Diabetes is a big threat to blood vessels all over the world. It quietly harms the small blood vessels that feed critical organs like the eyes, kidneys, heart, and nerves. When blood sugar stays high for too long, it starts a chain of damage to cells in many organs. Wondering “do your eyeballs have nerves?” Yes! This guide explains how diabetes damages these nerves and blood vessels.
High blood sugar makes advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These AGEs bind to proteins and fats in the blood, making inflammatory molecules. These molecules make blood vessels stiff and inflexible, leading to poor blood flow and affecting organs.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetes damages blood vessels and nerves through various mechanisms, including the formation of AGEs.
- Elevated blood sugar levels lead to reduced production of nitric oxide, affecting vascular flexibility.
- Multiple organ systems are affected by diabetes, including the eyes, kidneys, heart, and nerves.
- Factors such as smoking, high blood pressure, and a high-salt diet increase the risk of kidney failure from diabetes.
- Understanding the mechanisms of diabetes-related complications is key to protecting long-term health.
The Fundamentals of Diabetes and Vascular Health
It’s important to understand diabetes to see how it affects blood vessels and health. Diabetes mellitus is a long-term condition that changes how the body handles blood sugar, or glucose.
Understanding Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus means having too much glucose in the blood. If not managed, it can cause serious problems. High blood sugar can harm blood vessels and nerves, leading to health issues.
The body can’t make enough insulin or use it well, causing diabetes. Insulin is a hormone that lets cells use glucose for energy.
The Critical Role of Blood Glucose Regulation
Keeping blood glucose levels in check is key for healthy blood vessels and nerves. Uncontrolled blood glucose can damage these areas. It involves complex biochemical pathways that get disrupted by high glucose, causing damage.
Managing blood glucose is not just for diabetes. It’s also about avoiding complications like heart problems and nerve damage.
Why Blood Vessels and Nerves Are Vulnerable
Blood vessels and nerves are easily damaged by high blood glucose. This damage can cause atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in arteries. This can lead to heart attacks, strokes, and other heart diseases.
Nerve damage, or neuropathy, can cause pain, numbness, and weakness. It’s a common diabetes complication that can greatly affect a person’s life.
Biochemical Mechanisms of Blood Vessel Damage
High blood glucose levels start a chain of chemical reactions that harm blood vessels. When we have diabetes, our bodies can’t control blood sugar well. This leads to damage in our vascular system.
Formation of Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs)
Diabetes damages blood vessels by creating Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs). High glucose levels make AGEs, which attach to proteins and fats. This forms inflammatory molecules that weaken vessel walls.
This process speeds up blood vessel deterioration. It makes them more likely to get damaged.
Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Pathways
Oxidative stress and inflammation also harm blood vessels in diabetes. High glucose levels disrupt normal body processes. This leads to more oxidative stress.
This stress causes inflammation in blood vessels. Together, oxidative stress and inflammation harm blood vessels more.
Protein Kinase C Activation
Protein Kinase C (PKC) activation is another key mechanism. High glucose levels turn on PKC. This affects how blood vessels work.
PKC activation can make blood vessels more permeable. It also changes blood flow. This weakens blood vessel integrity.
Biochemical Mechanism | Effect on Blood Vessels |
Formation of AGEs | Weakens vessel walls through inflammatory molecules |
Oxidative Stress and Inflammation | Increases vascular damage through oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways |
PKC Activation | Alters blood vessel function, increasing permeability and affecting blood flow |
How Does High Blood Glucose Damage Blood Vessels
High blood sugar levels start a chain of events that harm blood vessels. This damage comes from several pathways, leading to serious problems.
Endothelial Dysfunction and Nitric Oxide Reduction
The endothelium, a thin layer of cells, is vital for blood vessel health. High blood sugar hurts this layer by cutting down nitric oxide production. Nitric oxide keeps blood vessels flexible and working well.
Without enough nitric oxide, blood vessels have trouble relaxing and blood flow gets worse. This is a big step towards vascular problems in diabetes.
Less nitric oxide also means more oxidative stress. This stress makes the endothelium dysfunction worse. It’s a cycle that worsens blood vessel damage.
Vascular Inflammation and Immune Response
High blood sugar also causes inflammation and immune system activation. It turns on inflammatory pathways, leading to more inflammatory molecules. These molecules weaken blood vessel walls.
This inflammation is a major reason for atherosclerosis and other vascular issues. The immune system’s response also plays a big part in worsening vascular damage. Keeping blood sugar in check is key to reducing inflammation and protecting blood vessels.
Blood Vessel Stiffening and Structural Changes
Long-term high blood sugar makes blood vessels stiffer and changes their structure. AGEs build up, and signaling pathways get activated. This remodeling makes blood vessels less flexible and more vulnerable to damage.
This stiffening affects the whole vascular system. It raises blood pressure and increases the heart’s workload. Managing blood sugar is vital to prevent these changes.
Diabetes impacts many body systems and organs, like the heart, kidneys, and eyes. Knowing how high blood sugar damages blood vessels is key to managing diabetes and preventing complications.
Microvascular Complications in Diabetes
The microvascular system is very sensitive to diabetes damage. High blood sugar levels harm the small blood vessels all over the body. This can cause serious health problems and lower the quality of life for people with diabetes.
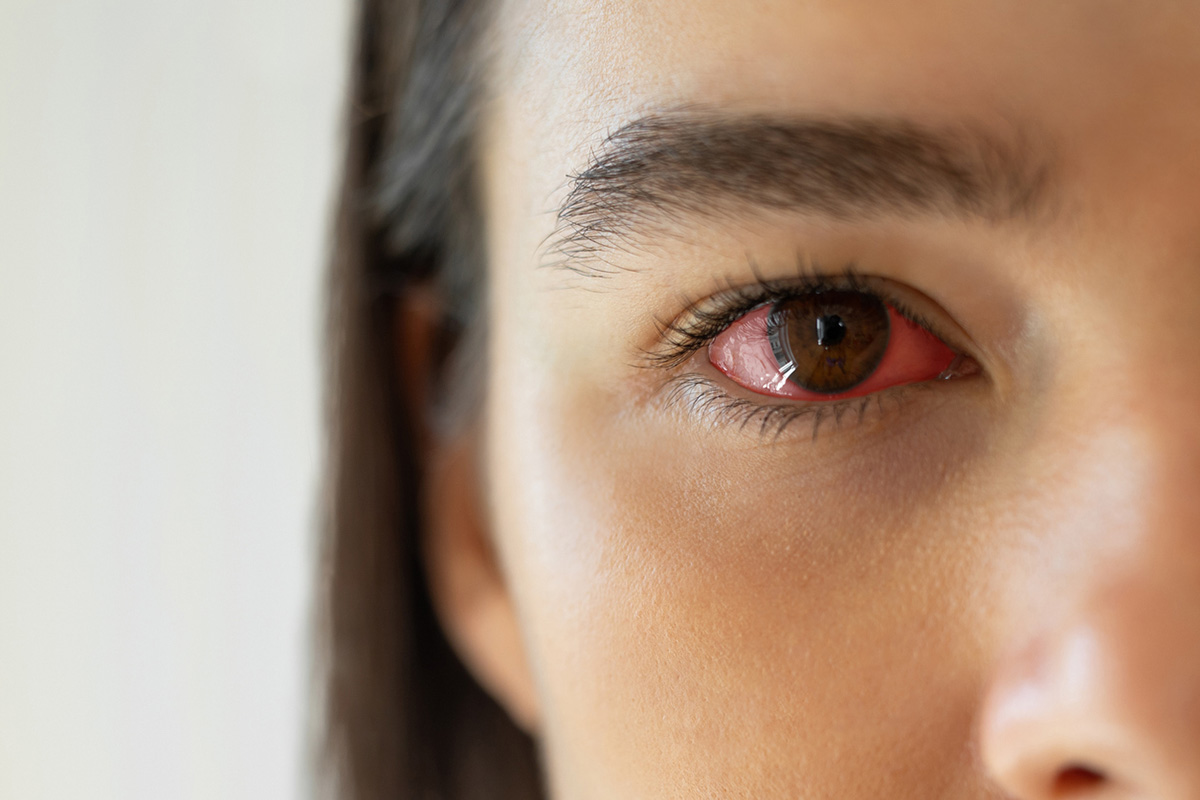
Damage to Eye Vessels
Diabetic retinopathy affects the retina’s blood vessels, causing vision issues and blindness. High blood sugar damages these vessels, leading to leaks or blockages. It’s a major reason for vision loss in adults with diabetes.
Kidney Vessel Damage
Diabetic nephropathy damages the kidney vessels due to high blood sugar. This makes it hard for the kidneys to filter waste, which can lead to kidney failure. Keeping blood sugar and blood pressure in check is key to preventing or slowing this damage.
Skin and Gum Issues
Diabetes can also harm the skin and gums, causing slow healing and gum disease. High blood sugar reduces blood flow to these areas, leading to infections. Good blood sugar control and regular dental visits are vital to prevent these problems.
It’s important for people with diabetes to understand and manage these complications. By controlling blood sugar and living a healthy lifestyle, they can lower their risk of these issues. This improves their overall well-being.
Macrovascular Disease in Diabetes
Diabetes affects blood vessels in many ways, with macrovascular disease being a big concern. Macrovascular disease damages the large blood vessels, leading to heart problems.
Accelerated Atherosclerosis Development
Macrovascular disease in diabetes speeds up atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is when plaque builds up in arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. High blood sugar levels in diabetes make this happen faster.
High glucose levels harm the blood vessel lining, making it easier for plaque to build up. This increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes in people with diabetes.
Coronary Artery Disease and Heart Failure
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a big problem in diabetes. CAD happens when the heart’s blood supply arteries get damaged. Plaque buildup in these arteries can reduce blood flow to the heart, causing chest pain or angina.
If CAD isn’t treated, it can lead to heart failure. Heart failure means the heart can’t pump enough blood. It’s a serious condition that affects daily life and needs careful management.
Peripheral Artery Disease and Stroke Risk
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is another issue with macrovascular disease. PAD is when the arteries outside the heart narrow due to plaque. It can cause leg pain when walking and limit mobility.
Also, diabetes increases the risk of stroke due to macrovascular disease. The damage to blood vessels makes them more likely to block, which can cause a stroke if it happens in the brain’s blood supply.
It’s important to know about the risks of macrovascular disease in diabetes. By keeping blood sugar levels under control and managing other heart risks, people with diabetes can lower their chance of these problems.
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Nerve Damage
Diabetic nerve damage comes from complex metabolic and vascular factors. It happens in people with diabetes due to high blood sugar levels. This damage affects the nerves over time.
Metabolic Pathways Leading to Neuropathy
Several metabolic pathways lead to diabetic neuropathy. Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) build up on nerve cells, disrupting their function. Oxidative stress also plays a big role, damaging nerve cells with reactive oxygen species.
Vascular Factors in Nerve Damage
Vascular factors also play a big role in nerve damage. Poor blood flow to nerves, due to blood vessel damage, causes ischemia. This leads to nerve dysfunction. Vascular damage is a key part of diabetic neuropathy.
Immune-Mediated Nerve Injury
Immune responses also contribute to diabetic neuropathy. Inflammation and immune reactions can harm nerves. Understanding these immune processes is key to treating neuropathy.
Diabetic neuropathy is a complex condition. It involves metabolic, vascular, and immune pathways. By understanding these, we can improve treatment and outcomes for patients.
Do Your Eyeballs Have Nerves? Ocular Complications in Diabetes
Diabetes is a big threat to many parts of our body, including our eyes. High blood sugar can harm both blood vessels and nerves in the eyes. This damage can affect many parts of our body if blood sugar stays high for too long.
The eyes are very sensitive to damage because of their complex nerves and blood vessels. Diabetes is the main reason for blindness in adults between 20 and 74. It’s very important to know how diabetes can harm our eyes.
The Complex Nervous System of the Eye
The eye has a complex nervous system that helps us see. The retina is not just a light-sensitive tissue; it’s like an extension of the brain. It has complex neural circuits. The optic nerve, which carries visual information to the brain, is also key.
Diabetic Impact on Ocular Nerves
Diabetes can harm the nerves in our eyes. Diabetic neuropathy can damage nerves that control eye movements and the autonomic nerves that control pupil size. Diabetes also causes diabetic retinopathy, which damages blood vessels in the retina and can lead to vision problems and blindness.
Diabetic Optic Neuropathy
Diabetic optic neuropathy is a serious complication of diabetes. It damages the optic nerve, which is vital for vision. High blood sugar, high blood pressure, and high cholesterol are risk factors for this condition.
Ocular Complication | Description | Potential Outcome |
Diabetic Retinopathy | Damage to the blood vessels in the retina | Vision problems, blindness |
Diabetic Optic Neuropathy | Damage to the optic nerve | Vision loss |
Ocular Neuropathy | Damage to the nerves controlling eye movements | Impaired eye movement, double vision |
We’ve looked at how diabetes affects our eyes, including serious problems like diabetic retinopathy and diabetic optic neuropathy. Knowing these risks is key to managing diabetes and keeping our vision safe.
What Organs and Body Systems Does Diabetes Affect
Diabetes is a complex condition that affects not only blood sugar levels but also multiple organs and body systems throughout the body. As we explore the various complications associated with diabetes, it becomes clear that this disease has a far-reaching impact on overall health.
Cardiovascular System Complications
The cardiovascular system is significantly affected by diabetes, leading to various complications. Accelerated atherosclerosis development is a major concern, as it increases the risk of coronary artery disease and heart failure. We know that people with diabetes are more likely to experience cardiovascular events, making it important to manage cardiovascular risk factors.
The damage to blood vessels through atherosclerosis is a cornerstone of diabetes-related cardiovascular complications. This process is exacerbated by factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and smoking. As a result, individuals with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing coronary artery disease, which can lead to heart attacks and other serious cardiovascular events.
Renal System Damage Progression
Diabetes can cause significant damage to the renal system, leading to diabetic nephropathy and potentially progressing to end-stage renal disease (ESRD). People with ESRD require dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive. We understand that early detection and management of diabetic nephropathy are critical in preventing the progression to ESRD.
The progression of renal damage in diabetes is characterized by the gradual loss of kidney function over time. This can be attributed to factors such as high blood glucose levels, hypertension, and genetic predisposition. Regular monitoring of kidney function and blood pressure control are essential in slowing the progression of renal damage.
Stage | Description | Typical GFR (mL/min/1.73m2) |
1 | Kidney damage with normal or increased GFR | >90 |
2 | Kidney damage with mildly decreased GFR | 60-89 |
3 | Moderately decreased GFR | 30-59 |
4 | Severely decreased GFR | 15-29 |
5 | End-stage renal disease (ESRD) |
Gastrointestinal and Genitourinary Systems
Diabetes can also affect the gastrointestinal and genitourinary systems, leading to various complications. Gastrointestinal motility disorders are common, causing symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Diabetes can also lead to genitourinary complications, including urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction.
These complications arise due to damage to the nerves and blood vessels that supply these systems. Maintaining good blood glucose control and addressing other risk factors can help mitigate these complications.
Clinical Manifestations of Diabetic Vascular and Nerve Damage
Diabetic vascular and nerve damage shows itself in many ways. It starts with early signs and can lead to serious complications. As diabetes worsens, it affects blood vessels and nerves, causing various symptoms.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Spotting diabetic vascular and nerve damage early is key. Numbness, tingling, and pain in the extremities are common signs of nerve damage. Vascular damage shows as coldness or discoloration of the skin, often in the feet. These signs mean it’s time to see a doctor.
These symptoms can start slowly and get worse. Poor blood sugar control, smoking, and high blood pressure can make them worse. Catching them early can help slow the disease.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing diabetic vascular and nerve damage requires a detailed approach. We start with a medical history and physical examination. Tests like electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS) check nerve function and damage.
- Comprehensive medical history
- Physical examination
- Electromyography (EMG)
- Nerve conduction studies (NCS)
- Vascular assessment through Doppler ultrasound
Long-term Consequences and Complications
The long-term effects of diabetic vascular and nerve damage are serious. Cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes are more likely. Diabetic nephropathy can lead to kidney failure, needing dialysis or a transplant.
Severe nerve damage and artery disease can cause foot ulcers and amputations. This highlights the importance of foot care and prevention. Managing these issues requires a team effort, including controlling blood sugar, making lifestyle changes, and using the right treatments.
Prevention and Management Strategies for Vascular and Nerve Protection
Managing diabetes is more than just keeping blood sugar in check. It’s about protecting your body from damage. Good management strategies are key to avoiding diabetes complications.
Glycemic Control Approaches
Keeping blood sugar levels stable is vital. This means checking your blood sugar often, adjusting your diet and exercise, and following your doctor’s advice on medications or insulin.
Checking your blood sugar regularly helps you see how different things affect it. Changing your diet and exercise based on this info can really help control your blood sugar.
Glycemic Control Method | Description | Benefits |
Regular Blood Glucose Monitoring | Checking blood sugar levels at different times of the day | Helps in understanding the impact of diet, exercise, and medication on blood sugar levels |
Dietary Adjustments | Making changes to diet based on blood glucose readings | Improves glycemic control, helps in maintaining a healthy weight |
Exercise Routine | Engaging in regular physical activity | Enhances insulin sensitivity, improves overall health |
Lifestyle Modifications and Their Impact
Making lifestyle changes is important for managing diabetes. Quitting smoking, being more active, and eating well are key changes.
Stopping smoking is very important because it helps prevent heart problems. Being active not only helps control blood sugar but also boosts heart health.
Lifestyle Changes and Their Benefits
- Smoking Cessation: Reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease and improves overall health.
- Increased Physical Activity: Enhances insulin sensitivity and contributes to better glycemic control.
- Healthy Diet: Helps in maintaining optimal blood glucose levels and supports overall health.
Pharmacological and Surgical Interventions
Along with lifestyle changes and blood sugar control, medicines and surgery might be needed. Medicines to control blood pressure and cholesterol are common. Surgery, like angioplasty or bypass surgery, might be needed for serious heart or artery problems.
By using a complete approach that includes managing blood sugar, making lifestyle changes, and sometimes medicines or surgery, people with diabetes can lower their risk of vascular and nerve problems.
Conclusion: The Importance of Comprehensive Diabetes Care
High blood glucose levels are a big threat to our blood vessels and nerves. If blood sugar stays high for too long, it causes damage to many parts of our body. Diabetes can lead to kidney failure, needing dialysis or a transplant to live.
We know that taking care of diabetes is key to avoiding serious problems. Diabetes management means keeping blood sugar in check, making healthy lifestyle choices, and using medicine and surgery when needed. By understanding and tackling diabetes-related issues, people with diabetes can lower their risk of heart disease, kidney failure, and other serious problems.
Our work on vascular protection and nerve protection is a big part of comprehensive diabetes care. We stress the need for a complete approach to keep people with diabetes healthy and improve their life quality.
FAQ
What organs are affected by diabetes?
Diabetes impacts many organs and systems. This includes the heart, kidneys, and digestive system. It can cause heart disease, kidney failure, and other issues.
How does high blood glucose damage blood vessels?
High blood sugar harms blood vessels in several ways. It damages the lining of blood vessels and reduces blood flow. This can hurt vital organs.
What are the biochemical mechanisms of blood vessel damage in diabetes?
Blood vessel damage in diabetes comes from several sources. This includes the buildup of harmful substances and inflammation. These factors weaken blood vessel walls.
What is diabetic neuropathy, and how does it occur?
Diabetic neuropathy is nerve damage from diabetes. It happens due to high blood sugar and poor blood flow. This can cause numbness and pain in the hands and feet.
How does diabetes affect the eyes?
Diabetes can harm the eyes by damaging blood vessels. This can lead to vision loss or blindness. It can also damage the optic nerve, causing vision problems.
What are the clinical manifestations of diabetic vascular and nerve damage?
Symptoms of diabetic damage include numbness and pain. Doctors use tests to diagnose these issues. Untreated, it can lead to serious problems like heart disease and amputations.
How can diabetes-related complications be prevented and managed?
To prevent complications, manage blood sugar levels. This includes diet, exercise, and sometimes medication. Quitting smoking and staying active also helps.
What body systems does diabetes affect?
Diabetes impacts many systems, including the heart and kidneys. Managing diabetes is key to avoiding serious problems in these areas.
How does hyperglycemia damage blood vessels?
High blood sugar damages blood vessels in several ways. It leads to the formation of harmful substances and reduces blood flow. This weakens vessel walls and affects function.
What are the microvascular complications of diabetes?
Diabetes can cause problems like vision loss and kidney failure. It also affects the skin and gums. These issues can have a big impact on quality of life.
References
Government Health Resource. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/54/6/1615