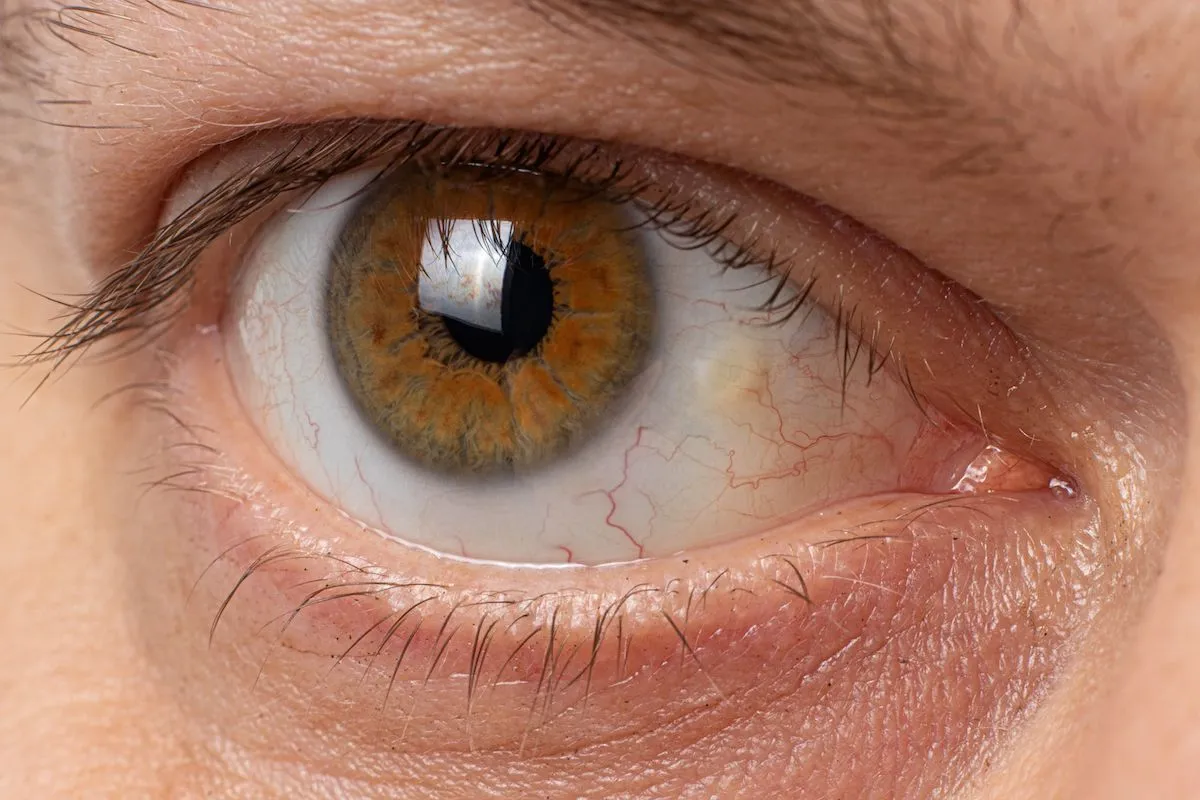
Have you noticed straight lines looking wavy or your central vision getting blurry? You might have an epiretinal membrane on your retina. This eye condition gets more common with age and can sneak up on you without warning.What is the membrane at the back of the eye? This guide explains the epiretinal membrane (ERM) and how serious it is.
An epiretinal membrane (ERM), also called macular pucker or cellophane maculopathy, is when cells form on the retina’s inside. This can mess with your vision. Knowing about ERM is key if you’re seeing vision problems, as it can really affect your daily life.
We’ll dive into what ERM is, how it affects your vision, and the treatments available to keep your eyes healthy.
Key Takeaways
- Epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a condition that affects the retina.
- ERM can cause vision disturbances, such as blurred central vision.
- The condition is more prevalent with age.
- Understanding ERM is key for timely treatment.
- Liv Hospital offers detailed eye exams and new treatment options.
Understanding Epiretinal Membrane (ERM)

Epiretinal membrane (ERM) is a condition where a fibrocellular layer grows on the retina’s surface. This affects the retina, which is key for seeing. It’s the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
Definition and Basic Anatomy
The retina lines the inside of the eye. It turns light into signals for the brain to understand as vision. ERM forms a membrane on the retina’s surface, causing vision issues due to its growth or thickening.
The retina has many layers, with the innermost being the internal limiting membrane. ERM grows here, causing vision problems. It’s more common in older people, and its exact cause is often unknown.
Alternative Names: Macular Pucker and Cellophane Maculopathy
ERM is also called macular pucker and cellophane maculopathy. These names highlight its effect on the macula, which handles central vision.
- Macular Pucker: This term describes the macula’s wrinkling due to ERM contraction.
- Cellophane Maculopathy: This name comes from the ERM’s thin, clear look, like cellophane.
Knowing these names helps in diagnosing and treating ERM. The condition’s severity and vision impact vary. So, accurate diagnosis and treatment are key.
The Membrane at the Back of the Eye: Structure and Function

The human retina is a complex neural network at the back of the eye. It lets us see the world around us. It’s made of nerve tissue that turns light into signals for the brain.
Normal Retinal Structure
The retina has layers like photoreceptor cells (rods and cones), bipolar cells, and ganglion cells. These work together to capture light and send visual info to the brain. The Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) forms on the inner retina, made of glial cells that can thicken and distort the retina.
The retina’s inner surface is key for clear vision. Any disruption, like an ERM, can cause vision problems. Normally, the retina’s inner surface is smooth, helping light reach photoreceptor cells well.
How ERM Forms on the Retinal Surface
ERM forms on the retina’s inner surface due to glial cell growth. This can happen with aging, retinal tears, or diseases. As these cells grow, they form a membrane that can wrinkle or thicken the retina, causing vision distortions.
ERM formation is a complex process involving cells and molecules. Knowing how it forms helps in finding treatments and management strategies.
Characteristics | Normal Retina | Retina with ERM |
Surface | Smooth | Wrinkled or thickened |
Cell Composition | Normal retinal cells | Glial cells, fibroblasts |
Visual Impact | Clear vision | Distorted vision, metamorphopsia |
Prevalence and Demographics of ERM
ERM is a big concern, mainly because it affects older people worldwide. Looking into ERM’s demographics shows why knowing its prevalence is key for health.
Statistical Incidence in the General Population
Research shows ERM impacts a large part of the population. It affects 7 to 11.8 percent of people. This range shows how different studies and criteria can change the numbers.
Here’s a table to help understand the numbers better:
Study Population | Prevalence Rate (%) |
General Population | 7 – 11.8 |
Age-specific (65+ years) | 15 – 20 |
Age-Related Prevalence Patterns
Age is a big risk factor for ERM. As people get older, ERM becomes more common. Studies show ERM affects 15 to 20 percent of those 65 and older.
There’s a clear link between age and ERM. This makes regular eye checks very important for seniors. As more people live longer, dealing with ERM will become even more critical for eye health.
ERM’s prevalence varies by age, showing the need for specific health plans. Knowing these patterns helps doctors plan better care and use resources wisely.
Types of Epiretinal Membrane
Knowing the different types of Epiretinal Membrane is key to figuring out how serious it is and what treatment is needed. There are two main types: Cellophane Macular Reflex (CMR) and Preretinal Macular Fibrosis (PMF).
Cellophane Macular Reflex (CMR)
Cellophane Macular Reflex is an early stage of ERM that often doesn’t show symptoms. It’s marked by a thin, clear membrane on the retina. CMR is usually found during routine eye checks.
Characteristics of CMR: The membrane in CMR is thin and doesn’t really affect vision. People with CMR might not notice anything wrong and might not need treatment right away.
Preretinal Macular Fibrosis (PMF)
Preretinal Macular Fibrosis is a more serious and advanced form of ERM. It has a thicker, more opaque membrane that can really mess with your vision. If not treated, PMF can lead to vision loss.
Characteristics of PMF: The membrane in PMF is thicker and more fibrotic, causing the retina to contract. This can severely impair vision, leading to problems like metamorphopsia and decreased visual acuity.
Differences in Severity and Prognosis
The main difference between CMR and PMF is how they affect vision. CMR is usually mild and might not get worse, but PMF can cause serious vision problems and needs quick medical help.
Characteristics | Cellophane Macular Reflex (CMR) | Preretinal Macular Fibrosis (PMF) |
Severity | Mild, often asymptomatic | Severe, can cause significant vision loss |
Membrane Characteristics | Thin, translucent | Thick, opaque, fibrotic |
Impact on Vision | Minimal | Significant visual disturbances |
Treatment Approach | Monitoring, conservative management | Surgical intervention often necessary |
It’s important for eye care professionals to understand these differences to choose the right treatment. It also helps patients know what to expect.
How Serious is Epiretinal Membrane?
ERM can be mild or severe, affecting vision differently. It’s important to know how it can impact your life.
Spectrum of Severity
ERM severity varies greatly. Some people might only notice slight vision changes. Others may face serious vision problems.
Mild ERM might not need strong treatment. But severe ERM can greatly reduce independence and happiness.
Impact on Vision Quality
ERM can harm vision quality. Symptoms include blurred, distorted, or double vision. The impact depends on the membrane’s severity and location.
- Blurred vision makes reading or clear tasks hard.
- Distorted vision makes straight lines look wavy.
- Double vision can mess with depth perception and daily tasks.
Potential Complications if Untreated
Untreated ERM can cause more problems. This includes losing vision and even retinal detachment. Regular eye checks are key to managing ERM.
Knowing ERM’s risks is why seeing a doctor is important. Early treatment can greatly help those with ERM.
Causes and Risk Factors of ERM
Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) comes from a mix of reasons. Knowing these helps in treating ERM well.
Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane
Often, ERM just happens without a known reason, called idiopathic ERM. Idiopathic ERM is more common in older people. It’s thought to be linked to aging, where the eye’s gel changes and can cause a membrane.
Secondary Causes
ERM can also come from other eye problems or injuries. Diabetic retinopathy, vein blockages, and eye injuries raise the risk. For example, in diabetic retinopathy, new blood vessels and tissue can form a membrane.
Risk Factors
There are several things that make ERM more likely. These include:
- Age: Older people are more likely to get ERM.
- Diabetes: Those with diabetic retinopathy are at higher risk.
- Retinal vein occlusion: This can lead to ERM.
- Ocular trauma: Eye injuries can cause ERM.
- Previous eye surgery or laser treatments: These may raise the risk of ERM.
Knowing these risk factors helps in catching ERM early. We suggest regular eye checks, mainly for those at risk, to watch for retina changes.
Symptoms and Signs of Epiretinal Membrane
It’s important to know the early signs of ERM to get medical help quickly. Symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane can really hurt your vision and daily life.
Early Warning Signs
The first signs of ERM include metamorphopsia, where straight lines look wavy. You might also see blurred vision or monocular diplopia, seeing double in one eye.
These signs can start off small, so it’s key to watch for any vision changes. Getting regular eye checks can spot ERM early.
Progressive Visual Disturbances
As ERM gets worse, vision problems get more serious. The membrane’s tightening can mess up central vision. This can lead to:
- Distorted vision
- Increased blurriness
- Harder time with tasks needing clear vision
Impact on Daily Activities
ERM symptoms can really mess with your daily life. Reading, driving, or even seeing faces can be tough. The distortion makes these tasks harder to do well.
Knowing how ERM affects daily life is key for patients and doctors. It helps in choosing the best treatment and ways to manage it.
Diagnosis of ERM
To diagnose Epiretinal Membrane, doctors use several methods. They do clinical exams and imaging studies. This process helps find the best treatment and improve patient care.
Clinical Examination Techniques
A detailed clinical exam is the first step. It includes:
- Visual Acuity Testing: Checking how clear your vision is.
- Dilated Fundus Examination: Eye drops are used to see the retina clearly.
- Slit-Lamp Biomicroscopy: A special tool to look at the retina closely.
These methods help doctors understand if you have ERM and how severe it is.
Imaging Studies
Imaging studies are key to confirming ERM. The main tool used is:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A test that takes detailed images of the retina without harm.
OCT is great for seeing the retina’s layers and finding ERM.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is important. It helps tell ERM apart from other eye problems. These include:
- Macular Degeneration: When the macula gets worse.
- Retinal Detachment: A serious issue where the retina peels off.
- Vitreomacular Traction Syndrome: When the vitreous gel pulls on the macula.
Getting the right diagnosis means you get the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Epiretinal Membrane
Treatment for ERM varies from watching it closely to surgery. The choice depends on how bad the symptoms are and how they affect your life and vision.
Conservative Management
For mild ERM symptoms, watching it closely is often the first step. This means regular checks with OCT imaging to see if the membrane or retina is changing. Observation is key for mild cases, as many don’t need surgery right away.
In some mild cases, visual rehabilitation is suggested. This helps patients get used to any vision problems caused by ERM. It might include using low vision aids or vision therapy.
Surgical Interventions
For severe ERM symptoms or big vision problems, surgery is needed. The most common surgery is pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with membrane peeling. This surgery removes the vitreous gel and carefully peels the ERM off the retina.
Surgical Procedure | Description | Benefits |
Pars Plana Vitrectomy (PPV) | Removal of vitreous gel and peeling of ERM | Improves vision, reduces distortion |
Membrane Peeling | Removal of the epiretinal membrane | Reduces traction on the retina |
Post-Treatment Care
After surgery for ERM, taking it easy is important for healing. Patients are told not to lift heavy things, bend, or do hard work for weeks. Follow-up appointments are set to check on healing and watch for problems.
Post-operative care might include eye drops to prevent infection and swelling. Patients can usually go back to normal activities in a few weeks. But, it can take months to fully recover.
Conclusion: Living with Epiretinal Membrane
Understanding Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) and its management can greatly improve life quality for those affected. It’s important to manage and monitor ERM to avoid complications and keep vision sharp.
We’ve talked about what ERM is, why it happens, its symptoms, how it’s diagnosed, and treatment options. Managing ERM well means using both non-surgical and surgical methods, based on how severe it is.
For those with ERM, proper care and follow-up are key. Regular visits to an eye doctor are essential. They help keep an eye on the condition and catch any changes early. This proactive approach helps manage the condition and keep life quality high.
In summary, managing ERM well means a team effort. Regular checks and quick action are vital. With the help of healthcare providers, people can manage their ERM and keep their vision intact.
FAQ
What is Epiretinal Membrane (ERM) and how does it affect vision?
Epiretinal Membrane is a condition where a layer of fibrous tissue forms on the retina. This causes vision problems. It can make vision distorted and blurry, affecting daily activities.
What are the alternative names for Epiretinal Membrane?
Epiretinal Membrane is also known as Macular Pucker and Cellophane Maculopathy. These names describe how it affects the macula, which is key for central vision.
How common is Epiretinal Membrane in the general population?
Epiretinal Membrane is more common with age. It’s seen more in older adults. As the population ages, it’s expected to become even more common.
What are the types of Epiretinal Membrane?
There are different types, like Cellophane Macular Reflex (CMR) and Preretinal Macular Fibrosis (PMF). These types vary in how severe they are and their outlook.
What are the symptoms of Epiretinal Membrane?
Symptoms include distorted and blurry vision. They can make daily activities like reading and driving hard. Early signs might be mild visual disturbances.
How is Epiretinal Membrane diagnosed?
Diagnosis uses clinical exams and tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT) and fluorescein angiography. These help figure out how severe it is and rule out other vision problems.
What are the treatment options for Epiretinal Membrane?
Treatment varies. For mild cases, conservative management might be enough. But for more severe cases, surgery like vitrectomy and membrane peeling is needed. Proper care after treatment is key for the best results.
Can Epiretinal Membrane be prevented?
Some risk factors, like age, can’t be prevented. But managing health conditions and keeping eyes healthy might lower the risk of getting it.
How does Epiretinal Membrane affect daily life?
It can greatly affect daily activities, like reading, driving, and recognizing faces. The severity of the condition and how well treatment works play a big role in its impact.
What is the prognosis for someone with Epiretinal Membrane?
The outlook varies based on how severe it is and how well treatment works. With the right care and follow-up, many can manage symptoms and keep their vision.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Epiretinal Membrane: Symptoms, Progression, and Prevalence with Age. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560703/