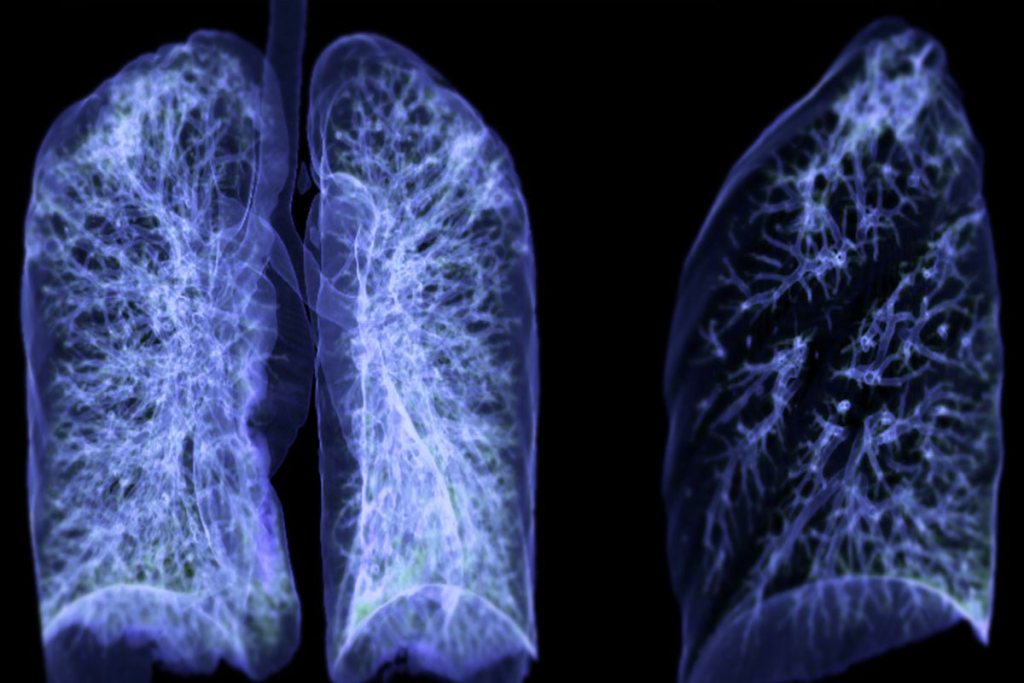
We are seeing a big change in how doctors check our health. PET scans are becoming key for looking at lung health. A PET scan, or Positron Emission Tomography, is a high-tech test. It helps doctors find and handle different health problems, like lung cancer staging imaging.
PET scans are great for seeing how active the body’s cells are. This is key for spotting diseases like lung cancer. They use a special drug that lights up on the scan. This shows doctors how well the lungs are working and helps them find problems.
PET scan technology is key for diagnosing and managing diseases like lung cancer. It’s a vital tool in modern medicine, showing how the body works at a metabolic level.
PET imaging uses a special tracer that’s injected into the body. This tracer goes to areas with lots of activity, like cancer cells. The PET scanner then picks up this radiation to create detailed images of the body’s activity.
The process involves several key steps:
FDG is the main tracer used in PET scans. It’s a glucose molecule with a radioactive atom. Cancer cells, with their high metabolism, take up more FDG, making them visible on PET scans.
“The use of FDG in PET scans has revolutionized the field of oncology, allowing for earlier detection and more accurate staging of cancer.”
An Oncologist
PET scans measure how much tracer is taken up in different body parts. High uptake means high metabolic activity, often a sign of cancer or other issues.
| Metabolic Activity Level | FDG Uptake | Indication |
| High | High | Cancer or inflammation |
| Low | Low | Normal tissue or benign condition |
Knowing how PET scan technology works helps doctors use it better for lung cancer and other diseases.
The main goal of a lung PET scan is to spot abnormal metabolic activity in the lungs. This tool is key for finding and handling lung issues, like cancer.
Lung PET scans look for metabolic changes in the lungs. They use a radioactive tracer, like FDG, to find areas with high glucose use. This is common in cancer cells. So, PET scans are very useful in finding cancer.
In lung cancer, PET scans show how far the disease has spread. This is important for planning treatment. Clinical guidelines say PET scans are best for staging lung cancer and checking if it has spread.
PET scans have many uses in pulmonary medicine. They are mainly for:
The table below shows the main uses of PET scans in pulmonary medicine:
| Application | Description |
| Diagnosing Lung Cancer | Finding cancer by looking for abnormal metabolic activity |
| Staging Lung Cancer | Finding out how far the disease has spread |
| Monitoring Treatment Response | Seeing if treatment is working by checking metabolic changes |
Doctors suggest a lung PET scan in different situations. These include:
Knowing when and why a lung PET scan is needed helps patients understand its importance in lung health.
The use of PET and CT scans together has changed how we diagnose lung conditions. This mix of technologies gives a clearer picture of what’s happening in the lungs. It helps doctors make more accurate diagnoses.
PET and CT scans are better when used together. PET scans show how active cells are, while CT scans give detailed pictures of the body. This combination boosts how sure doctors are about their findings.
Studies have shown that using PET-CT together is more accurate than using just one. For example, in lung cancer, PET-CT helps find the main tumor and check if cancer has spread.
By combining PET and CT images, doctors can see where active cells are in the body. This is key for figuring out how far the disease has spread. It also helps plan the best treatment.
| Imaging Modality | Information Provided | Clinical Utility |
| PET | Metabolic Activity | Disease detection, staging |
| CT | Anatomical Detail | Structural assessment |
| PET-CT | Combined Metabolic and Anatomical Information | Enhanced diagnostic accuracy, treatment planning |
The PET-CT combo has many advantages for lung health checks, mainly for lung cancer. It leads to more accurate diagnoses and better treatment plans. This way, doctors can tailor treatments to each patient’s needs.
As a result, patients get more precise diagnoses and treatments. This leads to better health outcomes for them.
Understanding how far lung cancer has spread is key. PET scans play a big role in this. Knowing the extent of cancer helps doctors choose the best treatment and predict how well a patient will do.
The TNM staging system is a way doctors classify lung cancer. It looks at three main things: the tumor size and spread (T), nearby lymph nodes (N), and if cancer has spread to other parts of the body (M).
Each part gets a score, and these scores are combined to find the cancer’s stage. This stage is very important for deciding how to treat the cancer.
PET scans are important for lung cancer staging because they show how active the tumor is. Unlike CT scans, which show the tumor’s size and shape, PET scans highlight areas where cancer is growing fast.
This helps doctors see how far the cancer has spread, including to distant parts of the body. This is important because other tests might miss these areas.
PET Scan Benefits in Staging:
Knowing how far lung cancer has spread is key for treatment planning. Doctors can then choose the best treatment, like surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy, based on this information.
| Stage | TNM Classification | Typical Treatment Approach |
| I | T1-2, N0, M0 | Surgery |
| II | T1-2, N1, M0 | Surgery, possibly followed by chemotherapy |
| III | T3-4, N2-3, M0 | Multimodal treatment including chemotherapy and radiation |
| IV | Any T, Any N, M1 | Palliative care, targeted therapy, or chemotherapy |
By using PET scan results in the TNM staging system, doctors can make treatment plans that are more tailored to each patient. This can lead to better outcomes for patients.
Getting ready for an FDG PET scan is key to getting good results. We help our patients through each step to make it easy.
To get ready for an FDG PET scan, patients need to follow certain diet rules. Fasting for 4-6 hours before the scan is usually needed. This helps keep glucose levels low in the body.
We also tell patients to stay away from high-sugar foods and drinks for 24 hours before the scan. This ensures the FDG tracer works right, giving us better scan results.
Staying away from caffeinated drinks and sugary foods is important. It helps the FDG tracer get absorbed by tissues correctly. This leads to more accurate scan results.
Some medicines can change how an FDG PET scan works. We ask patients to tell us about all their medicines. Some medicines might need to be stopped or changed before the scan.
It’s very important for patients to follow our advice on managing their medicines. This helps make sure the scan is accurate.
Keeping blood glucose levels in check is very important for FDG PET scan patients, like those with diabetes. We need patients to have their blood glucose levels checked before the scan. These levels should be below a certain level (usually 200 mg/dL) for the scan to go ahead.
High blood glucose levels can mess up the scan quality. They can compete with the FDG tracer for cell uptake. We help our patients manage their glucose levels before the scan.
Getting a PET scan is easy if you know what to expect. We want you to feel calm and ready for it. Knowing what happens can help a lot.
You’ll lie on a table in a big, doughnut-shaped machine. Our team will make sure you’re in the right spot. The scan is painless and looks at your lungs to see how active they are.
Key steps during the scan include:
The whole PET scan takes 30 to 60 minutes. But, getting ready and finishing up can take longer. It’s important to stay very quiet during the scan for the best pictures. Our team will help you find the best position.
Tips for the scan:
After the scan, you can go back to your usual day unless your doctor says not to. Drinking lots of water helps get rid of the tracer. Our team will give you instructions and answer any questions.
Post-scan care includes:
Understanding PET scan results, like SUV uptake, is key to checking lung health. PET scans show how active our lungs are. This helps doctors spot and treat different health issues.
Standardized Uptake Values (SUV) are important in PET scans. SUV shows how much a body part uses the tracer compared to the whole body. A higher SUV means more activity, which can point to cancer or other issues.
To figure out SUV, doctors compare the activity in certain areas to the dose and body weight. This makes it easier to compare scans and patients.
SUV levels tell us a lot about lung problems. Higher SUV values usually mean more serious tumors. Lower values might show less activity.
It’s important to remember that SUV values are just part of the diagnosis. Doctors also look at other images, medical history, and tests to make a correct diagnosis.
Radiologists study lung PET images closely. They look at SUV uptake, tracer distribution, and any unusual activity. They also think about the patient’s history, symptoms, and other tests.
When they analyze PET images, radiologists check for:
By combining PET scan results with other info, we get a full picture of lung health. This helps doctors plan the best treatment.
It’s important to know the limits of PET scans for lung imaging. They give valuable info on lung activity but have their own set of issues.
PET scans can’t spot small details well. They struggle to find tiny lesions or tell apart close structures. This can lead to wrong diagnoses, mainly when small or hard-to-spot issues are present.
Ground glass nodules (GGNs) are tricky for PET scans. They might show early lung cancer or pre-cancerous changes. But, they don’t always show up on PET scans because they don’t always light up.
The size of a lesion matters for PET scans. Lesions under 8-10 mm might not be seen because of the scan’s limits. This is due to its low detail and sensitivity.
To show these limits, here’s a table:
| Limitation | Description | Impact on Diagnosis |
| Spatial Resolution | Limited ability to detect small or closely situated structures | May lead to inaccurate or incomplete diagnoses |
| Ground Glass Nodules | Difficulty in detecting nodules with low metabolic activity | Potential for missing early-stage lung cancer or pre-invasive lesions |
| Small Lesion Detection | Lesions | Risk of missing small tumors or metastases |
PET scans are great for diagnosing, but they have their own limits. Knowing these limits helps in making accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
PET scans can sometimes show false positives. This happens when inflammation looks like cancer. It makes diagnosing lung cancer with PET scans tricky.
Many inflammatory conditions can cause FDG uptake. This can lead to false positives on PET scans. These include:
It’s important to tell infections from cancer. Both can show up on PET scans. But, there are clues to help tell them apart.
To get better at reading PET scans, several steps can be taken:
By using these methods, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses. This leads to better treatment plans.
Not all tumors can be found by PET scans. This is because of different reasons. PET scans work well for many cancers but miss some. Knowing this helps in planning treatment and checking for cancer.
Carcinoids are hard to spot because they don’t use much glucose. They can grow in many places, like the lungs. This makes them hard to see on PET scans.
Tumors that don’t use much energy are tough to find. PET scans look for areas that use a lot of energy. But slow-growing tumors or those with low energy might not show up.
Size also matters when it comes to finding tumors. Tumors smaller than 8-10 mm might not be seen by PET scans. Even if they are active, they can be too small to spot.
| Lesion Size | Detection Likelihood |
| < 8 mm | Low |
| 8-10 mm | Moderate |
| > 10 mm | High |
Many things can affect how well PET scans work. The type of tumor, where it is, and the patient’s health are important. For example, tumors near the brain or heart are harder to find. High blood sugar can also make it harder to see tumors.
It’s important to know these things when looking at PET scan results. This helps doctors make better choices for their patients.
Advanced PET techniques are changing how we find and treat lung cancer. New technologies and methods are being created. They aim to make PET scans more accurate and useful in lung cancer care.
Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) has been key in PET imaging for lung cancer. But, scientists are looking into new tracers. These could give more info on tumor biology.
For example, Fluorothymidine (FLT) is being studied. It might show how fast tumors grow. This could help figure out how aggressive lung cancer is.
“New PET tracers are vital for better lung cancer imaging. They can reveal tumor metabolism. This could lead to treatments tailored to each patient.”
One big challenge in lung PET imaging is breathing. It can blur images and lower accuracy. Respiratory-gated PETimaging fixes this by matching PET scans with breathing.
This method gives clearer lung images. It helps measure tumor size and location better.
New technologies are set to make PET imaging better for lung cancer. These include:
As these technologies grow, PET imaging will be even more important in lung cancer care. The future of lung cancer imaging looks bright, with new innovations on the horizon.
PET-CT scans help diagnose and treat lung conditions. But, they also raise concerns about radiation safety. It’s key to grasp the effects of radiation exposure.
PET-CT scans use radiation from both PET and CT parts. The dose varies based on the scan type and patient size. Typically, it’s between 10 to 25 millisieverts (mSv) for a whole-body scan.
For comparison, we naturally get about 3 mSv of radiation each year. So, a PET-CT scan is like getting several years’ worth of background radiation. Yet, the scan’s benefits often outweigh the risks.
When we look at PET-CT scans, we consider many things. They can save lives by spotting cancers early and tracking treatment. But, there’s a chance of getting secondary cancers from the radiation.
Deciding on PET-CT scans involves the patient’s health, the suspected condition, and other diagnostic options. In many cases, the scan’s benefits for accurate diagnosis and treatment planning are greater than the risks.
Medical facilities take many steps to reduce radiation exposure. These include:
Patients are also told how to reduce their exposure after the scan. Drinking water helps flush out the radioactive tracer.
Knowing about PET-CT scan radiation and safety steps helps patients make better choices about their care.
PET scans are key in lung cancer imaging and management. They help find abnormal activity and stage lung cancer. This shows their importance in medical care.
PET and CT scans together give more detailed information. They help doctors understand both the function and structure of the body. Even with some limitations, PET scans guide treatment plans well.
In summary, PET scans are essential for lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. As PET technology improves, so will lung cancer imaging. This highlights the need for ongoing research and investment in cancer care.
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a test that shows how active cells are in the body. It uses a special tracer that is injected into the blood. This tracer is then picked up by cells and sends signals to the PET scanner.
The scanner makes detailed images of these signals. This helps doctors see how active different parts of the body are.
A lung PET scan finds abnormal activity in the lungs. It helps doctors find and check how far lung cancer has spread. It’s good at spotting cancer because it shows where cells are most active.
Combining PET and CT scans gives doctors a complete view of the body. They can see both the structure and how active tissues are. This helps them find and understand lung cancer better.
The TNM system is used to classify lung cancer. It looks at the tumor size, lymph nodes, and if cancer has spread. PET scans help by showing how active tumors are and if cancer has spread.This information is key for planning treatment.
To get ready for a PET scan, avoid sugary foods and drinks. Also, manage your blood sugar. Our team will give you specific instructions to prepare.
During a PET scan, you lie on a table that slides into the scanner. The scan lasts about 30-60 minutes. You need to stay very quiet and not move.Our team will make sure you’re comfortable and guide you on how to breathe and position yourself.
PET scan results are analyzed by looking at Standardized Uptake Values (SUV). SUV shows how much FDG is taken up by tissues. High SUV levels often mean cancer is present.But, SUV can also be affected by inflammation. Our radiologists carefully review the images and provide a detailed report.
PET scans have some limits. They can’t always see small lesions or distinguish between certain types of nodules. It’s important to understand these limitations for accurate results.
Yes, inflammation can make PET scans show false positives. Our team uses different methods to tell the difference between cancer and inflammation. This helps ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!
WhatsApp us