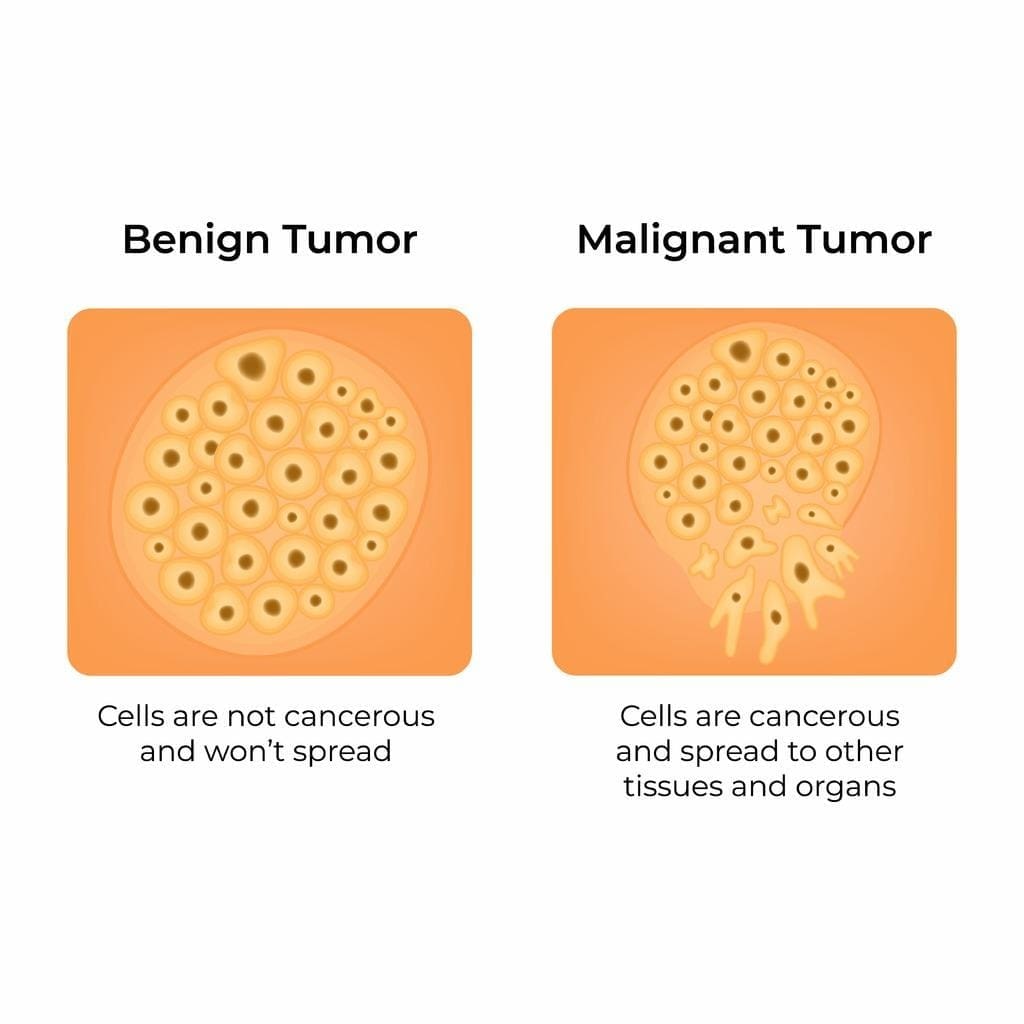
Getting a tumor diagnosis can be scary. But knowing if it’s benign or malignant is key. We’re here to help you understand the difference.
A benign tumor is not cancer and doesn’t harm nearby tissues or spread. In contrast, a malignant tumor is cancerous, grows into nearby tissues, and can spread. Knowing the difference is important for the right treatment and better health.
At Liv Hospital, we give our patients the knowledge and support they need. Knowing what kind of tumor you have is the first step to effective treatment and recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Benign tumors are non-cancerous and don’t spread to other parts of the body.
- Malignant tumors are cancerous and can invade nearby tissues and metastasize.
- The distinction between benign and malignant tumors is vital for treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers patient-centered care and support for tumor diagnosis and treatment.
- Understanding your tumor diagnosis is key to making informed decisions about your care.
Understanding Tumors: Basic Concepts and Definitions
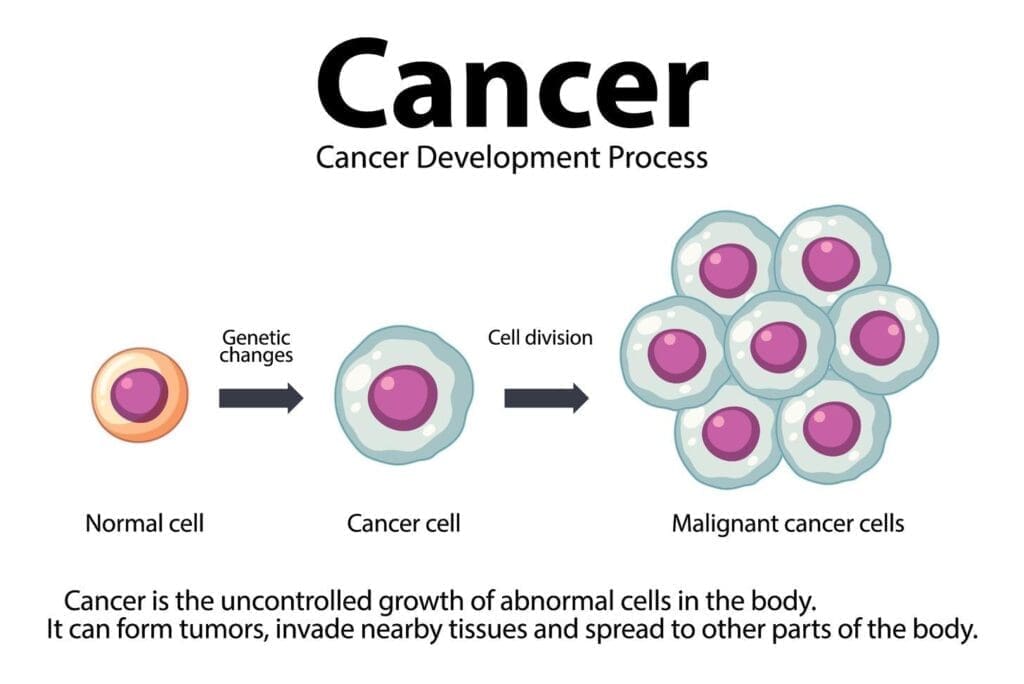
Tumors are abnormal cell growths that can be either benign or malignant. They can develop in any tissue or organ. Symptoms depend on their location, size, and nature.
What Exactly Is a Tumor?
A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue. It happens when cells divide more than they should or don’t die when they should. This can lead to health issues based on the tumor’s characteristics.
We divide tumors into two main types: benign tumors and malignant tumors. Benign tumors, like moles and uterine fibroids, grow slowly. They have smooth, defined borders and usually stay in one place.
How Abnormal Cell Growth Develops
Abnormal cell growth comes from genetic mutations. These mutations affect normal cell division and death. They can be caused by genetics, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices.
When cells grow abnormally, they form a mass. This mass may or may not cause symptoms. The growth pattern and behavior of these cells decide if the tumor is benign or malignant.
The Importance of Proper Tumor Classification
Proper tumor classification is key for treatment and predicting outcomes. It helps healthcare providers choose the best treatment plan.
Benign tumors don’t invade surrounding tissues or spread to other parts of the body. Malignant tumors can invade and metastasize, causing more severe health problems.
Benign Tumor Cancer: Characteristics and Behavior
Benign tumors are not cancerous and don’t spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors grow slowly and have clear edges.
Defining Features of Non-Cancerous Growths
Benign tumors grow slowly and have clear edges. They don’t invade nearby tissues or spread. This is why they’re usually not dangerous.
Growth Patterns and Well-Defined Boundaries
Benign tumors grow outward, pushing against nearby tissues. This makes them have clear edges.
Cellular Composition and Structure
Benign tumors have cells that look like the tissue they come from. They keep some normal function. This is different from cancer cells, which are very abnormal.
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
| Growth Rate | Slow | Rapid |
| Border Definition | Well-defined | Poorly defined |
| Metastasis | No | Yes |
| Cellular Structure | Resembles tissue of origin | Abnormal |
Malignant Tumors: Understanding Cancerous Growths
Malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body. They are dangerous because they grow fast and can spread quickly.
Defining Features of Cancerous Tumors
Cancerous tumors grow fast and have irregular shapes. This makes them hard to tell apart from normal tissue.
They also invade nearby tissues, causing harm. This is why treating them is so challenging.
Invasive Growth and Metastasis Process
Metastasis is how cancer spreads. First, it invades nearby tissue. Then, it enters the blood or lymph system.
Once in the bloodstream, it can reach other organs. This is why stopping its spread is key to treatment.
Cellular Abnormalities in Malignant Tissues
Malignant tissues have cells that grow out of control. They also have genetic mutations. These traits make them aggressive and hard to treat.
Studying these cells helps doctors find the right treatment. New tests help identify specific traits, leading to better care plans.
Key Differences Between Benign and Malignant Tumors
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors to choose the right treatment. The main differences are in how they grow, their borders, and if they can spread to other parts of the body.
Comparison of Growth Rates and Patterns
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t spread much. Malignant tumors grow fast and can spread to other areas. How fast and how a tumor grows is key to figuring out what it is.
- Benign Tumors: Slow-growing, expansive growth pattern.
- Malignant Tumors: Rapid growth, infiltrative growth pattern.
Borders and Tissue Invasion Capabilities
Benign tumors have clear borders and don’t invade nearby tissues. Malignant tumors have fuzzy borders and can spread to other tissues and organs.
- Benign tumors are typically encapsulated and do not invade surrounding tissues.
- Malignant tumors lack a clear capsule and can invade surrounding tissues and metastasize to distant sites.
Recurrence After Removal
Benign tumors rarely come back after being removed. Malignant tumors are more likely to come back. How likely a tumor is to come back depends on its type and how well it was removed.
- Benign Tumors: Low recurrence rate if completely removed.
- Malignant Tumors: Higher recurrence rate, if not completely excised.
Impact on Overall Health and Prognosis
Benign tumors usually don’t spread and have a good outlook. Malignant tumors can spread and have a worse outlook.
| Tumor Type | Growth Pattern | Metastasis | Prognosis |
| Benign | Slow, Expansive | No | Favorable |
| Malignant | Rapid, Infiltrative | Yes | Variable, often poorer |
Knowing these differences is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. Accurate diagnosis and classification help choose the best treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Common Types of Benign Tumors and Their Behaviors
Benign tumors are non-cancerous growths found in different parts of the body. We’ll look at the common types, their characteristics, and behaviors. This knowledge helps in deciding the right treatment.
Skin Growths: Moles, Lipomas, and Cysts
Skin growths are common benign tumors. Moles, lipomas, and cysts are often seen.
- Moles are usually harmless and are made of melanin-producing cells.
- Lipomas are soft, fatty tumors that are mostly benign. They can appear almost anywhere on the body.
- Cysts are abnormal, fluid-filled sacs that can form in the skin or other parts of the body.
These skin growths are usually not cancerous. They might not need treatment unless they cause symptoms or look bad.
Uterine Fibroids and Breast Fibroadenomas
Benign tumors can also happen in the reproductive system. Uterine fibroids and breast fibroadenomas are two examples.
- Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. They can lead to heavy menstrual bleeding and pelvic pressure.
- Breast fibroadenomas are benign breast tumors common in younger women. They are usually painless and can be removed if they cause discomfort or uncertainty.
Benign Tumors in Other Body Systems
Benign tumors are not just in the skin or reproductive system. They can happen in many other body systems.
| Body System | Common Benign Tumors | Characteristics |
| Nervous | Schwannomas, Neurofibromas | Slow-growing, often benign tumors arising from nerve tissue |
| Digestive | Adenomas, Lipomas | Benign tumors that can occur in the lining of the digestive tract or as fatty growths |
| Endocrine | Adenomas | Benign tumors of the endocrine glands, such as the thyroid or adrenal glands |
Knowing about different benign tumors is key for proper diagnosis and treatment. While they are not usually life-threatening, some can cause symptoms or complications that need medical care.
Diagnostic Approaches: Differentiating Between Benign and Malignant
Figuring out if a tumor is benign or malignant involves several steps. It’s key to get it right for the right treatment and to know how the patient will do.
Imaging Techniques for Tumor Assessment
Imaging is a big help in checking out tumors first. We use CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds to see the tumor’s size, where it is, and what it looks like. These tools help spot signs that might mean the tumor is bad.
For example, tumors that are bad often have weird shapes and can spread to nearby tissues. We can see these things on scans.
The Critical Role of Biopsy in Diagnosis
Even with scans, a biopsy is the best way to know for sure. It means taking a piece of the tumor for a closer look. Pathologists can then tell if it’s good or bad.
A study on PubMed shows how important biopsy results are for planning treatment.
Laboratory Tests and Tumor Markers
We also use lab tests and tumor markers to help figure things out. Tumor markers are things in the blood or tissues that might mean cancer is there. They’re not a sure thing, but they can give clues and help see if treatment is working.
Challenges in Accurate Diagnosis
Even with better tools, it’s not always easy to tell if a tumor is benign or malignant. Sometimes, they look the same, making it hard to decide. We have to look at all the info we get and sometimes do more tests to be sure.
Tumors are complex, so it’s not always simple. We need to use every tool we have to get it right.
Treatment Strategies Based on Tumor Classification
Choosing the right treatment for tumors depends on if they are benign or malignant. Knowing the difference is key. It affects treatment options, prognosis, and how well a patient can live with the condition.
Managing and Monitoring Benign Tumors
Benign tumors are not cancerous. They often need a gentler approach. Monitoring is common, with regular check-ups and scans to watch the tumor’s size and growth. Sometimes, surgical removal is needed if the tumor causes problems or grows in a bad spot.
For example, benign tumors like lipomas or uterine fibroids might not need treatment right away. Watchful waiting is an option. It lets patients avoid surgery but keeps an eye on the tumor.
Comprehensive Approaches for Malignant Tumors
Malignant tumors, being cancerous, need a stronger treatment plan. Multidisciplinary care often includes surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The right treatment depends on the tumor’s type, stage, and where it is, along with the patient’s health.
“The treatment of malignant tumors requires a coordinated approach, combining various modalities to achieve the best possible outcome.”
An Oncologist
Surgical Considerations for Different Tumor Types
Surgery is a common treatment for both benign and malignant tumors. For benign tumors, surgery aims to remove the tumor completely. For malignant tumors, surgery tries to remove the main tumor and sometimes affected lymph nodes or tissues.
| Tumor Type | Surgical Goal | Additional Treatments |
| Benign | Complete removal | None, or monitoring |
| Malignant | Remove primary tumor and affected tissues | Chemotherapy, Radiation Therapy |
Follow-up Care and Long-term Monitoring
Follow-up care is key for both tumor types. It helps catch any signs of the tumor coming back early. For malignant tumors, this might include scans, blood tests, and physical exams.
Dealing with a tumor diagnosis is tough. Our team is here to offer full care and support. We aim to help our patients get the best results possible.
Risk Factors and Prevention Measures
It’s important to know what can lead to tumors. Tumors can be benign or malignant. They are influenced by genetics, the environment, and lifestyle.
Common Risk Factors for Tumor Development
There are several things that can lead to tumors. These include:
- Genetic mutations from family or the environment
- Exposure to harmful substances like tobacco and chemicals
- Lifestyle choices like diet and exercise
- Infections from viruses and bacteria, like HPV
Table: Common Risk Factors and Their Associations
| Risk Factor | Associated Tumor Type |
| Tobacco Smoke | Lung, Mouth, Throat Cancer |
| UV Radiation | Skin Cancer |
| HPV Infection | Cervical, Anal, Oropharyngeal Cancer |
Lifestyle Modifications for Risk Reduction
Healthy choices can lower tumor risk. We suggest:
- Eating a balanced diet with fruits and veggies
- Staying active
- Avoiding tobacco and drinking less alcohol
- Protecting your skin from the sun
“Prevention is the best medicine. By understanding and mitigating risk factors, individuals can significantly reduce their likelihood of developing tumors.”
Screening Recommendations for Early Detection
Screening early is key to managing tumors. The right screening depends on age, gender, and risk. Common tests include:
- Mammograms for breast cancer
- Colonoscopy for colorectal cancer
- Pap smears for cervical cancer
- Low-dose CT scans for lung cancer in high-risk individuals
Liv Hospital’s Approach to Tumor Prevention and Care
At Liv Hospital, we focus on top-quality care and prevention. Our approach includes:
- Personalized risk assessment and counseling
- Advanced screening and diagnostic tools
- Teams for coordinated care
- Helping patients make healthy lifestyle choices
By understanding risks, taking preventive steps, and using advanced care, we can fight tumors together.
Conclusion: Understanding Your Diagnosis and Next Steps
Knowing if a tumor is benign or malignant is key to choosing the right treatment. We’ve looked at the main differences between these two types of tumors. This includes their characteristics, how they grow, and their effect on health.
Early detection and good medical care greatly improve treatment results for both types of tumors. By understanding your diagnosis, you can make smart choices about your care. This helps you manage your health well.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on giving you the best care and support during treatment. Our team is here to provide top-notch healthcare. We help you understand your diagnosis and guide you through treatment options.
Being informed and active helps you work well with your healthcare team. We aim to give you care that meets your specific needs. Our goal is to help you achieve the best health possible.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a benign and malignant tumor?
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t spread. Malignant tumors grow fast, spread, and can move to other parts of the body.
How are benign and malignant tumors diagnosed?
Doctors use X-rays, CT scans, MRI, biopsy, and lab tests to diagnose tumors. These methods help check the tumor’s cells and structure.
What are the common characteristics of benign tumors?
Benign tumors have clear edges, grow slowly, and don’t invade nearby tissues. They are usually not dangerous and can be removed by surgery.
What are the defining features of malignant tumors?
Malignant tumors grow fast, spread, and can move to other parts of the body. They are dangerous and need treatments like surgery, chemo, and radiation.
Can benign tumors become malignant?
Yes, some benign tumors can turn cancerous, but it’s rare. It’s important to watch them closely for any changes.
What are the risk factors for developing tumors?
Risk factors include genetics, exposure to harmful substances, infections, and lifestyle choices like smoking. Knowing these can help prevent and catch tumors early.
How are benign and malignant tumors treated?
Treatment depends on the tumor type. Benign tumors might just need watching or surgery. Malignant tumors need stronger treatments like surgery, chemo, and radiation.
What is the importance of proper tumor classification?
Correctly classifying tumors is key for choosing the right treatment and predicting outcomes. It helps doctors decide how to treat and what to expect.
Can malignant tumors be prevented?
Not all cancers can be prevented, but some risks can be lowered. Making healthy lifestyle choices, getting screened, and catching tumors early can help.
What is the role of screening in tumor detection?
Screening is vital for catching tumors early. It allows for better treatment and outcomes. It’s recommended for those at risk or during regular health checks.
References:
• Wikipedia. (n.d.). Benign tumor. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Benign_tumor
• Healthline. (n.d.). Benign tumors: Causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment. https://www.healthline.com/health/benign
• Cancer Research UK. (n.d.). Benign and malignant tumours and how cancers grow. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/what-is-cancer/how-cancers-grow





