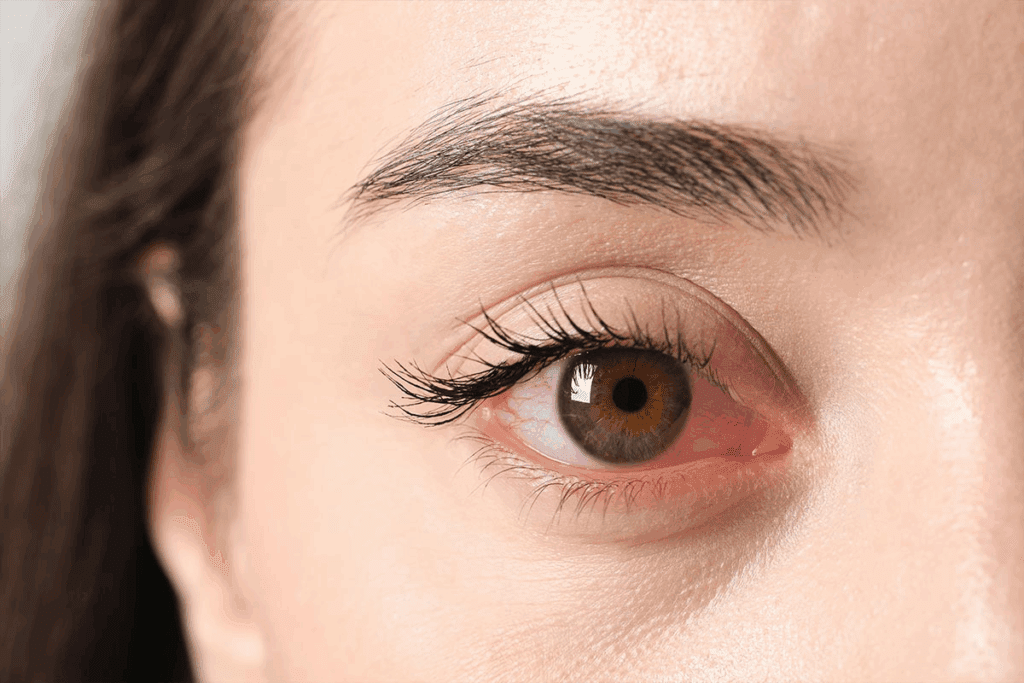
Optic disc edema is a serious eye problem that needs quick attention. We’ll talk about optic disc swelling and why it’s so important to spot it fast. What is disc edema? This essential guide explains 5 dangerous causes of optic disc swelling, symptoms, and treatments.
Knowing the signs and what causes it is key to acting quickly. Optic disc edema can mean serious health issues, like high blood pressure in the brain or diabetes.
Key Takeaways
- Optic disc edema is a critical clinical finding that requires prompt evaluation.
- Various factors can cause optic disc swelling, including increased intracranial pressure and systemic conditions.
- Recognizing the signs of optic disc edema is critical for timely intervention.
- Understanding the causes of optic disc edema is essential for effective management.
- Prompt recognition and evaluation are necessary to prevent permanent vision loss.
Understanding Optic Disc Edema

Optic disc edema is when the optic disc swells. This is a key area where the optic nerve fibers leave the eye. It can happen for many reasons and can affect one or both eyes. Knowing about optic disc edema helps doctors diagnose and treat it better.
Definition and Terminology
Optic disc edema is swelling of the optic disc due to fluid buildup. The term “edema” means fluid gathering. It’s important to tell it apart from other issues that might look similar.
The diagnosis of optic disc edema requires a thorough understanding of its causes and symptoms.
“
Anatomical Considerations
The optic disc is where the optic nerve fibers meet before leaving the eye. Its shape and function are tied to the optic nerve. Swelling here can be from high pressure inside the skull, inflammation, or other issues that block normal flow.
The optic nerve has axons from retinal ganglion cells. Any problem with axoplasm flow can cause swelling. Knowing the optic disc’s anatomy helps doctors figure out why it swells.
The Clinical Significance of Disc Edema

It’s very important to spot disc edema early. This swelling of the optic disc might mean serious problems like idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH) or cerebral venous thrombosis. Finding it early is key to checking it out thoroughly.
Why Prompt Recognition Matters
Spotting disc edema early is key because it can signal serious health issues. Catching it early can stop vision loss. Quick action is vital for the right treatment, which can really help patients.
Potential Underlying Pathologies
Disc edema can point to serious problems like IIH, brain tumors, or cerebral venous thrombosis. Knowing these possible causes helps doctors figure out what to do next.
Underlying Pathology | Key Characteristics | Diagnostic Approach |
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) | Elevated intracranial pressure without identifiable cause | Lumbar puncture, imaging studies |
Brain Tumors | Space-occupying lesions within the cranial vault | MRI or CT scans, biopsy |
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis | Thrombosis of the cerebral venous sinuses | MR venography, CT venography |
In conclusion, disc edema is very serious and needs quick attention. It can signal serious health issues. By knowing what causes it, doctors can give the best care fast.
Pathophysiology of Optic Disc Swelling
It’s important to understand the causes of optic disc swelling. This condition, also known as optic disc edema or swollen disc eye, happens when the optic nerve is affected by various factors.
Mechanisms Leading to Disc Edema
Optic disc edema is caused by high pressure inside the skull. This pressure goes to the optic nerve sheath. It leads to a buildup of material in the optic nerve head, causing it to swell.
“The increased intracranial pressure is a critical factor in the development of optic disc swelling,” as noted by medical professionals. “It is essential to understand the mechanisms behind this condition to provide appropriate treatment.”
Axoplasmic Flow Disruption
Axoplasmic flow disruption is key in optic disk swelling. Normally, axoplasmic flow moves important materials along the optic nerve. But, when pressure inside the skull goes up, this flow stops. This causes material to pile up, swelling the optic disc.
- Increased intracranial pressure
- Axoplasmic flow stasis
- Accumulation of axoplasmic material
- Swelling of the optic disc
Knowing these mechanisms helps doctors diagnose and treat edema of the optic disc better.
Key Visual Characteristics of Disc Edema
Optic disc edema shows several key signs that help doctors diagnose it. We look for specific signs of swelling in the optic disc.
Blurring of Disc Margins
One main sign of disc edema is when the optic disc margins get blurry. Normally, the edges of the optic disc are sharp. But with swelling, these edges get fuzzy. This fuzziness can be mild or severe, and it’s a big clue to the condition.
Elevation of the Optic Disc
Another important sign is when the optic disc gets raised. This happens because it swells up. The amount of elevation can vary, from a little to a lot. Doctors use special tools to check how high it is.
Vascular Changes and Venule Enlargement
Changes in blood vessels are also signs of disc edema. The disc might look more red because of more blood flow. Also, the small veins around the optic disc can get bigger. These changes can mean there’s more pressure inside the skull or other problems.
Visual Characteristic | Description | Clinical Significance |
Blurring of Disc Margins | Obscuring of the optic disc edges due to swelling | Primary indicator of disc edema |
Elevation of the Optic Disc | Raising of the optic disc above the surrounding retina | Signifies swelling and possible increased intracranial pressure |
Vascular Changes | Hyperemia and venule enlargement due to increased blood flow and pressure | Shows there might be a problem, like more pressure inside the skull |
It’s vital for doctors to spot these signs to treat disc edema right. Knowing what these signs mean helps doctors give the right care. They can also send patients to see specialists if needed.
Optic Disc Hyperemia: A Critical Diagnostic Feature
Hyperemia of the optic disc is a key sign that needs careful checking. It shows up as the optic disc looks redder than usual because of more blood flow. This often happens when the optic disc swells, a condition known as disc edema.
Distinguishing Hyperemia from Normal Variation
Telling hyperemia apart from normal optic disc looks can be tricky. Sometimes, the optic disc might look redder than usual for no reason. But, when it’s due to swelling, the redness is more obvious and comes with other signs.
To spot hyperemia, doctors look at the whole picture. They check the patient’s history, how well they can see, and other eye signs. Using ophthalmoscopy or fundus photography helps see the redness and swelling of hyperemia.
Relationship Between Hyperemia and Edema
Hyperemia and edema of the optic disc are linked. Edema is when the optic disc swells, often because of high pressure in the brain or other issues. Hyperemia happens because of the extra blood flow that comes with these problems.
Looking at why hyperemia and edema happen together helps us understand them better. For example, in idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), high brain pressure causes both swelling and increased blood flow in the optic disc.
Condition | Association with Hyperemia | Association with Edema |
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) | Common | Common |
Optic Neuritis | Possible | Possible |
Ischemic Optic Neuropathy | Rare | Common |
Getting how hyperemia and edema are connected is key to diagnosing and treating disc edema. By spotting hyperemia and knowing it’s linked to edema, doctors can find the cause and plan the right treatment.
Common Symptoms Associated with Optic Disc Edema
It’s important to know the symptoms of optic disc edema early. This helps in getting the right treatment. Optic disc edema shows itself in different ways. Knowing these signs helps doctors make better choices.
Visual Disturbances
Visual problems are a big sign of optic disc edema. These can include:
- Transient visual obscurations, where vision becomes temporarily blurry or dim
- Blurred vision, which can affect daily activities
- Double vision or diplopia, resulting from the swelling affecting the optic nerve
These visual issues can really affect someone’s life. So, it’s key to spot and treat them quickly.
Headaches and Other Neurological Symptoms
People with optic disc edema might also have headaches and other brain-related symptoms. These can include:
- Headaches, often described as severe and debilitating
- Pulsatile tinnitus, or ringing in the ears
- Nausea and vomiting, if the condition is linked to high brain pressure
These signs can point to other health issues that need attention.
Asymptomatic Presentations
Some people with optic disc edema don’t show any symptoms. This shows why regular eye checks are so important. Even without symptoms, the condition can be found during a routine eye exam.
Regular eye exams are key for catching optic disc edema, even in those without symptoms.
Knowing the symptoms of optic disc edema helps doctors treat it well. By spotting both obvious and hidden symptoms, we can give our patients the best care.
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH)
Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension (IIH) is a complex condition. It is marked by increased pressure in the brain without a known cause. Symptoms include headaches and vision problems. Understanding this condition is key for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
IIH mainly affects obese women of childbearing age. This suggests a link between obesity and the condition. Hormonal influences and obesity-related factors may contribute to IIH.
“The association between IIH and obesity is well-documented,” research shows. Weight loss can help improve symptoms.
Clinical Presentation in IIH
IIH symptoms include severe headaches and vision problems. These headaches can be pulsatile and accompanied by tinnitus. Vision issues range from brief vision loss to persistent field defects.
Patients may also experience transient visual obscuration. This is brief vision loss triggered by posture changes.
Diagnostic Criteria
Diagnosing IIH requires clinical evaluation, imaging, and lumbar puncture. The criteria include signs of increased pressure, high cerebrospinal fluid pressure, and no other causes.
- Presence of papilledema
- Normal neurological examination except for possible sixth nerve palsy
- Elevated cerebrospinal fluid pressure
- Normal cerebrospinal fluid composition
Accurate diagnosis is vital for managing IIH. It helps prevent long-term vision loss.
“Early recognition and treatment of IIH are critical to preventing irreversible vision loss,” emphasizes the importance of prompt medical intervention.
Space-Occupying Lesions and Increased Intracranial Pressure
Intracranial masses can lead to increased intracranial pressure, a serious condition that needs quick medical help. We will look at the different types of space-occupying lesions and their effects on health.
Types of Intracranial Masses
Intracranial masses can be either benign or malignant. They include brain tumors, abscesses, and hemorrhages. Brain tumors can be primary or metastatic, and their aggressiveness and impact on the brain vary greatly.
Other masses include meningiomas, which are usually benign and grow from the meninges. Acoustic neuromas are benign tumors affecting the vestibulocochlear nerve. Each type of mass has its own characteristics and can increase intracranial pressure differently.
Associated Symptoms
People with space-occupying lesions often have various symptoms. These include headaches, nausea, vomiting, and vision problems. Papilledema, or swelling of the optic disc, is a key sign of increased intracranial pressure.
Patients may also have neurological issues based on the mass’s location. For example, a tumor in the frontal lobe might cause personality changes or motor problems. A tumor in the temporal lobe could affect hearing or memory.
Papilledema as a Warning Sign
Papilledema is a critical finding that needs immediate attention. It often shows increased intracranial pressure and can signal a serious condition. Prompt recognition of papilledema is vital for early diagnosis and treatment.
Regular eye exams are key to spotting papilledema, mainly in those at risk for brain issues. Early detection can greatly improve patient outcomes by allowing for timely treatment.
Infectious and Inflammatory Causes of Disc Edema
It’s important to know the causes of disc edema to treat it right. Disc edema is when the optic disc swells. This swelling can come from infections or inflammation. We’ll look at key causes like Lyme disease and syphilis and how they affect patients.
Lyme Disease and Neuroretinitis
Lyme disease is spread by ticks and can harm the eyes. It causes neuroretinitis, leading to swelling of the optic disc. This swelling can make it hard to see.
To diagnose Lyme disease, doctors use tests and check the cerebrospinal fluid. Antibiotics like doxycycline or ceftriaxone help fight the infection and prevent complications.
Syphilis and Ocular Manifestations
Syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, can also cause disc edema. It can affect the eyes in many ways, including uveitis and optic neuritis. The inflammation from syphilis can cause the disc to swell.
Doctors diagnose syphilis with tests and treat it with penicillin. Quick treatment is key to avoid vision problems.
Other Infectious Etiologies
Other infections can also cause disc edema. These include:
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis, mainly in people with weakened immune systems
- Toxoplasmosis, which can cause retinochoroiditis and secondary disc edema
- Tuberculosis, which can affect the eye and lead to disc edema through inflammation
Identifying the cause of disc edema requires a detailed approach. This includes a thorough medical history, physical exam, and lab tests.
Infectious Cause | Ocular Manifestation | Diagnostic Approach |
Lyme Disease | Neuroretinitis, Disc Edema | Serological tests, Clinical evaluation |
Syphilis | Uveitis, Retinitis, Optic Neuritis | Serological tests |
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) | CMV Retinitis | Clinical evaluation, Laboratory tests |
In conclusion, disc edema can come from many causes. A detailed diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Understanding these causes helps doctors provide better care for patients with disc edema.
Systemic Conditions Leading to Optic Disc Swelling
Optic disc swelling often shows there’s a bigger health issue that needs quick help. These issues can affect many parts of the body, including the eyes. Knowing about these conditions helps doctors treat optic disc swelling right.
Hypertensive Emergencies
Hypertensive emergencies are a big reason for optic disc swelling. High blood pressure can push blood vessels in the eye too hard. Malignant hypertension is very high blood pressure that can harm organs like the eyes, kidneys, and heart. It’s very important to manage high blood pressure quickly to avoid losing vision or facing other serious problems.
Toxic-Metabolic Causes
Toxic-metabolic disorders can also cause optic disc swelling. Some medicines and metabolic issues can change the optic disc. For example, diabetic papillopathy is linked to diabetes and causes swelling in the optic disc. Other causes include not getting enough nutrients and being exposed to harmful substances. Finding and fixing the root cause is key to treating optic disc swelling in these cases.
Vascular Disorders
Vascular disorders can also lead to optic disc swelling. Issues like central retinal vein occlusion or carotid artery disease can affect blood flow to the optic disc. Treating vascular disorders means fixing the blood flow problem. This might involve changing your lifestyle, taking medicine, or surgery.
In summary, conditions like hypertensive emergencies, toxic-metabolic issues, and vascular disorders are major causes of optic disc swelling. Spotting these conditions and understanding their effects on the optic disc is vital for the right care and to avoid serious issues.
Diagnostic Approach and Differential Diagnosis
To diagnose disc edema, doctors use a mix of clinical exams and new imaging tech. This method helps find the real cause of disc edema and treat it right.
Clinical Examination Techniques
Clinical exams are key in spotting disc edema. Fundoscopy lets doctors see the optic disc up close. It shows signs like blurry disc edges, raised optic disc, and redness.
Visual field testing is also important. It checks for vision problems linked to disc edema, like blind spots. These issues help doctors understand how severe the problem is and what might be causing it.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging is a big part of diagnosing. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) gives clear pictures of the optic disc and retina. It measures the thickness of the nerve layer and spots small changes in the optic disc.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is also key. It finds reasons for disc edema, like brain tumors or high pressure inside the skull. MRI shows detailed brain and optic pathway images, helping doctors figure out what’s going on.
Conditions That Mimic Disc Edema
When diagnosing disc edema, it’s important to think about other conditions that look similar. For example, optic disc drusen can make the optic disc look swollen, just like disc edema. Also, congenital disc anomalies can have odd shapes or sizes.
Condition | Characteristics | Diagnostic Clues |
Optic Disc Drusen | Calcified deposits within the optic disc | Visible on ultrasound or OCT |
Congenital Disc Anomalies | Abnormal disc shape or size | Often identified on fundoscopy |
Papillitis | Inflammation of the optic disc | Associated with visual loss and pain |
By using clinical exams, advanced imaging, and knowing about similar conditions, doctors can make a correct diagnosis. This leads to the right treatment plan.
Conclusion: Importance of Early Recognition and Intervention
Early spotting and right treatment of optic disc edema are key to avoid problems and keep eyes healthy. We talked about what causes disc edema and why it matters. It’s important to find and treat it quickly.
Acting fast can really help patients, stopping vision loss and making life better. Doctors can help a lot by knowing the signs of optic disc edema. This way, they can give good care and support.
It’s very important to catch optic disc edema early. Waiting too long can cause permanent eye damage. Doctors need to watch closely for this condition and use all the tools they have to find the cause.
By acting early, we can help patients get better faster. Fixing the main problem is key. We need doctors to work together to give the best care. This way, patients have a good chance of getting better.
FAQ
What is optic disc edema?
Optic disc edema is when the optic disc swells. This can happen for many reasons. These include high pressure in the brain, certain health conditions, and infections.
What are the common symptoms of optic disc edema?
Symptoms can include seeing things out of the corner of your eye, headaches, and other brain-related issues. But, some people might not show any symptoms at all. That’s why regular eye checks are key.
What is idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), and how is it related to optic disc edema?
IIH is a condition where the brain’s pressure goes up without a clear reason. It’s more common in overweight women of childbearing age. It can cause swelling of the optic disc, leading to vision problems and headaches.
How is optic disc hyperemia related to disc edema?
Optic disc hyperemia means the optic disc looks redder than usual. This is because of more blood flow. It’s a key sign that helps doctors tell if the disc is swollen or not.
What are the possible causes of optic disc edema?
Causes can include tumors or bleeding in the brain, high blood pressure, diabetes, and infections like Lyme disease or syphilis.
How is optic disc edema diagnosed?
Doctors use eye exams and tests like OCT and MRI to diagnose it. These tools help see the optic disc and rule out other conditions.
What is the significance of blurring of the disc margins in optic disc edema?
When the disc margins blur, it means the optic disc is swollen. This is often seen with the disc getting higher and blood vessels getting bigger.
Can optic disc edema be asymptomatic?
Yes, some cases of optic disc edema don’t show symptoms. This is why regular eye exams are so important.
What are the systemic conditions that can lead to optic disc swelling?
Conditions like high blood pressure, certain medicines, or metabolic disorders can cause the optic disc to swell.
Why is early recognition and intervention important in cases of optic disc edema?
Catching it early and treating it quickly is key to avoid losing vision. Quick action can greatly improve a patient’s life.
What is the role of imaging modalities in diagnosing optic disc edema?
Tools like OCT and MRI are vital for checking the optic disc. They help find the real cause of swelling and guide treatment.
How do space-occupying lesions affect intracranial pressure and lead to optic disc edema?
Lesions like tumors or bleeding can raise brain pressure. This can cause the optic disc to swell. Seeing a swollen optic disc is a warning sign that needs quick attention.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10332214/