A sudden red spot in the eye can be scary. It’s important to know the causes and treatments of blood clots. This helps tell if it’s just surface bleeding or something more serious that needs urgent care. Have a blood clot inside eye? This guide explains the causes of a hyphema or vitreous hemorrhage and how to get relief.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on treating eye problems. This includes subconjunctival hemorrhages and retinal vein occlusions. Our team uses the latest tools to diagnose and treat eye issues.
Usually, a blood clot in the eye goes away in 7 to 14 days. To feel better, try using artificial tears and don’t rub your eye. If the clot doesn’t go away or hurts, you should see a doctor.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes of blood clots in the eye is key to the right treatment.
- Subconjunctival hemorrhages and retinal vein occlusions need different treatments.
- Liv Hospital offers detailed care for eye problems.
- Artificial tears can ease symptoms.
- Seeing a doctor is important if the clot doesn’t clear up or hurts.
Understanding Blood Clots in the Eye

It’s important to know why blood clots form in the eyes. These clots can come from injuries, strain, or health issues. We’ll look into these causes to help you understand better.
What Causes a Red Spot in the Eye
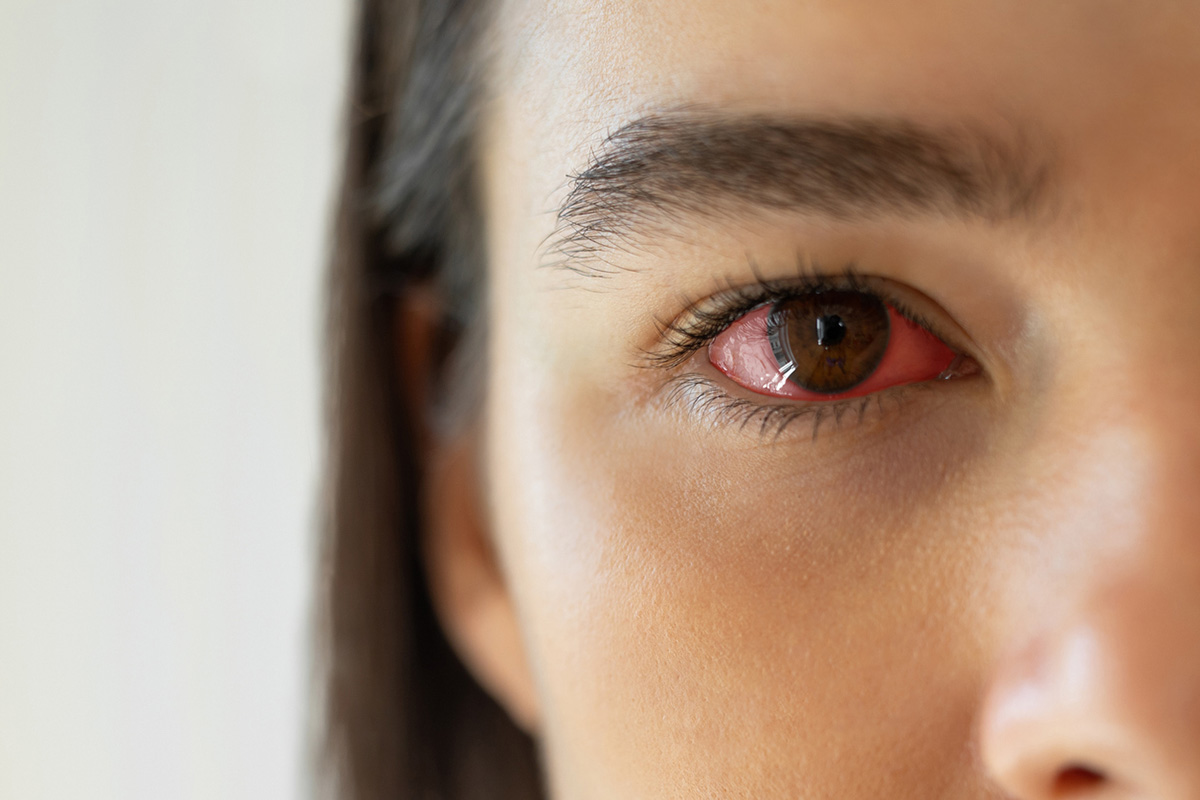
A red spot in the eye, or subconjunctival hemorrhage, happens when a blood vessel bursts. This bleeding is between the conjunctiva and sclera. It can be from eye trauma, sneezing, coughing, or straining. Also, high blood pressure and blood-thinning medications raise the risk.
Atherosclerosis, or hardening of arteries, is also a factor. It makes blood vessels more likely to break.
Distinguishing Between Normal Redness and Blood Clots
Not all eye redness is from blood clots. It can also be from irritation, dryness, or allergies. Blood clots show as a bright red spot without pain. It’s key to tell the difference to know how serious it is.
Characteristics | Normal Redness | Blood Clots |
Appearance | Diffuse redness | Bright red patch or spot |
Pain | Often accompanied by irritation or discomfort | Typically painless |
Causes | Irritation, dryness, allergies | Trauma, strain, hypertension, blood thinners |
How Eye Blood Clots Form
Eye blood clots happen when small blood vessels under the conjunctiva burst. This can be from high pressure or weak vessels. The leaked blood builds up, making a red spot.
Things that lead to these clots include physical strain, severe coughing or sneezing, and health issues affecting blood vessels. Knowing these factors helps in preventing and managing them.
Types of Blood Clot Inside Eye Conditions
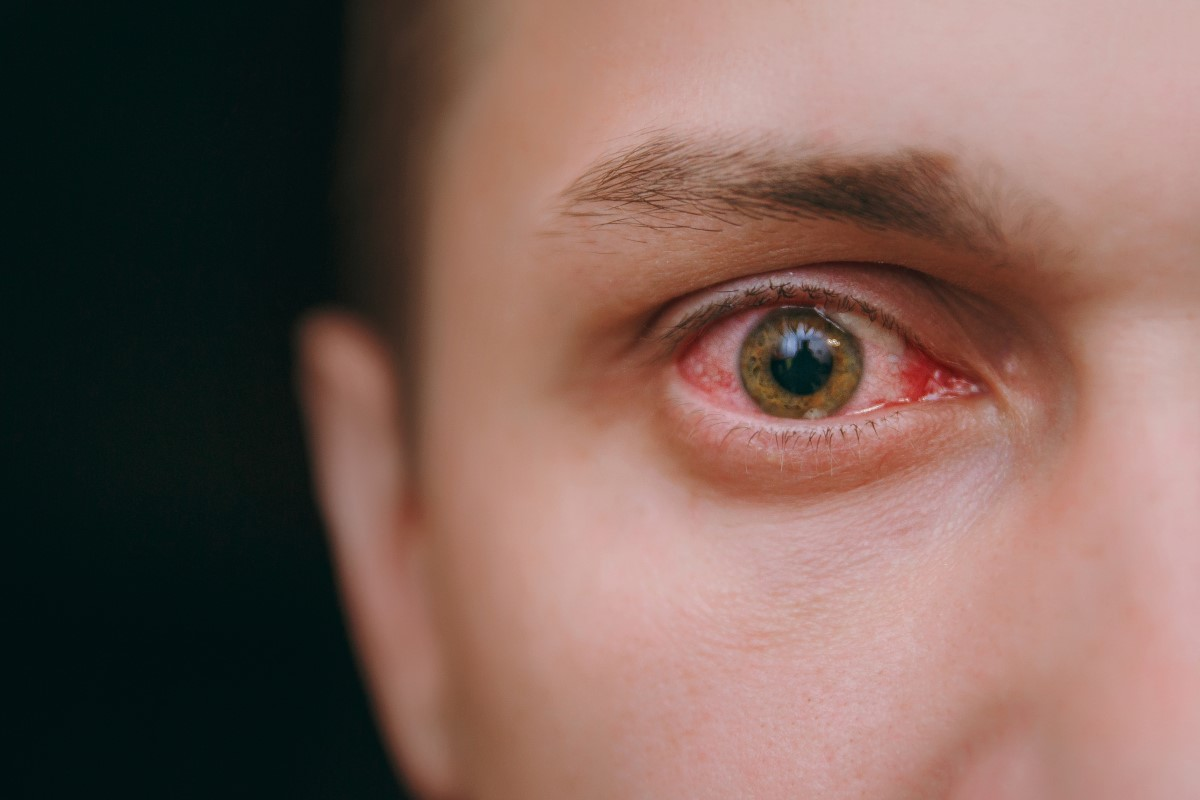
It’s important to know about the different blood clots that can happen in the eye. Each type has its own signs and effects on eye health. Knowing this helps doctors diagnose and treat them better.
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage: The Bright Red Spot
A subconjunctival hemorrhage happens when blood vessels burst under the eye’s clear surface. It shows up as a bright red spot on the eye’s white part. Even though it looks scary, it’s usually not serious and goes away in a couple of weeks.
Retinal Vein Occlusion: The Hidden Danger
Retinal vein occlusion is a serious issue where a vein in the retina gets blocked. This can cause sudden vision loss and is a medical emergency. It’s split into central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO) and branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO) based on where the blockage is.
Key Differences Between Eye Clot Types
Subconjunctival hemorrhage and retinal vein occlusion are different in symptoms, severity, and how they affect vision. Hemorrhages are usually harmless and don’t hurt your vision. But, vein occlusions can lead to serious vision loss and need quick medical help.
To understand the differences, let’s look at a comparison:
Condition | Symptoms | Severity | Impact on Vision |
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage | Bright red spot on the white of the eye | Generally benign | Minimal to none |
Retinal Vein Occlusion | Sudden vision loss | Serious | Significant vision loss |
We hope this info helps you understand the different eye clot conditions. If you notice any unusual symptoms or vision changes, see an eye doctor right away. They can give you the right diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes and Triggers
Blood clots in the eye can come from many sources. These include physical harm, health issues, and some medicines. Knowing what causes them helps in preventing and treating them.
Physical Factors: Trauma and Strain
Eye trauma is a big reason for blood clots. This can be from small injuries, like rubbing your eyes hard, to serious ones, like hitting your eye. Also, straining from heavy lifting, bending, or intense coughing can raise eye pressure. This might cause clots to form.
Common physical factors include:
- Eye injuries or trauma
- Heavy lifting or bending
- Intense coughing or sneezing
- Rubbing the eyes vigorously
Medical Conditions That Increase Risk
Some health issues can make you more likely to get blood clots in your eye. These include high blood pressure, diabetes, and bleeding disorders. High blood pressure can weaken blood vessel walls. This makes them more likely to break and clot.
Key medical conditions to be aware of:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Diabetes
- Bleeding disorders
- Vascular diseases
Medication-Related Causes
Some medicines can raise the risk of eye blood clots. Anticoagulants, meant to prevent clots, can sometimes cause them. Other drugs, like some antidepressants and blood pressure meds, can also lead to clots.
Medications that may increase risk:
- Anticoagulants
- Certain antidepressants
- Blood pressure medications
Knowing the common causes and triggers helps you lower your risk of eye blood clots. Regular eye exams and managing health issues are key to keeping your eyes healthy.
Recognizing Symptoms of Eye Blood Clots
It’s important to know the signs of blood clots in the eye to avoid serious problems. Eye blood clots, or eye clots, can show up in different ways. So, it’s key to know the symptoms of eye blood clots.
Visual Symptoms to Watch For
A bright red spot on the white part of the eye is a common sign of a blood clot eye. This can be scary, but often, it’s just a subconjunctival hemorrhage, which is usually not serious. But, it’s important to watch for any changes in this spot.
Other visual symptoms include:
- Floaters or dark spots in your vision
- Blurred vision
- Distorted vision
- Loss of peripheral vision
Pain and Discomfort Indicators
Some eye clots might not hurt, but others can cause discomfort or feel like pressure. If you have sudden or severe pain, get medical help right away. It could mean a serious issue with a clot behind the eye.
Changes in Vision That Signal Danger
Changes in vision can mean serious eye problems, including eye clots. Sudden changes like double vision, loss of vision, or seeing flashes of light are serious signs.
Symptom | Possible Cause | Action Required |
Bright red spot on the eye | Subconjunctival hemorrhage | Monitor; consult a doctor if it persists or is accompanied by other symptoms |
Floaters or dark spots | Retinal vein occlusion or other retinal issues | Seek immediate medical attention |
Sudden pain or pressure | Possible clot or other serious conditions | Seek immediate medical attention |
Knowing these symptoms can help you spot problems early. If you notice any of these signs, see an eye care professional. They can figure out what’s wrong and how to treat it.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
If you have eye blood clots, knowing when to get help is key. Eye blood clots can vary in severity. It’s important to know when to seek medical help to avoid complications.
Warning Signs That Require Emergency Care
Some symptoms mean you need to go to the emergency room right away. These include:
- Sudden vision loss or big changes in how you see
- Severe eye pain that won’t go away
- Increased redness or swelling around your eye
- Flashes of light or seeing floaters
If you have any of these symptoms, go to the emergency room or urgent care. A doctor said, “Quick action is key for sudden vision changes or severe eye pain.”
“Time is of the essence when dealing with possible vision-threatening conditions.”
Symptoms That Can Wait for Regular Appointment
Not all eye blood clots need emergency care. Mild symptoms that don’t get worse can wait for a regular doctor’s visit. These might include:
Symptom | Description |
Mild redness | A small, localized red spot without significant discomfort |
Minor discomfort | A feeling of irritation or dryness without severe pain |
What to Tell Your Doctor
When you see your doctor, tell them everything about your symptoms. Include when they started and what makes them better or worse. Be ready to talk about:
- Your medical history, including any eye problems before
- Any medicines you’re taking now
- Any recent eye injuries or trauma
Being informed helps you get the right care. If you’re unsure, it’s safer to get checked by a doctor.
Diagnosis Process for Eye Blood Clots
Diagnosing eye blood clots requires a detailed approach. This helps find the cause and the right treatment. At your visit, an eye care professional will do several tests to understand your situation.
Initial Eye Examination
The first step is a detailed eye check. The professional will check your vision, look at your eye’s parts, and search for clotting signs. As “A thorough eye exam is key to spotting eye blood clots and figuring out why they happen.”
This first check might include:
- Visual acuity tests to see how clear your vision is
- Looking outside and inside your eye for injuries or infections
- Ophthalmoscopy to see the retina and other inside parts
Advanced Diagnostic Tests
If the first check shows a blood clot, more tests are needed. These tests help confirm the clot and see how bad it is. They might include:
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) to get clear retina pictures
- Fluorescein angiography to see blood flow in the retina
- Ultrasound imaging to look at the eye’s shape
“More detailed tests are vital for managing eye blood clots by giving a clear view of the situation.”
Ruling Out Other Conditions
It’s important to tell eye blood clots apart from other issues that might look similar. Your eye doctor will look at other possible causes, like retinal detachment or high eye pressure. A medical expert says,
“It’s important to tell different eye problems apart to treat them right.”
By using your first check, more tests, and your medical history, your eye doctor can give a clear diagnosis. They will then suggest the best treatment for you.
Home Remedies for Subconjunctival Hemorrhage
Home remedies can help with subconjunctival hemorrhages. They can make you feel better and help your eyes heal. But, always talk to a doctor to make sure you’re getting the right care.
Cold Compress Application Technique
Using a cold compress is a good way to reduce swelling and pain. Here’s how to do it:
- Wrap an ice pack or a cold, damp cloth in a clean towel.
- Gently place the compress over your closed eye for 10-15 minutes.
- Repeat this process several times a day as needed.
Using Artificial Tears Effectively
Artificial tears can make your eye feel better by lubricating it. Here’s how to use them:
- Choose preservative-free drops to minimize irritation.
- Instill the drops as directed, usually 2-4 times a day.
- Consider using gel or ointment forms at night for prolonged lubrication.
Over-the-Counter Options for Comfort
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen can help with pain. But, always follow the instructions and talk to your doctor before taking any medicine.
Rest and Activity Modifications
Resting and changing your activities can help your eyes heal:
- Avoid strenuous activities that could increase eye pressure.
- Take regular breaks when engaging in visually demanding tasks.
- Ensure you’re getting enough sleep to help your body heal.
Using these home remedies can help with subconjunctival hemorrhage symptoms. They support healing. But, if your symptoms don’t get better or get worse, see a doctor.
Medical Treatments for Retinal Blood Clots
Treating retinal blood clots has improved a lot. Now, patients have many options to help them. We’ll look at injections, laser therapy, and when surgery might be needed.
Anti-VEGF Injection Procedures
Anti-VEGF injections are a key treatment for retinal blood clots. They’re often used for retinal vein occlusion. These injections help by stopping new blood vessels from growing and reducing leakage.
- Procedure: The injection goes into the vitreous gel of the eye.
- Benefits: It can lessen swelling and improve your vision.
- Frequency: You’ll need several injections over months.
Laser Therapy Options and Process
Laser therapy is also a good choice for retinal blood clots. It’s used for diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion. Laser burns are applied to the retina to reduce swelling and stop vision loss.
- Preparation: Your eye is numbed with drops or an injection.
- Application: The laser is applied to the retina.
- Follow-up: You might need more sessions, and follow-up care is key.
Medication Approaches
There are also medicines to help with retinal blood clots. These include corticosteroids to reduce swelling and anti-VEGF medications.
Surgical Interventions When Necessary
Sometimes, surgery is needed for retinal blood clots. This might include a vitrectomy, where the vitreous gel is removed.
- Indications: It’s for severe cases where other treatments don’t work.
- Risks and Benefits: Surgery has risks but can greatly improve vision and symptoms.
Dealing with retinal blood clots is tough. Our team is here to give you the best care and advice during treatment.
Preventing Future Eye Blood Clots
Preventing eye blood clots is easy with a few simple changes. By living a healthier lifestyle and managing health issues, you can lower your risk. This makes it easier to keep your eyes safe.
Lifestyle Changes That Make a Difference
Changing your lifestyle can help a lot. Regular exercise boosts blood flow and lowers clot risk. Eating right and managing stress also help your eyes stay healthy.
Don’t smoke and drink less alcohol. These habits harm your blood vessels and raise clot risk. Quitting smoking greatly improves your health, including your eyes.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
It’s key to manage health issues like high blood pressure and diabetes. These can up your risk for eye blood clots. Work with your doctor to control these with meds and lifestyle changes.
“Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of retinal vein occlusion and other eye-related complications.”
Proper Eye Care Practices
Good eye care is vital to avoid eye blood clots. Get regular eye exams to catch problems early. Also, protect your eyes from injury to prevent clots.
Dietary Considerations for Eye Health
Eating well supports your eye health and may lower clot risk. Include fruits, veggies, and omega-3s in your diet. Antioxidant-rich foods like leafy greens and berries are good for your eyes. Drinking water also keeps your eyes healthy.
- Incorporate foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon and walnuts, into your diet.
- Consume leafy greens like spinach and kale, which are high in antioxidants.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
Recovery Timeline and What to Expect
The recovery time for eye blood clots depends on the type and how serious it is. Each condition has its own healing time and follow-up care needs.
Healing Process for Subconjunctival Hemorrhages
Subconjunctival hemorrhages look like bright red spots on the eye’s white part. They usually heal in a few weeks. The body absorbs the blood, like a skin bruise.
As it heals, the color might change to yellow or green. This is a sign of healing.
Long-term Outlook for Retinal Vein Occlusions
Retinal vein occlusions are more serious and can affect vision a lot. The recovery time is longer and varies.
Some see vision improve over months. Others might have lasting vision issues. The outcome depends on the occlusion’s extent and other eye diseases.
Condition | Typical Recovery Time | Follow-up Care |
Subconjunctival Hemorrhage | 2-4 weeks | Usually not required unless recurrent |
Retinal Vein Occlusion | Several months to years | Regular check-ups with an eye specialist |
Follow-up Care Requirements
Follow-up care is key for eye blood clots, more so for serious cases like retinal vein occlusions. Regular visits to an eye specialist are important. They help track the condition and adjust treatments as needed.
When Normal Activities Can Resume
For subconjunctival hemorrhages, you can usually go back to normal activities right away. But for retinal vein occlusions, you might need to adjust activities based on your doctor’s advice.
“The key to recovery is not just the treatment itself, but also the follow-up care that ensures the condition is properly managed over time.”
— Medical Expert, Ophthalmologist
Talk to your healthcare provider about your situation. They can tell you when it’s safe to resume all normal activities.
Conclusion
It’s important to know about blood clots in the eye for good eye health. We’ve looked at why they happen, how to tell they’re there, and how to treat them.
Treating eye blood clots depends on the type and how bad it is. For some, like subconjunctival hemorrhages, simple steps like cold compresses help. But for others, like retinal vein occlusions, doctors might use injections or laser.
To avoid eye blood clots, change your lifestyle and take care of your eyes. Regular eye checks are key to catching problems early.
In short, eye blood clots are serious but can be handled well. Knowing the signs and getting help fast is key to keeping your eyes healthy.
FAQ
What are blood clots in the eye?
Blood clots in the eye happen when blood builds up in or around the eye. This can be due to things like subconjunctival hemorrhages or retinal vein occlusions.
What causes a blood clot under the eye?
A blood clot under the eye, often seen in subconjunctival hemorrhages, can be caused by physical trauma, strain, or underlying medical conditions that affect blood vessels.
How do I know if I have a blood clot in my eye?
Signs of a blood clot in the eye include a bright red spot, pain, discomfort, or changes in vision. These symptoms depend on the cause of the clot.
Can a blood clot in the eye be treated at home?
For subconjunctival hemorrhages, home remedies like a cold compress or artificial tears can help. But, serious conditions like retinal vein occlusions need medical help.
What are the treatments for retinal blood clots?
Treatments for retinal blood clots, often from retinal vein occlusions, include anti-VEGF injections, laser therapy, or medication. The choice depends on the severity and specific condition.
How can I prevent future eye blood clots?
To prevent future eye blood clots, make lifestyle changes, manage health conditions, and practice good eye care. This reduces risk factors.
What is the recovery process for eye blood clots?
Recovery varies by type of clot. Subconjunctival hemorrhages usually heal on their own. But, retinal vein occlusions may need ongoing treatment and follow-up care.
When should I seek immediate medical attention for an eye blood clot?
Seek immediate medical attention for severe pain, significant vision changes, or other warning signs of a serious condition.
Can medication cause blood clots in the eye?
Yes, some medications can increase the risk of eye blood clots. This is true for those that affect blood clotting or vascular health.
Are there any long-term effects of having a blood clot in the eye?
Long-term effects vary by cause. Subconjunctival hemorrhages usually don’t have lasting impacts. But, retinal vein occlusions can lead to persistent vision changes if not managed well.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551666/