Last Updated on November 14, 2025 by Ugurkan Demir
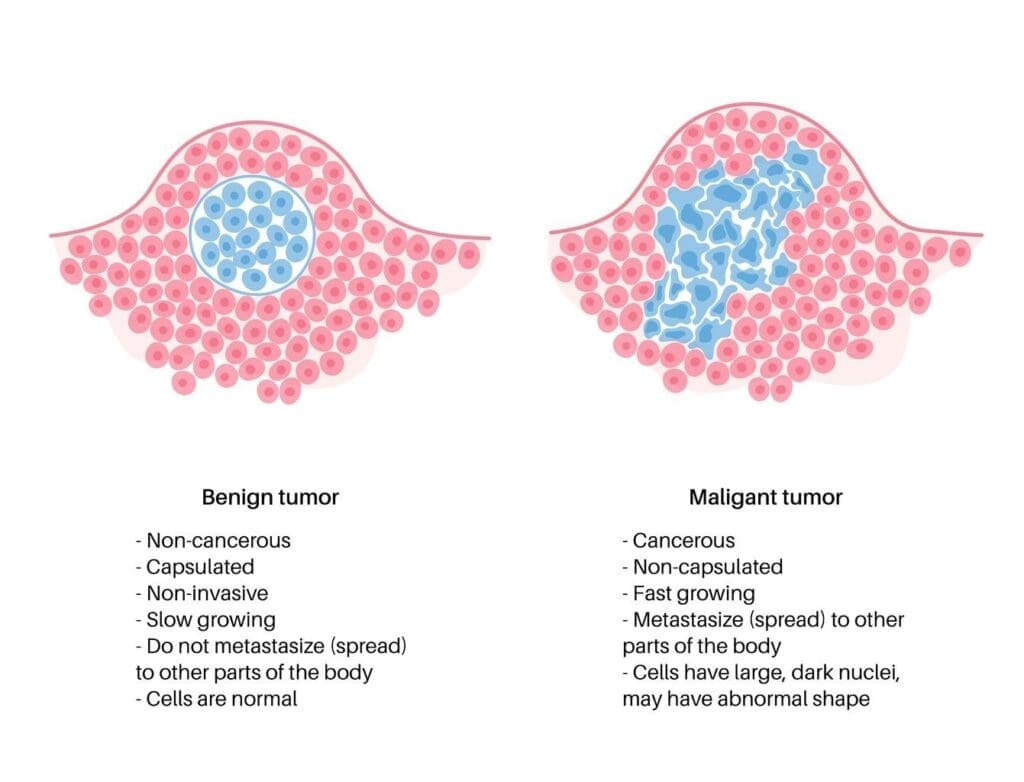
At Liv Hospital, we know that getting a tumor diagnosis can be scary. But, not all tumors are cancerous. A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that forms a lump or mass in the body. Tumors can be either benign or malignant.
The main difference between malignant and benign tumors is how they affect the body. Malignant tumors are cancerous and can grow into other tissues and spread. On the other hand, benign tumors are not cancerous and usually don’t spread.
Knowing what kind of tumor you have is key for the right treatment. At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare and support to our patients.
Tumors are divided into two main types. Knowing these types is key for planning treatment. Tumor classification helps doctors figure out what kind of tumor it is and how to treat it.
A tumor, or neoplasm, is an abnormal tissue mass. It happens when cells grow too much or don’t die when they should. These growths can be either benign or malignant, which is important for health.
Benign tumors are not cancerous. They don’t spread to other tissues or parts of the body. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous. They can spread to other areas and invade nearby tissues.
Tumors are classified as benign or malignant based on their behavior. Knowing this helps doctors tell the difference between the two.
Here are some key differences between benign and malignant tumors:
| Characteristics | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors |
| Growth Pattern | Slow, expansive growth | Rapid, invasive growth |
| Cellular Appearance | Cells resemble normal cells | Cells are abnormal and vary in size and shape |
| Metastasis | Do not metastasize | Can metastasize to distant sites |
For more details on how doctors check if a tumor is cancerous, visit Liv Hospital.
Benign tumors are not cancerous but can cause health problems. They can grow big enough to press on important organs. Knowing what they are is key to treating them right.
Benign tumors are different from cancerous ones. They are non-invasive and don’t spread to other parts of the body. Let’s look at these differences more closely.
There are many types of benign tumors, each unique. Some common ones include:
Benign tumors grow slowly and stay in one place. Their cells look like normal cells, with little abnormality. For more on benign vs malignant tumors, check out Baptist Health’s article.
In summary, benign tumors have clear differences from cancerous ones. Knowing these differences is vital for correct diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding malignant tumors is key to understanding cancer. We’ll look at what makes them different from benign tumors. We’ll see how they can harm patient health.
Malignant tumors can spread to other tissues and even to other parts of the body. This aggressive growth is what makes them cancerous. Their ability to spread and grow in new places is unique.
Invasion happens when cancer cells break through tissue boundaries. They can then enter blood vessels or lymphatic channels. Metastasis is when these cells start new tumors in other parts of the body. This complex process involves many cellular and molecular mechanisms.
Malignant cells have distinct features. They are irregularly shaped, have large nuclei, and grow quickly. These signs show their uncontrolled growth and genetic instability.
It’s important to know the difference between malignant and benign tumors. This knowledge helps doctors diagnose and treat them better. We’ll look at the main differences between these two types of tumors.
Malignant tumors have cells that look abnormal. These cells are often irregular in shape and size. Benign tumors, on the other hand, have cells that look like normal cells. These cells are usually the same in appearance.
Benign tumors grow slowly and are usually encapsulated. This makes them less likely to spread to nearby tissues. Malignant tumors grow faster and can spread to other areas of the body.
Malignant tumors can spread to other parts of the body. They do this through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. Benign tumors do not spread.
Benign tumors might come back if not all of it is removed. But this is usually not dangerous. Malignant tumors can also come back after treatment. They often need more intense treatment to manage.
| Characteristics | Malignant Tumors | Benign Tumors |
| Cellular Appearance | Abnormal, irregular cells | Normal, uniform cells |
| Growth Rate | Rapid growth | Slow growth |
| Invasion and Metastasis | Can invade and metastasize | Does not invade or metastasize |
| Recurrence | Can recur, often requires aggressive treatment | May recur if not completely removed |
Many people think all tumors are malignant, which can cause a lot of fear. We will look into why this myth exists and explain the difference between malignant and benign tumors.
The idea that all tumors are malignant comes from not knowing enough about tumors. Tumors are abnormal growths that can be either benign or malignant. The fear of cancer makes people think all tumors are cancerous.
Most tumors are actually benign. Studies show that benign tumors are much more common than malignant ones. For example:
Knowing the truth can help reduce fear and show why getting a proper diagnosis is key.
It’s very important to correctly classify tumors to know how to treat them. Benign tumors usually don’t need aggressive treatment and can be watched or removed. On the other hand, malignant tumors need strong treatments like surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
Understanding the difference between malignant and benign tumors is critical for good care. We must remember that not all tumors are malignant. Knowing this is essential for helping patients.
It’s important to know how common benign and malignant tumors are. This helps us understand cancer risk and make better health choices. We look at how often different tumors occur, their location, and who they affect most.
Benign tumors are more common than the harmful kind. Most tumors found are not cancerous. Many are discovered by chance during tests for other health issues.
Key statistics include:
Benign and malignant tumors happen more in some organs than others. For example:
Age, gender, and genetics affect who gets benign and malignant tumors.
Notable demographic patterns include:
Knowing these patterns helps doctors better understand risk. They can then plan better screening programs.
Getting an accurate diagnosis is key to figuring out what kind of tumor you have. This helps doctors plan the best treatment. We use different methods to tell if a tumor is benign or malignant. Each method gives us unique insights into the tumor.
Imaging is a big help in finding out about tumors. X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs help us see the tumor’s size, where it is, and what it looks like. These tools help us guess if a tumor is likely to be benign or malignant.
CT scans are great for finding tumors in organs inside the body. MRIs give us detailed pictures of soft tissue tumors. The right imaging tool depends on where and what kind of tumor we think it is.
A biopsy means taking a piece of tumor tissue for a closer look. Histopathology is when we look at this tissue under a microscope. This tells us if the tumor is benign or malignant.
When we do a biopsy, we check the tissue for any odd cell shapes or abnormal cell division. These signs can tell us if the tumor is likely to be malignant.
We also use molecular and genetic testing to learn more about the tumor’s genes. These tests look for specific genetic changes or markers linked to certain tumors.
This info is key for making treatment plans, mainly for malignant tumors. It helps us predict how the tumor might behave and how it might react to different treatments.
Screening recommendations change based on the tumor type, risk factors, and who the patient is. People at high risk for certain tumors, like breast or colon cancer, should get screened regularly.
For example, women over 40 should get mammograms to check for breast cancer. Those with a family history of colon cancer might need to start screenings earlier.
Knowing the warning signs and symptoms of tumors is important for catching them early. Look out for unexplained weight loss, changes in skin or moles, persistent pain, or unusual bleeding.
If you notice any of these, see a doctor right away. Catching tumors early can greatly improve treatment success.
Early detection is vital for better treatment results for tumor patients. Finding tumors early means they’re more likely to be treated successfully. This also increases the chances of survival.
Early detection often means less invasive treatments. This reduces the risk of complications and improves the patient’s quality of life.
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors to choose the right treatment. The type of tumor, where it is, and the patient’s health all play a role. Each case is unique.
Benign tumors usually don’t need a lot of treatment unless they cause problems. Watchful waiting is often the first step. This means checking the tumor with tests to see if it’s changing.
If needed, surgical removal can cure benign tumors. The goal is to take out the tumor without harming nearby tissue. Sometimes, minimally invasive surgical techniques are used. This means smaller cuts, less pain, and faster healing.
Malignant tumors, being cancerous, need more serious treatment. The main options are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. These are chosen based on the cancer’s type, stage, and the patient’s health.
Surgery tries to remove the tumor and some nearby tissue. Radiation therapy kills cancer cells with high-energy waves or particles. It can be from outside or inside the body. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells and is given through veins or by mouth.
Other treatments like targeted therapy and immunotherapy might also be used. Targeted therapy attacks specific cancer cells. Immunotherapy boosts the immune system to fight cancer.
Choosing a treatment for malignant tumors is very personal. It depends on the cancer’s details, the patient’s wishes, and their health. A team of doctors works together to create a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Dealing with tumors needs a team effort. This team makes sure patients get all the care they need from different experts.
Patients with tumors get help from many doctors. Each specialist is key in finding and treating tumors. Oncologists plan treatments, surgeons do operations, and radiologists use scans to check on tumors.
Pathologists look at tissue samples to figure out what kind of tumor it is. Nurses help patients with their care and support. Working together, these doctors and nurses make sure patients get the best care.
Creating a treatment plan is a big part of the team’s work. Plans are made just for each patient. They consider the tumor’s type, stage, and the patient’s health and wishes.
Patients might get surgery, chemo, or radiation, or a mix of these. The team works together to find the best plan. They keep checking and updating the plan to make sure it works best for the patient.
Patient-centered care is a big part of the team’s approach. It focuses on what the patient needs and wants. This makes sure care is personal and meets the patient’s unique situation.
This care model means doctors and patients talk openly. It helps patients make choices about their care. This way, care is not just better but also more effective.
It’s important to know the difference between benign and malignant tumors for good treatment and care. We’ve looked at what makes each type of tumor different. We’ve also talked about how to diagnose them and why a team of experts is key.
At Liv Hospital, we aim to give top-notch healthcare with full support for international patients. Our team works together to give care that fits each patient’s needs. This ensures the best results for our patients. Accurate diagnosis and treatment are key to managing tumors, as we’ve shown in this article.
We believe in working closely with patients and their families to offer the best care and support. Our dedication to outstanding healthcare is strong. We aim to make a real difference in the lives of those we help.
Malignant tumors are cancerous and can spread to other parts of the body. Benign tumors are non-cancerous and don’t spread or invade.
Tumors are classified by their growth patterns and how they spread. This helps doctors choose the right treatment.
Benign tumors grow slowly and don’t spread. They are usually contained and don’t come back after removal.
Malignant tumors can spread and invade tissues. They have irregular cells and can come back after being removed.
Doctors use imaging, biopsy, and histopathology for diagnosis. Molecular and genetic tests also help.
Accurate classification helps plan treatment and predict outcomes. Misclassification can lead to wrong treatments and worry.
No, not all tumors are malignant. Many are benign and don’t threaten health.
Benign tumors are often treated by removing them surgically or by monitoring them.
Malignant tumors may be treated with surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy. The choice depends on the tumor’s type and stage.
Early detection leads to better outcomes. It allows for timely treatment before the tumor grows or spreads.
A multidisciplinary team provides complete care. It includes surgeons, oncologists, and other specialists.
Tumor prevalence changes with age, gender, and other factors. Knowing these patterns helps assess risk and make decisions.
References:
• National Cancer Institute. (n.d.). What is cancer? – NCI. https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/understanding/what-is-cancer
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!