Diabetic retinopathy is a serious problem for people with diabetes. It can cause vision loss if not treated. About 1 in 3 people with diabetes get this condition, making it a big cause of vision loss. Effective management is key to stop the disease from getting worse. Overview of the 5 best eye injections for retinopathy used to manage various retinal conditions. Review your eye injections for retinopathy.
At top hospitals like Liv Hospital, patients get the latest treatments. This includes eye injections that have changed how we treat diabetic retinopathy. These injections, like anti-VEGF medications, go right into the eye. They help reduce swelling and stop vision loss. By stopping the disease, patients can keep their vision and live better.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetic retinopathy is a common complication of diabetes that can lead to vision loss.
- Eye injections are a primary treatment for managing diabetic retinopathy.
- Anti-VEGF medications are used to reduce swelling and prevent vision loss.
- Leading healthcare institutions offer advanced treatments, including eye injections.
- Effective management can preserve vision and quality of life.
Understanding Diabetic Retinopathy

Diabetic retinopathy is a serious problem for people with diabetes. It can cause severe vision loss if not treated right. Knowing about diabetic retinopathy helps us see why managing diabetes is so important.
What Causes Diabetic Retinopathy
High blood sugar damages the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy. Over time, these damaged vessels can leak fluid or blood. This causes vision problems.
Key factors contributing to the development of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Prolonged high blood sugar levels
- Poor diabetes management
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol levels
Prevalence and Risk Factors
Diabetic retinopathy is common in people with diabetes. The risk factors include how long you’ve had diabetes, how well you manage your blood sugar, and other health conditions like high blood pressure.
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Duration of Diabetes | The longer a person has diabetes, the higher the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy. |
| Blood Sugar Control | Poor control of blood sugar levels increases the risk of diabetic retinopathy. |
| Hypertension | High blood pressure can make diabetic retinopathy worse. |
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
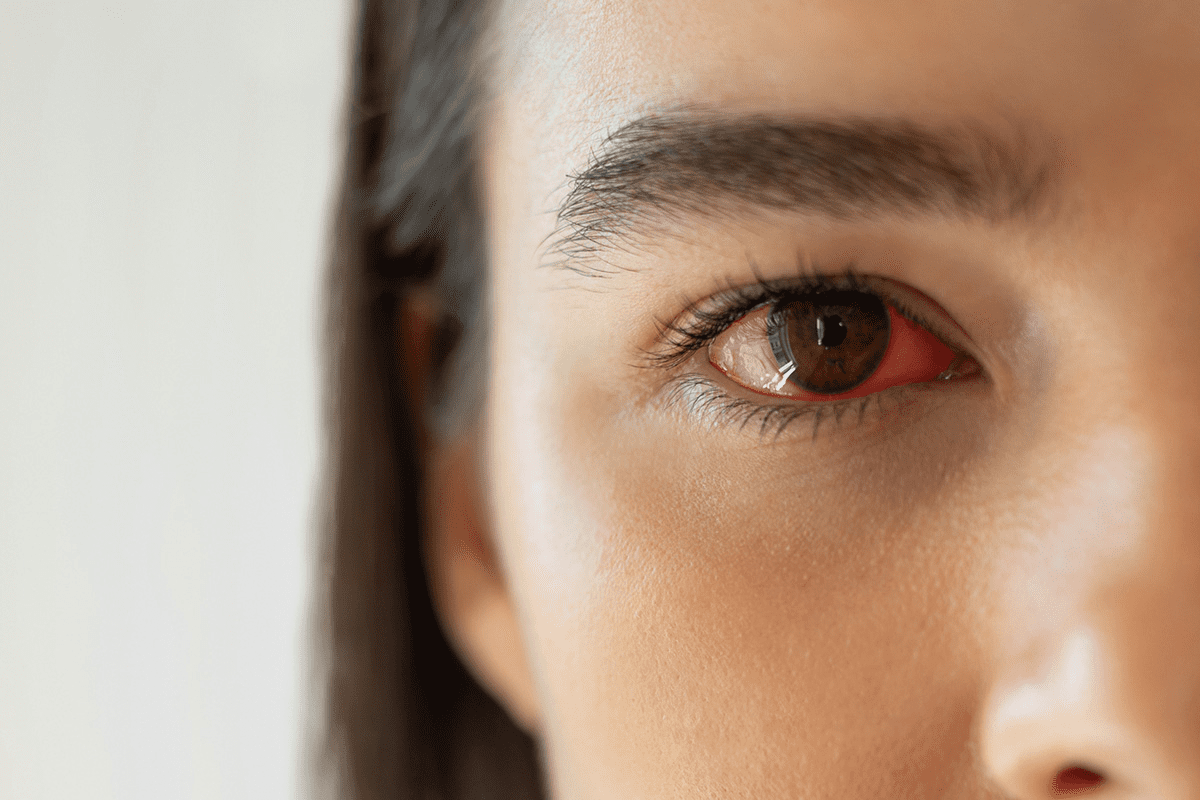
The symptoms of diabetic retinopathy vary. Common signs include blurred vision, seeing floaters, and trouble seeing in dim light. In severe cases, it can cause blindness.
“Early detection of diabetic retinopathy is key to avoiding severe vision loss. Regular eye exams are vital for those with diabetes.”
When Medical Intervention Becomes Necessary
When diabetic retinopathy gets worse, it’s time for medical help. This condition can harm your vision if not treated. We’ll talk about when you need to see a doctor.
Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy Requiring Treatment
Diabetic retinopathy goes through several stages. It starts with mild changes and can get worse. Treatment is key when it reaches a certain point.
Key stages that require medical intervention include:
- Moderate Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (NPDR): At this stage, retinal changes become more pronounced, and the risk of progression to more severe stages increases.
- Severe NPDR: Characterized by significant retinal damage and a high risk of progression to proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy (PDR): The advanced stage where new, fragile blood vessels grow in the retina, leading to a high risk of vision loss.
Diabetic Macular Edema
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication of diabetic retinopathy. It happens when fluid builds up in the macula. This can hurt your vision a lot. Treatment often includes injections that help reduce fluid and improve vision.
“The introduction of anti-VEGF therapy has revolutionized the treatment of diabetic macular edema, giving patients new hope.”
— Dr. [Last Name], Retina Specialist
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) is the most serious stage. It’s marked by new, fragile blood vessels in the retina. These can bleed or cause retinal detachment, leading to severe vision loss. Treatment usually involves laser therapy to stop new vessels from growing.
| Stage | Characteristics | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate NPDR | Noticeable retinal changes | Monitoring, Anti-VEGF injections |
| Severe NPDR | Significant retinal damage | Anti-VEGF injections, Laser photocoagulation |
| PDR | Growth of new, fragile blood vessels | Laser photocoagulation, Anti-VEGF injections |
Knowing about diabetic retinopathy stages and treatments is key. Regular eye checks and timely treatment can prevent vision loss.
Injections for Diabetic Retinopathy: Available Options
If you have diabetic retinopathy, knowing about injection treatments is key. This condition harms the blood vessels in your retina. It can cause vision loss if not treated.
There are two main types of injections for diabetic retinopathy: anti-VEGF medications and corticosteroid injections. Each has its own way of working, benefits, and possible side effects.
Anti-VEGF Medications
Anti-VEGF medications are a mainstay in treating diabetic retinopathy. They stop new blood vessels from growing in the retina. This helps reduce swelling and prevents vision loss.
Some well-known anti-VEGF medications include:
- Ranibizumab (Lucentis): Known for its effectiveness in treating diabetic macular edema.
- Aflibercept (Eylea): Used for both diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema.
- Faricimab (Vabysmo): A newer option that has shown promise in clinical trials for its ability to improve vision outcomes.
These medications are injected into the vitreous gel of the eye. Most people find them tolerable, but some might feel discomfort or see things differently briefly after.
Corticosteroid Injections
Corticosteroid injections are another choice, mainly for diabetic macular edema. They reduce inflammation in the eye. This can help lessen swelling and improve vision.
They’re good for those who don’t get better with anti-VEGF therapy. But, they can cause side effects like high eye pressure and cataracts.
Examples of corticosteroid injections for diabetic retinopathy include:
- Triamcinolone: Often used for its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Dexamethasone implant (Ozurdex): A sustained-release implant that can provide therapeutic benefits for several months.
When thinking about corticosteroid injections, it’s important to consider the benefits and risks. Always talk about these options with an eye care specialist.
Finding the Right Retina Specialist
Choosing the right retina specialist is key for managing diabetic retinopathy. The right specialist can greatly affect your treatment’s success. It’s important to find someone with the right skills and experience.
Types of Eye Specialists Who Perform Injections
Several eye specialists can give injections for diabetic retinopathy. Retina specialists are ophthalmologists with extra training in retinal diseases. They are experts in giving intravitreal injections, which put medicine directly into the eye.
Look for specialists with experience in diabetic retinopathy and a good track record. Ask your primary care doctor for suggestions or get referrals from people who have had similar treatments.
Questions to Ask When Choosing a Specialist
When you find possible retina specialists, ask important questions. This will help you choose the best one for you. Ask about their:
- Experience with diabetic retinopathy treatments
- Success rates with intravitreal injections
- Approach to patient care and follow-up
- Availability for urgent or emergency appointments
These questions will help you understand the specialist’s expertise and how they can help you manage your condition.
Insurance Considerations
Understanding your insurance is key to managing treatment costs. Before your appointment, check with your insurance to see what’s covered and what you’ll have to pay out of pocket.
It’s also wise to ask the specialist’s office about their billing and any financial help they offer. Knowing the financial side of your care lets you focus on your treatment and recovery.
Preparing for Your Eye Injection Appointment
Getting ready for your eye injection appointment is key. It helps make the experience smoother and less stressful. Being prepared can also make the treatment more effective.
Medical Evaluations Before Treatment
You’ll have some medical checks before your eye injection. These checks make sure you’re a good candidate for the treatment. You might have an eye exam, imaging tests like OCT, and a look at your medical history.
Key assessments include:
- Visual acuity testing to check your vision sharpness
- Eye pressure measurement to see if everything’s normal
- Dilated fundus examination to look at the retina and other eye parts
Medications to Avoid Before the Procedure
Some medicines might need to be stopped or changed before your injection. Tell your doctor about all the medicines you’re taking. This includes:
- Blood thinners (like warfarin or aspirin)
- Anti-platelet drugs
- Certain supplements that could affect bleeding
Your doctor will tell you which medicines to avoid and for how long.
What to Bring to Your Appointment
Bring these things to make your appointment go smoothly:
- A list of your current medicines and how much you take
- Any important medical records or test results
- A pair of sunglasses to wear after the procedure
- A friend or family member to come with you, if you can
Managing Anxiety About Eye Injections
It’s okay to feel a bit nervous about eye injections. Here are some tips to help:
Talk to your doctor about your worries. They can explain the procedure and clear up any misunderstandings.
Practical tips:
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Deep Breathing | Try deep breathing to calm down |
| Relaxation Techniques | Use guided imagery or meditation to relax |
| Support System | Bring a friend or family member for support |
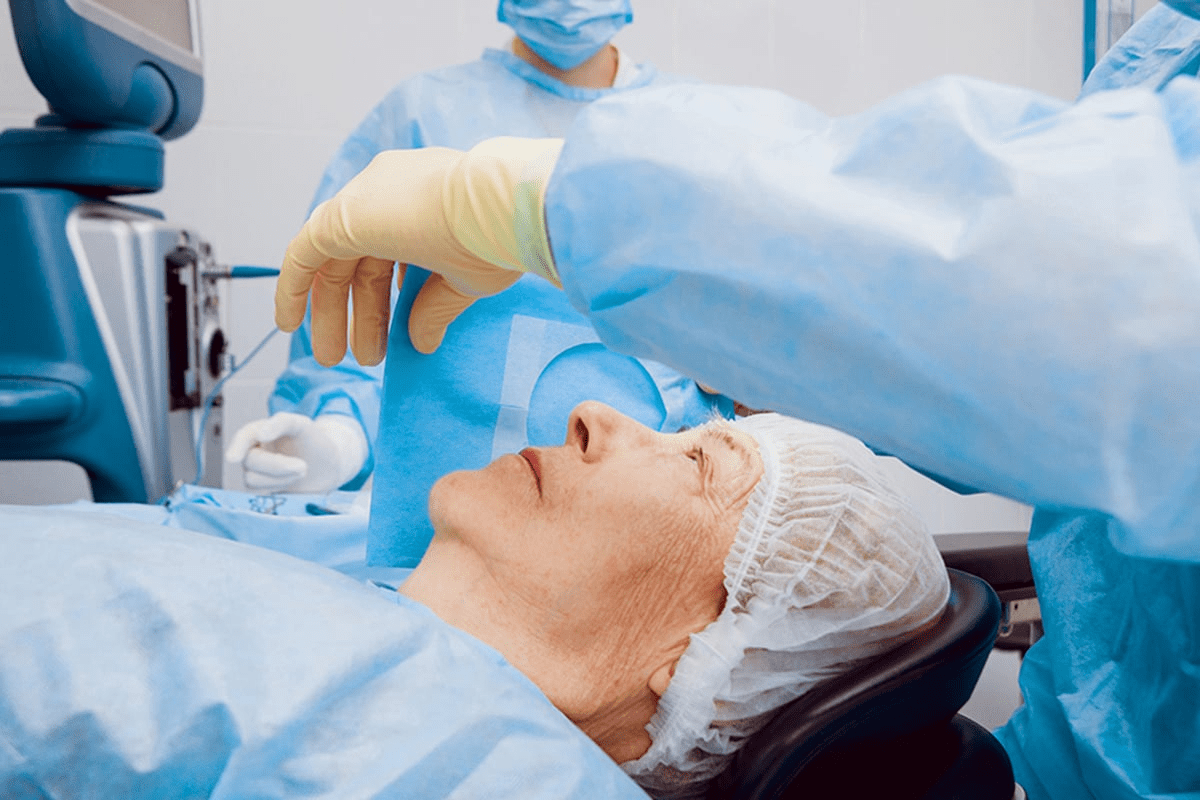
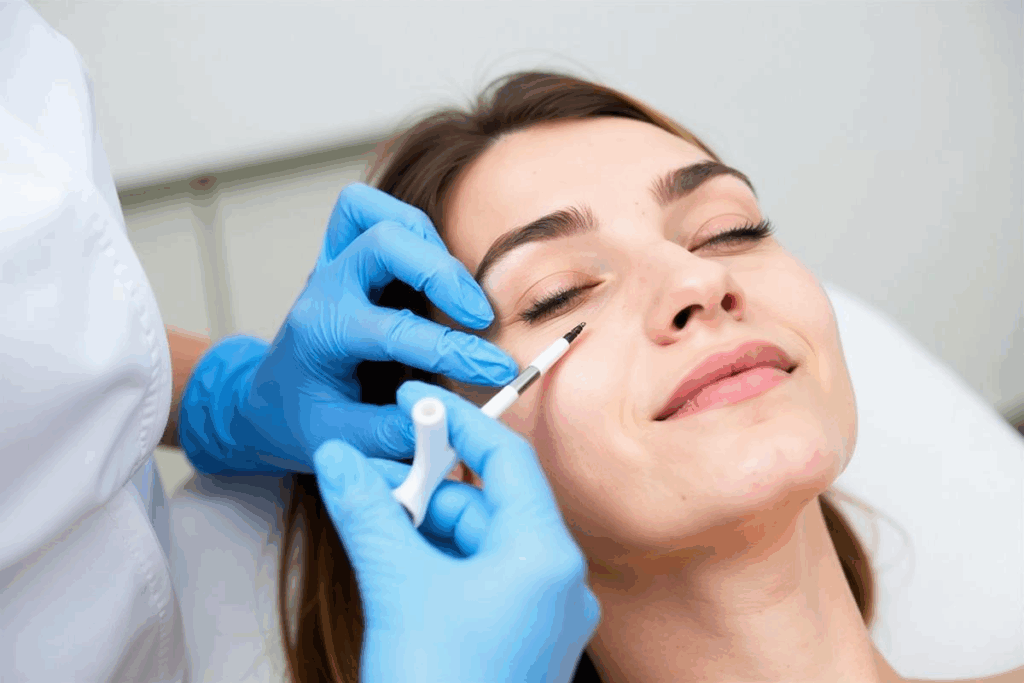
The Step-by-Step Eye Injection Procedure
Let’s walk you through the eye injection procedure for diabetic retinopathy. It’s designed to be comfortable and safe.
Pre-Injection Eye Examination
A detailed eye exam comes first. It checks your retina’s health and if the injection is needed. Tests like visual acuity and retina imaging might be used.
Numbing and Sterilization Process
To reduce pain, the eye is numbed with a local anesthetic. This can be eye drops or an injection. The eye is then cleaned to avoid infection. The numbing step is key to making the injection painless.
How the Injection Is Administered
A fine needle is used to put the medication into the vitreous gel inside the eye. The whole thing is usually quick, with little discomfort. The medication type, like anti-VEGF or corticosteroids, depends on your condition.
Duration and Discomfort Level
The whole process, from start to finish, takes 15 to 30 minutes. Some might feel a bit of discomfort or pressure, but it’s brief. Most people can go back to their day right after.
Knowing what happens during the eye injection can ease your worries. If you have questions, talk to your doctor.
What to Expect After Receiving Eye Injections
Knowing what to expect after eye injections can ease worries and help with recovery. Your eye might feel a bit sore after the procedure, but this usually goes away quickly.
Normal Side Effects
Some side effects are common after eye injections. You might feel a bit of discomfort, see things blurry, or feel like there’s something in your eye. These effects are usually short-term and go away in a few days.
Common side effects may include:
- Mild eye discomfort
- Blurred vision
- Eye redness
- Increased sensitivity to light
Warning Signs of Complications
While rare, complications can happen after eye injections. Knowing the warning signs is important.
| Warning Signs | Possible Complications |
|---|---|
| Severe eye pain | Infection or increased eye pressure |
| Vision loss or significant decrease | Retinal detachment or severe inflammation |
| Increased redness or swelling | Infection or allergic reaction |
Post-Injection Care Instructions
Proper care after eye injections is key to avoiding complications and getting the best results. Your doctor will give you specific instructions. Generally, you should:
- Avoid rubbing your eyes
- Use prescribed eye drops as directed
- Avoid swimming or submerging your head in water for a few days
Follow-up Appointments
Follow-up appointments are important for checking how the treatment is working and for any concerns or complications. Your doctor will schedule these based on your needs.
At these appointments, your doctor will check your vision, look for any complications, and decide if more injections are needed. It’s important to go to these appointments to get the best results.
Treatment Effectiveness and Outcomes
Eye injections have changed how we treat diabetic retinopathy, giving hope to those affected. It’s important to look at what makes this treatment work well.
Success Rates and Vision Improvement
Research shows eye injections can greatly improve vision for diabetic retinopathy patients. The success depends on the disease’s stage and the treatment type. For example, anti-VEGF injections help many patients see better.
“Intravitreal anti-VEGF therapy has become a cornerstone in the treatment of diabetic macular edema, with significant improvements in visual acuity observed in numerous clinical trials.”
N Engl J Med
Patients who get treatment early tend to do better. Below is a table showing how well eye injections work for vision improvement.
| Treatment | Success Rate | Average Vision Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Anti-VEGF Injections | 60-80% | 2-3 lines on the Snellen chart |
| Corticosteroid Injections | 50-70% | 1-2 lines on the Snellen chart |
Potential Risks and Complications
Eye injections are mostly safe, but there are risks. These include endophthalmitis, retinal detachment, and high eye pressure. We stress the need for careful patient selection and proper technique to avoid these issues.
Common complications include:
- Eye pain or discomfort
- Increased eye pressure
- Floaters
- Infection
Factors Affecting Treatment Response
Many things can affect how well eye injections work. These include how severe the diabetic retinopathy is, other eye conditions, and the patient’s overall health. Patients with well-controlled blood sugar tend to do better.
Realistic Expectations
It’s key for patients to know what to expect from eye injections. This treatment can improve vision and slow disease progression, but it’s not a cure. Regular treatment and follow-ups are needed for the best results.
We work with our patients to create a treatment plan that fits them. This way, they understand the benefits and risks of eye injections. This helps them make informed decisions about their care.
Long-Term Management and Lifestyle Modifications
Managing diabetic retinopathy well needs a mix of eye injections, keeping blood sugar in check, and eating right. We know it’s a big job, and we’re here to help. We’ll guide you on how to keep your eyes healthy and your overall health good.
Typical Injection Schedule
How often you get eye injections depends on how bad your diabetic retinopathy is. Usually, you get them every 4 to 8 weeks. It’s key to stick to this schedule to make sure the treatment works.
It’s also important to keep getting your eyes checked and adjust your treatment as needed. Your eye doctor will check how well the injections are working. They might change how often or what kind of medicine you get.
Blood Sugar Control and Its Impact
Keeping your blood sugar levels in check is critical for managing diabetic retinopathy. High blood sugar can harm the blood vessels in your retina. We suggest working with your doctor to keep your blood sugar in a healthy range.
Stable blood sugar levels can help slow down diabetic retinopathy. This means using the right medicine, eating the right foods, and making lifestyle changes that fit your needs.
Dietary Considerations
Eating well is important for managing diabetic retinopathy. Foods full of omega-3s, leafy greens, and antioxidants are good. Try to avoid foods high in sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats.
Eating right not only helps your eyes but also your overall health. It’s a good idea to talk to a nutritionist or your doctor to make a diet plan that’s right for you.
Combining Injections with Other Treatments
Sometimes, eye injections are used along with other treatments like laser therapy or surgery. The treatment plan depends on how advanced your diabetic retinopathy is.
A complete treatment plan is usually the best way to manage the condition. We work with a team of experts to make sure you get the best care. This means all parts of your treatment work together well.
By understanding the importance of long-term care and making the right lifestyle changes, people with diabetic retinopathy can manage their condition better. This helps protect their vision.
Conclusion: Living Well with Diabetic Retinopathy
Living with diabetic retinopathy can be tough, but it’s not impossible. With the right care, people can keep their vision sharp and live well. Eye injections play a big role in treatment, and sticking to the treatment plan is key.
Managing diabetic retinopathy means regular eye checks and sometimes eye injections. Keeping blood sugar in check, eating right, and using medical treatments can make a big difference. These steps help patients see better and feel better.
We urge patients to team up with their retina specialist. Together, they can create a treatment plan that works. With the right care, people with diabetic retinopathy can live full, active lives. They can keep their vision and stay healthy.
FAQ
What are eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
Eye injections treat diabetic retinopathy by putting medicine directly in the eye. This helps with swelling and can improve vision. It’s used for conditions like diabetic macular edema and proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
What types of medications are used in eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
Medicines like Lucentis, Eylea, and Avastin are common. They fight swelling and abnormal blood vessel growth. Corticosteroids, like Ozurdex, also help by reducing inflammation.
How often are eye injections needed for diabetic retinopathy?
The need for eye injections varies. It depends on the disease’s severity and how well the treatment works. Usually, injections are needed every 4-12 weeks, but this can change based on how you respond.
Are eye injections for diabetic retinopathy painful?
No, eye injections aren’t painful. A numbing agent is used before the injection. You might feel some pressure or discomfort, but it’s short-lived.
What are the possible side effects of eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
You might see redness, swelling, or increased eye pressure after an injection. Rare but serious issues like eye infections or retinal detachment can also happen.
How can I find a qualified retina specialist for eye injections?
Ask your doctor for a referral or check your insurance for specialists. You can also search online. Make sure to check the specialist’s credentials and patient reviews for the best care.
What should I expect during an eye injection procedure?
Your eye will be numbed and cleaned before the injection. The procedure is quick. You can usually go back to normal activities soon after.
How can I manage anxiety about eye injections?
Talk to your specialist about your worries. They can explain the process and offer reassurance. Try relaxation techniques like deep breathing to calm down before the procedure.
What is the success rate of eye injections for diabetic retinopathy?
Success rates vary based on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. Studies show eye injections can greatly improve vision and reduce vision loss risk in diabetic retinopathy patients.
Can eye injections be combined with other treatments for diabetic retinopathy?
Yes, eye injections can be used with other treatments like laser therapy, surgery, and managing blood sugar. This combination helps manage diabetic retinopathy effectively.
What is the typical injection schedule for diabetic retinopathy treatment?
The injection schedule varies based on your condition and treatment response. Regular check-ups with your specialist are key to finding the right schedule for you.
How do I prepare for an eye injection appointment?
Follow your specialist’s instructions, which may include stopping certain medications and bringing a driver. Be ready to ask questions about the procedure.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4411467/