Did you know that over 2 million PET scans are done every year in the United States? They help diagnose and monitor many medical conditions.
The duration of a PET scan can vary depending on factors such as scan type and patient health. This includes the scan type and the person’s health. A PET scan typically lasts between 30 minutes and a few hours, depending on the type of scan and patient factors.
Learning about the medical imaging process can ease worries. It makes the diagnostic test experience better for patients.
Key Takeaways
- The duration of a PET scan can vary based on the type of scan.
- Several factors influence the length of a PET scan procedure.
- Understanding the process can help reduce patient anxiety.
- PET scans are a key tool in medical imaging.
- The procedure usually lasts from 30 minutes to a few hours.
Understanding PET Scans: Basic Principles and Process

Learning about PET scans is key to understanding their role in health checks. PET scans are advanced imaging tools that show how our bodies work.
What is a PET Scan?
A PET scan, or Positron Emission Tomography scan, is a test that uses a special sugar to find diseases. It can spot cancer, brain issues, and heart problems. A tiny amount of radioactive sugar is given to the body, and the PET scanner picks up its signals.
This creates detailed pictures of what’s happening inside us. The benefits of PET scans include:
- They give metabolic info that other tests can’t.
- They find diseases early, before symptoms show.
- They check if treatments are working and if diseases come back.
How PET Scans Differ from Other Imaging Tests
PET scans are different from CT and MRI scans. While CT and MRI show body structures, PET scans look at how tissues work. This makes PET scans great for:
- Cancer diagnosis and staging: They see how far cancer has spread.
- Neurological assessments: They help diagnose and track brain and nerve problems.
- Cardiovascular evaluations: They check the heart’s function and health.
By mixing PET scan data with other images, doctors get a full picture of a patient’s health. This leads to better diagnoses and treatment plans.
The Complete PET Scan Timeline: From Preparation to Results
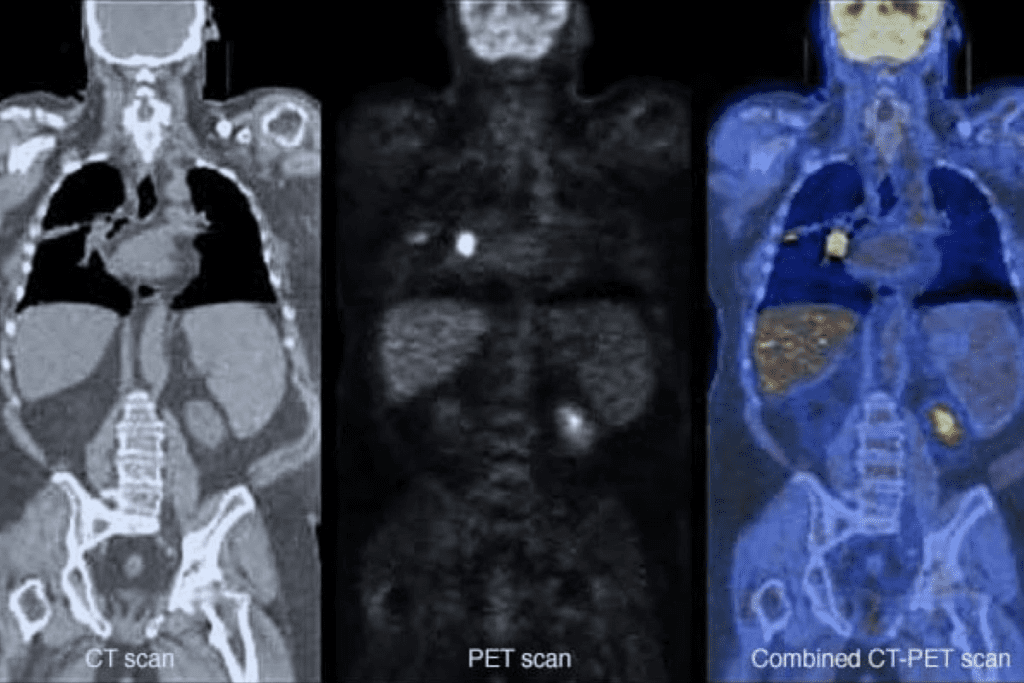
The PET scan timeline has several parts, like getting ready, getting the radiotracer, and the scan itself. Knowing these steps can make patients feel more at ease and ready for their test.
Pre-Scan Preparation Requirements
Before a PET scan, patients need to follow certain steps for the best results. These include:
- Dietary restrictions, like fasting for a while
- Avoiding hard exercise or certain medicines
- Removing jewelry or metal items that could mess with the scan
It’s key to follow the directions from the healthcare team or radiologist for a good scan.
Arrival and Registration Time
On the day of the PET scan, patients should arrive on time for registration. This involves:
- Checking in at the reception desk
- Providing ID and insurance info
- Filling out any needed paperwork or consent forms
After checking in, patients will be taken to the scanning area.
Radiotracer Injection and Uptake Period
A big part of the PET scan is getting a radiotracer injection. This is a tiny bit of radioactive material that shows how the body works. After the injection, the body absorbs the radiotracer. This time can change based on the scan type and radiotracer used.
Actual Scanning Duration
The PET scan itself usually takes 30 to 60 minutes. This depends on the scan type and body area being checked. During this time, the patient lies on a table that moves into the PET scanner. The scanner picks up signals from the radiotracer. The scan is usually painless, but some might feel claustrophobic or discomfort from staying very quiet for a long time.
Things that can affect how long the scan takes include:
- The scan’s complexity
- The patient’s health and ability to stay calm
- The technology used by the scanning place
Factors That Can Affect PET Scan Duration
The time it takes for a PET scan can vary. Knowing what affects it can help patients know what to expect. It also makes the scanning process more efficient.
Type of PET Scan Being Performed
There are many types of PET scans for different needs. The complexity of the scan can change its length. For example, a whole-body scan takes longer than one focused on the brain or heart.
PET scan types and their typical durations:
| PET Scan Type | Typical Duration |
| Whole-body PET scan | 30-60 minutes |
| Brain PET scan | 20-30 minutes |
| Cardiac PET scan | 30-45 minutes |
Patient-Specific Considerations
Things like a patient’s health and ability to stay calm during the scan matter. Patients with health issues or who feel anxious may need more time or special help.
Facility Equipment and Protocols
The technology and rules at the imaging center also affect scan time. Newer PET scanners and better software can speed up scans. Centers with efficient plans can also make the visit shorter.
Understanding these points helps patients prepare for their PET scan. They’ll know what to expect during the process.
Common Medical Conditions Evaluated with PET Scans
PET scans are used for many serious health issues, giving doctors important insights. They are a key tool in modern medicine. They offer both functional and anatomical information, helping diagnose and manage diseases.
Cancer Diagnosis and Staging
PET scans are very important in fighting cancer. They help see how far tumors have spread and if treatments are working. Cancer diagnosis and staging get better with PET scans because they show tumor activity.
The FDG-PET scan is often used for cancer. It uses fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) to find cancer cells. This scan is great for cancers like lymphoma, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer.
| Cancer Type | Use of PET Scan | Benefits |
| Lymphoma | Staging and assessing treatment response | Accurate assessment of disease extent and treatment efficacy |
| Lung Cancer | Diagnosis, staging, and evaluating recurrence | Improved accuracy in diagnosis and staging, guiding treatment decisions |
| Colorectal Cancer | Detecting recurrence and assessing metastasis | Early detection of recurrence, facilitating timely intervention |
Neurological Disorders
PET scans are also useful in neurology. They help diagnose and manage diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and epilepsy. They show brain function and metabolism, helping understand disease severity.
In neurology, PET scans can tell different types of dementia apart. They also check dopamine systems in Parkinson’s disease.
Cardiovascular Conditions
In cardiology, PET scans check heart muscle viability and coronary artery disease. They see if heart muscle can recover with treatment.
PET scans in cardiology look at heart perfusion and viability. They help decide if angioplasty or CABG is needed. Cardiovascular PET scans are key for heart function and viability, guiding treatment.
When PET Scans Are Not Recommended: Contraindications
Some conditions or situations make PET scans not suitable. It’s key to know these contraindications for patient safety and accurate results.
Absolute Contraindications
Absolute contraindications mean a PET scan is unsafe. Pregnancy is a big one because the scan’s radiation can harm the fetus. Another is known allergy to the radiotracer used in the scan.
Relative Contraindications
Relative contraindications are conditions that might make a PET scan risky. Diabetes can affect how the radiotracer works if not well-managed. Claustrophobia is also a concern because the scanner’s enclosed space can cause anxiety.
Special Population Considerations
Some groups need extra care with PET scans. Breastfeeding women might need to stop breastfeeding after a scan because of radioactive material in milk. Pediatric patients are also sensitive to radiation and need careful thought.
| Condition | PET Scan Consideration | Action |
| Pregnancy | Absolute Contraindication | Avoid PET scan unless absolutely necessary and after careful consideration. |
| Diabetes | Relative Contraindication | Manage blood sugar levels before the scan. |
| Claustrophobia | Relative Contraindication | Consider sedation or an open PET scanner. |
| Breastfeeding | Special Consideration | Temporarily stop breastfeeding after the scan. |
Knowing these contraindications helps healthcare providers use PET scans safely and effectively.
PET Scan Not Recommended: Clinical Scenarios and Alternatives
PET scans are valuable but not always the best choice for every medical condition. Their use depends on the condition, the patient’s health, and specific clinical scenarios.
Inappropriate Clinical Indications
There are times when PET scans are not the best choice. For example, if a condition is easily diagnosed with other tests, or if a PET scan won’t change treatment plans, other tests might be better.
For some injuries or infections, X-rays, CT scans, or ultrasounds are more suitable and cost-effective. PET scans are usually chosen when other tests are unclear or when detailed metabolic activity is needed.
When Other Tests Are More Appropriate
Often, other tests can give the needed information without a PET scan. For example, MRI scans are better for soft tissue and neurological conditions. CT scans are used for internal injuries and some cancers.
- MRI for soft tissue and neurological conditions
- CT scans for internal injuries and certain cancers
- Ultrasound for obstetric and some vascular conditions
The right test depends on the clinical presentation and suspected condition. A detailed clinical evaluation is key to choosing the best diagnostic path.
Knowing these rules is important for healthcare providers. It helps them make informed decisions about PET scans and guide patients through the diagnostic process.
PET Scan Limitations and Disadvantages
PET scans are a key tool in medical diagnostics but come with their own set of challenges. They help doctors diagnose and manage many conditions. Yet, it’s important for both doctors and patients to know about these limitations.
Technical Limitations
PET scans face technical hurdles. One big issue is the quality of the images they produce. This can be influenced by the type of tracer used and the PET scanner’s technology. Advanced PET scanners can improve image quality, but they’re not everywhere.
There are also challenges in detecting photons, which can lead to artifacts. This is more common in patients with metal implants or those who don’t follow pre-scan instructions. The quality of the scan also depends on how well the radiotracers are prepared and given.
Interpretation Challenges
Reading PET scans is complex and requires a lot of skill. False positives or negatives can happen for many reasons. These include patient movement, errors in correction, or certain medical conditions that affect tracer uptake.
How well a PET scan is interpreted also depends on the quality of the scan and the doctor’s experience. Standardizing protocols and training doctors are key to reducing mistakes.
Cost and Accessibility Issues
PET scans are pricier than other imaging tests like CT or ultrasound. This is mainly because of the cost of the scanner and the tracers. The high price can make them hard to get, mainly in areas with less healthcare or for those without good insurance.
Where you can get a PET scan is also a big issue. In some places, like rural areas, it’s hard to find a PET scan facility. This can be tough for people who can’t travel easily or need ongoing care.
| Limitation | Description | Impact |
| Technical Limitations | Resolution issues, artifacts from metallic implants | Affects image quality and diagnostic accuracy |
| Interpretation Challenges | Requires high expertise, potentially false results | Can lead to misdiagnosis or wrong treatment |
| Cost and Accessibility | High cost of PET scans and limited facility availability | Limits access to needed diagnostic care |
In summary, PET scans are valuable but have their own set of challenges. Understanding these can help doctors use them better in patient care. This way, they can balance the benefits with the drawbacks.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of PET Scans
It’s important to know the risks of PET scans for both patients and doctors. PET scans are useful for diagnosing, but they involve radiation and a radiotracer. These can cause side effects in some people.
Radiation Exposure Concerns
PET scans use a small amount of radiation from the radiotracer. Most patients are safe, but pregnant women and young kids should be careful. The radiation dose is usually between 4 to 7 millisieverts (mSv).
Key considerations regarding radiation exposure include:
- The risk of radiation-induced cancer, though small, is a worry.
- Pregnant women should avoid PET scans unless it’s really needed.
- The radiation dose is kept as low as possible (ALARA principle).
Allergic Reactions and Complications
Some people might have allergic reactions to the radiotracer in PET scans. These can be mild or severe. The injection can also cause reactions at the site.
Common allergic reactions and complications include:
- Mild reactions like rash or itching.
- Severe reactions, like anaphylaxis, though rare.
- Local reactions at the injection site, like redness or swelling.
Long-Term Safety Considerations
Research is ongoing about the long-term safety of PET scans. We know the immediate risks, but the long-term effects of repeated scans are not fully understood.
Long-term considerations include:
- The risk of increased cancer risk with repeated scans.
- The need for careful monitoring of patients who have many PET scans.
- Ongoing research to understand long-term risks and find safer options.
PET Scan Accuracy and False Results
It’s important to know how accurate PET scans are. They are a key tool in healthcare, but they’re not perfect.
Understanding False Positives
A false positive happens when a PET scan shows a condition like cancer that isn’t there. This can cause a lot of worry and extra tests. Things like inflammation, infection, or benign tumors can look like cancer on the scan.
Conditions like sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, and post-surgical inflammation can also cause false positives. Knowing this helps doctors understand PET scan results better.
Understanding False Negatives
A false negative is when a PET scan misses a real condition. This can delay getting the right treatment. The size and type of tumor, and how active the tumor cells are, play a big role.
Small tumors, low activity, and some cancers are more likely to be missed. This includes some prostate cancers.
Factors Affecting Scan Accuracy
Many things can change how accurate a PET scan is. This includes the type of tracer used, when the scan is done, how the patient is prepared, and the scanner’s tech. For example, moving during the scan can mess up the image.
To improve PET scan accuracy, prepare patients well, choose the right tracers, and use the latest scanner tech. Knowing what affects accuracy helps doctors make better choices.
Alternative Diagnostic Imaging Options
Diagnostic imaging has grown to include many options other than PET scans. Each has its own benefits and drawbacks. These alternatives are key for patients not fit for PET scans or when different info is needed.
CT Scans: Benefits and Limitations
CT scans are a common test that gives detailed images of the body. They are quick and have high-quality images, great for emergencies. But, they expose patients to a lot of radiation, a big drawback for those needing many scans.
CT scans are top for finding internal injuries, cancers, and heart diseases. They use X-rays from different angles to create detailed images.
MRI Scans: Benefits and Limitations
MRI scans are another choice, showing body parts without X-rays. They are great for soft tissues, helping with brain and spinal cord issues. But, they take longer than CT scans and can’t be used by everyone.
Patients with metal implants or pacemakers can’t have MRI scans. Those with claustrophobia also find them hard because of the machine’s design.
Ultrasound and Other Alternatives
Ultrasound uses sound waves to see inside the body. It’s good for the liver, kidneys, and thyroid, and for checking on babies during pregnancy.
Other options include X-rays for bones and lungs, and tests for bone density. The right test depends on the condition, patient health, and needed info.
| Imaging Test | Benefits | Limitations |
| CT Scan | Quick, high-resolution images | Significant radiation exposure |
| MRI Scan | High-contrast soft tissue images, no radiation | Long scanning times, contraindicated for some metal implants |
| Ultrasound | Non-invasive, no radiation, useful for certain organs | Limited depth penetration, operator-dependent quality |
Special Considerations: PET Scans During Pregnancy and for Diabetic Patients
Pregnant women and diabetic patients need special care when they get PET scans. This is to make sure they are safe and get the right diagnosis. We will look at what’s different for these groups.
Pregnancy and PET Scan Safety
PET scans during pregnancy are done with caution because of radiation risks. Radiation safety is key to avoid harming the fetus. This could lead to childhood cancer or developmental problems.
Doctors only use PET scans for pregnant women if it’s really needed. They weigh the benefits against the risks. Alternative imaging methods like ultrasound or MRI are chosen when they can be used instead.
Managing Diabetes for Accurate PET Scan Results
For diabetic patients, keeping blood sugar levels in check is important. High blood sugar levels can mess up how the radiotracer spreads. This could make the scan results not accurate.
Patients are told to follow a special diet or adjust their meds before the scan. This might mean fasting or changing their insulin schedule.
- Patients should tell their doctor about their diabetes plan.
- They might need to change their meds or insulin before the scan.
- It’s good to check blood sugar levels before and after the scan.
By managing diabetes and considering the needs of pregnant women, doctors can make PET scans safe and effective. This is for these special patient groups.
Conclusion: Making Informed Decisions About PET Scans
PET scans are a key tool in medicine, helping doctors understand many health issues. Knowing how PET scans work is important for your care. It helps you make smart choices about your health.
Thinking about a PET scan means looking at its good points and possible downsides. Things like the scan type, your health, and the equipment used can affect how well it works.
Knowing about PET scan advice helps you choose the right imaging tests. This lets you talk to your doctor about what’s best for you. It ensures you get the right test for your health needs.
Deciding wisely about PET scans is key to getting the best care. Understanding PET scans’ role in diagnosis and treatment helps you be more involved in your health. You can make choices that fit your situation and needs.
FAQ
What is a PET scan and how does it work?
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan is a medical test that shows how the body works. It uses a special tracer that is injected into the body. This tracer is then picked up by cells.
The PET scanner catches the radiation from the tracer. It makes detailed pictures of what’s inside the body.
How long does a PET scan usually take?
A PET scan’s time can vary. It depends on the scan type, the patient’s health, and the scanner. On average, it takes from 30 minutes to several hours.
What are the common medical conditions evaluated with PET scans?
PET scans are used for many health issues. They help find and track cancer, brain problems, and heart diseases. They show how far the disease has spread and if treatment is working.
Are PET scans safe for pregnant women?
PET scans are not usually safe for pregnant women. They might harm the unborn baby. But, in some cases, the benefits might be worth the risk. Doctors might suggest other tests or special PET scan setups.
Can diabetic patients undergo PET scans?
Yes, diabetic patients can have PET scans. But, they need to prepare carefully. This might mean changing their medicine, fasting, or checking their blood sugar.
What are the limitations and disadvantages of PET scans?
PET scans have some downsides. They can have technical problems and be hard to understand. They can also be expensive and not available everywhere. Some people might not be able to have them because of health issues or fear of tight spaces.
What are the risks and side effects of PET scans?
PET scans might have some risks. These include getting too much radiation, allergic reactions, and long-term health worries. But, these risks are usually small. Doctors try to make them even smaller.
Are there alternative diagnostic imaging options to PET scans?
Yes, there are other imaging tests. These include CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound. Each has its own good points and bad points. Doctors pick the best one for each patient.
How accurate are PET scans?
PET scans are usually right, but not always. They can sometimes show things that aren’t there or miss things that are. How accurate they are can depend on the tracer, how well the patient prepares, and the scanner.
What are the benefits of PET scans in cancer diagnosis and treatment?
PET scans are very helpful in fighting cancer. They help doctors see how big the cancer is, if treatment is working, and if it might come back. They help make treatment plans better and improve patient care.
References
- Kapoor, M., & Kasi, A. (2022). PET Scanning. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. Retrieved fromhttps://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559089/


































