Have you had a cough that won’t go away, even with usual treatments? It might be linked to your thyroid health thyroid cough.
Studies show that thyroid issues, like goiter and nodules, can cause coughing. This happens because they press on the trachea and laryngeal nerves. We’ll look into how thyroid problems can lead to coughing, based on medical research.
It’s important to understand how thyroid issues and coughing are connected. This helps in finding the right diagnosis and treatment. By studying this link, we can find better ways to treat these problems.
Key Takeaways
- Thyroid disorders can cause coughing due to pressure on the trachea and laryngeal nerves.
- Goiter and nodules are common thyroid issues that can lead to coughing.
- Understanding the connection between thyroid health and coughing is essential for proper diagnosis.
- Effective treatment plans can be developed by addressing the underlying thyroid issues.
- Medical research supports the link between thyroid problems and respiratory symptoms.
The Connection Between Thyroid and Respiratory Symptoms
It’s important to know how the thyroid gland works and where it is. It’s in the neck, around the trachea. This is close to important nerves.
Understanding the Thyroid Gland’s Location and Function
The thyroid gland helps control how our body uses energy. It’s in the neck, near the Adam’s apple. When it gets too big, it can press on nearby nerves and cause breathing problems.
Here are some key things about the thyroid gland:
- Location: Neck, below the Adam’s apple, wrapping around the trachea.
- Function: Produces hormones (T3 and T4) that help our body work right.
- Relationship with surrounding structures: Close to the laryngeal nerves and trachea.
How Thyroid Disorders Can Affect Breathing and Coughing
Thyroid problems can make it hard to breathe and cause coughing. An enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) can squeeze the trachea, making it hard to breathe. Also, thyroid nodules or swelling can irritate nearby tissues, leading to a cough.
Thyroid disorders can affect breathing in several ways:
- Direct pressure on the trachea from an enlarged thyroid gland.
- Irritation of the laryngeal nerves, affecting vocal cord function and potentially causing coughing.
- Hormonal imbalances affecting the respiratory system.
Mechanisms Behind Thyroid-Related Cough
Coughing linked to thyroid problems isn’t random. It’s due to how the thyroid gland works. This gland in the neck controls many body functions, including breathing. When it doesn’t work right, breathing problems can happen, including coughing.
Direct Pressure on the Trachea
Thyroid issues can cause coughing by pressing on the trachea. Thyroid nodules or an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) can irritate or compress the trachea. This leads to a persistent cough.
Research shows that thyroid nodules, mainly those at the back of the thyroid, can irritate the trachea. They can also compress the recurrent laryngeal nerve, causing a chronic cough.
- Thyroid nodules can grow large enough to press against the trachea.
- An enlarged thyroid gland can cause tracheal deviation or compression.
- Direct pressure on the trachea can irritate the cough receptors.
Compression of Laryngeal Nerves
Another way thyroid problems cause coughing is by compressing laryngeal nerves. The recurrent laryngeal nerve, near the thyroid gland, can be affected by nodules or enlargement. This nerve compression or irritation can cause coughing and other symptoms like hoarseness.
The recurrent laryngeal nerve is at risk because of its location. When thyroid issues affect this nerve, it can disrupt normal function. This leads to various respiratory symptoms.
Hormonal Effects on the Respiratory System
Thyroid hormones greatly influence the respiratory system. Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can impact breathing, potentially causing coughing. For example, hypothyroidism can change the respiratory muscles and lower lung function, leading to breathing issues.
The effects of hormonal imbalances on breathing are complex. Hormonal imbalances can alter respiratory rate, lung function, and comfort. This can contribute to coughing.
Types of Thyroid Conditions That Can Cause Coughing
The health of the thyroid gland is linked to breathing problems, like coughing. Different thyroid issues can affect breathing, leading to coughing. We will look at the thyroid disorders that can cause coughing.
Goiter and Enlarged Thyroid
A goiter, or an enlarged thyroid gland, is a big reason for thyroid-related coughing. When the thyroid gets bigger, it can press on the esophagus and windpipe. This causes coughing as a reflex. This can happen due to iodine lack, thyroid nodules, or inflammation.
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths on the thyroid gland that can cause coughing. These nodules can be solid or fluid-filled and may make the thyroid gland bigger. This can put pressure on nearby structures. Most thyroid nodules are not cancerous but can cause discomfort and breathing problems, including coughing.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland, causing neck pain and discomfort. This inflammation can release thyroid hormones into the blood, leading to symptoms like coughing. There are different types of thyroiditis, each with its own characteristics.
Hypothyroidism and Coughing
Hypothyroidism, where the thyroid gland doesn’t make enough hormones, can also cause coughing. The exact reason is not fully understood, but it can change the respiratory system. This can lead to coughing. Hypothyroidism also raises the risk of other respiratory problems that can cause coughing.
In conclusion, many thyroid conditions can lead to coughing. It’s important to find the cause and treat it properly. Understanding the cause of thyroid-related coughing helps us find better treatments. This improves life quality for those affected.
Understanding Thyroid Cough: Characteristics and Patterns
Exploring the link between thyroid issues and coughing is key. It’s important to know how a thyroid cough acts. This helps us tell it apart from other coughs.
Dry, Persistent Cough
A thyroid cough is usually a dry, persistent cough. It doesn’t have phlegm or mucus. This cough keeps going, even when it seems like it should stop.
Thyroid Cough vs. Common Cold Cough
Telling a thyroid cough from a cold cough is important. A cold cough often comes with other symptoms like a runny nose. But a thyroid cough might just be that, without other symptoms. It also doesn’t get better with cold treatments.
Can Thyroid Make You Cough at Night?
Yes, thyroid problems can make you cough at night. This cough gets worse when you lie down. It’s because of the pressure on your trachea or laryngeal nerves. This can mess up your sleep and make you uncomfortable.
Thyroid Cough With or Without Phlegm
Thyroid coughs are often dry, but sometimes they can have phlegm. Whether or not you cough up phlegm depends on your thyroid condition and other factors.
The “Something Stuck in Throat” Feeling and Thyroid Problems
Many people with thyroid disorders feel like something is stuck in their throat. This feeling can be scary and affect daily life. We will look into why thyroid issues cause this feeling and what it means for those who have it.
Why Thyroid Disorders Cause Throat Discomfort
Thyroid problems can cause throat discomfort because of the gland’s location and growth. An enlarged thyroid gland or goiter can press on the esophagus or trachea. This creates the feeling of something being stuck.
Medical Expert, an endocrinologist, explains, “The thyroid gland is in the neck, around the trachea. So, thyroid enlargement can press on the airway or esophagus.”
This pressure can make the throat feel full or blocked. Thyroid nodules or inflammation can also irritate and cause discomfort, adding to the sensation.
Distinguishing Between Thyroid-Related and Other Causes
Thyroid disorders can cause a “something stuck in throat” feeling, but it’s not the only reason. Conditions like GERD, postnasal drip, or stress can also cause similar feelings. It’s important to find the real cause for the right treatment.
Doctors look at the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and do tests to figure out the cause. They check the thyroid gland and do function tests to see if thyroid issues are the problem.
Does the Thyroid Move When You Swallow?
Yes, a healthy thyroid gland moves when you swallow. Doctors check this during exams. An abnormal or fixed thyroid gland might mean thyroid disease or other problems.
“The thyroid gland’s movement during swallowing is a key sign of its health. If it doesn’t move right, it could mean there’s a problem that needs looking into,” says Medical Expert, a thyroid specialist.
When the Feeling of Food Stuck in Throat Is Thyroid-Related
If the feeling of food stuck in the throat is due to thyroid issues, it often comes with other symptoms. These include trouble swallowing, voice changes, or neck swelling. Tests like ultrasound or a barium swallow study can show if thyroid enlargement or nodules are the cause.
Knowing why you feel like something is stuck in your throat is key to managing it. If you have persistent discomfort, seeing a healthcare professional is important. They can find the cause and suggest the right treatment.
Diagnosing Thyroid-Related Cough
To figure out if a cough is linked to thyroid problems, we need a detailed check-up. We look at many things to find out if thyroid issues are the cause. This helps us rule out other possible reasons and find the real thyroid problem.
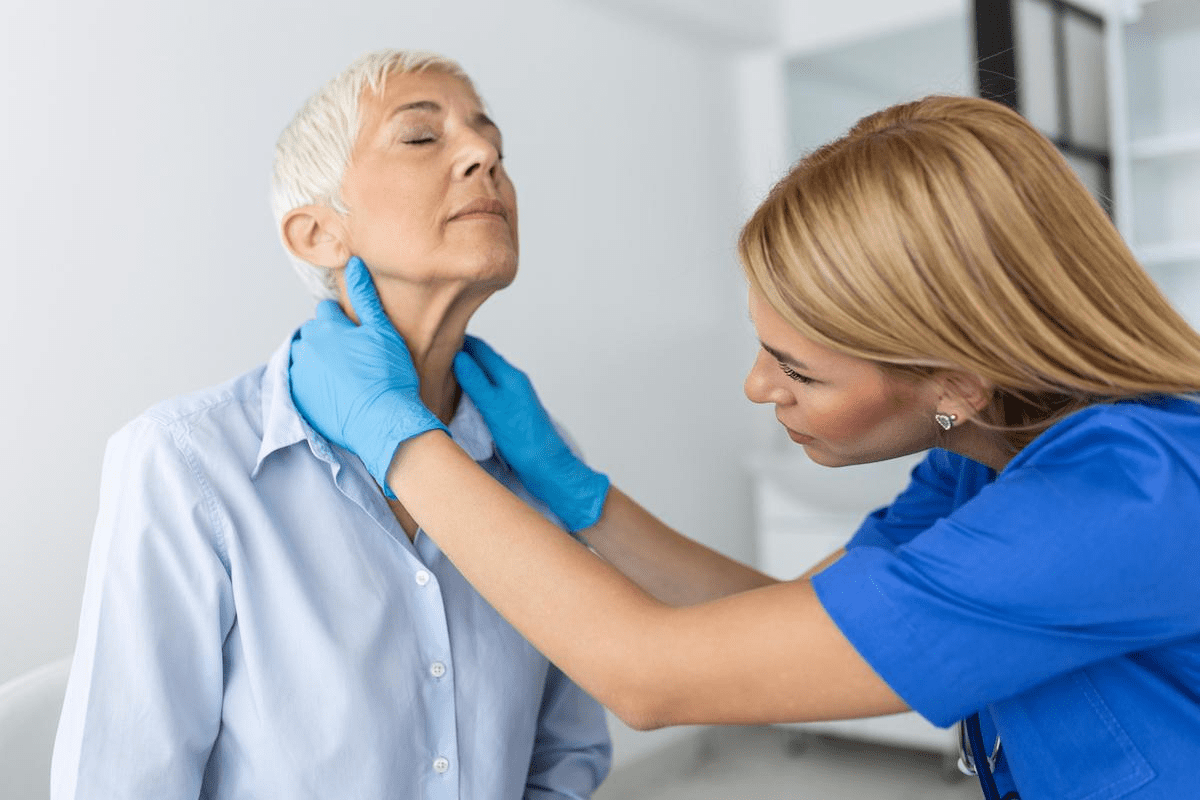
Physical Examination and Neck Assessment
A physical check is key in finding out about thyroid-related cough. A doctor will look at the neck for any signs of trouble. They look for swelling or tenderness that might mean thyroid problems.
They check for an enlarged thyroid gland or nodules. These can press on the trachea or affect nearby areas.
Thyroid Function Tests
Thyroid function tests (TFTs) are blood tests. They measure thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). These tests show if the thyroid gland is working right.
Abnormal results can show hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. Both can cause or add to coughing.
Imaging Studies for Thyroid Evaluation
Imaging studies help us see the thyroid gland and what’s around it. We use:
- Ultrasound: Gives clear pictures of the thyroid gland. It helps spot nodules, cysts, or swelling.
- CT Scan or MRI: Shows more detail of the thyroid and nearby areas. It’s good for seeing how big the thyroid is or if there are big nodules.
These studies help us find out why the cough is happening. They guide us in deciding what to do next.
Ruling Out Other Causes of Chronic Cough
We also check for other reasons of chronic cough. Many things can cause coughing that lasts a long time. We look at:
- Respiratory infections
- Asthma or COPD
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
- Allergies
By looking at all these possibilities and doing thorough thyroid checks, we can find out if thyroid issues are the cause. Then, we can make a good plan to treat it.
Thyroid Cough Treatment Options
Understanding thyroid cough treatment means knowing the thyroid issue at hand. We’ll look at treatments for thyroid conditions, including medications and surgery. This helps tackle the root cause of the cough.
Addressing the Underlying Thyroid Condition
First, we must diagnose and treat the thyroid issue. This might involve tests to see if the thyroid is working too much or too little. Getting the right diagnosis is key for the right treatment.
Medication Approaches for Different Thyroid Disorders
Medicine is a big part of treating thyroid-related coughs. For example, levothyroxine helps with low thyroid levels. Antithyroid drugs, on the other hand, are for high levels.
Thyroid Disorder | Common Medication | Purpose |
Hypothyroidism | Levothyroxine | Normalize thyroid hormone levels |
Hyperthyroidism | Antithyroid medications (e.g., Methimazole) | Reduce thyroid hormone production |
Surgical Interventions for Thyroid Nodules and Goiter
Surgery might be needed for thyroid nodules or goiter causing cough. Surgery can ease pressure on the trachea and help breathing. The choice to have surgery depends on the size and symptoms.
Symptom Management for Persistent Cough
Managing the cough is also important, alongside treating the thyroid. This might include cough medicines or other treatments. Drinking plenty of water and using a humidifier can also help.
By treating the thyroid and managing symptoms, we can effectively treat thyroid cough. This improves life quality.
When to See a Doctor About Possible Thyroid Cough
Thyroid problems can sometimes show up as a cough. It’s important to know when to get help. A cough can mean many things, but a long or severe one might point to a thyroid issue.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
Some symptoms with a cough might mean a thyroid problem. Look out for:
- Difficulty swallowing or feeling like something’s stuck in your throat
- Visible swelling or neck enlargement
- Voice changes, like hoarseness
- Persistent cough that lasts for weeks or months
- Shortness of breath or wheezing
If you notice any of these, see a doctor right away.
Which Specialists to Consult: Endocrinologist vs. ENT
Choosing the right specialist for thyroid issues can be tricky. Both endocrinologists and ENT specialists can help with thyroid problems.
An endocrinologist deals with hormone disorders, including thyroid issues. They can manage your thyroid function and symptoms.
An ENT specialist focuses on ear, nose, and throat conditions. They can check throat and neck problems that might cause your cough.
Questions Your Doctor May Ask
Your doctor will ask several questions to figure out your cough’s cause. They might ask:
- How long have you had the cough?
- Have you noticed neck swelling or voice changes?
- Do you have a history of thyroid problems or other conditions?
- Have you recently traveled or been around someone sick?
What to Expect During Your Appointment
At your visit, expect a detailed check of your neck and thyroid. Your doctor might also run tests to find out what’s causing your symptoms.
Being ready with your symptoms and medical history can make your appointment more effective.
Conclusion
It’s key to understand how thyroid issues can cause coughing. This article has shown how thyroid problems can lead to coughing. We’ve looked at the reasons behind this connection.
A summary on thyroid cough shows why treating the thyroid is important. Knowing the signs of thyroid cough helps people get the right medical help.
To manage thyroid cough, a full plan is needed. This includes finding the cause, treating the thyroid, and managing symptoms. If you have a persistent or severe cough, see a doctor. They can help find the cause and create a treatment plan.
FAQ
Can thyroid problems cause a persistent cough?
Yes, thyroid issues can lead to a persistent cough. This is because the thyroid gland is close to the trachea and laryngeal nerves. These nerves can be affected by thyroid disorders.
What types of thyroid conditions can lead to coughing?
Several thyroid conditions can cause coughing. These include goiter, thyroid nodules, thyroiditis, and hypothyroidism. They affect the thyroid gland and nearby structures.
How do thyroid nodules cause coughing?
Thyroid nodules can press on the trachea or laryngeal nerves. This irritation leads to coughing.
Can hypothyroidism cause a cough?
Yes, hypothyroidism can cause coughing. It might be due to hormonal effects on the respiratory system or related conditions like thyroiditis.
What are the characteristics of a thyroid-related cough?
A thyroid-related cough is usually dry and lasts a long time. It’s different from a cold cough. It can happen at any time, even at night.
Can thyroid issues cause a feeling of something stuck in the throat?
Yes, thyroid disorders can make you feel like something is stuck in your throat. This is because the gland may be enlarged or have nodules pressing on nearby structures.
Does the thyroid gland move when you swallow?
Yes, a normal thyroid gland moves up when you swallow. Abnormal movement can indicate thyroid problems.
How is thyroid-related cough diagnosed?
Diagnosing thyroid-related cough involves a physical exam, thyroid function tests, and imaging studies. It also includes ruling out other causes of chronic cough.
What are the treatment options for thyroid cough?
Treatment for thyroid cough includes addressing the underlying thyroid condition. It also involves medication, surgery for nodules or goiter, and managing cough symptoms.
When should I see a doctor about a possible thyroid cough?
See a doctor if you have a persistent cough, trouble swallowing, or neck swelling. These signs can indicate thyroid-related issues.
Which specialists should I consult for thyroid cough?
You may need to see an endocrinologist for thyroid issues or an ENT specialist for throat and respiratory symptoms.
Can thyroiditis cause coughing?
Yes, thyroiditis can cause coughing. This is because the gland swells and may press on nearby structures.
Is thyroid cough always without phlegm?
Thyroid cough is often dry, but it’s not always without phlegm. Whether or not you have phlegm depends on your thyroid condition and other factors.
References:
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://virginiaent.com/thyroid-disorders-and-the-effects-on-the-throat/






