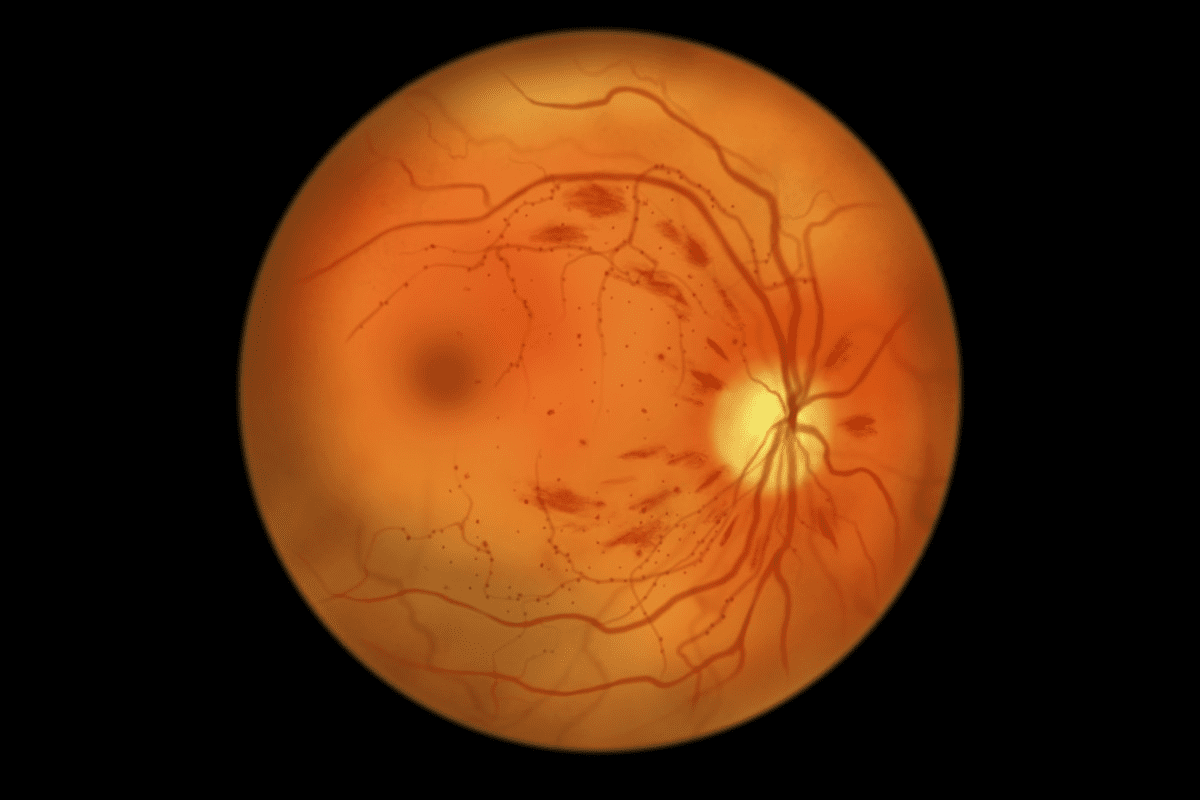
Drusen in the eye are small, yellowish deposits that build up under the retina. They are a key sign of age-related macular degeneration. This condition is a top reason for vision loss in those over 50. At Liv Hospital, we focus on spotting these early signs to offer timely, tailored care. Learn about drusen macular degeneration. This essential guide explains what drusen are, how they affect your vision, and treatment.
These deposits are made of lipids, proteins, and cellular waste. They sit between the retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane. Knowing about drusen and their link to macular degeneration is key for catching the problem early and stopping blindness.
Key Takeaways
- Drusen are small yellow deposits under the retina associated with age-related macular degeneration.
- They are composed of lipids, proteins, and cellular debris.
- Early detection of drusen is critical for preventing vision loss.
- Liv Hospital offers world-class ophthalmology expertise for proactive care.
- Understanding drusen helps in grasping the risks tied to macular degeneration.
The Nature and Composition of Drusen

Drusen form from a mix of lipids, proteins, and debris. They build up between the retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane. This mix is key to understanding how they affect age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Cellular and Biochemical Composition
Drusen are made of lipids, proteins, and debris. Research shows these parts are linked to AMD’s disease process. They contain lipids like cholesterol and proteins like complement factors and crystallins.
Studies have shown drusen’s makeup can change a lot between people. This change affects how fast AMD progresses. Knowing this helps in making better treatments.
Component | Description | Significance in AMD |
Lipids | Includes cholesterol and phospholipids | Contributes to drusen formation and AMD progression |
Proteins | Encompasses complement factors and crystallins | Plays a role in inflammation and drusen stability |
Cellular Debris | Remnants of retinal pigment epithelium cells | Influences retinal health and AMD severity |
Location Between Retinal Pigment Epithelium and Bruch’s Membrane
Drusen sit between the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch’s membrane. This spot is important for retinal health. It affects how nutrients and waste move, which can harm the RPE and lead to AMD.
Drusen here can make Bruch’s membrane thicker. This makes the retina work worse. Knowing this helps in finding ways to stop or slow AMD.
The Anatomy of the Eye in Relation to Drusen Formation
Knowing how the eye works is key to understanding drusen. The eye is a complex organ. Its structure is important for age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
Structure of the Retina and Macula
The retina is at the back of the eye. It turns light into signals for the brain. The macula, at the retina’s center, is key for clear vision and detail. The macula’s layers of photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium work together for sharp vision.
The retina has layers like:
- Photoreceptor layer
- Retinal pigment epithelium
- Bruch’s membrane
These layers are vital for eye health. Any problem, like drusen, can harm vision.
The Role of Bruch’s Membrane
Bruch’s membrane is thin tissue between the retina and choroid. It helps exchange nutrients and waste. Changes in Bruch’s membrane, like thickening, can lead to drusen.
Retinal Pigment Epithelium Function
The retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is between photoreceptors and Bruch’s membrane. It does important jobs like:
- Phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments
- Regeneration of visual pigments
- Maintenance of the blood-retina barrier
The RPE’s role is vital for photoreceptor health and vision quality. RPE problems can cause drusen and AMD.
Classification of Drusen in the Eye
Drusen are divided into two types: hard and soft. Knowing about drusen types helps doctors understand the risk of Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD). It also guides them in choosing the right treatment.
Hard drusen are small, clear, and yellowish. They often show up early in AMD and don’t usually cause big vision problems. Soft drusen, on the other hand, are bigger and more spread out. They are more likely to lead to neovascular AMD.
The kind of drusen can tell doctors about AMD risk. Soft drusen are linked to vision problems like distorted vision and blind spots. Eye exams can spot drusen spots, showing drusen eye disease.
Drusen, and soft ones in particular, signal a high risk of AMD. Knowing about drusen types helps manage eye disease and slow AMD. Regular check-ups and early action can help keep vision sharp.
FAQ
What are drusen in the eye?
Drusen are small yellow deposits that build up under the retina. They are a key sign of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
What is the composition of drusen?
Drusen are made of lipids, proteins, and waste products. These materials gather between the retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane.
Where are drusen located in the eye?
Drusen form between the retinal pigment epithelium and Bruch’s membrane. This area is vital for retinal health and can lead to macular degeneration.
What is the role of Bruch’s membrane in drusen formation?
Bruch’s membrane is a thin tissue layer between the retinal pigment epithelium and the choroid. Its health is key to preventing drusen and keeping the retina intact.
What are the different types of drusen?
Drusen are divided into hard and soft types. Each type has its own characteristics and impact on AMD and vision.
What are hard drusen?
Hard drusen are small and distinct. They are not usually a big problem for vision but can signal early AMD.
What are soft drusen?
Soft drusen are bigger and more likely to cause vision loss. They are a higher risk for AMD progression.
How do drusen affect vision health?
Drusen can lead to vision issues like blurred or distorted vision. The severity depends on their size and location.
Can drusen be a sign of macular degeneration?
Yes, drusen are a key indicator of age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Their presence suggests a higher risk of AMD worsening.
How are drusen diagnosed?
Drusen are diagnosed during a thorough eye exam. Techniques like optical coherence tomography (OCT) are used for retinal imaging.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10606451/