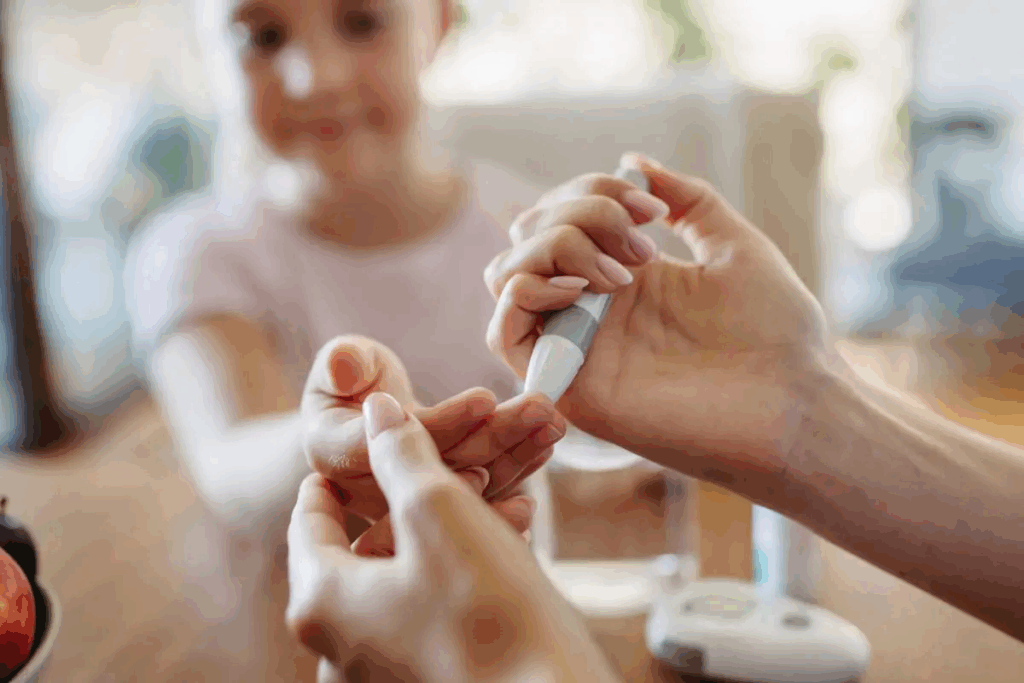
Rapid rises in glucose can happen for many reasons, not just what we eat. Stress hormones, our lifestyle, and some health conditions can lead to a glucose spike. Understand the key link between stress glucose level blood spikes. Learn the causes of high glucose and proven methods for effective control.
Anyone can have a glucose spike, even if they don’t have diabetes. Knowing why it happens is key to staying healthy and avoiding diabetes problems.
At Liv Hospital, we use the latest tests and create plans just for you to manage your blood sugar well.
Key Takeaways
- Many things can cause glucose spikes, like stress, diet, and lifestyle.
- It’s important to understand these reasons for good health.
- Custom plans can help control blood sugar.
- Advanced tests are vital for finding the real causes.
- Liv Hospital provides full support for those dealing with glucose issues.
Understanding Blood Sugar Regulation
Keeping blood sugar levels in check is essential. It involves many parts of our body working together. When we eat, our body breaks down food into glucose. This glucose then moves through our blood.
Insulin is key in helping glucose get into our cells. There, it’s used for energy or stored for later.
The Role of Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin and glucagon are two hormones from the pancreas. They help control blood sugar levels. Insulin lowers blood glucose by helping it get into cells. On the other hand, glucagon raises blood glucose by releasing stored glycogen.
The balance between these hormones keeps our blood sugar in a healthy range.
Normal Blood Sugar Ranges
Normal blood sugar levels are between 70 to 99 mg/dL when fasting. After meals, they can go up to 140 mg/dL. Keeping these levels right is key to avoid high or low blood sugar.
Stress can raise glucose levels. This happens because our body releases cortisol and adrenaline during stress.
Knowing how insulin and glucagon work is important. It helps us manage our glucose levels. This is key to controlling blood sugar spikes and staying healthy.
The Science Behind Blood Sugar Spikes

Understanding blood sugar spikes is key to managing glucose levels. These spikes happen when blood glucose levels jump up, often after eating foods high in carbs or sugar. We’ll look at how the body reacts to these spikes, focusing on the differences in how glucose is processed.
Immediate vs. Delayed Glucose Responses
The body’s glucose response can be quick or slow, depending on the food and our insulin sensitivity. Immediate glucose responses happen with foods like refined carbs and added sugars. These foods quickly raise blood glucose, leading to a big insulin release to help cells absorb glucose.
Delayed glucose responses come from eating complex carbs or meals with protein and healthy fats. These responses lead to a slower rise in blood glucose and a steady insulin release.
Glucose Response Type | Characteristics | Examples of Foods |
Immediate | Rapid increase in blood glucose, insulin surge | White bread, sugary drinks |
Delayed | Gradual increase in blood glucose, sustained insulin release | Oatmeal with nuts, vegetables |
How the Body Processes Glucose
Glucose processing starts with absorption into the bloodstream through digestion. Insulin, produced by the pancreas, is key in getting glucose into cells. This happens mainly in muscles and the liver for energy or storage.
Eating foods high in refined carbs and sugars leads to quick insulin spikes. High-carb meals without protein can also worsen glucose spikes. Knowing how foods affect glucose processing helps us manage blood sugar better.
Understanding blood sugar spikes helps us manage glucose levels. Knowing the science behind these spikes lets us make better food choices and lifestyle habits. This promotes stable blood sugar and better metabolic health.
What Spikes Blood Sugar Levels: What Makes Your Sugar Go Up and Does Pain Raise Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar levels can rise for many reasons. It’s important to know these to manage blood sugar well.
Physiological Pathways of Blood Sugar Elevation
There are several ways blood sugar can go up. Stress, whether it’s physical or emotional, makes our body release hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones help release glucose into the blood, getting ready for action.
Key physiological pathways include:
- The release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline
- The breakdown of glycogen to glucose in the liver
- Increased glucose production through gluconeogenesis
Pain can also make blood sugar levels go up. For example, a bad sunburn can cause glucose levels to rise. This is because pain is seen as a stressor, leading to the release of stress hormones.
The Difference Between Acute and Chronic Spikes
It’s important to know the difference between acute and chronic blood sugar spikes. Acute spikes happen quickly, like after eating or getting stressed. They usually go back to normal once the cause is gone.
Chronic spikes, though, last longer. They can be caused by things like eating too much sugar, not moving enough, or constant stress. These long-term spikes can cause serious problems like insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
The main differences between acute and chronic spikes are:
- Duration: Acute spikes are short-term, while chronic spikes are long-term.
- Causes: Acute spikes can be triggered by immediate factors like meals or stress, whereas chronic spikes are often due to ongoing lifestyle factors.
- Impact: Acute spikes are generally less harmful than chronic spikes, which can lead to significant health issues.
Recognizing Blood Sugar Spikes: Signs and Symptoms
It’s important to know the signs of high blood sugar early. This helps prevent serious problems. When blood sugar goes up, the body shows signs. Knowing these signs helps you act fast.
Physical Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
High blood sugar shows in many ways. You might notice:
- increased thirst and dry mouth
- frequent urination
- fatigue and tiredness
- blurred vision
- slow healing of cuts and wounds
Drinking too much water can make it hard for your body to handle sugar. So, feeling thirsty and needing to pee a lot is a big warning sign.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Knowing when to get help is key. If you have:
- severe hyperglycemia symptoms
- confusion or trouble focusing
- severe dehydration
- vomiting or diarrhea that lasts more than a few hours
you need to see a doctor right away. Quick action can stop serious problems, like diabetic ketoacidosis, which is very dangerous.
Keep an eye on your blood sugar and how your body reacts. This way, you can manage your health better.
Stress and Blood Sugar: The Cortisol Connection
When we feel stressed, our body’s ‘fight-or-flight’ response kicks in. This releases hormones that affect our blood sugar levels. This natural response helps us react to threats, but long-term stress harms our glucose control.
The Fight-or-Flight Response
The fight-or-flight response is our body’s way to react to danger. It releases stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. Cortisol is key in controlling blood sugar by making glucose available in the blood.
- Cortisol helps the liver make glucose.
- It stops some cells from taking in glucose, so glucose is there for the brain and muscles.
How Psychological Stress Triggers the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
Psychological stress turns on the HPA axis, a system that controls stress response. The HPA axis leads to cortisol release, affecting glucose metabolism.
- The hypothalamus sends out corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
- CRH makes the pituitary gland release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH).
- ACTH makes the adrenal glands produce cortisol.
Cortisol’s Effect on Glucose Uptake and Production
Cortisol affects glucose in many ways. It boosts gluconeogenesis and stops muscles and fat from taking in glucose. This makes glucose available for the brain and other glucose-dependent tissues.
Knowing how cortisol and glucose interact is key to managing blood sugar, mainly when stressed. By understanding these physiological pathways, we can find ways to lessen stress’s impact on our glucose levels.
Dietary Factors That Cause Blood Sugar Spikes
The food we eat greatly affects our blood sugar levels. Some foods can cause spikes. Knowing how different foods impact our glucose is key to managing blood sugar.
High Glycemic Index Foods
Foods with a high glycemic index (GI) are quickly digested. This leads to a fast rise in blood sugar. Examples include white bread, sugary snacks, and refined grains. Regularly eating these foods can make you more likely to develop type 2 diabetes.
To control blood sugar, it’s best to eat fewer high GI foods. Choose low to moderate GI foods like whole grains, non-starchy veggies, and most fruits instead.
Refined Carbohydrates and Added Sugars
Refined carbs and added sugars also raise blood sugar quickly. They are quickly turned into glucose, causing blood glucose to spike. Common culprits include sugary drinks, baked goods, and processed snacks.
Lowering your intake of refined carbs and added sugars can help keep blood sugar stable. Eating whole, unprocessed foods as much as you can is a good strategy.
The Impact of Carbohydrate-Heavy Meals Without Protein
Meals high in carbs but low in protein can cause blood sugar to spike. Protein slows down carb digestion, which helps control blood glucose. Adding protein to meals, like lean meats, fish, or legumes, can help manage this.
It’s important to balance carbs with protein and healthy fats to manage blood sugar spikes after meals. This approach not only controls glucose but also supports overall nutrition.
Hydration and Blood Glucose Levels
Staying hydrated is key for our health, and it’s very important for managing blood sugar. If we don’t drink enough water, our bodies can’t work right. This includes keeping blood sugar levels in check.
How Dehydration Affects Insulin Sensitivity
Dehydration hurts insulin sensitivity, making it tough for glucose to get into cells. When we’re dehydrated, our bodies make more cortisol, a stress hormone that raises blood sugar. Proper hydration is key for keeping insulin sensitivity, helping glucose get into cells better.
Adequate water intake keeps our bodily fluids balanced. This is important for cells to work right, including those that regulate glucose.
The Relationship Between Water Intake and Glucose Control
Drinking enough water is linked to better glucose control. Water helps flush out extra glucose from the blood through urination. When we’re well-hydrated, our kidneys work better, lowering the risk of high blood sugar.
Studies show that even a little dehydration can raise blood glucose levels a lot. So, keeping adequate hydration is a simple yet effective way to manage blood sugar spikes.
Lifestyle Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Stability
Many lifestyle factors can change how stable our blood sugar is. These include sleep, smoking, and hormonal changes. Knowing about these can help us manage our blood sugar better.
Sleep Deprivation and Insulin Resistance
Not getting enough sleep can raise cortisol levels and make insulin resistance worse. When we don’t sleep well, our body can’t control glucose as well. This leads to higher blood sugar levels.
A study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism showed sleep issues hurt insulin sensitivity. Getting enough sleep is key for keeping blood sugar healthy.
Impact of Smoking on Glucose Metabolism
Smoking also affects how our body handles glucose. It can harm the pancreas and lower insulin production. This makes blood sugar levels go up. Smoking also causes inflammation, which makes insulin resistance worse.
Smoking’s effects on glucose are complex. It changes how our body uses insulin and regulates glucose. Quitting smoking is a big step towards better glucose metabolism and health.
Smoking Status | Impact on Glucose Metabolism |
Non-smoker | Normal glucose metabolism |
Current smoker | Impaired insulin sensitivity and glucose regulation |
Former smoker | Improved glucose metabolism compared to current smokers |
Hormonal Fluctuations During Menstrual Cycles
Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can also affect blood sugar. Shifts in estrogen and progesterone can change how well insulin works. This can lead to ups and downs in blood sugar levels.
It’s important for women with diabetes or at risk to watch their blood sugar closely during their cycle. Monitoring blood sugar levels closely during the menstrual cycle can help identify patterns and inform management strategies.
Non-Food Related Blood Sugar Spikes in Clinical Settings
Clinical settings face unique challenges in managing blood sugar levels, mainly in hospitals. Blood sugar spikes can happen for reasons not related to food, making patient care harder.
Stress-Induced Hyperglycemia in Hospitalized Patients
Stress-induced hyperglycemia is a big issue in hospitals. It affects up to half of the patients, even when they’re not eating. This happens because the body’s stress response releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
These hormones make the liver release glucose into the blood, raising blood sugar levels. We know managing stress is key in hospitals to keep blood glucose stable.
Medical Conditions That Affect Blood Sugar
Some medical conditions can also affect blood sugar levels in hospitals. For example, patients with diabetes, pancreatitis, or those having surgery may see blood glucose changes. This is because of their condition or the stress of surgery.
Medical Condition | Effect on Blood Sugar |
Diabetes | Directly impacts insulin production or sensitivity |
Pancreatitis | Can lead to inflammation of the pancreas, affecting insulin production |
Surgery | Stress response can cause hyperglycemia |
It’s important for healthcare providers to understand these factors. By knowing why blood sugar spikes happen, we can create better plans to help patients.
Effective Strategies to Control Blood Sugar Spikes
Managing blood sugar levels is key to staying healthy. It involves meal planning, staying hydrated, and exercising regularly. These steps help control blood sugar spikes and keep you healthy.
Balanced Meal Planning: Pairing Carbohydrates with Protein
One effective way to manage blood sugar is through balanced meals. Combining carbs with protein slows down glucose absorption. This reduces sudden spikes in blood sugar.
For example, a balanced breakfast with carbs and protein sets a stable tone for the day.
Medical Expert, a renowned nutritionist, once said,
“The key to managing blood sugar is not just about cutting down on carbs, but about creating a balanced meal that includes a good mix of protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.”
This method keeps blood sugar stable and provides energy all day.
Optimal Hydration Practices
Staying hydrated is vital for blood sugar management. Dehydration can raise blood sugar levels. Drinking enough water helps prevent this.
- Drink at least 8-10 glasses of water per day.
- Avoid sugary drinks that can cause a spike in blood sugar.
- Monitor urine color to ensure proper hydration; it should be pale yellow.
Exercise Recommendations for Glucose Management
Regular exercise is essential for managing blood sugar. It improves insulin sensitivity, helping glucose enter cells better. Both aerobic and resistance training are beneficial.
It’s recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises on two or more days a week. Enjoying your exercise routine makes it easier to stick to. This boosts its effectiveness in managing blood sugar levels.
Stress Management Techniques for Blood Sugar Control
Managing stress is vital for controlling blood sugar spikes. Many methods have shown to be helpful. Chronic stress can raise blood glucose levels because of stress hormones like cortisol. By using stress-reduction techniques daily, people can manage their blood sugar and health better.
Meditation and Mindfulness Practices
Meditation and mindfulness are great for stress management. They calm the mind, lower stress hormones, and boost insulin sensitivity. Regular meditation can lower cortisol levels, which helps control blood sugar.
Mindfulness, like deep breathing and mindful eating, also helps manage stress. Being more aware of thoughts and body sensations helps respond to stress better. This keeps blood sugar levels healthier.
Yoga and Other Physical Stress-Reduction Methods
Yoga combines movement with deep breathing, making it a good stress-reducer. It improves insulin sensitivity, lowers cortisol, and boosts well-being. Regular yoga practice is beneficial.
Other physical methods, like tai chi and walking, also help. They reduce stress and improve health, aiding in better blood sugar control.
Tracking Stress Patterns Alongside Blood Glucose
Tracking stress and blood glucose levels together offers insights. Using a stress diary or a mobile app logs stress and blood glucose. This helps spot patterns and connections.
This info helps create personalized stress management plans. It leads to better blood sugar control for individuals and healthcare providers.
Conclusion: Creating a Comprehensive Blood Sugar Management Plan
To control blood sugar spikes, we need to use many strategies. This includes changing our lifestyle and managing stress. A good plan includes eating right, managing stress, and making lifestyle changes.
By planning meals well, staying hydrated, and exercising, we keep our blood sugar stable. Stress management, like meditation and yoga, is also key. It helps us handle blood sugar better.
A solid plan helps people make smart health choices. It lowers the risk of problems from high blood sugar. We can help people control their blood sugar by giving them the right tools and advice.
FAQ:
What causes blood sugar spikes?
Blood sugar spikes happen through many ways. Stress hormones, what we eat, and our lifestyle play big roles. Stress makes our body release cortisol and adrenaline, raising glucose levels.
How does stress affect blood sugar levels?
Stress activates the body’s stress response. This leads to more cortisol, which blocks glucose uptake in muscles. It also boosts gluconeogenesis, causing blood sugar to rise.
What dietary factors contribute to blood sugar spikes?
Foods with lots of refined carbs and sugars cause quick insulin spikes. Eating high-carb meals without protein makes things worse, leading to blood sugar spikes.
How does dehydration impact blood sugar control?
Dehydration makes it harder for the body to move sugar into cells. It also makes it tough to get rid of excess glucose. Even a little dehydration can make blood sugar hard to control.
What lifestyle factors affect blood sugar stability?
Not getting enough sleep raises cortisol and makes insulin resistance worse. Smoking messes with glucose metabolism. Hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle can also affect blood sugar.
Can pain raise blood sugar levels?
Yes, pain can increase blood sugar levels. For example, sunburn can cause glucose levels to go up through stress pathways.
How can I manage blood sugar spikes?
To manage blood sugar spikes, pair carbs with protein to slow down absorption. Drink plenty of water. Do some moderate exercise like walking. Get 7-9 hours of quality sleep. Also, try stress-reduction techniques.
What stress management techniques can help control blood sugar?
Stress management techniques like meditation, mindfulness, yoga, and tracking stress can help. They help manage stress and keep blood sugar in check.
How can I create a complete blood sugar management plan?
To manage blood sugar, plan balanced meals, stay hydrated, exercise regularly, manage stress, and monitor blood glucose levels. This approach helps keep blood sugar levels stable and promotes good health.
References:
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7530333/


































