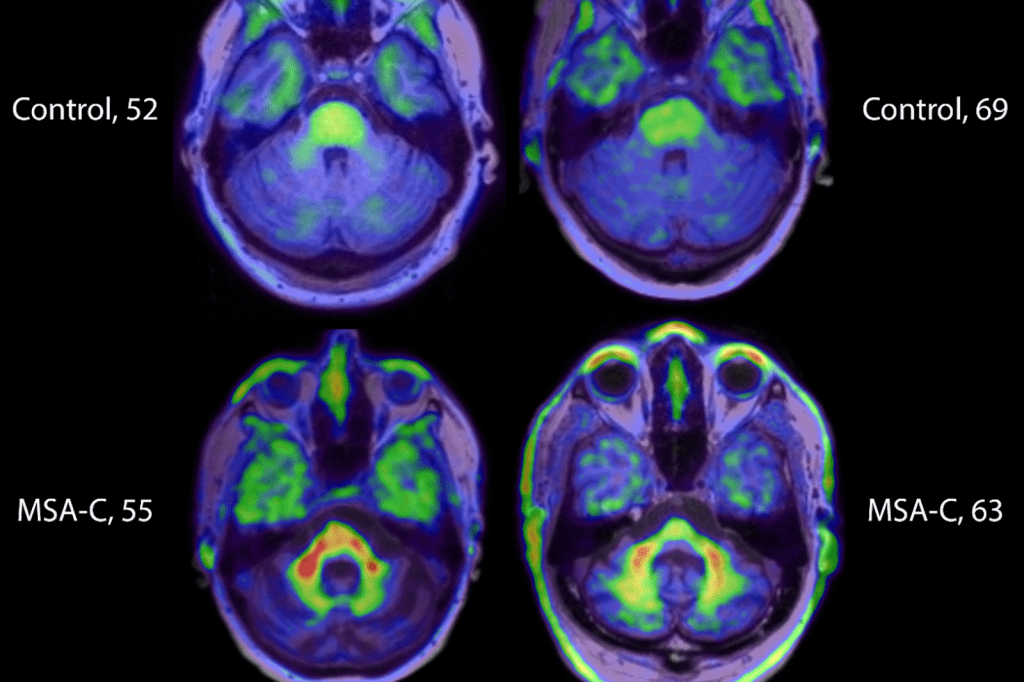
Anxiety disorders affect millions globally, causing distress and disrupting daily life. A SPECT scan, often used as a brain scan for anxiety, helps doctors study how the brain functions in people with this condition. It measures blood flow and activity in different regions of the brain, offering insights into anxiety’s neural roots.A SPECT brain scan for anxiety can reveal activity patterns linked to anxious states, which may support diagnosis and guide treatment planning. The big question is whether such a scan can truly show anxiety. Understanding what SPECT scans can and cannot do is essential for both doctors and individuals seeking effective help.
Key Takeaways
- SPECT scans evaluate brain function and can provide insights into anxiety disorders.
- They assess blood flow and activity in different brain parts.
- SPECT scans can aid in diagnosis and treatment planning for anxiety.
- Understanding SPECT scan capabilities is important for healthcare providers and individuals.
- SPECT scans are a valuable diagnostic tool for assessing anxiety.
Understanding SPECT Scans
SPECT scans are key in nuclear medicine. They show how the brain and other organs work. This tech has changed how doctors diagnose, letting them see how the body’s cells work.
What is a SPECT scan?
A SPECT scan uses a tiny bit of radioactive tracer. It’s injected into the body. The tracer goes to certain parts, like the brain, and sends out gamma rays. The scanner picks up these rays, making images that show how well these areas are working.
How SPECT scans work
Getting a SPECT scan starts with a tracer injection. This tracer goes to specific parts of the body. The scanner then moves around the patient, catching the gamma rays. It turns this info into detailed images of the body’s activity.
Common uses in medicine
SPECT scans are used a lot in medicine. They’re big in neurology and psychiatry. Here are some ways they’re used:
| Medical Application | Description |
| Neurological disorders | SPECT scans help find and track diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. |
| Psychiatric conditions | They check how the brain works in people with mental health issues. |
| Cancer diagnosis | SPECT scans help spot and keep an eye on some cancers. |
SPECT scans give doctors important info about the body. They help decide on treatments and check if they’re working.
The Neurobiology of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders have a complex neurobiological basis. They involve interactions between brain regions and neurotransmitter systems.
Brain Regions Involved in Anxiety
Several brain areas are key in anxiety disorders. The amygdala handles emotional information. The prefrontal cortex helps with decision-making and emotional control. The hippocampus is important for memory and affects anxiety through its connections.
Neurotransmitter Systems in Anxiety
Neurotransmitters play a big role in anxiety. The GABAergic system is key, as GABA calms brain activity. Serotonin and norepinephrine also influence anxiety.
Structural vs. Functional Brain Changes
Anxiety can lead to brain changes. Structural changes might alter brain region sizes. Functional changes affect how the brain works. Knowing these changes helps in finding treatments.
| Brain Region | Structural Changes | Functional Changes |
| Amygdala | Increased volume | Hyperactivity |
| Prefrontal Cortex | Reduced volume | Altered connectivity |
| Hippocampus | Reduced volume | Disrupted pattern separation |
Understanding anxiety disorders’ neurobiology is key. This includes brain regions, neurotransmitters, and brain changes. Imaging techniques like SPECT scans help diagnose and treat anxiety.w
Brain Scan for Anxiety: Available Options
Neuroimaging has led to many brain scan options for anxiety disorders. These advancements have changed psychiatry, giving doctors and researchers tools to study anxiety’s roots.
Types of Neuroimaging Techniques
There are many neuroimaging methods for anxiety, each with its own strengths. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) are used to see brain activity. Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) looks at blood flow in the brain, giving clues about its function.
“The right neuroimaging method depends on the question or need,” says a top neuroscientist. “Knowing each method’s strengths and weaknesses is key for correct results.”
Functional vs. Structural Imaging
Neuroimaging is split into functional and structural types. Functional imaging, like fMRI and SPECT, shows brain activity or blood flow. It helps understand anxiety’s neural roots. Structural imaging, like MRI, looks at brain anatomy, spotting any issues.
- Functional imaging techniques assess brain activity
- Structural imaging techniques provide detailed anatomy
- Combining both approaches offers a complete view
Clinical vs. Research Applications
Neuroimaging is used in both clinical and research settings for anxiety. Clinically, it aids in diagnosis and tracking treatment. In research, it helps scientists study anxiety’s neural basis and find new treatments.
A leading anxiety researcher, says, “Neuroimaging could change how we diagnose and treat anxiety. It offers a deeper look at the neural causes.”
SPECT Imaging in Mental Health
SPECT imaging has changed a lot in mental health. It now helps doctors diagnose and treat patients better.
Historical Development
SPECT imaging started in nuclear medicine. It was first used to check blood flow and organ function. Then, it was used for brain and mental health studies.
The first SPECT studies in psychiatry were in the 1980s. They looked at schizophrenia and depression. SPECT showed how the brain works, helping doctors understand more.
As SPECT got better, it became more useful. It could show brain activity better and help doctors make decisions.
Current Applications in Psychiatry
Now, SPECT imaging helps with many mental health issues. It shows how different parts of the brain work. This is useful for anxiety, depression, and schizophrenia.
Clinical utility: SPECT scans help doctors find out which brain areas are causing problems. This helps them choose the right treatment. It can make treatment more effective.
Controversies and Limitations
Even with its benefits, SPECT imaging has its critics. Some say it’s not always accurate. It also involves radiation, which is a concern.
Regulatory and professional guidelines are needed to use SPECT right. Researchers are working to make it better. They want to improve how it works and make it safer.
Can SPECT Diagnose Anxiety?
SPECT scans are being studied to see if they can diagnose anxiety. Anxiety affects millions and getting it right is key to treating it.
Research findings on anxiety patterns
Research shows SPECT scans can spot brain activity patterns in anxiety. People with anxiety often have different brain blood flow, like in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex. SPECT imaging can identify these patterns, helping diagnose anxiety.
A study in a Journal found SPECT scans can tell anxiety patients apart from healthy people. This shows SPECT might help diagnose anxiety, when used with a doctor’s evaluation.
Sensitivity and specificity concerns
Despite promising research, there are worries about SPECT’s sensitivity and specificity for anxiety. Sensitivity means it correctly finds those with anxiety, and specificity means it correctly finds those without.
Some studies say SPECT might not be sensitive or specific enough for anxiety diagnosis alone. This highlights the need for a full diagnostic approach that includes SPECT, clinical assessment, and other tools.
Expert consensus on diagnostic value
Experts agree SPECT scans offer useful insights into anxiety disorders but shouldn’t be the only tool for diagnosis. A multi-modal approach is best, combining SPECT with clinical evaluation and other methods.
The American Psychiatric Association and others see SPECT’s value in research and sometimes in diagnosis. But they don’t recommend it for routine use in treating anxiety.
Perfusion SPECT Brain Studies in Anxiety
Perfusion SPECT scans give us a peek into the brain’s blood flow patterns linked to anxiety. This imaging method is key in grasping the brain’s complex workings in anxiety disorders.
Blood Flow Patterns in Anxiety Disorders
Studies reveal that people with anxiety have different blood flow patterns in their brains. Perfusion SPECT lets doctors see these changes. It helps them understand the brain’s inner workings.
Research shows anxiety is linked to more activity in the amygdala and insula. These areas are key for handling emotions and stress.
Regional Cerebral Blood Flow Changes
Looking at regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) changes is a big part of perfusion SPECT studies in anxiety. It helps researchers spot which brain areas are impacted by anxiety.
- More rCBF in the amygdala and anterior cingulate cortex is tied to higher anxiety.
- Less rCBF in the prefrontal cortex might mean trouble with emotional control.
- The type of anxiety and the person’s symptoms can affect rCBF changes.
Interpretation Challenges
While perfusion SPECT offers insights into anxiety, figuring out what it means can be tough. Several things make it complex:
- Everyone’s brain is different.
- Many psychiatric conditions can look similar.
- It’s important to control factors like medication and health conditions.
Despite these hurdles, perfusion SPECT is a valuable tool for studying anxiety. Ongoing research is working to better understand how brain activity, blood flow, and anxiety symptoms are connected.
Comparing SPECT vs MRI for Psychiatry
SPECT and MRI are two imaging tools used in psychiatry. Each has its own benefits. They help doctors see how the brain works and what it looks like.
Structural Capabilities
MRI is better at showing the brain’s structure. It gives clear images of the brain’s anatomy. This helps find problems like tumors or lesions.
SPECT, on the other hand, looks at how the brain functions. It doesn’t focus on the brain’s structure.
Key differences in structural capabilities:
- MRI provides detailed anatomical images
- SPECT is more focused on functional aspects
- MRI is better suited for detecting structural lesions
Functional Assessment Differences
SPECT is great for looking at brain function. It shows how blood flows in different parts of the brain. This can help diagnose psychiatric conditions.
MRI can also look at brain activity. It does this by measuring blood flow changes. But SPECT is better for certain situations.
Functional assessment highlights:
- SPECT is useful for assessing regional cerebral blood flow
- fMRI (a type of MRI) measures changes in blood flow to map brain activity
- SPECT can be more appropriate for certain clinical applications
Cost and Accessibility Factors
The cost and availability of SPECT and MRI differ. MRI machines are pricier and less common than SPECT. This affects how easy it is to get a scan.
Considerations for cost and accessibility:
| Factor | SPECT | MRI |
| Equipment Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
| Accessibility | More widely available | Less accessible in some areas |
Choosing between SPECT and MRI depends on what you need to know. It’s about the type of information you want and what’s available. Knowing what each can do helps doctors make better plans for treatment.
DATScan and Anxiety Evaluation
DATScan has become a key topic in medical research for anxiety evaluation. Anxiety disorders are common and need precise, quick diagnostic tools.
What is a DATScan?
A DATScan is a nuclear medicine test. It uses a tiny amount of radioactive material to see dopamine in the brain. It mainly helps diagnose Parkinson’s disease by checking the brain’s dopamine system.
Relationship to Anxiety Disorders
DATScan isn’t used to diagnose anxiety directly. Yet, research looks into its role in understanding anxiety’s brain roots. Studies hint that changes in dopamine systems seen with DATScan might link to anxiety disorders.
Differential Diagnosis Applications
In clinics, DATScan aids in differentiating between Parkinson’s disease and anxiety symptoms. It helps doctors find the right treatment, leading to better patient care.
The role of DATScan in anxiety shows how brain and mental health issues are connected. It points to the need for a detailed approach to diagnosis and treatment.
PET Scan for Anxiety Assessment
PET scans give a unique view into anxiety disorders, unlike SPECT scans. They are used in neuroimaging to study brain function, including anxiety. This helps us understand the brain better.
Distinguishing Features of PET Scans
PET scans are different from SPECT scans in many ways. PET scans offer higher resolution images and more detailed brain function information. They measure various physiological processes, not just blood flow like SPECT.
“PET scans could change how we see anxiety disorders,” studies say. They let researchers look at brain chemistry and metabolism in new ways.
Research Applications in Anxiety
PET scans are used in research to study anxiety in several ways:
- They look at brain glucose metabolism changes linked to anxiety.
- They study the role of neurotransmitters in anxiety disorders.
- They check how anxiety affects brain function in different areas.
These studies give us important insights into anxiety disorders. They could lead to better treatments.
Clinical Utility Considerations
PET scans are promising in anxiety research but their use in clinics is limited. Cost, availability, and interpreting data are big challenges.
As research improves, PET scans might become more useful in clinics. They could help diagnose and monitor anxiety treatments better.
fMRI Applications in Anxiety Research
fMRI has changed how we study anxiety disorders. It lets researchers see brain activity by tracking blood flow changes. This gives us clues about the brain’s role in anxiety.
Task-based vs. resting-state fMRI
fMRI studies fall into two types: task-based and resting-state. Task-based fMRI scans people doing specific tasks. It shows which brain areas are active during these tasks. Resting-state fMRI, on the other hand, looks at brain activity when people are relaxed.
Task-based fMRI helps us understand anxiety by looking at how the brain reacts to fear and emotions. For example, it shows that people with anxiety have different brain activity when they see emotional pictures.
Resting-state fMRI shows that anxiety is linked to changes in brain activity and connections. It finds issues in the default mode network and other brain networks.
Key findings in anxiety disorders
Studies using fMRI have found important things about anxiety. These include:
- The amygdala, key for emotions, is too active in response to threats.
- There are changes in the default mode network and its connections with other brain areas.
- The prefrontal cortex, important for controlling emotions and thoughts, is not working right.
| Finding | Description | Implication |
| Amygdala hyperactivity | Increased response to threat-related stimuli | Enhanced fear response |
| Altered default mode network connectivity | Changes in intrinsic brain activity | Potential biomarker for anxiety |
| Prefrontal cortex abnormalities | Impaired emotion regulation | Difficulty in managing anxiety |
Limitations for clinical use
Even though fMRI has helped a lot in studying anxiety, it has some big challenges for use in clinics. These include:
- It’s very expensive and not easy to get.
- There are many ways to do fMRI studies, which can make results hard to compare.
- We don’t fully understand how to use fMRI findings to help patients.
Fixing these problems is key to using fMRI in clinics for anxiety.
Functional Brain Scan Limitations
Functional brain scans give us valuable insights into brain activity. But, they face technical and interpretative challenges. It’s key to understand these to accurately read scan results and make good clinical decisions.
Technical Challenges
Scans like SPECT face technical hurdles that affect their accuracy. One big issue is scan resolution. High-resolution imaging is needed to spot small changes in brain activity. But, reaching this high resolution is hard due to tech limits.
Another challenge is processing scan data. The algorithms used to analyze brain activity can greatly influence the results. Different software can give different outcomes. A researcher noted, “The choice of data processing pipeline can significantly affect the results of functional brain scans, highlighting the need for standardization.”
“The complexity of brain function and the limitations of current neuroimaging techniques mean that results must be interpreted with caution.”
Expert in Neuroimaging
Interpretation Variability
Interpreting functional brain scans can vary a lot between professionals. The clinician’s experience and the criteria used for analysis can lead to differences in diagnosis. This shows why standard protocols for scan interpretation are so important.
Correlation vs. Causation Issues
Another big issue with functional brain scans is telling correlation from causation. A scan might show a link between certain brain activity and anxiety disorders. But, it’s hard to say if these patterns cause the disorder or just go with it.
To tackle these issues, we need more research and better imaging and analysis tools. By facing and solving these challenges, we can make functional brain scans more useful in diagnosing and treating anxiety disorders.
Anxiety Brain Mapping: Current State
Brain mapping for anxiety has made big strides, giving us new insights into anxiety disorders. This progress is thanks to better neuroimaging and analysis methods.
Biomarker Development Efforts
Researchers are working hard to find reliable biomarkers for anxiety. Biomarkers help diagnose early, track disease, and predict treatment success. Studies have found possible biomarkers linked to brain activity, structure, and connections in anxious people.
Key findings include:
- Altered activity in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex regions
- Changes in the volume and thickness of certain brain structures
- Disrupted connectivity within neural networks
Pattern Recognition Approaches
Pattern recognition is key in studying neuroimaging data. It helps find patterns linked to anxiety, shedding light on the brain’s workings. Tools like fMRI and EEG are essential in this research.
Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning has changed anxiety brain mapping by analyzing big data. It can spot complex patterns, classify anxiety disorders, predict treatment success, and tailor treatments.
| Machine Learning Application | Description | Potential Impact |
| Classification | Identifying anxiety disorders based on neuroimaging patterns | Enhanced diagnostic accuracy |
| Predictive Modeling | Forecasting treatment response based on brain mapping data | Personalized treatment planning |
| Clustering | Grouping patients based on neurobiological profiles | Targeted therapeutic interventions |
Combining machine learning with anxiety brain mapping is a big leap in psychiatric research. It could lead to more accurate and effective treatments.
Brain Imaging for Anxiety Treatment Planning
Healthcare providers use brain imaging to make anxiety treatment plans more personal. This technology is key in diagnosing and treating anxiety disorders.
Predicting Treatment Response
Brain imaging helps predict how well a patient will do with different treatments. Functional brain imaging techniques like fMRI and SPECT scans show the brain’s inner workings. This helps doctors pick the best treatment options.
Monitoring Treatment Effects
It also lets doctors track how treatments work over time. By looking at brain activity before and after treatment, they can see if it’s working. This helps them adjust the treatment for better results.
Personalized Medicine Approaches
Using brain imaging in treatment planning is a big part of personalized medicine. It allows doctors to tailor treatments to each patient’s brain. This approach can lead to better results and fewer side effects.
Cost Considerations for Anxiety Brain Scans
It’s important to know the costs of anxiety brain scans before making decisions about mental health care. The price can change a lot based on the scan type and insurance coverage.
Insurance Coverage Issues
Patients worried about brain scans for anxiety often wonder if their insurance will pay for it. Insurance coverage for these scans can be tricky. It depends on the insurance plan and if the scan is needed for medical reasons.
Most insurance plans cover tests that are medically necessary. But, what counts as necessary can differ between insurers. Some plans might not cover certain scans, like SPECT or PET scans, for anxiety.
Comparative Costs of Different Modalities
The cost of brain scans for anxiety can vary a lot. For example, functional MRI (fMRI) and SPECT scans cost differently. This is because of the technology and how complex the scan is.
| Imaging Modality | Average Cost | Insurance Coverage |
| fMRI | $1,000 – $2,500 | Variable |
| SPECT Scan | $800 – $2,000 | Often Covered |
| PET Scan | $1,500 – $3,500 | Variable |
Value Assessment in Clinical Practice
When deciding on brain scans for anxiety, cost isn’t the only thing to think about. We also look at how accurate the scan is and how it helps in planning treatment. These scans can give important details that lead to better treatments.
The scans’ value comes from helping doctors make better decisions. This can lead to better patient outcomes. But, we must also think about the costs and what’s best for each patient.
Ethical Considerations in Neuroimaging for Mental Health
Neuroimaging in mental health raises important ethical questions. As it becomes more common in diagnosis and treatment, several key issues need attention.
Incidental Findings Management
Managing incidental findings is a big concern. Neuroimaging can sometimes find unexpected issues not related to the original purpose. It’s important to share important health info without causing unnecessary worry.
Privacy Concerns
Privacy is a major issue. Neuroimaging data is very personal and sensitive. Keeping this data safe and private is essential for patient trust and legal compliance, like HIPAA in the U.S.
Potential for Stigmatization
Stigmatization is another big worry. Neuroimaging results can be misunderstood, leading to stigma. This can harm how society views and treats people with mental health issues.
| Ethical Issue | Description | Mitigation Strategy |
| Incidental Findings | Unexpected abnormalities found during neuroimaging | Clear protocols for disclosure and follow-up |
| Privacy Concerns | Risk of sensitive information disclosure | Robust data security measures and compliance with privacy laws |
| Stigmatization | Misinterpretation of neuroimaging findings leading to stigma | Education and awareness campaigns to promote understanding |
In conclusion, the ethics of neuroimaging in mental health are complex. We need a balanced approach to use this technology. It must protect patients’ rights and well-being while benefiting from its advantages.
Future Directions in Anxiety Neuroimaging
The field of anxiety neuroimaging is on the verge of a big change. New technologies and research methods are leading the way. These advancements will greatly help us understand and treat anxiety disorders.
Emerging Technologies
New tools are being made to make neuroimaging better. For example, advances in MRI technology let us see brain details like never before. “The use of artificial intelligence in neuroimaging analysis is changing the game,” a study found. “It makes data analysis more accurate and quicker.”
Multimodal Imaging Approaches
Using different neuroimaging methods together, like SPECT, MRI, and fMRI, gives us a deeper look at anxiety. This way, we can see both the brain’s structure and how it works.
Integration with Other Biomarkers
Combining neuroimaging with genetic markers is an exciting area of study. This could lead to better diagnoses and treatments for anxiety.
Conclusion: The Role of SPECT in Anxiety Assessment
SPECT scans are now a key tool in studying anxiety disorders. They give us a look into how the brain works and what it does. We’ve talked about what SPECT imaging can and can’t do in this article.
SPECT scans play a big role in checking for anxiety. They look at how blood flows in the brain to find signs of anxiety. Even though they can’t diagnose on their own, they help doctors a lot. They add to what doctors already know and use other tests for.
To wrap it up, SPECT scans are very helpful in understanding and checking for anxiety. As scientists learn more, using SPECT scans with other tests might make diagnosing and treating anxiety better. This could help people with anxiety get the right help sooner.
FAQ
What is a SPECT scan and how is it used to diagnose anxiety?
A SPECT scan is a test that looks at brain activity. It shows how blood flows in the brain. This helps doctors see if someone has anxiety by looking at brain activity patterns.
Can a SPECT scan diagnose anxiety disorders?
A SPECT scan can give clues about brain function. But, it’s not enough on its own to say someone has anxiety. Doctors usually use it along with other tests and their own evaluation.
How does a SPECT scan differ from an MRI or CT scan?
A SPECT scan looks at brain activity, not just its structure. MRI and CT scans show the brain’s shape. SPECT scans can spot changes in brain activity linked to anxiety.
What are the limitations of using SPECT scans for anxiety diagnosis?
SPECT scans have some downsides. They can be hard to interpret and have technical issues. They should be part of a bigger diagnostic process.
Can SPECT scans be used to monitor treatment response in anxiety disorders?
Yes, SPECT scans can track how well treatments work. They show changes in brain activity. This helps doctors adjust treatment plans.
Are there other neuroimaging techniques used to diagnose anxiety?
Yes, other tests like fMRI, PET scans, and DATScans are used too. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses for studying anxiety.
How do perfusion SPECT brain studies relate to anxiety?
Perfusion SPECT studies look at blood flow in the brain. Anxiety can change this flow. These studies help find which brain areas are affected by anxiety.
What is the cost of a SPECT scan for anxiety, and is it covered by insurance?
The cost of a SPECT scan varies by location and provider. Insurance coverage also differs. But, many plans do cover SPECT scans for diagnosing anxiety.
Are there any ethical considerations when using neuroimaging for anxiety diagnosis?
Yes, there are ethical issues. Like dealing with unexpected findings and keeping patient privacy. Doctors must think about the benefits and risks of using these tests for anxiety.
References
- Best, S. R. D., et al. (2021). Brain SPECT as an Imaging Biomarker for Evaluating Neurologic Disorders. Frontiers in Psychiatry.
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/psychiatry/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.713141/full - Chen, J., et al. (2011). A review of neuroimaging studies of anxiety disorders. PMC.
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3090288/ - Doruyter, A. G., et al. (2018). Nuclear Neuroimaging in Social Anxiety Disorder: A Review. Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/59/12/1794 Journal of Nuclear Medicine



































