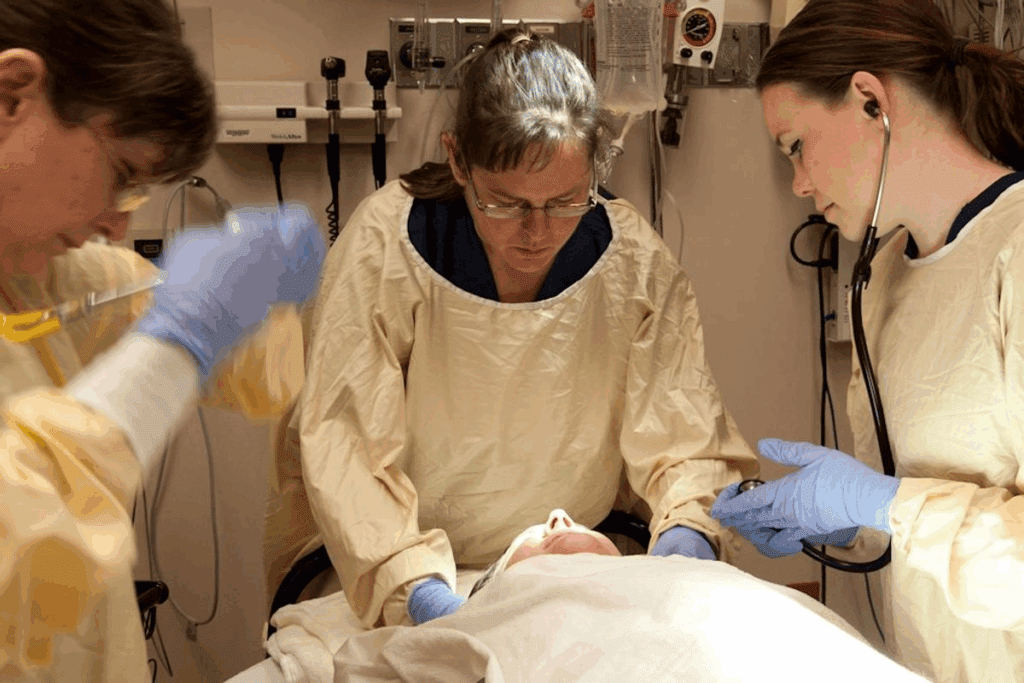
Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries trauma surgeon duties.
These medical professionals assess the condition of critically injured patients. They perform emergency surgeries to stabilize their condition. Their expertise also includes providing critical care surgery. They manage the complex needs of trauma patients throughout their recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries.
- They perform emergency surgeries to save lives and stabilize patients.
- Critical care surgery is a key part of their duties.
- Trauma patient care involves managing complex medical needs during recovery.
- The role requires a broad range of skills, from initial assessment to surgical intervention.
The Role of Trauma Surgeons in Emergency Medicine
Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries.
Defining Trauma Surgery as a Specialty
Trauma surgery is a special part of surgery. It deals with sudden injuries. Trauma surgeons learn to handle many injuries, from broken bones to internal bleeding.
This job needs technical skills, knowledge, and the ability to stay calm under pressure.
Differences Between Trauma Surgeons and Other Surgical Specialists
Trauma surgeons are different because they handle many injuries at once. They don’t just focus on one part of the body. They need to understand how different injuries work together.
They also have to decide which injuries to treat first. This is based on how serious each injury is.
| Characteristics | Trauma Surgeons | Other Surgical Specialists |
| Scope of Practice | Manage multiple types of injuries across various body systems | Focus on specific areas of the body or types of surgery |
| Training | Broad-based training in trauma care and surgery | Specialized training in their area of expertise |
| Work Environment | Often work in emergency settings, requiring rapid decision-making | May work in elective or scheduled surgery settings |
Primary Trauma Surgeon Duties in the Emergency Department
Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries.
Rapid Response and Initial Patient Evaluation
When a patient arrives, trauma surgeons must act fast. They focus on those with severe injuries first. They do a quick check to see if the patient’s airway, breathing, and circulation are okay.
Key components of the initial evaluation include:
- Assessing the patient’s airway, breathing, and circulation
- Identifying possible bleeding or other serious injuries
- Calling in the trauma team for help
Critical Decision-Making in the Golden Hour
The “golden hour” is the first hour after an injury. It’s when quick medical action can greatly improve patient outcomes. Trauma surgeons must decide fast on surgery, imaging, and other treatments.
“The first hour after injury is the most critical period for determining patient outcomes. Prompt and effective treatment during this time can significantly reduce morbidity and mortality.”
Good decision-making in this time needs clinical skill, experience, and awareness. Trauma surgeons must quickly understand diagnostic results and decide on surgery.
| Decision Point | Key Considerations | Potential Interventions |
| Initial Assessment | Airway, Breathing, Circulation | Intubation, Oxygen Therapy, Fluid Resuscitation |
| Diagnostic Imaging | X-rays, CT Scans, Ultrasound | Surgical Intervention, Angioembolization |
| Surgical Intervention | Nature and Severity of Injuries | Damage Control Surgery, Definitive Repair |
By making quick, informed decisions, trauma surgeons can greatly improve patient care in the emergency department.
Trauma Assessment and Diagnostic Responsibilities
Trauma assessment is key in emergency medicine. It needs a careful plan to find and fix injuries fast. Trauma surgeons use both clinical checks and special tools to spot serious problems quickly.
Primary Survey (ABCDE) Techniques
The primary survey quickly finds life-threatening injuries. It uses the ABCDE method:
- A – Airway care with neck protection
- B – Checking breathing and air flow
- C – Looking at blood loss and circulation
- D – Examining the nervous system
- E – Checking the body and environment
This method makes sure serious injuries are found and treated right away.
Secondary Survey Protocols
After the first check, a second survey looks for more injuries. It’s a detailed check from head to toe, including:
- Taking a full medical history
- Doing a detailed physical check
- Running important tests
This step is key to finding injuries that weren’t seen at first.
Utilizing Advanced Imaging and Diagnostic Tools
Modern imaging and tests are vital in trauma care. Tools like computed tomography (CT) scans, ultrasound, and X-rays help see how bad injuries are. They help doctors make the best choices for patient care.
Good trauma care mixes clinical skills, careful checks, and modern tools. By sticking to these steps and using the right tools, trauma surgeons can give the best care to trauma patients.
Resuscitation and Patient Stabilization Procedures
Resuscitation and stabilization are key in initial trauma care. They need quick and accurate actions. Trauma surgeons must know how to use advanced life support techniques well.
Advanced Trauma Life Support Implementation
The Advanced Trauma Life Support (ATLS) protocol helps manage acute trauma cases. It focuses on checking the patient’s airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs) first. Then, it does a detailed secondary survey to find all injuries.
ATLS implementation means fast assessment and action. It makes sure critical conditions are treated quickly.
Fluid and Blood Product Administration
Fluid resuscitation is vital in initial trauma care. It aims to restore blood volume and keep vital organs well-perfused. The choice between crystalloids and colloids, and when to use blood products, depends on the patient’s situation and injuries.
Damage control resuscitation aims to use fewer crystalloids. It also focuses on using blood products early to prevent bleeding problems.
Managing Shock and Hemodynamic Instability
Shock is a serious condition that needs quick action. Trauma surgeons must be good at spotting the type of shock and treating it right.
To manage hemodynamic instability, a mix of fluid resuscitation, blood products, and medicine is used. The goal is to get vital organs well-perfused again.
Emergency Surgical Interventions and Operative Care
Effective emergency surgical care is key for trauma patients. It needs a detailed approach to care. Trauma surgeons must act fast and do complex surgeries under pressure.
Damage Control Surgery Approaches
Damage control surgery is vital for severely injured patients. It starts with surgery to stop bleeding and prevent infection. Then, the patient is resuscitated and gets definitive surgery later.
Key principles of damage control surgery include:
- Rapid control of hemorrhage
- Control of contamination
- Temporary closure of the abdomen
- Resuscitation in the ICU
- Definitive surgery once the patient is stabilized
Time-Critical Operative Techniques
Time is of the essence in emergency surgery. Surgeons need to quickly fix vital functions and prevent more harm. They use their skills and judgment to decide the best steps for each patient.
Managing Multiple Trauma Injuries Simultaneously
Handling multiple trauma injuries at once is a big challenge. Trauma surgeons must quickly assess injuries, decide what to do first, and work with a team.
| Injury Type | Initial Management | Definitive Care |
| Head Injury | Rapid assessment, stabilization | Neurosurgical intervention |
| Thoracic Injury | Chest tube insertion, stabilization | Thoracic surgery |
| Abdominal Injury | Damage control surgery | Definitive abdominal surgery |
Managing multiple trauma injuries needs a team effort. This includes trauma surgeons, nurses, and specialists. Good communication and clear roles are key to the best care for patients.
Critical Care Management in the Trauma ICU
Trauma ICU patients need careful care. This includes watching them closely and helping them recover. The goal is to keep them stable and prevent more harm.
Continuous Monitoring and Assessment
Watching patients closely is key in the trauma ICU. Healthcare teams keep an eye on vital signs and brain function. This helps spot problems early.
They use many tools to monitor patients. For example, they check blood pressure and oxygen levels. This helps them act fast if something goes wrong.
Ventilation and Respiratory Support
Many trauma ICU patients need help breathing. This is because of chest injuries or big surgeries. They might need a machine to breathe for them.
Doctors use special breathing techniques to protect the lungs. They also try prone positioning to help with breathing problems.
Managing Organ System Failures
Trauma patients can face organ failures. This can happen from their injuries or later complications. A team of experts works together to handle these issues.
For example, kidney problems might need dialysis. Heart issues might need special medicines or machines. The team acts fast to support failing organs.
With a detailed and active care plan, trauma ICU teams can make a big difference. They help patients recover better and live longer.
Comprehensive Trauma Surgeon Duties by Injury Type
Trauma surgeons handle many duties, depending on the injury type. They must be skilled in treating thoracic, abdominal, vascular, neurological, and orthopedic traumas. Each injury type needs a special approach.
Thoracic and Cardiopulmonary Trauma Management
Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries. heart, and major blood vessels. They often need quick actions like tube thoracostomy or thoracotomy for serious issues.
Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma Procedures
Abdominal and pelvic traumas are common in polytrauma patients. Trauma surgeons use FAST exams to find bleeding fast. They might do exploratory laparotomy to fix or remove damaged organs.
Vascular Injury Repair Techniques
Vascular injuries are tough because they can cause a lot of blood loss. Trauma surgeons use techniques like ligation, primary repair, and grafting to fix blood flow. The right method depends on the injury’s location and severity.
Coordinating Care for Neurological and Orthopedic Injuries
Trauma surgeons work with teams for neurological and orthopedic injuries. For neurological traumas, they team up with neurosurgeons. For orthopedic injuries, they work with orthopedic specialists. This ensures the patient gets the best care.
In summary, trauma surgeons face many challenges based on the injury type. Understanding these needs helps them provide better care and improve patient outcomes.
Wound Management and Surgical Recovery Oversight
Trauma surgeons are key in managing wounds and overseeing recovery after surgery. Good wound care is vital to avoid complications and get the best results for trauma patients.
Complex Traumatic Wound Care
Complex wounds need careful attention. This includes debridement, dressing, and sometimes negative pressure wound therapy. The aim is to help wounds heal and lower the chance of infection.
Infection Prevention and Control
Stopping infections is a big part of wound care. Ways to do this include antibiotic prophylaxis, using sterile technique for dressing changes, and watching for infection signs.
Surgical Site Monitoring and Intervention
Keeping an eye on the surgical site is key to catching problems early. This means checking how the wound is healing, looking for infection signs, and acting fast if needed.
By using these methods, trauma surgeons can greatly improve patient results. They can lower the chance of wound problems and help patients recover well from surgery.
Trauma Surgeon Duties in Team Leadership and Coordination
Trauma surgeons lead teams to care for critically injured patients. They make sure care is well-coordinated and meets each patient’s needs.
Directing Multidisciplinary Trauma Teams
Leading a trauma team is a big job. A trauma surgeon must be able to make fast decisions and communicate well. The team includes nurses, anesthesiologists, and other experts.
Key Responsibilities:
- Coordinating the initial assessment and stabilization of the patient
- Overseeing the implementation of treatment plans
- Making critical decisions regarding patient care
Collaboration with Subspecialty Services
Working with specialists is key for trauma care. Trauma surgeons team up with neurosurgeons, orthopedic surgeons, and vascular surgeons. This helps address specific injuries.
| Subspecialty Service | Role in Trauma Care |
| Neurosurgery | Manages head and spinal cord injuries |
| Orthopedic Surgery | Treats fractures and musculoskeletal injuries |
| Vascular Surgery | Repairs vascular injuries |
Communication with Emergency Medical Services
Talking to EMS is important for trauma surgeons. They get updates on the patient’s condition and guide pre-hospital care.
Post-Operative and Follow-Up Care Responsibilities
Trauma surgeons are key in patient care after surgery. They help with recovery and manage any problems that come up. Good care after surgery is vital for the best results and a smooth move to rehab.
Recovery Monitoring and Progression
Watching how patients recover is very important. Trauma surgeons keep a close eye on patients, looking for any changes. They check vital signs, how wounds heal, and the patient’s overall health regularly.
Complication Recognition and Management
Even with the latest surgery methods, problems can happen. Trauma surgeons must quickly spot and deal with issues like infections or bleeding. A top doctor said,
“The ability to recognize and respond to complications in a timely manner is a hallmark of excellent trauma care.”
Long-term Rehabilitation Planning and Coordination
Trauma surgeons also plan for long-term care. They work with teams to create plans for each patient. These plans cover physical, emotional, and social needs to help patients get back to their lives.
By focusing on these areas, trauma surgeons greatly improve patient outcomes. Good post-operative care and rehabilitation planning are key to managing trauma well.
Day-to-Day Trauma Surgeon Duties and Workflow
Effective trauma care depends on surgeons managing their work well. They need to balance urgent surgeries with planned ones. Trauma surgeons handle many tasks, from emergency surgeries to keeping detailed records.
Trauma Call Schedules and Readiness
Trauma surgeons take turns on call, ready to respond to emergencies anytime. They must stay physically and mentally sharp. This readiness is key to making quick, life-saving decisions.
Balancing Emergency and Scheduled Procedures
One big challenge for trauma surgeons is managing both urgent and planned surgeries. They need to manage their time well. They must also decide what to do first based on urgency and importance.
| Duty | Priority Level | Time Allocation |
| Emergency Response | High | Variable |
| Scheduled Surgeries | Medium | Fixed |
| Medical Record Management | Low | Flexible |
Documentation and Medical Record Management
Keeping accurate and timely records is key in trauma care. Surgeons must document patient information correctly. This data helps in future care decisions and is important for legal and administrative reasons.
“The art of medicine is long, but life is short.” – Hippocrates
This old saying highlights the need for good time management and prioritization in trauma surgery.
Administrative and Quality Improvement Responsibilities
Trauma surgeons do more than just operate. They handle important administrative tasks that keep a trauma center running smoothly. These tasks help ensure top-notch patient care, make the most of available resources, and follow all rules and regulations.
Trauma Center Protocol Development
Trauma surgeons help create and update care plans for trauma patients. These plans are based on the latest research and best practices. They aim to make care consistent and better for everyone.
Performance Improvement Initiatives
Improving quality is key in trauma care. Trauma surgeons lead efforts to review patient results, spot areas for betterment, and make changes to improve care quality.
Resource Allocation and Management
In a trauma center, managing resources well is essential. Trauma surgeons help decide how to use resources, manage money, and make sure the center is ready for emergencies.
| Administrative Duty | Description | Impact on Trauma Care |
| Protocol Development | Creating and updating care protocols | Standardizes care, improves outcomes |
| Performance Improvement | Analyzing outcomes, identifying improvements | Enhances quality of care, reduces errors |
| Resource Management | Allocating resources, managing budgets | Ensures readiness for emergencies, optimizes resource use |
Education and Training Obligations
Trauma surgeons are key in teaching the next generation. They share their knowledge and skills with aspiring surgeons.
Teaching Residents and Fellows
Trauma surgeons teach residents and fellows. They guide them in complex surgeries and offer feedback. They need technical skills, patience, and good communication to teach well.
Continuing Medical Education Requirements
Trauma surgeons must keep up with new discoveries. They do this through CME, like attending conferences and online courses. CME helps them stay licensed and up-to-date.
Trauma Team Training and Simulation
Trauma surgeons also train trauma teams. They use simulation exercises and team-building activities.
“Simulation-based training has been shown to improve team performance and reduce errors in high-pressure environments like trauma care”
, according to a study on trauma team training.
Research and Evidence-Based Practice Implementation
Trauma surgeons are key in advancing the field through research and evidence-based practice. This is important for better patient care and quality treatment.
Clinical Research Participation
Trauma surgeons take part in clinical research to create new treatments and improve old ones. This is vital for moving the field forward and giving patients the best care.
Adopting Innovative Surgical Techniques
Using innovative techniques is a big part of trauma surgery. Surgeons need to keep up with new methods and use them in their work to improve patient care.
Outcome Analysis and Quality Metrics
Outcome analysis helps check if treatments work and where they can get better. Trauma surgeons use quality metrics to see how they’re doing and make smart choices based on data.
By mixing research, evidence-based practice, and constant checking, trauma surgeons can give top-notch care to their patients.
Ethical and Legal Aspects of Trauma Surgery
Dealing with ethics and law is key in trauma surgery. Trauma surgeons make tough choices. They balance patient care with legal and ethical rules.
Informed Consent in Emergency Situations
Getting informed consent is hard in emergency trauma cases. Patients might not be able to say what they want. Surgeons must act for the patient’s best while following legal and ethical rules.
End-of-Life Decision Making
Trauma surgeons often make end-of-life decisions. They need to be sensitive and know the legal and ethical rules. These choices are made with the patient’s family and healthcare team.
Medicolegal Documentation Requirements
Good medicolegal documentation is vital in trauma surgery. It helps patient care and protects against legal problems. Surgeons must carefully document patient info, treatment plans, and decision-making.
The mix of ethics and law in trauma surgery requires a lot of professionalism and knowledge. Understanding these areas helps trauma surgeons give the best care. It also reduces legal risks.
Conclusion: The Evolving Landscape of Trauma Surgery
The field of trauma surgery is changing fast. New medical technologies and care methods are leading the way. Trauma surgeons play a crucial role in emergency medicine by managing life-threatening injuries.leadership.
They handle many tasks, from first checking patients to after-surgery care. Trauma cases are complex, so surgeons work with a team. They lead in making sure patients get the best care.
New technologies and surgical methods are changing trauma surgery. These advancements help trauma surgeons treat patients better. They can now offer more tailored care.
It’s important for trauma surgeons to keep up with new ideas and practices. This way, they can improve patient care and help make trauma surgery better.
FAQ
What are the primary responsibilities of a trauma surgeon in the emergency department?
Trauma surgeons quickly assess patients and make important decisions. They start life-saving actions within the golden hour.
What is the role of trauma surgeons in patient stabilization and resuscitation?
They use advanced trauma life support to manage shock and instability. They give fluids and blood to stabilize patients.
How do trauma surgeons assess trauma patients?
They use a systematic approach for assessment. This includes primary and secondary surveys and advanced diagnostic technologies.
What are the key differences between trauma surgeons and other surgical specialists?
Trauma surgeons need special skills and training for complex injuries. They work in high-pressure environments.
What is damage control surgery, and when is it used?
It’s a strategy for severely injured patients. It controls bleeding and contamination quickly. Then, the patient is stabilized before definitive repair.
How do trauma surgeons manage multiple trauma injuries simultaneously?
They prioritize injuries and work with teams. They use quick operative techniques to manage multiple injuries.
What are the responsibilities of trauma surgeons in the trauma ICU?
They monitor patients continuously and support ventilation. They manage organ system failures in critically ill patients.
How do trauma surgeons coordinate care for different types of injuries?
They coordinate care for various injuries. They work with subspecialty services for complete care.
What is the role of trauma surgeons in wound management and surgical recovery?
They oversee wound care and infection prevention. They monitor surgical sites for optimal recovery.
How do trauma surgeons balance emergency and scheduled procedures?
They manage call schedules and prioritize emergencies. They coordinate with OR staff for balancing procedures.
What are the administrative responsibilities of trauma surgeons?
They develop protocols and lead performance improvement. They manage resource allocation.
How do trauma surgeons stay current with the latest techniques and research?
They participate in continuing education and research. They adopt new techniques to improve outcomes.
What are the ethical considerations in trauma surgery?
They navigate consent in emergencies and end-of-life decisions. They also handle medicolegal documentation.
How do trauma surgeons contribute to the education and training of other healthcare professionals?
They teach residents and fellows. They participate in trauma team training and continuing education.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Trauma Surgeon Responsibilities Emergency Surgery Critical Care. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18496391/


































