The liver is key to our body’s health, making it impossible to remove completely. Yet, doctor removed liver during surgery. This is called hepatectomy or liver resection.
At our institution, we know the question of liver removal is complex. We aim to offer top-notch healthcare, supporting patients from around the world. While removing the whole liver is not possible, taking out up to 70% is common and can save lives.
Advanced techniques and careful protocols drive continuous improvements in patient outcomes and international standards.
Key Takeaways
- The liver cannot be entirely removed due to its vital functions.
- Certain sections of the liver can be surgically removed through hepatectomy.
- Liver resection is a lifesaving procedure with improving outcomes.
- Up to 70% of the liver can be removed in targeted surgical resections.
- Advanced techniques enhance patient safety and recovery.
The Liver’s Essential Functions and Structure
Our liver is more than just an organ. It’s a powerhouse that handles many important tasks. It keeps us healthy by breaking down nutrients and toxins.
Key Metabolic and Detoxification Roles
The liver is key in breaking down carbs, fats, and proteins. It makes sure our cells get what they need for energy and repair.
Detoxification is another big job of the liver. It cleans the blood from the digestive tract before it reaches the rest of the body. It removes toxins and breaks down drugs, keeping us safe.
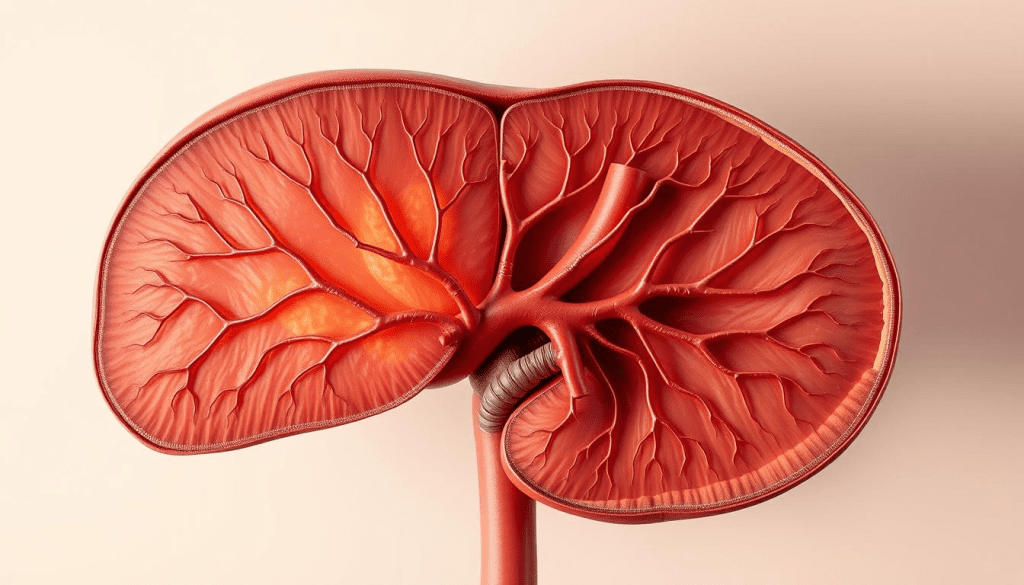
Anatomical Structure and Blood Supply
The liver’s anatomical structure helps it do its job well. It’s divided into lobes and has a special blood system. It gets blood from the hepatic artery and the portal vein.
This system makes sure the liver gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs. It also gets blood rich in nutrients from the digestive tract.
| Component | Function | Significance |
| Hepatic Artery | Supplies oxygenated blood | Essential for liver cell function |
| Portal Vein | Brings nutrient-rich blood from the digestive tract | Critical for nutrient processing and detoxification |
| Bile Ducts | Transports bile to the gallbladder and intestines | Aids in fat digestion and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins |
The liver’s structure and blood supply are key to its work. Knowing this helps us see how important the liver is for our health.
The Remarkable Regenerative Capacity of the Liver
The liver can heal itself after injuries or surgery. This is key for patients having liver surgery. It lets the liver get back to normal.
The liver’s healing is a complex process. Liver regeneration happens thanks to stem cells and the growth of liver cells.
How Liver Regeneration Works
Liver regeneration is a detailed process. It involves many cell types working together. When liver tissue is damaged, the remaining cells grow to replace it.
This growth is guided by growth factors and other signals. For example, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) helps liver cells grow.
Scientific Evidence of Liver Regrowth
Many studies show the liver’s ability to grow back. For instance, after a liver resection, it can return to its original size in weeks.
Research also shows that the liver can regenerate a lot after surgery. This is good news for patients. It means a lot of liver tissue can be removed and the liver can heal.
We know the liver’s ability to heal is very important. It’s a key reason liver surgery can be successful. Understanding how the liver regenerates helps us appreciate its amazing healing powers.
What is Liver Resection?
Liver resection, or hepatic resection, is a surgery that removes a part of the liver. It’s done for many reasons, like removing tumors or treating liver diseases.
Definition and Medical Purposes
Liver resection means taking out a part of the liver. It’s used to treat liver cancer, remove tumors, and fix liver injuries that other treatments can’t fix.
We do liver resections for:
- Removing primary liver tumors or metastases
- Dealing with benign liver lesions
- Fixing liver damage from trauma
- Managing certain liver diseases
Types of Liver Resections
There are different liver resections, based on how much and where the liver tissue is removed. The main types are:
| Type of Resection | Description |
| Minor Resection | Removing one or two liver segments |
| Major Resection | Removing three or more liver segments |
| Anatomical Resection | Removing liver tissue by its segments |
| Non-Anatomical Resection | Removing liver tissue without following segments |
Common Conditions Requiring Liver Resection
Liver resection is needed for many liver issues, including:
- Liver Cancer: Like hepatocellular carcinoma
- Metastatic Tumors: Tumors that spread to the liver
- Benign Lesions: Non-cancerous growths like adenomas
- Liver Trauma: Severe liver injuries
Understanding liver resection helps patients see the complexity of this surgery. It shows how it treats various conditions.
How Much of the Liver Can Be Safely Removed?
Liver resection is a complex procedure. Knowing the safe limits of liver removal is key for success. The liver can grow back, which helps it handle big surgeries.
Usually, up to 70% of the liver can be removed if the rest is healthy. This rule is based on the liver’s ability to heal itself. It also ensures enough liver function for detox and metabolism.
The 70% Threshold Explained
The 70% rule is a general guideline, not a strict rule. It’s based on years of clinical experience and research. When up to 70% of the liver is taken out, the rest must be enough to keep the body going until it heals.
Liver regeneration is a complex process. It involves many liver cells working together. It depends on the patient’s health, any liver diseases, and the quality of the remaining liver.
Factors Affecting Safe Resection Volume
Several factors affect how much liver can be safely removed. These include:
- The health and quality of the remaining liver tissue
- The presence of underlying liver conditions such as cirrhosis or steatosis
- The patient’s overall health status and ability to recover from surgery
- The expertise of the surgical team and the quality of post-operative care
Understanding these factors is vital for safe liver resection. By carefully considering these, surgeons can improve outcomes and lower risks.
When a Doctor Removed Liver During Surgery: Procedure Explained
Liver resection surgery is a complex process. It requires a detailed check-up before surgery and skilled hands during it. When a surgeon removes part of the liver, it’s important to know the steps involved.
Preoperative Assessment and Planning
We do a detailed check-up before surgery. This helps us understand the patient’s health and the liver disease’s extent. We look at:
- Detailed medical history and physical examination
- Imaging studies like CT scans and MRI to see the liver’s shape and disease spread
- Liver function tests to check how well the liver is working
Accurate preoperative planning is key. It helps us choose the best surgery approach and prepare for possible issues.
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
The surgery has several important steps:
- Making an incision to reach the liver
- Dissecting the liver to find and tie off blood vessels and bile ducts
- Removing the diseased liver part while keeping healthy tissue
- Rebuilding the liver and closing the incision
Precision is critical to avoid blood loss and ensure the liver works right after.
Intraoperative Monitoring and Considerations
During surgery, we watch several key things:
| Parameter | Importance | Monitoring Method |
| Blood Loss | Too much blood loss can cause problems | Watching vital signs and blood loss closely |
| Liver Function | Ensuring the liver can support the body | Testing liver function during and after surgery |
| Anesthesia Levels | Keeping the right anesthesia for comfort and safety | Monitoring anesthesia levels all the time |
By managing these factors well, we can reduce risks and improve surgery outcomes for patients.
Modern Surgical Techniques for Liver Resection
Modern surgery has changed liver resection for the better. New tech and methods make procedures safer and more effective. We’ll look at the latest techniques, like open surgery, laparoscopic, and robotic-assisted liver surgery.
Traditional Open Surgery Approaches
Open surgery for liver resection uses a big cut in the belly. It’s been a mainstay for years, used for complex cases. The big plus of open surgery is seeing the liver and nearby areas clearly, making precise cuts easier.
But, open surgery takes longer to recover from and hurts more after surgery. Yet, it’s a key option for some patients needing liver surgery.
Laparoscopic Liver Surgery Benefits
Laparoscopic liver surgery uses small cuts and a laparoscope. It’s popular for less pain, shorter stays, and quicker healing. It’s best for smaller tumors or lesions.
This method needs special training. But, its benefits make it a good choice for many.
Robotic-Assisted Liver Surgery Advancements
Robotic-assisted liver surgery is the newest in minimally invasive surgery. It uses a robot to improve the surgeon’s skills, like precision and control. It offers better views and more accurate cuts than traditional laparoscopy.
The robot helps by reducing hand shakes and showing a 3D view. This makes it a favorite for liver surgery.
Choosing the Right Surgical Approach
Choosing a surgery method depends on many things. Like the patient’s health, the tumor’s size and location, and the surgeon’s skill. A team approach helps pick the best surgery for each patient. We work with patients to find the best plan for them.
In short, modern liver surgery offers many options. Knowing the pros and cons of each helps us give personalized care. This ensures the best results for each patient.
Recovery After Liver Resection Surgery
The journey to recovery after liver resection surgery includes several key steps. These include immediate post-operative care and monitoring. We know this time can be tough for patients. Our goal is to offer full support during the recovery.
Immediate Post-Operative Care
Right after surgery, patients are watched closely in the ICU or a special recovery area. Our medical team manages pain, looks for complications, and checks the patient’s overall health. This early stage is key for a good recovery.
Patients get pain relief through medicines, and we keep a close eye on them. We also teach them breathing exercises and how to move to avoid problems like pneumonia or blood clots.
Typical Recovery Timeline (4-8 Weeks)
The recovery time after liver resection surgery is usually 4 to 8 weeks. It’s important to follow our post-operative instructions closely for a smooth recovery.
- In the first week, patients often feel a lot of pain and tiredness, needing lots of rest.
- By 2-4 weeks, most can start doing light activities, like short walks, but should avoid hard tasks.
- At 4-8 weeks, patients can usually go back to most of their normal activities, but might feel tired.
Monitoring Liver Function and Regeneration
Watching liver function and regeneration is a big part of recovery. We do regular blood tests to check liver enzymes and function, making sure the liver is healing well and working right.
Liver regeneration is amazing, and we keep a close eye on it through tests and blood work. Patients are told to eat well and avoid alcohol to help their liver during this time.
Potential Complications and Risks
Liver resection surgery comes with risks and complications. It’s important for patients and doctors to know these to get the best results.
Short-Term Surgical Complications
Like other big surgeries, liver resection can have immediate problems. These include:
- Bleeding and hemorrhage: There’s a chance of losing a lot of blood during or after surgery.
- Infection: Any surgery can lead to infection.
- Bile duct injury: Damage to the bile ducts can cause leaks or blockages.
- Liver failure: The liver might not work right after surgery, if a big part is removed.
Long-Term Health Considerations
After surgery, patients may face ongoing health issues. These can be:
- Liver regeneration issues: Sometimes, the liver doesn’t grow back as hoped.
- Metabolic changes: Changes in liver function can affect overall health.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Patients might need to change their diet due to liver changes.
Impact on Cancer Recurrence Rates
For cancer patients, liver resection raises concerns about cancer coming back. Factors include:
- The original cancer stage: How big the cancer was can affect if it comes back.
- Surgical margins: It’s key to remove tissue with clear edges.
- Adjuvant therapies: Treatments like chemotherapy can change the chance of cancer coming back.
It’s vital for patients to talk to their doctors about these risks. This way, they can make informed choices about their treatment.
Survival Rates and Outcomes After Liver Resection
It’s important for patients and doctors to understand what happens after liver surgery. This surgery removes part of the liver for different reasons, like cancer or tumors. Knowing the results helps everyone make better choices.
The success of liver surgery is seen in how long patients live and their quality of life. Thanks to new surgical methods and better care before and after surgery, results have gotten much better.
Outcomes for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
Surgery for cancer that has spread to the liver can greatly improve survival chances. Research shows that some patients can live up to five years after surgery. This is a big improvement.
How long a patient lives depends on how much cancer is in the liver and if it’s in other parts of the body. Doctors use a team approach, including chemotherapy, to help patients do better.
Outcomes for Primary Liver Tumors and Other Conditions
For tumors that start in the liver, like HCC, surgery can be a cure. The success of surgery depends on the size of the tumor, how well the liver works, and any liver disease.
Studies show that some HCC patients can live up to five years after surgery. For other liver cancers, surgery might also offer a chance for a cure.
| Condition | 5-Year Survival Rate | Influencing Factors |
| Metastatic Colorectal Cancer | 30-58% | Extent of liver involvement, extrahepatic disease |
| Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) | Up to 70% | Tumor size, liver function, underlying liver disease |
| Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma | Varies | Tumor location, surgical margins, lymph node status |
Results after liver surgery vary a lot. They depend on the type of problem, how much surgery is needed, and the patient’s health. A team of doctors is key to finding the best treatment and predicting how well a patient will do.
Alternatives When Complete Liver Removal Isn’t Possible
For those who can’t have their liver removed, there’s hope. If removing the liver is not an option because of damage or disease, other treatments are needed.
Liver Transplantation Options
Liver transplantation is a good choice for severe liver problems. It involves swapping a sick liver with a healthy one from a donor. This is for patients with advanced liver disease, certain cancers, or sudden liver failure.
The transplant process includes:
- Evaluation to see if you’re a good match
- Being listed for a transplant
- The transplant surgery
- Monitoring and care after surgery
For more on liver cancer treatment, including transplant, check MD Anderson’s liver cancer treatment page.
Non-Surgical Treatment Alternatives
For those not suited for surgery or transplant, non-surgical treatments can help. These include:
- Ablation therapies: Methods like radiofrequency or microwave ablation to kill cancer cells
- Embolization therapies: Ways to block blood flow to liver tumors
- Chemotherapy and targeted therapy: Treatments that slow disease growth
- Radiation therapy: Beams that target cancer cells
These treatments can be used alone or together, based on the patient’s condition and health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while we can’t remove the whole liver, we can take out big parts of it. At Livhospital.com, we focus on giving top care to patients getting liver surgery. We aim for the best results for everyone.
Liver surgery is complex and needs careful planning before it starts. Our team follows the latest research and standards for liver surgery. This way, we make sure patients get the best care possible.
Understanding how the liver can grow back is key to safe surgery. Knowing this helps us give patients the right info and support. This leads to a successful surgery for them.
We work hard to give top-notch healthcare to patients from all over. Our goal is to make sure every patient gets care that’s just right for them. This includes help from the start to after they recover.
FAQ
Does the liver regenerate after surgery?
Yes, the liver can regrow after surgery. This includes after a liver resection or hepatectomy. This ability helps patients recover from such procedures.
Can a portion of the liver be removed?
Yes, parts of the liver can be removed. This is done through a procedure called liver resection or hepatic resection. It’s often used to remove tumors or diseased liver parts.
How much of the liver can be safely removed?
Up to 70% of the liver can be removed safely. This is if the remaining liver tissue is healthy. The safe amount removed depends on the patient’s health and the liver’s condition.
What is liver resection?
Liver resection, or hepatic resection, is a surgery that removes a liver part. It’s done for medical reasons, like removing liver tumors.
What are the benefits of laparoscopic liver surgery?
Laparoscopic liver surgery has many benefits. These include smaller cuts, less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times. This is compared to traditional open surgery.
How long does it take to recover from liver resection surgery?
Recovery from liver resection surgery usually takes 4-8 weeks. But, this time can vary based on the patient’s health and surgery extent.
What are the possible complications of liver resection?
Liver resection, like any major surgery, has possible complications. These include short-term and long-term health issues. It’s important for patients and healthcare providers to understand these risks.
Can liver resection improve survival rates for certain conditions?
Yes, liver resection can improve survival rates for some conditions. This includes metastatic colorectal cancer and primary liver tumors.
What alternatives are available when liver resection is not possible?
When liver resection isn’t possible, other options are considered. These include liver transplantation and non-surgical treatments. The choice depends on the patient’s condition and health.
How is liver regeneration monitored after surgery?
Liver function and regeneration after surgery are closely monitored. This is done through various tests and exams. It ensures the liver is recovering as expected.
Reference
Lim, J. S. H., et al. (2024). Liver resection, and technical advances to mitigate post-hepatectomy liver failure: A multicenter prospective study. Annals of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, 28(2), 53-68.

































