoloration
Leukemia cells in the skin can cause a variety of lesions, which may be tender or painful. The look of these changes can differ based on the type of leukemia.
It’s key to understand why skin changes happen in leukemia. Spotting these symptoms early can help get the right treatment sooner.
Specific Skin Symptoms by Leukemia Type
Different types of leukemia show unique skin signs that help doctors diagnose them. It’s important for both patients and doctors to know these signs. This helps in recognizing the symptoms of various leukemia types.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Skin Manifestations
AML often shows specific skin symptoms. These include chloromas, greenish tumors from leukemia cells. Patients might also see petechiae, small spots from bleeding under the skin, and ecchymosis, bigger bruises.
In some cases, AML can lead to leukemia cutis. This is when leukemia cells invade the skin, causing lesions or nodules.
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Skin Symptoms
CLL can also show skin symptoms, but they are less common than in AML. CLL patients might get pruritic skin lesions or feel itchy all over. They could also get herpes zoster infections, which are more serious because CLL weakens the immune system.
Skin Changes in Other Leukemia Types
Other leukemia types, like Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), also have skin symptoms. ALL can cause leukemia cutis, just like AML. CML might show neutrophilic dermatosis, with skin lesions and inflammation.
In conclusion, the skin symptoms of leukemia vary by type. Knowing these symptoms is key for early diagnosis and treatment.
Other Physical Signs of Leukemia
Leukemia can show many physical signs, important for catching it early. These signs change based on the leukemia type and how it grows. Knowing these signs helps get medical help fast.
Pallor and Fatigue
Pallor, or paleness, is common in leukemia patients. It happens because of fewer red blood cells, causing anemia. Fatigue also occurs, making it hard for the body to carry oxygen. These symptoms can really affect a person’s life, making simple tasks hard.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes are a sign of leukemia too. They get big because leukemia cells build up there. Seeing swollen lymph nodes means the disease might be getting worse. If swelling doesn’t go away, see a doctor.
Bone and Joint Pain
Leukemia patients often feel pain in bones and joints. This pain comes from leukemia cells in the bone marrow or joints. The pain can be different for everyone, and might come with other symptoms like fatigue and pallor. Spotting these signs early can help get the right treatment.
In short, knowing about these signs can help find and treat leukemia early. If you or someone you know has these symptoms, getting medical help is key.
Childhood vs. Adult Leukemia: Differences in Presentation
It’s important to know how leukemia shows up in kids versus grown-ups. This cancer affects the blood and bone marrow differently in each age group. This is because of many factors like biology, environment, and genes.
Unique Symptoms in Children
Kids with leukemia have symptoms that are not the same as adults. Some common signs include:
- Petechiae: Small spots on the skin from low platelet counts.
- Bone pain: Pain in the bones from leukemia cells.
- Fatigue: Feeling very tired or unwell.
- Swollen lymph nodes: Big lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
Children might also have childhood leukemia skin rashes. These rashes can show the disease is affecting the skin.
How Adults Typically Present
Adults with leukemia often have symptoms that are not as clear-cut as in kids. Some common signs are:
- Fatigue: Feeling very tired or weak.
- Weight loss: Losing weight without trying.
- Recurring infections: Getting sick a lot because of a weak immune system.
- Bleeding or bruising easily: Bleeding or bruising a lot because of low platelet counts.
Adults might also have adult leukemia symptoms like night sweats, fever, or swollen lymph nodes. These can sometimes be confused with other illnesses.
In summary, it’s key to know how leukemia shows up in kids and adults. This helps doctors diagnose and treat it correctly and quickly.
The Diagnostic Journey: From Symptoms to Diagnosis
Diagnosing leukemia is a detailed process. It starts with a doctor’s visit and ends with a diagnosis. Doctors use medical tests to find cancer cells in the blood or bone marrow.
Initial Doctor’s Visit and Physical Examination
The first step is a detailed medical history and physical check-up. Doctors look for signs like swollen lymph nodes, an enlarged spleen or liver, and pallor. They also ask about symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, and frequent infections.
A physical exam is key. It helps find any signs that might point to leukemia. For example, small red or purple spots on the skin could mean a low platelet count, common in leukemia patients.
Blood Tests and What They Reveal
Blood tests are vital in diagnosing leukemia. A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is often the first test. It shows the levels of red and white blood cells and platelets. If these levels are off, it could mean leukemia.
More tests, like flow cytometry, might follow. They help figure out if the white blood cells are cancerous.
- A CBC test can reveal abnormal levels of blood cells.
- Blood smear tests can help identify abnormal cells.
- Flow cytometry can characterize the specific type of leukemia cells.
Bone Marrow Biopsy Procedure
A bone marrow biopsy is the key test for leukemia. It takes a sample from the hipbone and checks for cancer cells. This test shows the type and severity of leukemia.
This biopsy is essential for knowing how far the disease has spread. It helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques for Leukemia
Modern ways of finding and understanding leukemia are changing fast. These new methods make diagnosing leukemia more accurate and quicker. This lets doctors create treatment plans that really fit each patient’s needs.
Cytogenetic Testing
Cytogenetic testing looks at leukemia cells’ chromosomes for genetic issues. This info is key for knowing how the leukemia might behave and what treatment to choose. Chromosomal abnormalities show how aggressive the leukemia could be.
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry is a detailed lab method for checking cell characteristics. It helps figure out the leukemia type by looking at cell surface proteins. This is important for telling apart acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Molecular Testing
Molecular testing looks at leukemia cells’ genes for specific changes. Tools like polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and next-generation sequencing (NGS) find these genetic changes. They help decide on the best treatment.
| Diagnostic Technique | Purpose | Key Benefits |
| Cytogenetic Testing | Analyzes chromosomal abnormalities | Provides prognostic information, guides treatment |
| Flow Cytometry | Identifies cell surface proteins | Distinguishes between leukemia types, aids diagnosis |
| Molecular Testing | Detects genetic mutations | Influences treatment decisions, personalized medicine |
Acute vs. Chronic Leukemia: Detection Differences
Acute and chronic leukemia differ in how fast they grow and how they affect the body. Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It’s divided into these two types based on how fast it grows and the type of cells involved.
Acute leukemia grows quickly and involves immature cells that can’t work right. This leads to severe symptoms that need quick medical help. Chronic leukemia grows slower and involves more mature cells. It starts with milder symptoms that might not seem like leukemia at first.
Rapid Onset of Acute Leukemia
Acute leukemia, like Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), shows up fast with severe symptoms. Symptoms include tiredness, frequent infections, and easy bruising or bleeding. Because it grows fast, it needs quick treatment to manage well.
The American Cancer Society says, “Acute leukemia needs quick treatment because it grows fast and aggressively.” Finding and starting treatment early is key to better survival chances for those with acute leukemia.
Gradual Development of Chronic Leukemia
Chronic leukemia, like Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML), grows slowly. In the early stages, it might not show symptoms, making it hard to find just by symptoms. Regular blood tests are important to catch chronic leukemia early.
“Chronic leukemia can often be managed with watchful waiting initially, but treatment becomes necessary as the disease progresses.”
– National Cancer Institute
Chronic leukemia’s slow growth means there are many treatment options. These range from just watching it to targeted therapies, based on the disease’s stage and the patient’s health.
Knowing the difference between acute and chronic leukemia is key for both patients and doctors. It helps in finding and treating the disease in the best way possible, leading to better outcomes for patients.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Knowing the risk factors for leukemia helps in taking steps to prevent it. Some risks can’t be changed, but understanding them helps make better health choices.
Known Risk Factors for Leukemia
Several things can raise your chance of getting leukemia. These include genetic traits, exposure to chemicals like benzene, and radiation. Also, having had chemotherapy or radiation for other cancers increases your risk. Some genetic disorders, like Down syndrome, make you more likely to get leukemia.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Genetic Predispositions | Inherited genetic mutations that increase leukemia risk |
| Chemical Exposure | Exposure to chemicals like benzene |
| Radiation Exposure | High levels of ionizing radiation |
Preventive Measures and Limitations
While not all leukemia cases can be prevented, avoiding certain risks can help. Stay away from benzene and other harmful chemicals. Also, try to limit your exposure to radiation. If you have a family history of leukemia or known genetic risks, getting genetic counseling is a good idea.
Prevention is key, and understanding the risk factors for leukemia is the first step towards reducing the incidence of this disease.
It’s important to remember that many leukemia cases don’t have known risk factors. This shows how complex the disease is. Researchers are working hard to learn more about leukemia’s causes and how to prevent or catch it early.
Treatment Approaches After Diagnosis
Knowing the type and stage of leukemia is key to finding the right treatment. Each plan is made just for the person, taking into account their health and needs.
Standard Treatment Options
Leukemia treatments often include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and sometimes bone marrow transplantation. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Targeted therapy aims at specific cancer cell flaws, helping to protect normal cells.
| Treatment Type | Description | Benefits |
| Chemotherapy | Uses drugs to kill leukemia cells | Effective in treating various types of leukemia |
| Targeted Therapy | Targets specific abnormalities in cancer cells | Reduces harm to normal cells |
| Bone Marrow Transplantation | Replaces diseased bone marrow with healthy marrow | Can potentially cure leukemia |
Emerging Therapies
New treatments are giving hope to leukemia patients. CAR-T cell therapy is a leading option. It changes a patient’s T cells to fight leukemia. Other new treatments include immunotherapy and new targeted therapies.
These new treatments are being tested in clinical trials. They show great promise in helping leukemia patients.
When to Seek Emergency Care
Knowing when to seek immediate medical help is key for leukemia patients. They must watch their health closely. They need to know when a situation is life-threatening.
Serious Complications Requiring Immediate Attention
Certain complications can arise suddenly in leukemia patients, needing emergency care. These include:
- Severe bleeding: If you experience heavy bleeding that doesn’t stop, it’s vital to seek immediate help.
- High fever: A fever above 101.5°F (38.6°C) that persists or is accompanied by other symptoms like chills or sweating.
- Shortness of breath: Difficulty breathing or feeling like you’re not getting enough air.
- Severe pain: Sudden, severe pain, specially if it’s localized to a specific area like the abdomen or bones.
Communicating Effectively with Healthcare Providers
Effective communication with your healthcare team is vital, specially when seeking emergency care. Here are some tips:
- Be prepared: Carry a list of your medications, allergies, and contact information for your healthcare providers.
- Be clear: Explain your symptoms in detail, including when they started and any factors that make them better or worse.
- Ask questions: Don’t hesitate to ask about your treatment or any concerns you have.
By being aware of serious complications and communicating well with healthcare providers, leukemia patients can get the timely care they need.
Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of leukemia greatly improves treatment chances. It’s important for people to know the signs and symptoms. This knowledge helps catch the disease early, leading to better medical care.
Leukemia support groups are also key. They help patients and their families deal with the disease’s challenges. These groups offer a place to share experiences, get emotional support, and find helpful resources.
By raising awareness and pushing for early detection, we can help more people survive leukemia. Staying informed and proactive about health is a big step in fighting this disease.
FAQ
What are the early warning signs of leukemia?
Early signs of leukemia include feeling very tired and losing weight. You might also get sick a lot or bruise easily. Other signs are pale skin, swollen lymph nodes, and pain in bones or joints.
What are leukemia spots, and how do they appear?
Leukemia spots, or petechiae, are small, red or purple marks on the skin. They happen when small blood vessels bleed. These spots can show up anywhere on your body and might be accompanied by bruising.
How is leukemia diagnosed?
Doctors use a physical exam, blood tests, and a bone marrow biopsy to diagnose leukemia. Blood tests show abnormal white blood cell counts. A bone marrow biopsy confirms leukemia cells.
What are the different types of leukemia, and how do they affect the body?
There are several types of leukemia, like AML, CML, ALL, and CLL. Each type affects the body differently. Symptoms and treatment options vary by type.
Can leukemia be prevented?
While you can’t prevent leukemia for sure, some risks can be lowered. Avoiding radiation and harmful chemicals helps. Eating well and exercising regularly may also reduce your risk.
What are the treatment options for leukemia?
Treatments for leukemia include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, radiation, and bone marrow transplants. The right treatment depends on the leukemia type, stage, and your health.
How does leukemia affect children differently than adults?
Leukemia in children can be more severe, with symptoms like bone pain and fatigue. Children might need more aggressive treatments.
What are the advanced diagnostic techniques used in leukemia diagnosis?
Advanced tests for leukemia include cytogenetic testing, flow cytometry, and molecular testing. These tests find specific genetic mutations, helping guide treatment.
When should I seek emergency care for leukemia?
Go to the emergency room for serious issues like severe bleeding, trouble breathing, or intense pain. It’s key to talk openly with your doctor about your symptoms and worries.
Are there any support groups or resources available for leukemia patients and families?
Yes, many support groups and resources exist for leukemia patients and families. You can find online forums, local groups, and organizations focused on leukemia research and awareness.
Reference
National Cancer Institute (NCI) – Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treatment:https://www.cancer.gov/types/leukemia/patient/child-all-treatment-pdq



































