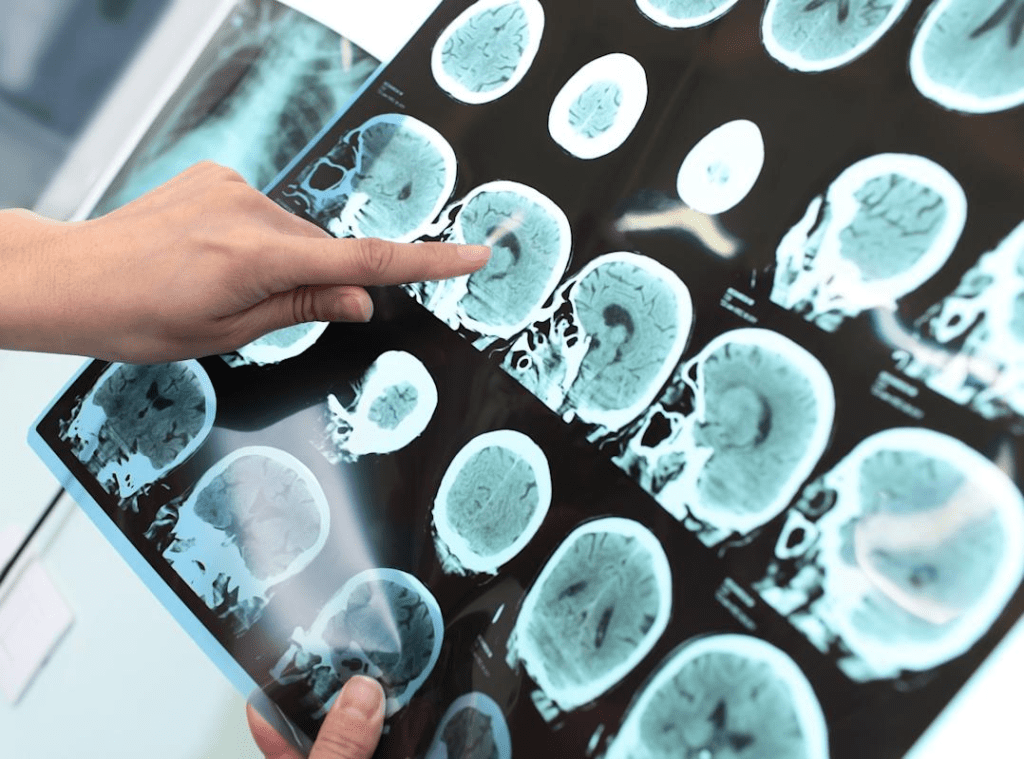
SPECT scans are key in medical imaging of nuclear medicine colors, showing us what’s inside our bodies. The colors on a SPECT scan mean a lot for diagnosing and treating health issues. Red on a SPECT scan shows where things are very active or have intense metabolic processes. Knowing what the spectral color meaning is helps doctors make the right calls.
This article will explain the importance of colors on SPECT scans. We’ll focus on what red means and how it helps in medical diagnosis.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the meaning of colors on a SPECT scan is key for accurate medical diagnoses.
- The color red on a SPECT scan can show areas of high metabolic activity.
- Nuclear medicine colors give us important insights into the body’s inner workings.
- Getting SPECT scan colors right is essential for good treatment plans.
- SPECT scans are a powerful tool in medical imaging.
The Fundamentals of SPECT Imaging
SPECT, or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography, is a way to see inside the body. It helps doctors understand how the body works. This is key in nuclear medicine for diagnosing and tracking diseases.
Definition and Basic Principles
SPECT uses a special dye that glows when it’s in certain parts of the body. This dye is injected into the patient. The SPECT scanner picks up the glow to make detailed 3D pictures of the body’s inside.
The core idea of SPECT is catching gamma rays from a special dye. This dye sticks to certain parts of the body. For example, it can attach to bones, helping doctors spot bone problems.
How SPECT Differs from Other Imaging Techniques
SPECT is different from MRI or CT scans. MRI and CT scans show what the body looks like. But SPECT shows how the body works. This is why SPECT is great for checking heart health or finding cancer.
| Imaging Modality | Primary Use | Information Provided |
| SPECT | Functional imaging, cancer detection, myocardial perfusion | Physiological processes, metabolic activity |
| MRI | Soft tissue imaging, neurological disorders | Anatomical detail, tissue characteristics |
| CT | Trauma, internal injuries, vascular diseases | Anatomical detail, structural information |
Knowing how SPECT works is important. It helps doctors understand the body’s functions. This knowledge helps them make better choices for patient care.
The Science Behind Nuclear Medicine Colors
Colors in nuclear medicine are key for making diagnoses. They show how much tracer activity is in the body. This isn’t just for looks; it’s based on science to help doctors make accurate diagnoses.
Color Mapping in Medical Imaging
In nuclear medicine, color mapping shows where and how much radiopharmaceuticals are in the body. Each color means a different level of tracer activity. The colors used can change based on the scan type and the doctor’s preference.
Doctors assign colors to the radiopharmaceutical signal levels. For example, high activity areas might show up as red or orange. Lower activity areas are shown in blue or green.
Why Colors Matter in Diagnostic Interpretation
Colors are vital for diagnostic interpretation. They make complex data easy to understand quickly. The color scale used can greatly affect how doctors read nuclear medicine images.
- Colors help spot abnormal tracer uptake, which can mean disease.
- Different color scales can show different data aspects, leading to a deeper understanding.
- Using the same color mapping helps compare scans and track disease changes or treatment effects.
In summary, the science of nuclear medicine colors is essential for reading diagnostic images right. Knowing how colors show tracer uptake levels helps doctors make better care decisions.
Understanding the SPECT Color Spectrum
In nuclear medicine, the SPECT color spectrum helps us see where radiopharmaceuticals go in the body. This is key for finding and treating health issues.
Colors in SPECT imaging make it easier for doctors to understand complex data. Each color shows how much of the radiopharmaceutical is present. This can tell us if something is normal or not.
Standard Color Scales Used in Nuclear Medicine
Nuclear medicine uses several color scales for SPECT data. Here are a few common ones:
- Rainbow Color Scale: This scale is easy to follow, going from blue (low uptake) to red (high uptake).
- Hot Metal Color Scale: It goes from black (low uptake) to red and yellow to white (high uptake), making it easy to see differences.
- Cool Color Scales: Some places like cooler colors because they are less jarring and offer a fresh view.
Each color scale has its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of scale can really affect how we understand SPECT images.
How Data is Translated into Visual Information
Turning raw SPECT data into pictures involves a few steps:
- Data Acquisition: The SPECT scanner takes in data on where the radiopharmaceutical is.
- Reconstruction: This data is then turned into a three-dimensional image.
- Color Mapping: The image is then colored based on the data, making it easier to see.
This colored image helps doctors spot important patterns and problems. It’s vital for making diagnoses and treatment plans.
The Significance of Red in SPECT Scans
In SPECT scans, the color red is very important. It shows where there’s a lot of tracer uptake. This color is key in nuclear medicine for spotting interesting or abnormal areas.
Colors in SPECT imaging, like red, show how much tracer is in different parts of the body. Red means high metabolic activity or a lot of tracer. This can mean different things, like health issues or diseases.
What Red Typically Represents
Red spots on a SPECT scan mean “hot spots” with more tracer. This can be because of inflammation, infection, or tumors. For example, in bone scans, red might show where bones are breaking down a lot, which could mean cancer or a fracture.
Quantitative Values Associated with Red Areas
The numbers behind red areas on SPECT scans come from how much tracer is there. These numbers help compare different parts of the scan. For instance, in heart scans, red might show where blood flow is good or better than usual.
| Color | Tracer Uptake Level | Typical Interpretation |
| Red | High | Increased metabolic activity or tracer accumulation |
| Yellow/Green | Moderate | Normal or slightly reduced activity |
| Blue | Low | Reduced tracer uptake, potentially indicating pathology |
A nuclear medicine expert says, “The color scale in SPECT scans is very important for understanding results. Red areas catch the eye and mean we need to look closer.”
“The interpretation of SPECT scans requires a thorough understanding of the color scale and its implications for patient diagnosis.”
” Nuclear Medicine Specialist
Knowing about red in SPECT scans is key for both doctors and patients. It helps in finding and treating many health problems, from heart issues to brain disorders.
Hot Spots vs. Cold Spots: The Temperature Analogy
The temperature analogy in nuclear medicine helps us understand hot and cold spots. These spots show where the tracer is most or least active. This is key in SPECT imaging, where we see how radiopharmaceuticals spread.
Defining “Hot” Areas in SPECT Imaging
In SPECT imaging, “hot” areas have a lot of tracer uptake. These areas show up as warm colors, like red or orange.
Comparing Red Zones to Other Color Indicators
Red zones on a SPECT scan mean high activity or blood flow. On the other hand, cold spots, shown in blue or green, have less tracer uptake. It’s important to compare these colors to make accurate diagnoses.
| Color Indicator | Tracer Uptake Level | Typical Representation |
| Red | High | Hot Spots |
| Blue/Green | Low | Cold Spots |
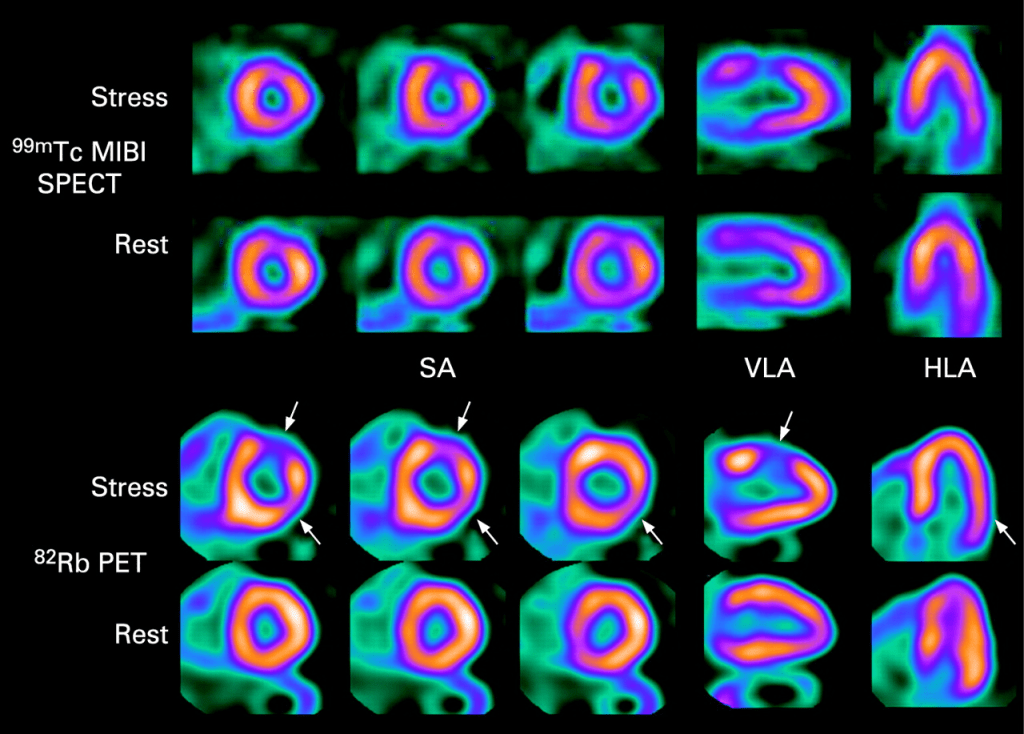
Red Areas in Cardiac SPECT Scans
Understanding red areas in cardiac SPECT scans is key to knowing about heart health. Cardiac SPECT scans help doctors see how well the heart works and find any problems. They are a vital tool for checking the heart’s function and finding any issues.
Myocardial Perfusion Imaging Interpretation
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) with SPECT is a common way to check for heart disease. Red areas on these scans mean good blood flow to the heart. But, it’s important to know how to read these images well and understand the patient’s situation.
Key factors in interpreting MPI include:
- Intensity of radiotracer uptake
- Distribution of the radiotracer across the myocardium
- Comparison with rest and stress images
Clinical Significance of Red in Heart Scans
Red areas in cardiac SPECT scans show good blood flow to the heart. But, low uptake areas (blue or black) might mean the heart is not getting enough blood or have scar tissue.
| Color Representation | Clinical Interpretation |
| Red | High radiotracer uptake, indicating good myocardial perfusion |
| Blue/Black | Low radiotracer uptake, potentially indicating ischemia or scar |
It’s important to understand the colors in cardiac SPECT scans to make accurate diagnoses. By correctly reading red areas, doctors can learn a lot about a patient’s heart health.
Brain SPECT Interpretation and Red Regions
SPECT imaging of the brain offers insights into cerebral blood flow. It helps diagnose and manage neurological disorders. The scan shows brain activity through colors, with red indicating high blood flow or metabolic activity.
Cerebral Blood Flow Assessment
Brain SPECT is key for checking brain tissue function. It spots areas with less or more blood flow, linked to neurological issues. Red areas on a brain SPECT scan usually show high cerebral blood flow.
This high blood flow can be normal or a sign of disease. Nuclear medicine colors in brain SPECT imaging show blood flow and metabolic activity. This color mapping is vital for diagnosis, helping doctors spot patterns of specific neurological disorders.
Neurological Conditions Associated with Red Areas
Red regions on brain SPECT scans can point to several neurological conditions. For example, high metabolic activity or inflammation shows up as red due to increased blood flow. Conditions like cerebrovascular disease, certain types of epilepsy, and inflammatory brain disorders can alter blood flow seen on SPECT images.
It’s important to understand the patient’s medical history and symptoms when looking at SPECT findings. Nuclear medicine physicians must consider all this information when interpreting red areas on brain SPECT scans.
By combining SPECT findings with clinical data, healthcare providers can make better decisions for patient care. This approach makes brain SPECT imaging more useful in neurological practice.
Bone Scan Uptake and Red Coloration
Understanding skeletal SPECT imaging is key for accurate diagnosis. Skeletal SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography) is a nuclear medicine technique. It gives detailed info about the skeletal system.
Skeletal SPECT Imaging Principles
Skeletal SPECT uses small amounts of radioactive tracers. These tracers, like technetium-99m labeled bisphosphonates, build up in bone. This shows bone metabolism and helps find skeletal pathologies.
This method is very good at spotting changes in bone activity. It can show fractures, infections, and tumors. The color scale shows how much tracer is there, with red meaning high uptake.
Pathological Conditions Indicated by Red Areas
Red areas on a bone scan mean increased bone activity. This can be from many conditions, including:
- Fractures: Acute fractures show high uptake as they heal.
- Bone Metastases: Cancer in the bone causes increased uptake.
- Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease increases bone activity around joints.
- Infections: Osteomyelitis, or bone infection, shows up as increased uptake.
| Condition | Typical Presentation on Bone Scan |
| Fracture | Increased uptake at the fracture site |
| Bone Metastasis | Multiple areas of increased uptake |
| Osteoarthritis | Increased uptake around affected joints |
| Osteomyelitis | Focal area of increased uptake |
Understanding bone scans well needs knowing the patient’s history and the imaging of skeletal pathologies.
“Color scales in bone scans help spot and measure bone metabolism changes. This aids in diagnosing and managing skeletal disorders.”
Nuclear Medicine Colors: Standardization and Variations
Standardizing nuclear medicine colors is key but needs more focus. Medical images’ meaning heavily depends on color. Yet, different color scales and manufacturer variations cause inconsistencies.
Color Scale Protocols Across Institutions
Different places use different color scales for scans. This can confuse doctors when they look at images. Some use a rainbow scale, while others stick to grayscale or monochrome.
The need for a common color standard is clear. Standardization efforts are underway to make color use in nuclear medicine more uniform.
Manufacturer Differences in Color Representation
Not just institutions, but also different makers of nuclear medicine gear have their own color rules. This means scans from different makers can look very different.
| Manufacturer | Default Color Scale | Customization Options |
| GE Healthcare | Rainbow | Yes |
| Siemens Healthineers | Grayscale | Yes |
| Philips Healthcare | Monochrome | Yes |
Knowing these differences is vital for doctors to interpret images correctly. They must understand the specific color scale used in the images they analyze.
Technical Aspects of SPECT Image Normalization
In nuclear medicine, SPECT image normalization is key for standardizing images. This is vital for making sure images are consistent and reliable. It helps doctors make accurate diagnoses.
How Images Are Processed and Standardized
SPECT images go through several steps to improve their quality and standardize them. Image processing techniques are used to fix issues like attenuation and scatter. Normalization adjusts the intensity of images to a common scale. This makes it easier to compare scans from different patients.
The process includes several important steps:
- Data acquisition and reconstruction
- Correction for attenuation and scatter
- Normalization to a standard intensity scale
Standardizing these steps helps nuclear medicine departments ensure their images are consistent. This is true both within their institution and when compared to external benchmarks.
Impact of Normalization on Color Appearance
The normalization process greatly affects the color appearance of SPECT images. Colors in these images show different levels of tracer uptake. Red usually means high activity. Normalization makes sure these colors are accurately shown and consistent across images.
Without proper normalization, color variations could lead to misreading of images. For example, a red area on a SPECT scan might show high metabolic activity. But if the normalization is wrong, this could be misinterpreted.
By ensuring images are properly normalized, doctors can trust the color information for accurate diagnoses. This makes SPECT imaging more useful in nuclear medicine.
Radiopharmaceuticals and Their Influence on Color Patterns
It’s key to know how radiopharmaceuticals affect SPECT image colors for correct diagnosis. These substances emit radiation. SPECT imaging catches this radiation to show the body’s inside parts.
Common Tracers Used in SPECT Imaging
SPECT imaging uses many radiopharmaceuticals. Each is made to focus on certain body areas or functions. Here are some common ones:
- Tc-99m: Technetium-99m is often used because it’s good for attaching to many compounds.
- I-123: Iodine-123 is for thyroid imaging and other special uses.
- Xe-133: Xenon-133 helps with lung studies.
These tracers go to different body parts based on their chemical makeup. SPECT imaging picks up on this to make the images we see.
How Different Isotopes Affect Image Appearance
The type of isotope used changes how SPECT images look, including their colors. Isotopes vary in half-life, energy, and how they act in the body. This affects their distribution and how they show up on scans.
| Isotope | Primary Use | Effect on Image |
| Tc-99m | Bone, brain, and cardiac imaging | Provides high-resolution images with good contrast |
| I-123 | Thyroid imaging | Offers detailed thyroid function and structure |
| Xe-133 | Lung ventilation studies | Allows for assessment of lung function and ventilation patterns |
The table shows how different isotopes are used and their effects on SPECT images. Knowing these differences helps in understanding the colors and what they mean for diagnosis.
Choosing the right radiopharmaceutical for a test helps doctors get better information from SPECT imaging. This improves diagnosis and care for patients.
Clinical Interpretation of Red Areas by Specialists
Nuclear medicine physicians are key in reading SPECT images, focusing on red areas. They are vital in figuring out what these red spots mean for a patient’s health.
How Nuclear Medicine Physicians Read SPECT Images
These doctors look at SPECT images for color patterns, intensity, and where the radiopharmaceutical is. They use their knowledge of the body’s structure and how it works to spot odd spots, like red ones on the scan.
Reading SPECT images needs a deep grasp of body anatomy and how it functions.It also requires understanding the patient’s symptoms and other test results.
Contextualizing Color Information with Patient History
Doctors look at the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and other test results when reading SPECT images. This info is key to figuring out if red spots mean a certain health issue.
For example, a patient with heart disease might show red spots on a heart scan, meaning their heart isn’t getting enough blood. On the other hand, a brain tumor might show red spots on a brain scan, showing it’s active.
By mixing their nuclear medicine skills with the patient’s health history, doctors can give clear and helpful insights from SPECT images. This helps guide how to care for and treat patients.
Patient Guide to Understanding SPECT Scan Results
Getting to know your SPECT scan results can seem tough, but it’s doable with a guide. A SPECT scan is a big step towards figuring out and managing your health. It gives your doctor the info they need to decide on your treatment.
Nuclear medicine is key in finding out what’s going on inside your body. SPECT scans are a big part of this. They show detailed images, using colors to show how active different parts of your body are.
What Patients Should Know About Their Images
The colors on your SPECT scan mean something. Red areas show high activity or uptake. Blues and greens mean lower activity. Knowing this helps you understand your scan.
Don’t think your scan results are looked at alone. Your doctor will also think about your health history, symptoms, and other tests when they look at your SPECT scan.
Common Concerns About “Red Areas” on Scans
Many patients worry about “red areas” on their scans. But, it’s important to remember that red doesn’t always mean there’s a problem. Sometimes, red just shows normal activity.
To get a better idea of what your SPECT scan colors mean, let’s compare:
| Color | Typical Representation | Possible Interpretation |
| Red | High activity or uptake | Could indicate areas of high metabolic activity, inflammation, or certain types of tumors |
| Blue/Green | Low activity or uptake | May represent areas of low metabolic activity or reduced blood flow |
As you can see, the meaning of colors on a SPECT scan depends on the scan’s context and the condition being looked at. Your doctor is the best one to explain what the colors on your scan mean for you.
If you’re worried about your SPECT scan results, talk to your doctor. They can offer personalized advice and help ease your worries.
Common Misinterpretations of SPECT Scan Colors
Misunderstanding SPECT scan colors can cause wrong diagnoses. It’s key to correctly read these colors to diagnose diseases. But, several things can make this hard.
Artifacts and False Positives
Artifacts in SPECT scans come from technical or patient issues. These can look like real health problems, leading to wrong positives. For example, attenuation artifacts happen when dense materials block the scan, confusing the color data.
“Artifacts can really mess up SPECT scan accuracy,” say nuclear medicine experts. Knowing what causes these artifacts is vital for correct image reading.
- Motion artifacts from patient movement
- Attenuation artifacts from dense materials
- Scatter artifacts from photon scattering
When Red Doesn’t Indicate Pathology
Red on a SPECT scan usually means high activity. But, it doesn’t always mean disease. For instance, normal physiological uptake in some spots can seem abnormal. It’s important to look at the patient’s whole story when reading these images.
Red spots might just be normal variations or harmless conditions. Doctors need to see the big picture of the patient’s health to avoid wrong diagnoses.
“The key to accurate SPECT scan interpretation lies in understanding both the technical aspects of the imaging and the clinical context of the patient.”
Knowing about possible misreads and taking a detailed look at images can help doctors get it right. This leads to better care and results for patients.
Conclusion: The Continuing Importance of Color in Nuclear Medicine
Color is key in nuclear medicine, like in SPECT imaging. Knowing the meaning of different colors, like red, is vital for making accurate diagnoses.
Nuclear medicine colors are very important. They tell doctors about the health of organs and tissues. This helps in diagnosing and treating many health issues.
In SPECT imaging, colors help doctors see complex data easily. This shows how important color is in medical imaging. It highlights the need for ongoing education in reading nuclear medicine images.
As nuclear medicine grows, so does the role of color in patient care. Understanding colors helps doctors make better diagnoses and treatment plans.
FAQ
What does the color red typically represent on a SPECT scan?
Red on a SPECT scan shows high tracer uptake. This can mean different things depending on the scan’s purpose.
How do nuclear medicine physicians interpret red areas on SPECT images?
Doctors look at the scan’s context, the patient’s history, and the tracer used. They decide if the red area is normal or not.
What is the difference between hot spots and cold spots in SPECT imaging?
Hot spots are red and show high tracer uptake. Cold spots are blue and show low uptake. Each can mean different things about the body.
Why is standardization of nuclear medicine colors important?
Standardizing colors helps ensure images are interpreted the same way everywhere. This reduces mistakes.
How do different radiopharmaceuticals affect SPECT image colors?
Different tracers change how SPECT images look. This is because different isotopes take up and distribute in the body in unique ways.
What should patients know about understanding their SPECT scan results?
Red areas on a SPECT scan can mean many things. Patients should talk to their doctor to understand what it means for them.
Can red areas on a SPECT scan be misinterpreted?
Yes, red areas can be misread. This can happen due to technical issues or other problems. It’s important for experts to carefully look at the images.
How are SPECT images processed and standardized?
Images are made consistent through normalization. This adjusts the colors and intensity to help doctors accurately read them.
What are the common color scales used in nuclear medicine?
Nuclear medicine uses different color scales. These include thermal scales like the “hot iron” scale and proprietary ones from manufacturers. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks.
How does SPECT differ from other imaging modalities like PET or MRI?
SPECT uses radioactive tracers and focuses on how tissues and organs work. This is different from PET or MRI, which use other methods to show different information.
References
Weinsaft, J. W., et al. (2007). Diagnostic impact of SPECT image display on assessment of myocardial perfusion: Color versus gray-scale images. Journal of Nuclear Cardiology, 14(4), 484-489. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17826319/























