Last Updated on October 20, 2025 by
Cancer treatments vary, but chemotherapy is widely used. It targets fast-growing cells, like cancer cells. But it can also harm healthy cells, leading to serious side effects.
In this article, we’ll look at the risks of different cancer treatments. We’ll focus on the side effects of each. Knowing these risks helps patients and doctors choose the best treatment. What is the difference between obstructive disease vs restrictive lung disease? Get the amazing facts on how each condition impacts.
It’s important to know about the cancer treatment modalities. These treatments have their own benefits and risks. They help fight cancer in different ways.
We’ll look at the main types of cancer treatments. We’ll see how they affect patients’ quality of life.
The main treatments are chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgery. Each targets cancer cells in its own way.
Side effects of cancer treatment are measured by their impact on quality of life. This includes symptoms like pain, fatigue, and cognitive changes.
Healthcare providers use tools and scales to measure these effects. This ensures patients get the best care.
Knowing about cancer treatments and their side effects helps patients and doctors make better choices. This way, they can plan treatments that work best for each person.

Recent research has shown that chemotherapy carries a high risk of side effects. This is a common treatment for many cancers. A study in the 2025 JAMA Network Open highlights the severity of these side effects.
The 2025 JAMA Network Open study gives us important insights. It shows that chemotherapy patients often see a big drop in their physical health. This is worrying because these effects can last long after treatment ends.
This study stresses the importance of caring for patients fully. It shows we need to address both immediate and long-term side effects. This way, healthcare providers can support patients better during their treatment.
Chemotherapy side effects can be divided into short-term and long-term. Short-term effects include nausea, fatigue, and hair loss right away. Long-term effects, on the other hand, can show up months or years later, affecting patients’ lives and health.
Both short-term and long-term side effects are major concerns for chemotherapy patients. By understanding the difference, we can tailor our support and treatment plans. This helps address the unique challenges each type of side effect poses.
It’s key to know the difference between short-term and long-term side effects. This knowledge helps us create better care plans. We must think about the long-term effects of chemotherapy when choosing treatments and caring for patients.
Cancer survivors, like those with breast cancer, often see a drop in their physical health. It’s key to grasp how big this drop is and what it means.
Breast cancer survivors face many physical challenges after treatment. These include weaker muscles, less mobility, and more tiredness. These issues can greatly affect their daily lives, impacting not just them but also their families and caregivers.
Research shows breast cancer survivors have unique recovery challenges. Treatments like surgery, chemo, and radiation can harm their physical health for a long time. For example, lymphedema often occurs after breast cancer surgery, causing swelling and pain in the arm.
The emotional effects of cancer and its treatment also play a big role. Anxiety, depression, and stress can make physical symptoms worse, creating a tough cycle to overcome.
Measuring health decline in cancer survivors involves looking at several physical health areas. This includes checking physical function, symptom burden, and overall quality of life. The Short Form 36 (SF-36) health survey is used to do this, giving a full picture of a survivor’s health.
Studies reveal a big drop in physical health in the first year after treatment. Some survivors take longer to get better than others. Age, how intense the treatment was, and any health issues before cancer play big roles in recovery.
It’s vital to understand how much physical health drops in breast cancer survivors. By measuring this decline and finding out who’s at risk, doctors can offer better support and help. This can improve survivors’ quality of life.
Chemotherapy is a key treatment for many cancers. But it can also cause a variety of side effects. These can be mild or severe and affect many parts of a patient’s life.
Pain and fatigue are two common side effects of chemotherapy. Pain can come from the drugs or the cancer itself. Fatigue, or feeling very tired, can also be a sign of cancer or its growth. It’s important to manage these symptoms to keep the patient’s quality of life good.
Chemotherapy side effects can make everyday tasks hard. Fatigue, pain, or other issues like nausea or hair loss can make things tough. We help patients by giving them the care and resources they need to manage their condition.
Many patients say they have cognitive changes, known as “chemo brain.” This can include memory problems, trouble focusing, or learning new things. The exact cause is not known, but it’s thought to be linked to how chemotherapy affects the brain.
It’s key to understand and tackle these common side effects of chemotherapy. By recognizing the challenges, we can improve the treatment experience and quality of life for cancer patients.
Cancer treatments save lives but can harm the lungs. This harm comes from treatments like chemotherapy and radiation. Knowing about these issues helps doctors care for patients better.
Chemotherapy is key in fighting cancer, but it can hurt the lungs. Some drugs are too harsh for lung tissue, causing inflammation and scarring. The risk depends on the treatment and how much is given.
Some drugs linked to lung harm are:
People on these drugs need to watch for signs like breathing trouble or coughing.
Radiation therapy can also harm the lungs, causing inflammation. This is called radiation pneumonitis. It can be mild or severe, depending on the damage.
Things that raise the risk of radiation pneumonitis include:
Doctors often use steroids to treat radiation pneumonitis.
Both chemotherapy and radiation can cause breathing issues after treatment. These problems can make daily life hard.
To help with breathing issues, patients might:
It’s vital for doctors to closely watch and manage these lung problems. This ensures the best results for patients.
Cancer treatments can harm lung health, causing different problems. It’s important to know the difference between obstructive and restrictive lung diseases. This helps manage these conditions better.
Obstructive lung disease makes it hard to breathe because of blocked airways. Chemotherapy and radiation can damage lung tissue and airways. Symptoms include shortness of breath, wheezing, and a chronic cough. We need to watch for these signs in cancer patients to help them sooner.
Restrictive lung disease means the lungs can’t fully expand. This can happen due to lung inflammation or scarring. Cancer therapy can lead to this by causing fibrosis or inflammation. Patients may find it hard to breathe and have less lung capacity. We should think about the risk of restrictive lung disease when planning cancer treatment.
It’s key to tell obstructive and restrictive lung diseases apart for cancer patients. Both can come from cancer treatment, but they need different treatments. Knowing the cause and type of lung disease is critical for better patient care.
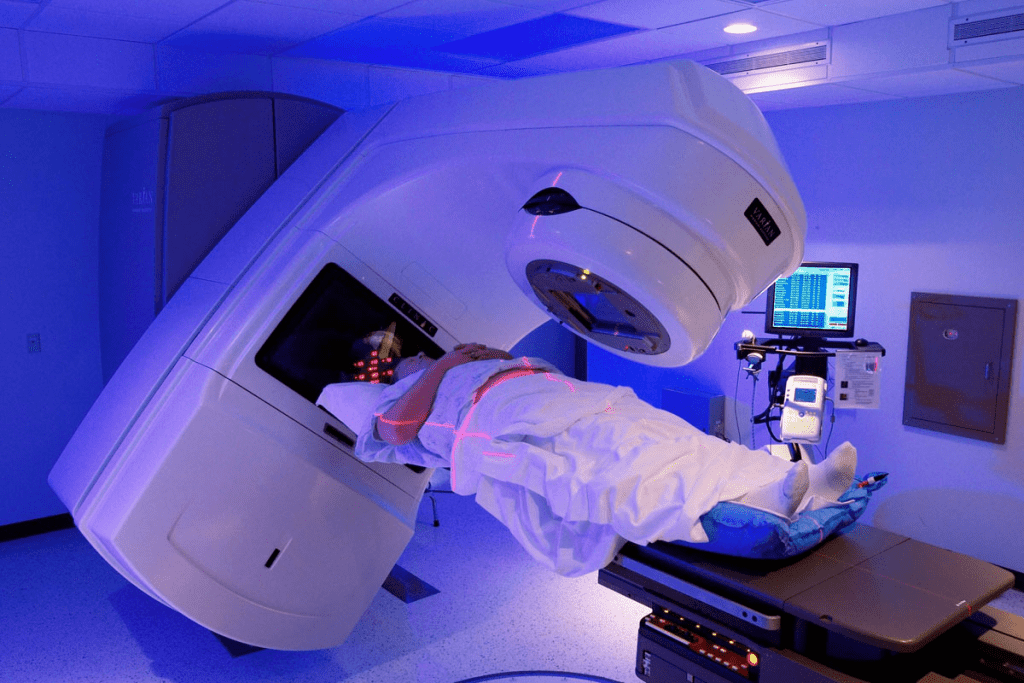
Radiation therapy is a common cancer treatment. It has its own set of side effects. We will look at both immediate and long-term impacts.
Radiation therapy can harm specific tissues. For example, it can damage the lungs if treated in the chest area. This might cause inflammation or scarring.
The extent of tissue damage depends on several factors. These include the radiation dose, the area treated, and the treatment technique. Knowing these helps reduce some side effects.
Radiation therapy also has long-term risks. These include getting secondary cancers, heart disease, and other conditions. These risks are linked to the area exposed to radiation.
Managing these risks is key for cancer survivors. We need to weigh the benefits of treatment against these risks. This helps create treatment plans that are effective yet safe.
Understanding radiation therapy’s side effects is vital. It helps healthcare providers support patients better during treatment.
Surgery is key in cancer treatment, but comes with risks. These include challenges in recovery and long-term effects on function. Cancer surgeries are complex, aiming to remove tumors and manage complications.
Recovery after surgery is a critical part of cancer treatment. Complications during this time can affect the surgery’s success. Common issues include:
It’s important to watch patients closely and provide good care after surgery. Many hospitals are using new methods to manage pain and prevent infections, aiming to improve patient outcomes.
Surgeries can also affect a patient’s long-term function and quality of life. For example:
A study shows that surgery’s long-term effects on function are significant. Rehabilitation programs tailored to each patient’s needs are key to helping them regain function and improve their quality.
We believe every patient’s journey is unique. So, we support personalized care plans for those undergoing cancer surgery.
The fight against cancer is getting a boost from new treatments like antibody-drug conjugates. These therapies are changing how we treat cancer. It’s important to know both the good and the bad sides of these treatments.
We’re moving towards treatments that target cancer more precisely. This means less harm to healthy cells. But these treatments come with their own set of challenges.
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are a new type of cancer therapy. They link a drug to an antibody that finds cancer cells. This way, the drug goes straight to the tumor, sparing healthy cells.
But some ADCs can cause vision problems. These include blurred vision and dry eyes. We must watch patients closely for any eye issues.
Immunotherapy uses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. It has changed how we treat many cancers. But it can also cause unique side effects.
These side effects, called immune-related adverse events (irAEs), can be mild or serious. They can even be life-threatening. It’s key to tell patients about these risks and the need to report any new symptoms right away.
Hospitals are working hard to make treatments better for patients. They use new methods and teams to help patients. This makes treatments safer and more effective.
Hospitals are using new ways to make cancer treatments safer. They create personalized treatment plans for each patient. This means treatments are tailored to fit each person’s needs.
They also use state-of-the-art technology to target treatments. For example, radiation therapy can focus on tumors, not healthy tissues. This makes treatments more effective and safer for organs like the lungs.
Teams of different healthcare professionals are key in hospitals. They include doctors, nurses, and more. Working together, they give patients the best care possible.
Supporting patients emotionally and mentally is also important. Hospitals offer counseling, support groups, and educational programs. These help patients deal with their treatment and recovery.
Hospitals are making big strides in reducing side effects. This improves the lives of cancer patients. As healthcare advances, we’ll see even more ways to support patients.
When dealing with cancer, it’s key to balance treatment success with keeping the patient’s quality of life good. Cancer treatment isn’t just about getting rid of the disease. It’s also about keeping the patient’s overall health in check. We’ve seen how treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can cause lung problems, like fluid in the lungs and breathing issues.
Good cancer care means looking at how treatments affect the lungs and the risk of scarring. Knowing how exercise can affect lung inflammation hours later helps in making personalized plans. By focusing on both treatment success and quality of life, we can make cancer treatment better. This way, patients can live their best lives despite the disease.
We aim to provide top-notch healthcare with full support for patients from around the world. This ensures patients get the care they need to face cancer’s challenges. And they can keep their quality of life as good as possible.
Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can harm the lungs. They can cause damage, inflammation, and breathing issues. These problems fall into two main categories: obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
Obstructive lung disease makes it hard to breathe out because of airway blockages. Restrictive lung disease, on the other hand, makes it hard to expand the lungs. Both can be caused by cancer treatments.
Chemotherapy can cause many side effects. These include pain, tiredness, and “chemo brain,” which affects thinking. These issues can make daily life and quality of life hard.
Cancer treatments, like chemotherapy and radiation, can damage the lungs. This damage can lead to inflammation, scarring, and breathing problems. It can also make it hard to breathe.
Radiation therapy can harm nearby tissues and increase the risk of long-term lung problems. The severity of these risks depends on the dose and how long the radiation lasts.
Hospitals are using new methods and teams to reduce side effects. They plan treatments carefully, monitor patients closely, and offer supportive care. This approach helps minimize side effects.
New cancer treatments, like antibody-drug conjugates and immunotherapy, have unique side effects. For example, antibody-drug conjugates can cause vision problems. Immunotherapy can lead to immune-related side effects.
Exercise is usually good, but intense workouts can cause temporary inflammation, including in the lungs. The link between exercise and lung inflammation in cancer patients is complex and needs more study.
Cancer treatments can weaken survivors’ physical health, often seen in breast cancer patients. The extent of this decline varies based on treatment type, duration, and individual factors.
Restrictive lung disease after cancer therapy is marked by reduced lung volume and difficulty expanding the lungs. This can be due to inflammation, scarring, or fibrosis from treatments.
Side effects are tracked using standard tools and patient reports. This helps doctors understand how treatments affect quality of life. It guides decisions on care.
Subscribe to our e-newsletter to stay informed about the latest innovations in the world of health and exclusive offers!