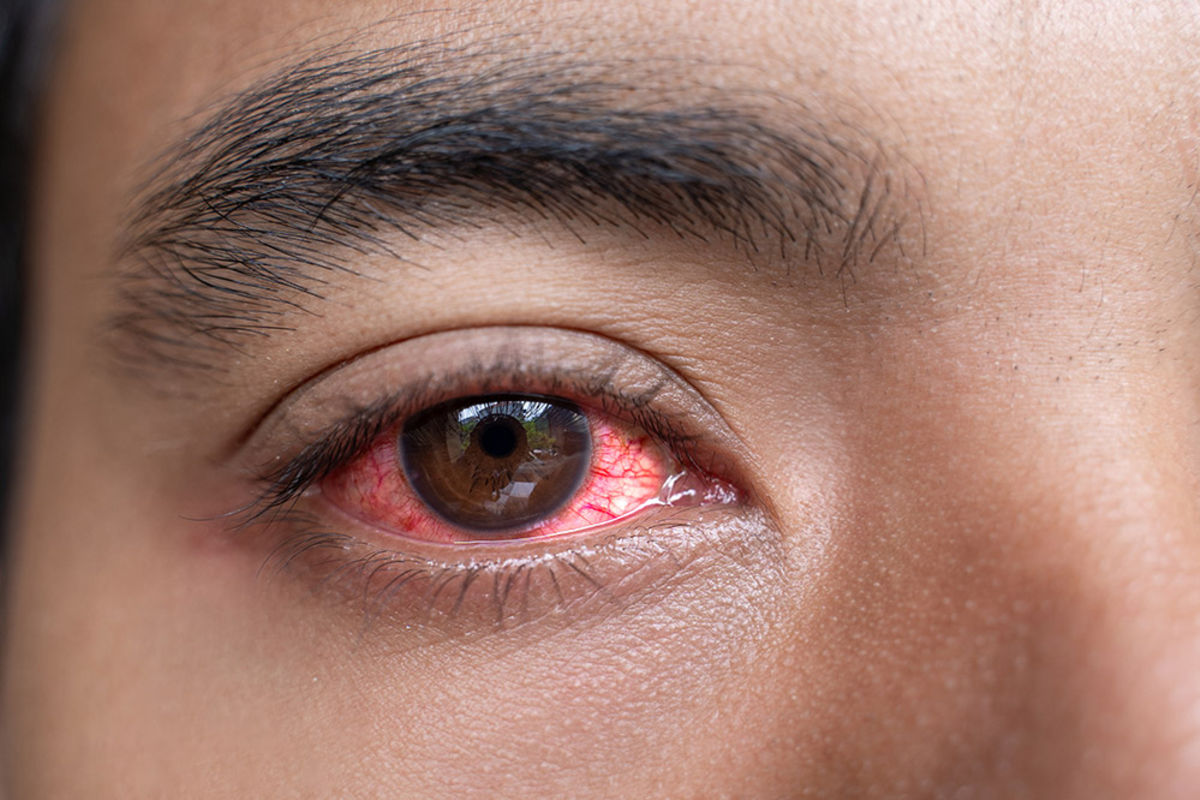
A blood clot in the eye is a serious issue. It can cause sudden vision loss and permanent damage if not treated quickly. If you’re having vision problems, it’s very important to see a doctor right away. Have an eyelid blood clot? This essential guide explains the common causes and how to get quick relief from the swelling.
Blood clots can happen for many reasons. One reason is vitreous hemorrhage, where blood bleeds into the vitreous. This is a gel-like fluid in the eye. It’s a serious condition that needs quick medical help to avoid worse problems.
We will look at the causes, symptoms, and eye clot treatment options. Knowing these can help protect your vision. It’s key for quick action and avoiding long-term damage.
Key Takeaways
- Recognizing the symptoms of a blood clot in the eye is key for quick medical help.
- Vitreous hemorrhage is a serious condition that needs immediate attention.
- There are many treatment options for blood clots in the eye.
- Quick treatment can stop permanent vision loss.
- Understanding the causes and symptoms is vital for managing the condition.
Understanding Blood Clots in the Eye

It’s important to know about blood clots in the eye. They can hurt your vision and are linked to many health issues.
What Causes Blood Clots in the Eye
Blood clots in the eye happen when blood vessels get blocked. This can be because of high blood pressure, diabetes, or blood clotting problems. High blood pressure and diabetes are big reasons because they damage blood vessels.
A subconjunctival hemorrhage, a type of eye blood clot, can be caused by sneezing or coughing. But sometimes, a serious health issue might be behind it. It’s key to know that some causes are harmless, but others can be serious.
The Impact on Vision and Eye Health
Blood clots can affect vision differently. Sometimes, they don’t cause much trouble, but other times, they can lead to serious vision loss. The clot’s location and size decide how much it will affect your vision.
- Vision distortion
- Blind spots
- Loss of peripheral vision
Blood clots can also cause serious problems like vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. This shows why getting medical help quickly is so important.
Why Physical Removal Is Not Possible
It’s not possible to remove blood clots from the eye because they are in delicate areas. Treatment aims to fix the cause and manage symptoms to avoid more problems.
We’ll talk about treatment options later, like medicines and surgery. For now, it’s important to know that while you can’t remove the clot, you can manage its effects with the right care.
Types of Eye Blood Clots
Retinal vein occlusions are a big deal when it comes to eye blood clots and vision. These happen when a vein in the retina gets blocked. This can lead to vision loss. We’ll look at the different types of retinal vein occlusions and how they affect the eye.
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) happens when the main vein draining the retina gets blocked. This can cause sudden vision loss. It’s a serious condition often linked to diseases like high blood pressure and diabetes.
The symptoms of CRVO can vary. But they often include:
- Sudden blurring or loss of vision in one eye
- Distorted vision
- Blind spots
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO)
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) affects the smaller veins branching off the main retinal vein. It’s more common than CRVO and can cause vision problems. The blockage in BRVO is usually less severe than in CRVO, but it needs medical attention.
Common symptoms of BRVO include:
- Blurred vision
- Floaters
- Vision distortion
Prevalence and Statistics
Retinal vein occlusion, including CRVO and BRVO, is rare. It affects less than 1% of adults worldwide. But it gets more common with age, hitting older adults harder.
Studies show:
- CRVO happens in about 1 in 1,000 adults each year.
- BRVO is more common, affecting around 4 in 1,000 adults yearly.
- Both conditions can cause significant vision problems if not treated.
Knowing about the different eye blood clots is key to managing and treating them. We’ll dive deeper into symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options next.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Eye Clots
Knowing the signs of eye clots is key to getting the right treatment. Eye clots, or retinal vein occlusions, can cause different symptoms. These symptoms can affect your vision in various ways.
Common Warning Signs
The signs of eye clots include blurry vision, sudden or gradual vision loss, and floaters. These signs can be scary and mean you need to see a doctor fast.
At times, a vitreous hemorrhage can happen. This leads to sudden vision changes that need quick medical help.
Progression of Symptoms
The way symptoms get worse can depend on the type and how bad the clot is. Symptoms can start slowly or suddenly. Knowing how they progress helps doctors decide what to do next.
For example, a CRVO can cause more severe symptoms than a BRVO.
Differences in Symptom Presentation
How symptoms show up can vary a lot. Things like where the clot is, how big it is, and your overall health play a part. This means everyone’s experience can be different.
Symptom | Description | Possible Cause |
Blurry Vision | Loss of sharpness in vision | Retinal Vein Occlusion |
Floaters | Spots or specks in the visual field | Vitreous Hemorrhage |
Sudden Vision Loss | Rapid decline in vision | Central Retinal Vein Occlusion |
Spotting these symptoms early is critical. It helps get medical help fast and might stop more vision loss. If you notice any of these signs, see an eye doctor right away.
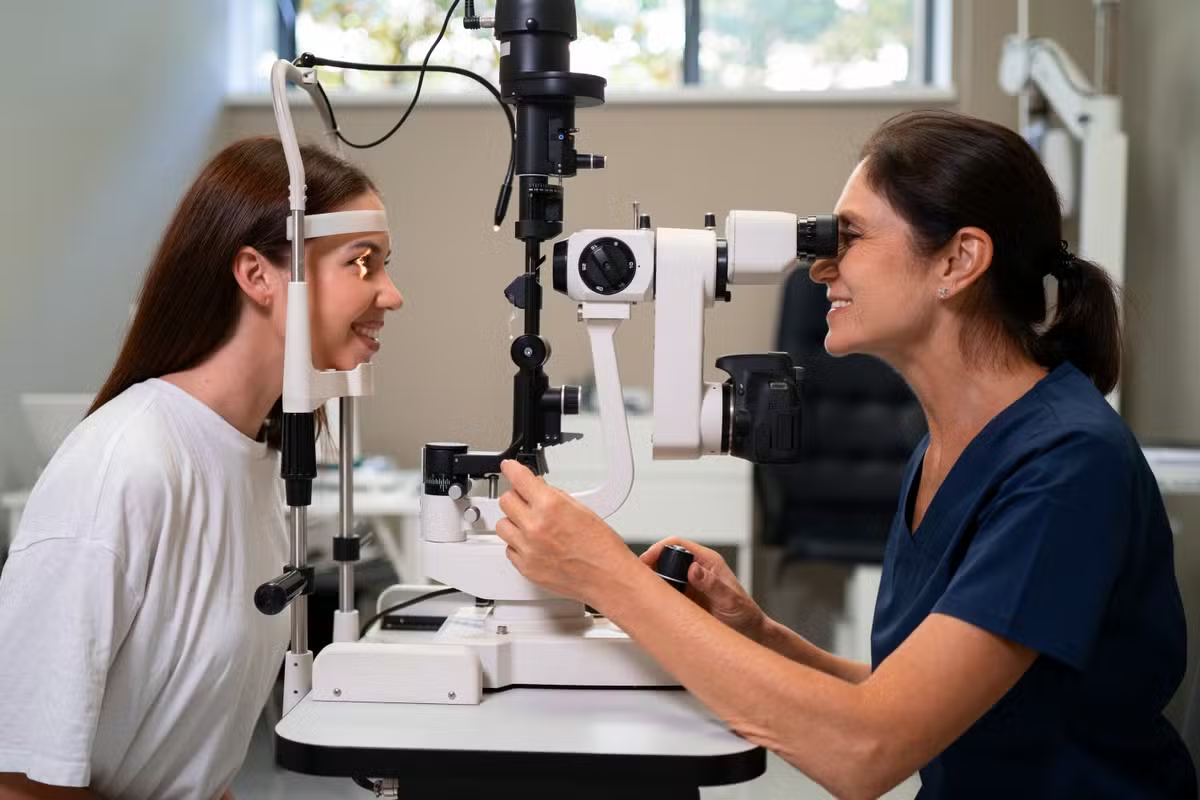
Diagnosing Blood Clots in the Eye
Diagnosing blood clots in the eye needs careful checks and special tools. Finding and treating them early is key to avoid vision loss.
Initial Eye Examination
The first step is a detailed eye check. An eye doctor will:
- Look at your medical history to find any conditions that might cause the clot.
- Do a vision test to see how clear your sight is.
- Use a special eye exam to look at the back of your eye.
Doctors say a blood clot in the eye is often spotted during this first check. This helps understand the clot and its cause.
Advanced Diagnostic Imaging
More tests might be needed to see the clot’s effect on the eye. These include:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): This test takes pictures of the retina without hurting it. It shows if the clot has damaged anything.
- Fluorescein Angiography: A dye is injected to make blood vessels in the retina show up. This helps find blockages or leaks.
Differential Diagnosis Considerations
When checking for eye blood clots, other possible causes must be thought of too. This includes retinal detachment or other eye problems. A detailed check helps make sure the right diagnosis is made.
Getting the right diagnosis is the first step to good treatment. By using the first eye exam and special imaging, doctors can understand the problem well. Then, they can plan the best treatment.
Risk Factors for Developing Eye Clots
Eye clots can be caused by several factors. These include age, medical conditions, and lifestyle choices. Knowing these risks helps prevent and treat eye clots effectively.
Age-Related Factors
As we get older, the chance of getting eye clots goes up. Age-related changes like high blood pressure and atherosclerosis play a big role. Older people are more at risk because of these changes in their blood vessels.
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some medical conditions make eye clots more likely. These include:
- High blood pressure, which can harm blood vessels in the eye.
- Atherosclerosis, or hardening of arteries, which can cause clots.
- Diabetes, which can change blood vessels and increase clot risk.
- Glaucoma, a condition that can raise eye pressure and lead to clots.
- Blood clotting disorders, which make clots more likely.
Managing health is key to lowering eye clot risk.
Lifestyle Factors Contributing to Eye Clots
Lifestyle choices also affect eye clot risk. Smoking, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can up the risk. A diet rich in saturated fats and cholesterol can also lead to atherosclerosis, raising the risk even more.
Understanding and tackling these risk factors can help prevent eye clots. It’s a step towards better eye health.
Comprehensive Eye Clot Treatment Options
Treating blood clots in the eye requires a variety of methods. Each method is chosen based on the clot’s type and how severe it is. The goal is to fix the vision problem and improve the patient’s health.
The Goals of Treatment
The main aim of treating eye clots is to save vision and stop it from getting worse. We also work to find and treat the cause of the clot. This helps keep the patient’s vision and quality of life better.
First-Line Treatment Approaches
Medicine is often the first step in treating eye clots. Anti-VEGF therapy is a common method. It involves injecting drugs into the eye to reduce swelling and protect vision. Corticosteroids are also used to fight inflammation.
Treatment Based on Clot Type and Severity
The treatment plan changes based on the clot’s type and how serious it is. For example, Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) and Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) need different approaches. Knowing the clot’s details helps us choose the right treatment for each patient.
Clot Type | Common Treatments | Goals |
CRVO | Anti-VEGF therapy, Corticosteroids | Reduce swelling, Improve vision |
BRVO | Laser therapy, Anti-VEGF therapy | Restore vision, Prevent further loss |
Vitreous Hemorrhage | Vitrectomy, Observation | Clear blood from the vitreous, Restore vision |
The Importance of Early Intervention
Acting fast is key when treating eye clots. Quick action can greatly improve the outcome. We stress the need to see a doctor right away if symptoms appear. This ensures the best chance for a good outcome.
Medication-Based Treatments for Blood Clots in Eyes
Medications are key in treating eye blood clots. They offer many effective options. The right medication depends on the clot’s type, severity, and the patient’s health.
Anti-VEGF Therapy Explained
Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (anti-VEGF) therapy is common for eye retinal issues. It involves eye injections to block VEGF. This protein causes abnormal blood vessel growth.
Benefits of anti-VEGF therapy:
- Reduces swelling and leakage from abnormal blood vessels
- Slows down or stops the growth of new blood vessels
- Improves vision in many patients
Corticosteroids and Their Application
Corticosteroids are used to treat eye clots. They reduce inflammation and swelling in the retina. These can be given through injections or implants.
Key considerations for corticosteroid use:
- Short-term use can be effective for acute inflammation
- Long-term use may lead to side effects like cataracts or glaucoma
- Careful monitoring is necessary to manage possible side effects
Anticoagulants and Thrombolytics
Anticoagulants and thrombolytics prevent or dissolve blood clots. Their use in eye clots is complex and less common. They might be considered in specific cases.
Types of anticoagulants and thrombolytics:
- Anticoagulants: Prevent new clot formation and stop existing clots from getting bigger
- Thrombolytics: Dissolve existing clots
Managing Side Effects of Medications
Medications for eye clots can be very effective but have side effects. It’s important to manage these side effects for treatment success.
Common side effects and their management:
Side Effect | Management Strategy |
Increased eye pressure | Monitoring and medication to lower eye pressure |
Cataract formation | Cataract surgery if necessary |
Infection | Prompt antibiotic treatment |
Surgical and Procedural Interventions
When other treatments don’t work, surgery is often needed for eye clots. These treatments aim to tackle the complex issues of eye clots. They offer relief when other methods fail.
Laser Therapy Options
Laser therapy is a key surgical option for eye clots, like diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusions. Laser photocoagulation helps reduce swelling, stops vision loss, and lowers the risk of complications.
Laser therapy is precise, targeting the problem area without harming nearby tissue. It’s often paired with other treatments to boost its success.
Vitrectomy Procedures
A vitrectomy removes the vitreous gel from the eye. It’s usually for severe cases like vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment due to eye clots.
In a vitrectomy, the surgeon takes out the vitreous gel and any blood or debris. This clears the eye and can improve vision.
When Surgery Is Necessary vs. Optional
Choosing surgery for eye clots depends on several factors. These include the clot’s severity, the patient’s health, and any underlying conditions.
Surgery is often needed for severe cases, like big vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment. For minor clots, surgery might be optional. It depends on the patient’s symptoms and quality of life.
- Necessary surgery is for severe cases, like big vitreous hemorrhage or retinal detachment.
- Optional surgery might be for less severe cases, based on the patient’s quality of life and surgery benefits.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Help
Eye clots can cause serious problems if not treated quickly. Knowing when to get medical help is key. A condition called vitreous hemorrhage, where blood bleeds into the eye, needs immediate care.
Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Attention
Some symptoms mean you need to see a doctor right away. These include:
- Sudden loss of vision or big changes in how you see
- Severe eye pain
- Seeing flashes of light or more floaters
- A curtain or shadow falling over your vision
What to Tell Your Healthcare Provider
When you go to the doctor, tell them everything about your symptoms and health history. Be ready to talk about:
- When your symptoms started and how long they’ve lasted
- Any eye problems or surgeries you’ve had before
- Your health history, like diabetes or high blood pressure
- What medicines you’re taking now
Sharing all this info helps doctors figure out what’s wrong and how to fix it.
The Consequences of Delayed Treatment
Waiting too long to treat eye clots can cause permanent vision loss. The longer you wait, the more damage there might be.
Condition | Consequence of Delayed Treatment |
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) | Permanent vision loss if not treated promptly |
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) | Potential for significant vision impairment |
Vitreous Hemorrhage | Risk of retinal detachment and vision loss |
Knowing the dangers of waiting too long to get help is very important. It shows why you should seek emergency care when you see warning signs.
Managing Underlying Conditions to Prevent Eye Clots
It’s key to manage health conditions to stop eye clots. By controlling factors that lead to clots, people can lower their risk of serious eye problems.
Controlling High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure raises the risk of eye clots. We suggest keeping blood pressure in check with lifestyle changes and, if needed, medicine. Keeping blood pressure healthy protects the blood vessels in the eyes.
- Regular exercise
- A balanced diet low in sodium
- Stress management techniques
Managing Diabetes and Cholesterol
Diabetes and high cholesterol increase eye clot risk. We stress the need to manage these conditions with lifestyle changes and treatments. Good management can lower the risk of eye clots and other issues.
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly
- Maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine
- Adhering to medication regimens as prescribed
Addressing Blood Clotting Disorders
For those with blood clotting disorders, managing the condition is critical to avoid eye clots. We help patients create a tailored treatment plan. This may include anticoagulant therapy and regular check-ups.
Lifestyle Modifications for Prevention
Along with managing health conditions, lifestyle changes can also prevent eye clots. We advise:
- Quitting smoking
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular physical activity
By making these changes and managing health conditions, people can greatly reduce their risk of eye clots.
Recovery and Prognosis After Eye Clot Treatment
After treatment for eye clots, patients often wonder about their recovery. The recovery time can vary a lot. It depends on the clot’s type and severity, and the treatment used.
Initial Recovery Phase
At first, patients might feel some discomfort. This can include dryness, irritation, or sensitivity to light. These symptoms usually go away on their own with proper eye care.
Follow-up care is key during this time. It helps monitor healing and catch any problems early. Regular visits to your healthcare provider are important for the best results.
Long-Term Vision Outcomes
The long-term vision after treatment depends on several things. This includes how big the clot was and how well the treatment worked. Some people see a big improvement, while others might have lasting vision changes.
“The key to successful recovery is early intervention and proper follow-up care. By working closely with your healthcare provider, you can maximize your chances of achieving the best possible outcome.”
Follow-Up Care Requirements
Follow-up care is vital for tracking recovery and managing any issues. How often you need to see your healthcare provider will vary. But usually, it’s several times in the first few months after treatment.
Follow-Up Care | Frequency | Purpose |
Initial Follow-Up | 1-2 weeks post-treatment | Assess initial healing and address any immediate concerns |
Subsequent Follow-Ups | Monthly for 3-6 months | Monitor progress, adjust treatment as necessary, and manage complications |
Coping with Permanent Vision Changes
For some, treatment might not fully fix their vision, leading to permanent changes. Dealing with these changes can be tough. But, there are resources to help. Seeing a low vision specialist can help find ways to use your remaining vision.
It’s important to stay positive and proactive about your eye health. This way, you can adjust to any permanent vision changes and live well.
Conclusion
Eye clots need quick medical help and the right treatment. We’ve looked at eye clots from many angles. This includes what causes them, how to spot them, and how to treat them.
Managing eye clots well means knowing all your treatment options. This is key for those dealing with this issue.
We talked about how to stop eye clots from happening again. Things like controlling blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol are important. These steps can lower your risk of getting eye clots.
There are many ways to treat eye clots. These include medicines, surgery, and changes in your lifestyle. Together, these can help manage the condition.
It’s very important to get medical help right away if you think you have an eye clot. With the right care, you can get better and avoid lasting eye damage. Treating eye clots well means using a mix of treatments and lifestyle changes.
FAQ
What are the main causes of blood clots in the eye?
Blood clots in the eye often come from high blood pressure, diabetes, and blood clotting disorders. These issues can harm the eye’s blood vessels, causing clots.
What are the symptoms of an eye clot?
Symptoms include sudden vision loss, blurred vision, and eye pain. The symptoms’ severity and how they progress depend on the clot’s type and location.
Can blood clots in the eye be physically removed?
No, it’s not possible to remove eye clots physically because of their location in delicate eye structures. Treatment focuses on the underlying cause and managing symptoms.
What are the treatment options for blood clots in the eye?
Treatments include medications like anti-VEGF injections, corticosteroids, and anticoagulants. Sometimes, laser therapy or vitrectomy surgery is needed.
How can I prevent blood clots in the eye?
Preventing eye clots involves managing conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes. A healthy lifestyle and regular eye exams are also key.
What is the prognosis after treatment for an eye clot?
The outcome depends on the clot’s type and severity, and how well treatment works. Some may see big improvements, while others might face permanent vision changes.
How are blood clots in the eye diagnosed?
Diagnosis includes a detailed eye exam, visual acuity tests, and dilated eye exams. Advanced imaging like optical coherence tomography (OCT) is also used.
What are the risk factors for developing eye clots?
Risk factors include age, certain medical conditions, lifestyle choices like smoking, and genetic predispositions.
When should I seek emergency medical help for an eye clot?
Get immediate medical help for sudden vision loss, severe eye pain, or other severe symptoms.
Can lifestyle modifications help prevent eye clots?
Yes, a healthy diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing stress can help keep your eyes healthy and reduce clot risk.
What is the role of anticoagulants in treating eye clots?
Anticoagulants help prevent more clots from forming. They might be prescribed for certain eye clots, based on the cause and other health factors.
Are there any long-term complications of eye clot treatment?
Long-term complications can include medication side effects, the need for ongoing treatment, and sometimes, permanent vision changes.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9256508/