Our eyes have a special defense that works on their own, separate from our body’s immune system. Many think our eyes are protected like the rest of our body. But, science shows a more complex truth.Learn about the ocular immune system and the concept of immune privilege that protects the delicate eye tissues. Key facts on the ocular immune system.
Yes, the eyes have their own immune system. It’s made to keep them safe from harm and infection. This system keeps a balance to protect our vision and fight off germs.
Key Takeaways
- The eyes have a distinct immune system that operates independently.
- This system is designed to protect the eyes from infection and injury.
- A delicate balance is maintained to preserve vision while fighting infections.
- The eye’s defense mechanism is complex and sophisticated.
- Understanding this system is key to keeping our eyes healthy.
Understanding the Ocular Immune System
Our eyes have a special immune system to keep our vision safe. It uses unique ways to protect the eye’s delicate parts. This helps us see clearly every day.
What Makes the Eye’s Immune System Special
The eye’s immune system is different from others in the body. It keeps the eye safe from harm while fighting off bad germs. This balance is key to avoiding vision problems.
The eye’s immune system can slow down harmful immune reactions. It does this with special molecules and cells. These help keep the eye’s sensitive parts safe.
The Concept of Immune Privilege
The eye has a special status called “immune privilege.” This means the immune system is controlled to avoid harming the eye. It’s important for keeping the eye healthy despite germs.
Immune privilege doesn’t mean the eye is completely protected. It’s about having the right amount of protection. This helps keep the eye’s delicate tissues safe and vision clear.
Feature | Description | Importance |
Immunosuppressive Molecules | Produced to dampen excessive immune responses | Prevents damage to delicate eye structures |
Specialized Immune Cells | Present to manage and regulate immune responses | Ensures appropriate response to pathogens |
Immune Privilege | A state of modulated immune response | Protects the eye from immune-mediated damage |
Anatomy of Eye Immunity: Structure and Components
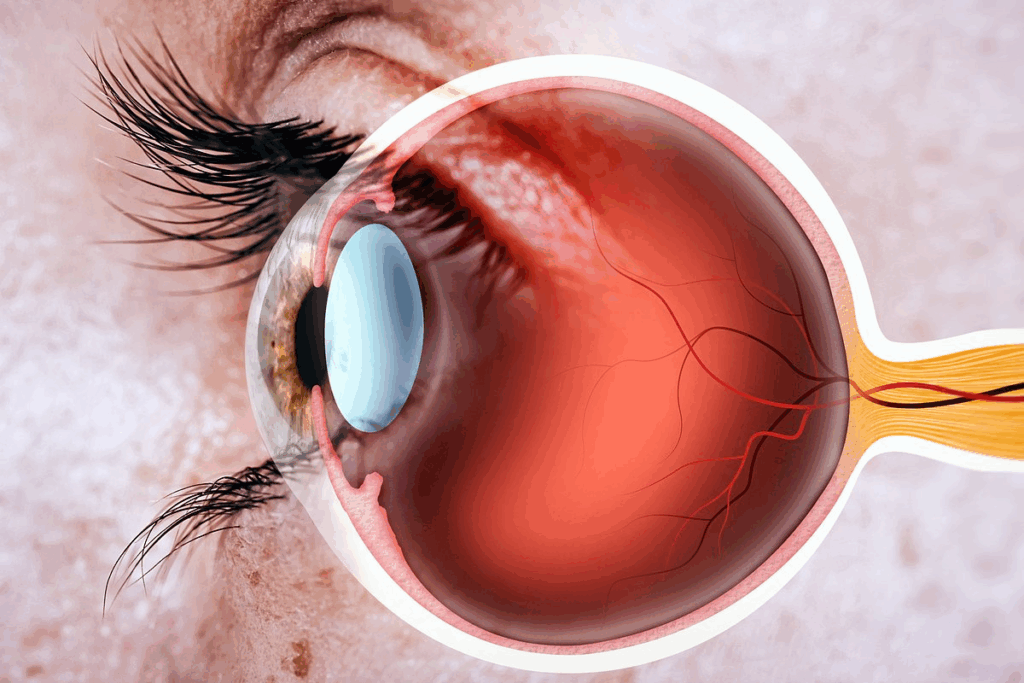
The eye’s immune system is complex, with many parts working together. It protects our eyes from infections and diseases. This system includes physical barriers, molecules that calm the immune system, and special immune cells.
Physical Barriers of the Eye
The eye has strong physical barriers to fight off pathogens. The cornea, the eye’s outer layer, stops foreign particles from getting in. The tear film also helps by having enzymes and proteins that fight off pathogens.
The eyelids and eyelashes block dust and debris. The conjunctiva, a thin membrane, helps by producing mucins to trap pathogens.
Immunosuppressive Molecules
The eye also uses immunosuppressive molecules to control the immune response. These molecules, like Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β), prevent too much inflammation. This is important to protect the delicate eye tissues.
These molecules help keep the immune response in check. They stop the activation of immune cells and reduce inflammation. This balance is key to keeping the eye healthy.
Specialized Immune Cells
The eye has specialized immune cells that are vital for defense. Macrophages clean up pathogens and debris. Dendritic cells detect pathogens and start the immune response.
T cells and mast cells also play a role in the eye’s defense. Together with physical barriers and immunosuppressive molecules, they form a strong defense against threats.
Immune Privilege: Why Your Eyes Need Special Protection
The eyes have a special immune system to protect them. This is because the eyes are very important for us to see the world. They are also very delicate and can easily get hurt.
The Evolution of Ocular Immune Privilege
The eyes’ special protection came from the immune system’s development. As our immune system grew, it had to protect the eyes carefully. This is because the eyes are so delicate and important.
Over time, our body learned how to keep the eyes safe. It does this by balancing protection against damage. This balance is very important for the eyes to work right.
Benefits of Immune Separation
Having immune privilege in the eyes has many benefits. One big one is that it stops too much inflammation. This helps keep the eyes working well without getting damaged.
It also keeps the eyes clear and transparent. This is key for good vision, like in the cornea and lens. Clear vision is very important.
The eye’s immune system can handle some antigens without causing harm.
Consequences When Privilege Breaks Down
If the eyes’ immune privilege fails, problems can happen. Autoimmune diseases can attack the eyes. This can cause a lot of damage.
Uveitis, an inflammation of the uvea, can also occur. This shows how important it is to keep the eye’s immune system in balance. This helps prevent eye problems.
In summary, the immune privilege of the eyes is very important. Knowing about it helps us understand how to keep our eyes healthy.
The Front Line: Tear Film and Surface Defense
Our eyes face many dangers, but the tear film protects us. It’s a mix of fluids that keeps our eyes safe. This layer is key to eye health and stopping infections.
Antimicrobial Properties of Tears
Tears do more than just keep our eyes moist. They have special proteins and enzymes that fight off germs. These work together to keep our eyes safe from harm.
Key antimicrobial components in tears include:
- Lysozymes, which break down bacterial cell walls
- Lactoferrin, which sequesters iron, making it unavailable for microbial growth
- Immunoglobulin A, an antibody that neutralizes pathogens
Lysozymes, Lactoferrin, and Immunoglobulin A
Lysozymes are enzymes that kill certain bacteria by breaking their cell walls. Lactoferrin stops bacteria from growing by taking away their iron. Immunoglobulin A is an antibody that fights off toxins and germs on our eyes.
How Tears Prevent Pathogen Attachment
The tear film also helps remove germs from our eyes. Its constant flow and renewal help keep our eyes clean. Some proteins in tears can even stop germs from sticking to our eyes.
This shows how important the tear film is for our eye health. By understanding how tears protect us, we can appreciate the amazing systems that keep our eyes safe.
Cellular Defenders: Immune Cells in the Eye
The eye’s immune system has many cells working together. They keep the eye healthy and working right. These cells fight off infections and diseases.
Macrophages and Their Role
Macrophages are key in the eye’s defense. They are big cells that eat and break down bad stuff. They help keep the eye safe by removing harmful things.
Dendritic Cells as Sentinels
Dendritic cells watch over the eye for dangers. They grab and deal with invaders, then tell T cells to fight back. This helps keep the eye safe without causing too much damage.
Mast Cells and Inflammatory Response
Mast cells are important in the eye’s fight against allergies and inflammation. When they get the signal, they release chemicals that make blood vessels open up. This brings more immune cells to the fight, but can also cause allergies.
T Cells Patrolling the Cornea
T cells are vital for the eye’s defense. They move around the cornea and other parts of the eye, looking for and fighting off specific enemies. They help keep the eye safe and prevent damage from the immune system itself.
Immune Cell Type | Function in the Eye | Key Characteristics |
Macrophages | Phagocytosis, tissue homeostasis | Large phagocytic cells, removal of debris and pathogens |
Dendritic Cells | Antigen presentation, initiation of immune response | Capture and process antigens, present to T cells |
Mast Cells | Inflammatory response, allergic reactions | Release histamine and other mediators upon activation |
T Cells | Cell-mediated immunity, antigen recognition | Patrol ocular tissues, respond to specific antigens |
The Uvea: Command Center of Ocular Immunity
The uvea is a key part of the eye that helps keep it healthy. It’s located between the sclera and retina. It plays a big role in keeping the eye’s immune system in check.
Anatomy and Function
The uvea has three main parts: the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Each part does something important for the eye’s health. The iris controls light, the ciliary body makes aqueous humor, and the choroid gives the retina oxygen and nutrients.
The uvea’s structure is designed to support its immune functions. It has lots of blood vessels and immune cells. These work together to protect the eye from harm.
Immune Cell Populations
The uvea has different types of immune cells like macrophages, dendritic cells, and T cells. These cells are important for fighting off infections in the eye.
Immune Cell Type | Function |
Macrophages | Engulf and digest cellular debris and pathogens |
Dendritic Cells | Act as sentinels, detecting pathogens and presenting antigens to T cells |
T Cells | Play a key role in cell-mediated immunity, directly killing infected cells or aiding other immune responses |
Regulation of Immune Responses
The uvea controls the immune response through a complex system. This is important to avoid too much inflammation that could harm the eye.
The balance between immune activation and suppression is critical for ocular health. The uvea keeps this balance by making anti-inflammatory cytokines. These molecules help reduce too much immune activity.
When Protection Fails: Ocular Immune-Related Disorders
The eye’s immune system can fail due to various disorders. These issues can harm our vision and eye health. We will look at autoimmune diseases, inflammatory conditions, and allergic reactions in the eye.
Autoimmune Eye Diseases
Autoimmune eye diseases happen when the immune system attacks the eye’s tissues. Uveitis and scleritis are examples. They cause inflammation and can lead to serious damage.
- Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, causing pain, light sensitivity, and vision problems.
- Scleritis: Inflammation of the sclera, leading to pain and vision threats.
Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory eye conditions can come from infections, injuries, or autoimmune responses. Treating these conditions requires a detailed plan to reduce inflammation and prevent damage.
- Conjunctivitis: Inflammation of the conjunctiva, often from infection or allergy.
- Keratitis: Inflammation of the cornea, caused by infection, injury, or contact lens use.
Allergic Reactions in the Eye
Allergic reactions happen when the eye meets an allergen, triggering an immune response. Symptoms can vary from mild to severe.
- Allergic Conjunctivitis: An allergic reaction affecting the conjunctiva, causing itching, redness, and swelling.
- Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis: A severe form of allergic eye disease, linked to atopic dermatitis.
In summary, ocular immune-related disorders include many conditions that can harm eye health. Knowing about these conditions is key to managing and treating them effectively.
Supporting Your Eye’s Immune Health
Eating right, living healthy, and getting medical help can boost your eye’s immune health. Knowing how these actions work together helps you keep your vision sharp.
Nutrition and Eye Immunity
Eating a balanced diet is key to keeping your eyes healthy. Key nutrients for your eyes include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids
- Lutein and zeaxanthin
- Vitamin C
- Vitamin E
- Zinc
You can find these nutrients in foods like leafy greens, nuts, and fish. Eating these foods helps shield your eyes from harm and boosts your immune system.
Nutrient | Food Sources | Benefits for Eye Health |
Omega-3 fatty acids | Salmon, walnuts | Reduces inflammation |
Lutein and zeaxanthin | Spinach, kale | Protects against blue light damage |
Vitamin C | Oranges, strawberries | Antioxidant properties |
Lifestyle Factors
How you live affects your eye health. Regular exercise, not smoking, and protecting your eyes from UV radiation are important. Wearing sunglasses that block 100% of UV rays can greatly lower eye damage risk.
Medical Interventions and Treatments
Sometimes, medical help is needed for eye health. Regular eye exams catch problems early. Treatments like anti-inflammatory meds or immunosuppressive therapy may be needed for some conditions.
By eating well, living healthily, and getting medical care when needed, you can keep your eyes strong and your vision clear.
Conclusion: The Remarkable Balance of Eye Immunity
The ocular immune system is key to keeping our eyes healthy. It protects the eye from harmful invaders while avoiding too much inflammation. This could harm the delicate eye tissues.
We’ve looked into how the eye’s immune system works. This includes the tear film, immune cells, and the uvea. They all play a part in keeping the eye balanced. The eye’s immune system is amazing at adapting and keeping our vision clear.
It’s important to support our eye health and immune system. This helps us see well and stay healthy overall. By learning about the eye’s immune system, we can take better care of our eyes. This helps prevent eye problems caused by the immune system.
The eye’s immune balance shows how amazing our bodies are at staying healthy. By understanding this, we can take better care of our eyes and overall health.
FAQ
Do eyes have their own immune system?
Yes, the eyes have a special immune system called the ocular immune system. It protects them from infections and injuries.
What is immune privilege, and how does it relate to the eyes?
Immune privilege means the eyes can avoid damage from the immune system. This unique feature helps keep the eyes healthy.
How do tears help protect the eyes from infection?
Tears have proteins like lysozymes and lactoferrin that fight off pathogens. This helps prevent infections.
What types of immune cells are involved in protecting the eyes?
Immune cells like macrophages and T cells are key to eye health. They help defend against pathogens.
What is the uvea, and what role does it play in ocular immunity?
The uvea is a tissue layer in the eye with immune cells. It helps regulate immune responses and keeps the eye healthy.
What happens when the ocular immune system fails?
Failure can cause disorders like autoimmune eye diseases. It can also lead to inflammation and allergic reactions.
How can I support my eye’s immune health?
Eat a balanced diet and live a healthy lifestyle. Medical care is also important when needed.
Why is the ocular immune system important?
It’s vital for eye health and preventing vision loss. Its unique features make it a key part of our immune system.
Can the immune system attack the eyes?
Yes, sometimes the immune system mistakenly attacks the eyes. This can cause autoimmune diseases or inflammation.
How does the ocular immune system interact with the general immune system?
The ocular immune system works with the general immune system. But it also has special features for independent function and immune privilege.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2945205/