Diabetic retinopathy is a serious eye condition that can cause vision loss if not treated. At Liv Hospital, we are committed to providing world-class healthcare for international patients. New medical science has changed how we treat diabetic retinopathy. Now, eye injections are a key treatment. Details on the use of a diabetic retinopathy treatment injection to preserve vision. The effectiveness of diabetic retinopathy treatment injection.
These injections have changed how we fight diabetic retinopathy. They give us hope to save sight and stop blindness. By using anti-VEGF injections, we can lower the risk of losing vision. This improves life quality for those affected.
Key Takeaways
- Intravitreal eye injections are a primary treatment for diabetic retinopathy.
- Anti-VEGF injections help preserve vision and prevent blindness.
- Modern eye injection therapies offer new hope for managing diabetic retinopathy.
- Liv Hospital provides extensive support for international patients.
- Early treatment can significantly improve outcomes for those with diabetic retinopathy.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy

Knowing about diabetic retinopathy is key for people with diabetes. It can cause serious vision loss if not treated. This condition damages the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision problems and, if untreated, blindness.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy
High blood sugar levels harm the blood vessels in the retina, causing diabetic retinopathy. Over time, these vessels can leak fluid or blood. This swelling or new, fragile vessels can lead to vision loss. High blood glucose levels are the main cause, making diabetes management vital to prevent this condition.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy goes through several stages, each with its own signs. The stages are:
- Background or Mild Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: The first stage, where small areas of swelling (microaneurysms) occur in the retina’s blood vessels.
- Moderate Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: As it gets worse, more blood vessels are damaged, and the retina gets less blood.
- Severe Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: Many more blood vessels are blocked, leading to less blood for the retina and new, fragile vessels.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy: The most severe stage, where new, fragile blood vessels grow in the retina, which can leak blood and cause severe vision loss.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy start off subtle but get more obvious as the disease advances. Common signs include:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters or dark spots
- Difficulty seeing in low light
- Vision loss
People with diabetes should watch for these symptoms and get regular eye exams. Early detection is key when the disease is more treatable.
When Eye Injections Become Necessary
Knowing when to start eye injections is key in managing diabetic retinopathy. As the disease gets worse, the chance of losing vision grows. So, acting quickly is very important.
Progression Indicators for Treatment
There are signs that show you might need eye injections for diabetic retinopathy. These include:
- Diabetic macular edema (DME), where fluid in the macula can harm your vision.
- Abnormal blood vessel growth that can cause bleeding or retinal detachment.
- Loss of vision or big changes in how well you can see.
Watching for these signs helps doctors know when to start eye injection therapy.
Benefits of Early Intervention
Starting eye injections early can greatly improve diabetic retinopathy treatment. The advantages are:
- It can slow down or stop the disease from getting worse.
- It lowers the chance of losing a lot of vision.
- It helps keep your vision sharp and improves your life quality.
Early treatment tackles current problems and prevents future ones.
Diagnostic Tests That Determine Treatment Need
Diagnostic tests are vital in figuring out if you need eye injections. Important tests are:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): Gives detailed retina images, showing fluid or thickening.
- Fluorescein Angiography: Shows abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage.
These tests help doctors see how bad diabetic retinopathy is. They decide if you need eye injection treatment or shots to the eye with eye injections medications.
Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment Injection Mechanisms
Intravitreal injections are key in treating diabetic retinopathy. They target the main causes of vision loss. These injections put medication directly into the vitreous humor, the eye’s gel-like substance. This ensures the treatment reaches the right areas.
The Science Behind Intravitreal Injections
Intravitreal injections use a fine needle to put medication into the vitreous humor. This method allows for high concentrations of the drug to reach the retina. This makes the treatment more effective. The procedure is done in a clinical setting and is safe when done by experts.
The science behind intravitreal injections is simple. It delivers drugs directly to the disease site. This is very helpful in treating diabetic retinopathy, where the main problems are abnormal blood vessel growth and fluid leakage.
Targeting Abnormal Blood Vessel Growth
Intravitreal injections treat diabetic retinopathy by targeting abnormal blood vessel growth. Medications like anti-VEGF agents are injected to stop new, fragile blood vessels from growing. These vessels can cause vision problems. By stopping their growth, intravitreal injections help prevent further vision loss.
Reducing Retinal Fluid Leakage
Intravitreal injections also help reduce retinal fluid leakage. They use medications that stop new blood vessel growth and reduce inflammation and leakage. This lets the retina work better, improving vision for patients.
Anti-VEGF Medications: The Primary Treatment Option
In recent years, anti-VEGF medications have become key in treating diabetic retinopathy. These drugs target vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a major cause of the condition.
Ranibizumab (Lucentis): Uses and Effectiveness
Ranibizumab is made for use inside the eye. It’s very effective in treating diabetic retinopathy. Studies have shown it improves vision and reduces eye thickness.
Aflibercept (Eylea): Treatment Protocol
Aflibercept is given as an eye injection every 4 to 8 weeks. It’s based on how bad the condition is. This drug helps slow down the disease by reducing VEGF activity.
Faricimab (Vabysmo): The Newer Option
Faricimab is a newer drug that looks promising. It targets VEGF and Ang-2, giving a two-pronged attack. This could be a good choice for some patients.
Bevacizumab (Avastin): Off-Label but Effective
Bevacizumab is used off-label for diabetic retinopathy but works well. It’s important to consider its use carefully because it’s not officially approved for this purpose. Yet, it’s a treatment option for some.
| Medication | Dosing Frequency | Mechanism of Action |
|---|---|---|
| Ranibizumab (Lucentis) | Monthly or as needed | Anti-VEGF |
| Aflibercept (Eylea) | Every 4 to 8 weeks | Anti-VEGF |
| Faricimab (Vabysmo) | Every 4 weeks initially, then extended | Anti-VEGF and Anti-Ang-2 |
| Bevacizumab (Avastin) | Variable, often every 4 to 6 weeks | Anti-VEGF |
Choosing the right anti-VEGF medication depends on several factors. These include how bad the diabetic retinopathy is, how the patient responds, and possible side effects. Knowing these options is key for effective treatment planning.
Corticosteroid Injections for Macular Edema
Corticosteroid injections are a key treatment for macular edema linked to diabetic retinopathy. They reduce inflammation in the retina. This helps improve vision and lowers the risk of losing more sight.
There are several types of corticosteroid injections for macular edema. We’ll look at the most common ones:
Triamcinolone Acetonide (Triesence)
Triamcinolone acetonide is a corticosteroid injection used for years to treat eye inflammation, including macular edema. It’s given as an intravitreal injection. Studies show it can reduce retinal thickness and boost visual acuity.
Dexamethasone Implant (Ozurdex)
The dexamethasone implant is a biodegradable device that slowly releases dexamethasone. It’s placed in the eye’s vitreous gel. This implant offers long-lasting treatment, reducing the need for frequent injections. It’s effective in reducing macular edema and improving vision.
Fluocinolone Acetonide (Iluvien)
Fluocinolone acetonide is a slow-release implant used as a corticosteroid. It’s designed for continuous treatment up to 36 months. It’s a convenient option for long-term treatment. Studies show it’s effective in reducing macular edema and improving vision.
When Steroids Are Preferred Over Anti-VEGF
Corticosteroid injections are often chosen when anti-VEGF treatments don’t work or aren’t suitable. They’re beneficial for patients with persistent or chronic macular edema. The choice between corticosteroids and anti-VEGF treatments depends on the patient’s health, condition severity, and past treatment responses.
The benefits of corticosteroid injections include:
- Reduced inflammation and edema
- Improved visual acuity
- Potential for less frequent injections with sustained-release implants
But, it’s important to consider the risks and side effects. These can include increased intraocular pressure and cataract formation.
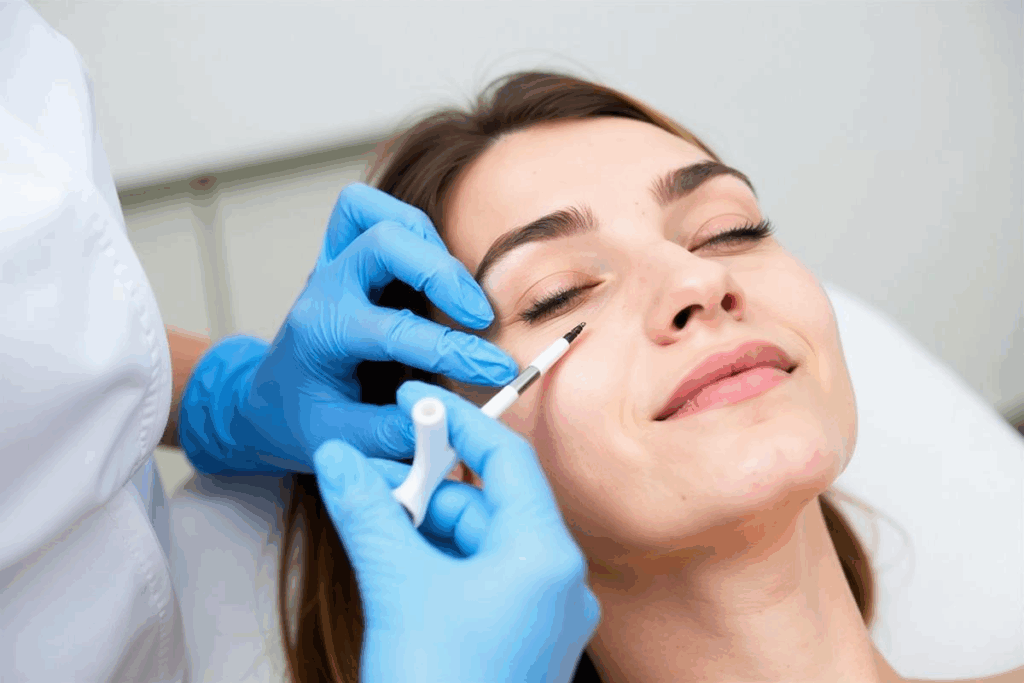
The Eye Injection Procedure: What to Expect
Getting an eye injection is a simple and mostly painless process. Knowing what to expect can help ease your worries. We’re here to guide you through each step.
Before the Procedure: Preparation Steps
Before your eye injection, our team will get you ready. This includes:
- Administering topical anesthesia to numb the eye
- Cleaning the eye to prevent infection
- Discussing any concerns or questions you may have
Preparation is key for a smooth procedure. Knowing what’s happening can make you feel more comfortable.
During the Injection: Step-by-Step Process
The actual injection is quick. Here’s what you can expect:
- The doctor will use a speculum to gently hold your eyelids open.
- The eye is cleaned again with an antiseptic solution.
- The injection is administered using a very fine needle.
- You may feel a slight pressure or discomfort, but this is usually minimal.
It’s normal to feel a bit apprehensive, but our experienced team is with you every step of the way.
After the Procedure: Recovery and Care
After your eye injection, we’ll guide you on caring for your eye. This may include:
- Using antibiotic drops to prevent infection
- Avoiding rubbing or touching your eye
- Monitoring for any signs of complications
Recovery is typically straightforward, and most people can go back to their normal activities soon after.
Managing Discomfort and Side Effects
While side effects are usually mild, you might feel some discomfort, such as:
- Mild burning or stinging
- Increased tearing
- A feeling of having something in your eye
These symptoms usually go away on their own. If you’re worried, don’t hesitate to reach out to our team for advice.
Understanding the eye injection procedure and what to expect can help you feel more confident. If you have any questions or concerns, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Treatment Frequency and Long-Term Management
Knowing how often diabetic retinopathy injections are needed is key for long-term care. The schedule for these injections varies. It depends on the disease stage, how the patient responds, and other factors.
Initial Monthly Injection Schedule
The treatment starts with injections every month. This aggressive start aims to manage the disease well from the start. Consistency is key during this time to get the best results.
At first, patients get injections of anti-VEGF medicines like ranibizumab (Lucentis) or aflibercept (Eylea). These are given directly into the eye’s vitreous gel. This helps reduce swelling and stops vision loss.
Maintenance Phase Protocols
After the first phase, the treatment schedule changes based on how the patient responds. The maintenance phase closely watches the patient and gives injections as needed. This personalized approach keeps the treatment effective while avoiding unnecessary treatments.
Regular check-ups are important in the maintenance phase. They help track the disease and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Signs of Treatment Success
Good results from diabetic retinopathy treatment include better vision, less retinal fluid, and stable disease. Patients often see a big improvement in their life quality because of the treatment.
Success isn’t just about seeing better. It’s also about the retina’s overall health.
When Treatment Can Be Reduced or Stopped
Deciding to reduce or stop treatment depends on the patient’s response and disease stability. Sometimes, treatment can be paused, but close monitoring is needed to catch any signs of relapse early.
Managing diabetic retinopathy long-term needs teamwork between the patient and healthcare provider. The treatment plan must adapt to the patient’s changing needs.
Innovative Advances: Susvimo and Port Delivery Systems
Treatment for diabetic retinopathy is getting better with new tech like Susvimo. It’s a refillable eye implant that keeps delivering medicine. This means fewer eye injections for patients, giving them hope.
Continuous Medication Delivery
Susvimo slowly releases medicine, keeping the eye’s levels just right. This steady release can help patients with diabetic retinopathy see better.
Benefits and Candidate Selection
Susvimo makes treatment easier and might help patients see better. Doctors pick who gets this implant based on how bad the diabetic retinopathy is and how well they’ve done with other treatments.
Refill Process
Refilling Susvimo is easy, avoiding complicated procedures. This new way to treat eyes is a big step forward in fighting diabetic retinopathy.
With Susvimo and Port Delivery Systems, patients with diabetic retinopathy have more choices than ever. These new glaucoma injections and eye injection technologies are key in the battle against losing vision.
FAQ
What are eye injections used for in treating diabetic retinopathy?
Eye injections, like intravitreal injections, are used to treat diabetic retinopathy. They deliver medications directly into the eye. This helps reduce abnormal blood vessel growth and fluid leakage in the retina, helping to preserve vision.
What are the different types of eye injections available for diabetic retinopathy?
For diabetic retinopathy, there are mainly two types of eye injections. Anti-VEGF medications, such as Ranibizumab (Lucentis), Aflibercept (Eylea), Faricimab (Vabysmo), and Bevacizumab (Avastin), are used. Corticosteroid injections like Triamcinolone Acetonide (Triesence), Dexamethasone Implant (Ozurdex), and Fluocinolone Acetonide (Iluvien) are also used.
How do anti-VEGF medications work in treating diabetic retinopathy?
Anti-VEGF medications stop the growth of abnormal blood vessels in the retina. They reduce fluid leakage and slow disease progression. This helps preserve vision.
What is the procedure for receiving an eye injection for diabetic retinopathy?
The procedure starts with numbing the eye with anesthetic drops. The eye is then cleaned before injecting the medication into the vitreous gel. The whole process is quick, and most people can go back to normal activities soon after.
What are the possible side effects of eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
Side effects can include mild discomfort, redness, or irritation in the eye. Serious but rare side effects include infection, retinal detachment, or increased eye pressure.
How often are eye injections needed for diabetic retinopathy treatment?
The frequency of injections varies based on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. At first, injections might be given monthly. Then, the frequency can decrease. The treatment plan is customized for each patient.
Can diabetic retinopathy be cured with eye injections?
Eye injections can manage diabetic retinopathy and preserve vision. But, they are not a cure. Ongoing treatment and monitoring are needed to control the disease.
What are the benefits of Susvimo and Port Delivery Systems for diabetic retinopathy?
Susvimo and Port Delivery Systems provide continuous medication delivery to the eye. This reduces the need for frequent injections. These systems can offer more consistent treatment and better patient outcomes.
Are there any alternative treatments to eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
Eye injections are a main treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Other treatments include laser photocoagulation or vitreoretinal surgery for advanced cases. The best treatment plan is decided by an eye care professional based on the individual’s condition.
How can I prepare for an eye injection procedure?
To prepare for an eye injection, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions. This may include stopping certain medications, arranging for transportation, and having someone accompany you to the appointment.