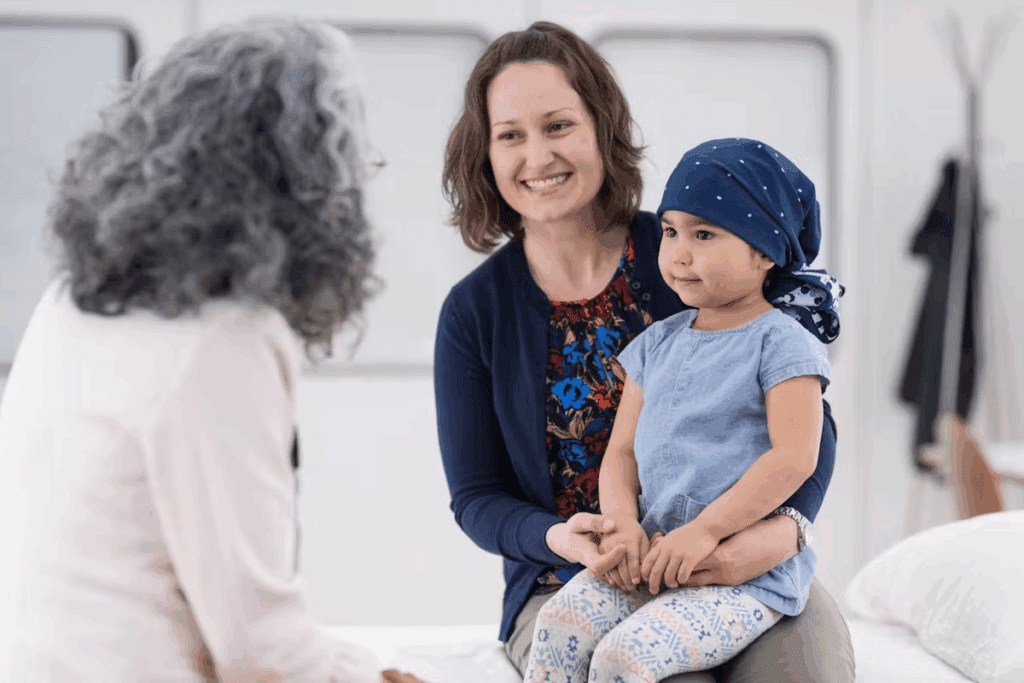
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, and it’s the most common cancer in children and teens. Explaining the significance of Petechiae and leukemia and when this symptom is a medical emergency.
Despite its prevalence among childhood cancers, leukemia remains a rare disease overall.
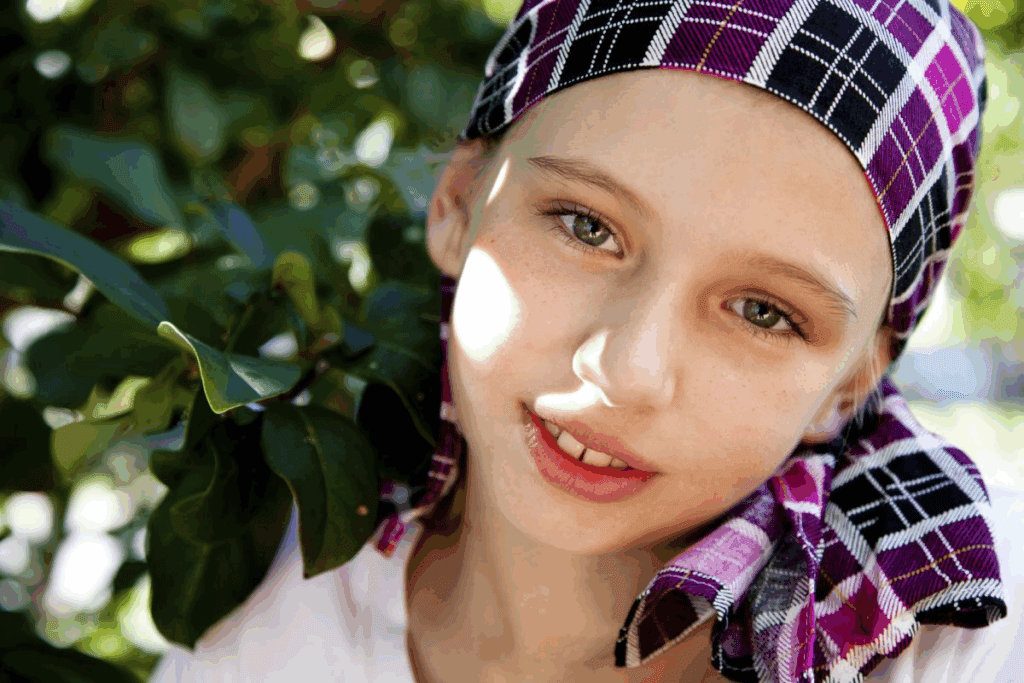
Petechiae, small spots on the skin, can be a sign of leukemia. They happen when small blood vessels bleed.
Key Takeaways
- Leukemia is the most common cancer in children.
- Petechiae can be a symptom of leukemia.
- Childhood leukemia is a rare disease overall.
- Understanding the signs and symptoms of leukemia is important.
- Early detection is key to effective treatment.
Childhood Leukemia: Prevalence and Basic Understanding

It’s important to know about childhood leukemia to catch it early and treat it well. Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It happens when there’s too many white blood cells.
In kids, leukemia is split into types based on the cell type and how fast it grows.
How Common is Leukemia in Children?
Leukemia is the top cancer in kids, making up 30% of all childhood cancers. Most kids and teens get acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), which is 3 in 4 cases. The rest are acute myeloid leukemia (AML).
ALL affects approximately 3 to 4 children per 100,000 each year. AML is rarer, affecting 1 in a million kids.
Leukemia is more common in kids aged 2 to 5 for ALL. Knowing this helps parents and doctors watch for signs.
Risk Factors and Possible Causes
We don’t know all about leukemia causes in kids. But some risks are known. Kids with Down syndrome are at higher risk. So are those exposed to lots of radiation or certain chemicals.
| Risk Factor | Description |
| Genetic Conditions | Conditions like Down syndrome increase leukemia risk. |
| Radiation Exposure | High levels of radiation exposure can increase risk. |
| Chemical Exposure | Exposure to certain chemicals may elevate leukemia risk. |
Scientists are working to understand how genes and the environment mix to cause leukemia. Knowing these risks helps find leukemia early and might prevent it in kids.
Petechiae and Leukemia: The Critical Connection
Petechiae, small red spots on the skin, can signal leukemia in children. These spots are linked to a low platelet count, known as thrombocytopenia.
What Are Petechiae and How Do They Appear?
Petechiae are tiny, pinpoint spots on the skin from broken blood vessels. They are red or purple and can look like a rash. Petechiae are not itchy or painful, but they can hint at a serious issue like leukemia.
The Mechanism: How Leukemia Causes Petechiae
Leukemia can lower platelet production, causing thrombocytopenia. With fewer platelets, blood can’t clot well, leading to petechiae. Leukemia cells can also invade the bone marrow, affecting blood cell production, including platelets.
Petechiae vs. Leukemia Bruising: Key Differences
Petechiae and bruising both relate to bleeding, but they look and cause different things. Petechiae are small, flat spots. Bruising, on the other hand, causes larger skin discolorations. Knowing these differences helps doctors diagnose the cause.
Where Petechiae Typically Appear in Leukemia Cases
In leukemia, petechiae often show up on the lower extremities, arms, and torso. They can also be seen on mucous membranes and inside the mouth. The spots’ location and density can suggest how severe the condition is.
Types of Childhood Leukemia
It’s important to know about the different types of leukemia in kids. This helps find and treat it early. Leukemia in children is divided into types based on the cells affected and how fast it grows.
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) is the most common leukemia in kids. It happens most often between 2 and 5 years old. ALL happens when the bone marrow makes too many immature lymphocytes, which are white blood cells.
Symptoms of ALL include feeling very tired, looking pale, and getting sick often. These signs make parents take their kids to the doctor. Treatment for ALL usually includes chemotherapy and sometimes a bone marrow transplant.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is less common in kids than in adults but is serious. AML affects the myeloid cells in the bone marrow. This leads to abnormal white blood cells that block normal blood cell production.
AML symptoms are similar to ALL and may include fever, losing weight, and bruising easily. Treatment for AML often includes strong chemotherapy and sometimes a bone marrow transplant.
Less Common Types of Childhood Leukemia
There are rarer types of leukemia in kids, like Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML). These are very rare in kids. It’s key for parents to know the signs, like petechiae, which are small spots on the skin that can mean bleeding disorders, including leukemia.
Early diagnosis and treatment can greatly help kids with these conditions.
Recognizing Warning Signs: Beyond Petechiae
Petechiae are a key sign of leukemia, but knowing other warning signs is also important. Leukemia symptoms can differ from child to child. It’s vital for parents and caregivers to be aware of these signs.
Petechiae as an Early Warning Sign of Leukemia
Petechiae are often one of the first signs of leukemia. They show up as small spots on the skin, like on the legs, arms, and torso. Spotting petechiae early can help parents get their child checked out sooner.
Other Physical Symptoms to Watch For
There are other signs that might mean a child has leukemia. These include:
- Pale skin due to anemia
- Fatigue or feeling weak
- Frequent infections due to a compromised immune system
- Easy bruising or bleeding
- Swollen lymph nodes, spleen, or liver
Knowing these symptoms can help spot leukemia early.
Behavioral and Systemic Changes
Leukemia can also show up in how a child acts and feels. This might include:
- Loss of appetite
- Weight loss
- Feeling cold
- Irritability or lethargy
These changes can be small, so it’s important to watch a child’s health closely.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Petechiae
Knowing when to see a doctor for petechiae is key. These small spots on the skin can show many health issues. It’s important to know when to go for a check-up to get the right treatment.
Emergency Symptoms Requiring Immediate Care
If your child has a fever over 100.4°F (38°C) and petechiae, get help right away. Also, watch for severe headache, trouble breathing, or confusion. These signs might mean a serious problem that needs quick doctor attention.
Differentiating Benign Petechiae from Concerning Cases
Not every petechiae case is serious. But, some signs can mean a bigger problem. For example, if there are many spots, or if you see bruising, fatigue, or pale skin, see a doctor. These could point to leukemia or other blood issues.
What Information to Provide Your Doctor
When you see your doctor for petechiae, bring lots of details. Tell them about the look and spread of the spots, any sickness or injuries, and other symptoms. This info helps your doctor diagnose and treat you faster.
Diagnosis Process for Childhood Leukemia
Diagnosing childhood leukemia involves several steps. Blood tests and physical exams are key to finding out if a child has leukemia. This helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Initial Blood Tests and Physical Examination
The first step is a complete blood count (CBC). It checks the blood for red and white blood cells and platelets. If the CBC shows something off, it might mean leukemia.
A physical exam also looks for signs like petechiae. These are small spots on the skin that could mean leukemia.
Bone Marrow Biopsy and Advanced Diagnostics
If tests suggest leukemia, a bone marrow biopsy is done. This test looks for cancer cells in the bone marrow. Other tests, like imaging and genetic analysis, help figure out the leukemia type and how serious it is.
The Role of Petechiae in Diagnosis
Petechiae can be a sign of leukemia. If a child has these spots and other symptoms like tiredness, weight loss, or often getting sick, they need to see a doctor. While petechiae can mean other things, they’re a clue to look into more.
It’s important for parents and caregivers to know about the diagnosis process. Spotting signs like chronic petechiae and leukemia early can help kids get the right treatment sooner. This can make a big difference in their health.
Treatment Approaches for Childhood Leukemia
Understanding childhood leukemia is key to treating it. This includes knowing about petechiae. Thanks to new treatments, more kids are surviving leukemia, like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL).
Standard Treatment Protocols
Chemotherapy is the main treatment for most childhood leukemia. It uses many drugs at different times. This helps fight leukemia while keeping side effects low.
For ALL, treatment has phases: induction, consolidation, and maintenance. Each phase attacks leukemia cells at different times.
Petechiae, small blood spots on the skin, are a worry during treatment. Petechiae vs leukemia bruising is important to know. Petechiae often mean low platelet count, common in leukemia patients.
Managing Petechiae and Thrombocytopenia During Treatment
It’s important to manage petechiae and low platelet count during treatment. This means checking platelet counts often and giving transfusions when needed. Also, avoiding activities that could cause bleeding is advised.
New and Emerging Therapies
New treatments are being tested for childhood leukemia. These include targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and CAR-T cell therapy. These have shown great promise, like in treating relapsed or refractory ALL.
Managing leukemia and petechiae appearance is a big part of treatment. It helps control the disease and lowers the risk of problems. As research gets better, the future for kids with leukemia looks brighter.
Living with Childhood Leukemia: Support and Coping
Living with childhood leukemia is tough for kids and their families. They need lots of support and ways to cope. Getting through the diagnosis and treatment is hard, so having good resources is key.
Resources for Families
There are many resources for families facing childhood leukemia. These include support groups, counseling, and educational materials. The Leukemia & Lymphoma Society is a big help, providing information and support.
Long-term Prognosis and Survival Rates
Thanks to new treatments, kids with leukemia have a better chance of survival. The survival rate depends on the type of leukemia and other factors. But overall, the outlook is much brighter than before.
Monitoring for Recurrence and Late Effects
After treatment, kids need regular check-ups to watch for any signs of leukemia coming back or late effects. These visits help doctors catch any problems early. This way, they can act fast to help.
Conclusion
Petechiae can be an early sign of leukemia in kids. It’s important for parents and caregivers to know about this. This way, they can spot symptoms early and get help fast.
Seeing tiny red spots or unexplained bruises is a big clue. These signs point to leukemia. It’s key not to overlook them and to watch for other changes too.
Leukemia is serious but treatable. With the right care, many kids get better. Being informed and watching closely helps families get their kids the help they need.
FAQ
What is leukemia and how does it affect children?
Leukemia is a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow. It can cause symptoms like petechiae, fatigue, and infections in kids. Knowing the signs is key for early treatment.
What are petechiae and how are they related to leukemia?
Petechiae are small spots on the skin from bleeding. They’re a common sign of leukemia in kids. You can find them on the skin, mucous membranes, and conjunctiva.
What are the different types of leukemia that affect children?
Kids can get Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) and Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). ALL is the most common, making up 80% of cases. AML is more aggressive and needs quick treatment.
What are the risk factors and possible causes of leukemia in children?
The exact causes of leukemia in kids are not known. But, genetic conditions like Down syndrome and environmental factors like radiation can increase risk. Family history and past radiation therapy also play a role.
How is leukemia diagnosed in children?
Doctors use blood tests, physical exams, and bone marrow biopsies to diagnose leukemia. Petechiae can hint at leukemia, leading to more tests for confirmation.
What are the treatment approaches for childhood leukemia?
Treatment for childhood leukemia includes chemotherapy, radiation, and supportive care. The treatment plan depends on the leukemia type, stage, and the child’s health.
How can petechiae be managed during leukemia treatment?
Managing petechiae involves checking platelet counts, avoiding injuries, and using medications. Sometimes, platelet transfusions are needed to prevent bleeding.
What are the long-term prognosis and survival rates for childhood leukemia?
Thanks to better treatments, the survival rate for kids with leukemia is around 90% after five years. But, it varies based on the leukemia type and stage.
What resources are available for families affected by childhood leukemia?
Families can find support through groups, forums, and counseling services. These resources offer emotional support, advice, and help with treatment challenges.
How can I differentiate between benign petechiae and those that may be indicative of leukemia?
Benign petechiae are small and scattered, without other symptoms. Leukemia-related petechiae are widespread, with symptoms like fatigue, fever, and bruising. They may signal a serious condition.
What information should I provide to my doctor if I’m concerned about petechiae or leukemia?
Share your medical history, symptoms, family history, and previous conditions with your doctor. Discuss your concerns and ask about diagnosis and treatment options.
References:
- American Cancer Society. (2023). Childhood leukemia risk factors. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/childhood-leukemia/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html
- Kaatsch, P. (2010). Epidemiology of childhood cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 36(4), 277-285. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20434220/




































