Epiretinal membrane, also known as macular pucker or epiretinal pucker, is a thin scar tissue layer on the macula. It can cause blurry vision and make everyday tasks hard. This condition affects how well you see. What is an epiretinal pucker? This complete guide explains the causes, symptoms, and the best treatment options available.
At Liv Hospital, we focus on treating this condition with top-notch eye care. Our team uses the newest methods to check and treat ERM. We aim to help patients see better and feel better.
Knowing about epiretinal membrane is key to keeping your eyes healthy. This guide will help you understand how to treat this common eye problem.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the causes and symptoms of epiretinal membrane
- Exploring the latest diagnostic techniques for ERM
- Overview of available treatment options for macular pucker
- The importance of thorough checks and caring treatment
- Liv Hospital’s dedication to excellent eye care
What Is Epiretinal Pucker?
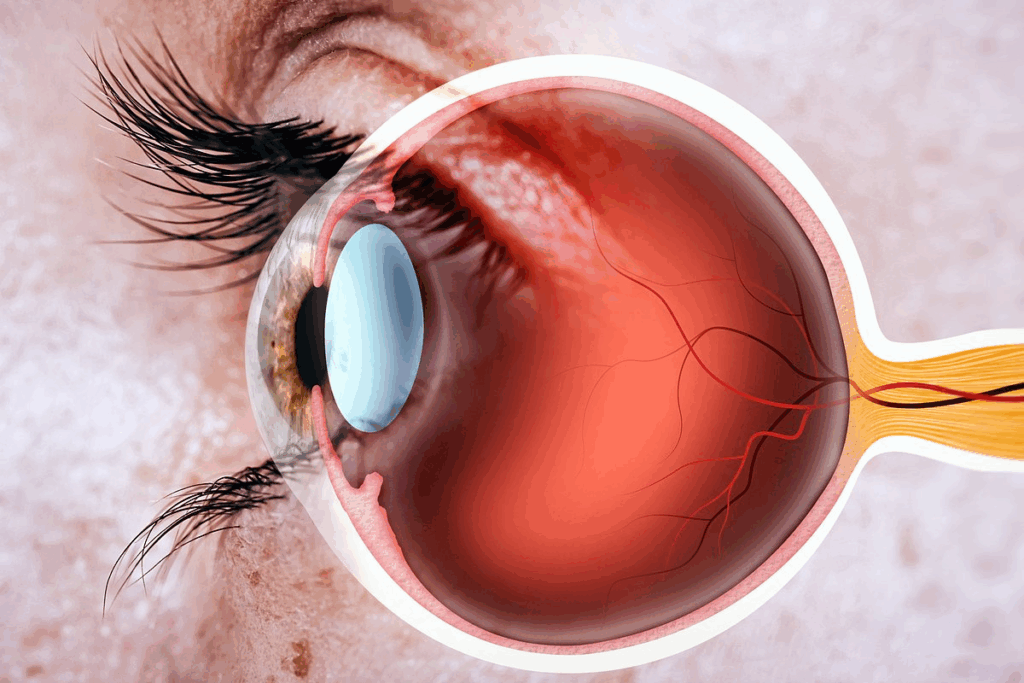
Epiretinal membrane, also known as epiretinal pucker, is a condition that affects the retina. It forms a fibrocellular layer on the retina’s surface. This can lead to visual disturbances.
Definition and Structure
Epiretinal pucker is when fibrocellular tissue grows on the retina’s inner surface. This can cause macular puckering and visual distortion. The membrane can contract, making the retina wrinkle or distort. This affects how well you can see.
The structure of the epiretinal membrane varies. Some are thin, while others are thicker and more fibrotic. Knowing the membrane’s composition and thickness is key to choosing the right treatment.
Prevalence and Demographics
Research shows that epiretinal membrane affects about 7 to 11.8 percent of people. Its occurrence increases with age. It’s more common in older adults, often linked to other retinal conditions.
- Prevalence increases with age, significantly after 50.
- ERM is more common in those with a history of retinal detachment or other retinal diseases.
- Both eyes can be affected, but the severity can differ.
Impact on Vision
An epiretinal membrane can cause significant visual disturbances. These include metamorphopsia (distorted vision) and decreased visual acuity. The severity of these symptoms varies among individuals.
The impact on vision depends on the membrane’s location and thickness. Membranes near the central macula tend to cause more severe visual symptoms.
“The formation of an epiretinal membrane can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life, necessitating proper diagnosis and treatment to restore optimal vision.”
Common Causes of Epiretinal Pucker
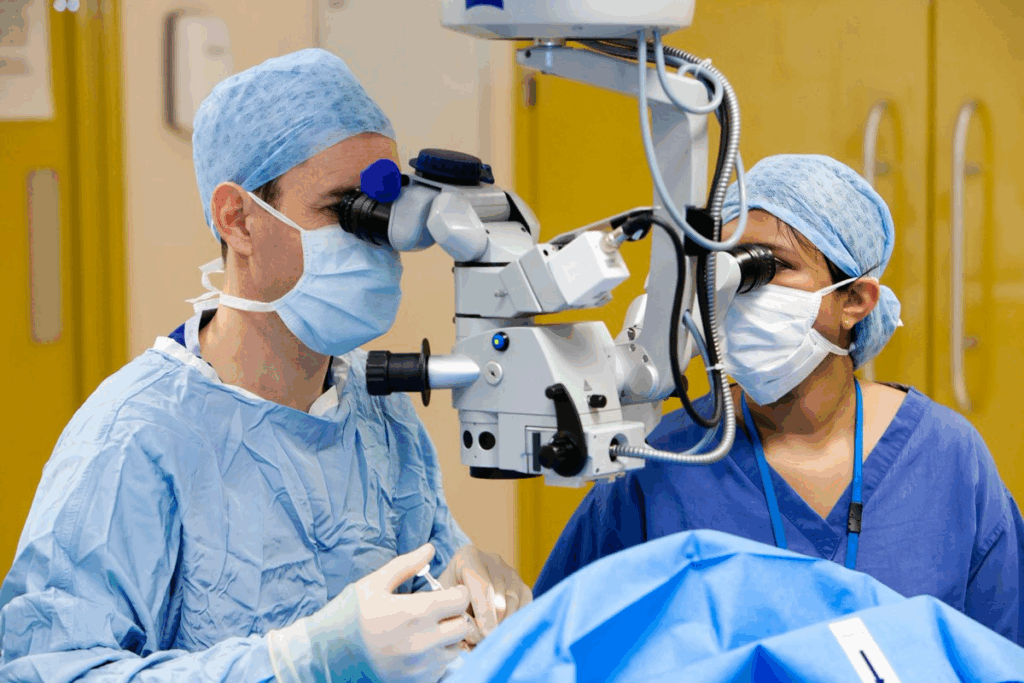
Epiretinal pucker can be caused by several factors. These can be divided into idiopathic and secondary causes. Knowing these causes helps in diagnosing and treating the condition.
Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane (95% of Cases)
In about 95% of cases, the cause of epiretinal membrane is unknown. Idiopathic epiretinal membrane is more common in older adults. This suggests that age-related changes in the vitreous gel may play a role.
We will look into how these changes contribute to epiretinal pucker.
Secondary Causes (Diabetic Retinopathy, Retinal Vein Occlusion)
Secondary causes make up a smaller percentage of epiretinal pucker cases. Conditions like diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion can cause epiretinal membrane. These conditions lead to vascular changes in the retina.
This can result in the growth of fibrocellular tissue on the retinal surface.
Relationship with Posterior Vitreous Detachment
Posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) is closely linked to epiretinal membrane formation. Studies show that PVD is present in 75 to 93% of eyes with epiretinal membrane. The process of PVD can stimulate the formation of epiretinal membrane.
This is possibly due to the mechanical stress it imposes on the retina.
Understanding the relationship between PVD and epiretinal pucker is key to developing effective treatments. By acknowledging the underlying causes, we can manage the condition better and improve patient outcomes.
Recognizing Symptoms of Epiretinal Pucker
It’s important to know the signs of epiretinal pucker to get help quickly. This condition can cause many visual problems that affect daily life. Knowing these symptoms helps patients get the right care.
Visual Distortions (Metamorphopsia)
Metamorphopsia is a key symptom of epiretinal pucker. It makes straight lines look wavy. This can make it hard to read or drive.
People often say things look irregular or their central vision is off. This can make daily tasks tricky.
Decreased Visual Acuity
Decreased visual acuity is another common sign. It means your vision isn’t as sharp. How much it affects you can vary.
Many patients see things more blurry or have trouble seeing details. This can really change your life, affecting work and personal stuff.
Progression of Symptoms
How symptoms get worse can differ a lot. Some people might not notice much change, while others see their vision get much worse.
Symptom | Description | Impact on Daily Life |
Visual Distortions | Straight lines appear wavy or distorted | Difficulty with reading, driving |
Decreased Visual Acuity | Blurred vision, loss of sharpness | Challenges with daily tasks, work-related activities |
Progression of Symptoms | Variable rate of symptom worsening | Potential for significant impact on quality of life |
Diagnosing Epiretinal Pucker
Getting a correct diagnosis for epiretinal pucker is key to finding the right treatment. We use a mix of clinical checks and imaging tests to spot this condition well.
Comprehensive Eye Examination
First, we do a detailed eye check to find epiretinal pucker. We check the retina’s health and look for signs of membrane formation. This includes:
- Visual acuity tests to see how sharp your vision is
- Dilated fundus exams to see the retina
- Slit-lamp biomicroscopy to look at the retinal surface
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a key imaging test for diagnosing epiretinal pucker. It gives us clear images of the retina. We can:
- See the retinal surface and find epiretinal membranes
- Check the retina’s thickness and any swelling
- Look at how the membrane connects with the retina
Fluorescein Angiography and Other Tests
We might use fluorescein angiography to check the retinal blood vessels. This helps us see if there’s any leakage or lack of blood flow. Other tests, like fundus photography, help us document the retina’s state and watch for changes.
The info from these tests helps us create a treatment plan that fits your needs.
When to Seek Treatment for Epiretinal Pucker
Deciding to get treatment for epiretinal pucker depends on several things. These include how bad the symptoms are and how they affect your daily life. Knowing these factors helps figure out the best action to take.
Severity Assessment
Figuring out how bad epiretinal pucker is means looking at how much it messes with your vision. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a key tool here. It gives clear pictures of the retina and the membrane.
Getting a full eye check is important to see how bad the pucker is. This check includes:
- Visual acuity testing
- OCT imaging
- Fundus examination
Severity Level | Visual Acuity | Distortion Level | Recommended Action |
Mild | 20/40 or better | Minimal distortion | Monitoring |
Moderate | 20/50 to 20/100 | Noticeable distortion | Consider treatment |
Severe | Worse than 20/100 | Significant distortion | Treatment recommended |
Impact on Daily Activities
Epiretinal pucker can really mess with things like reading, driving, and seeing faces. If these problems start to get in the way of your daily life, it’s time to think about treatment.
If you’re having trouble reading or seeing things clearly, it’s a good idea to talk to a retina specialist.
Consulting with a Retina Specialist
Talking to a retina specialist is key to finding the right treatment. They can tell you how bad the pucker is and what treatment you need. This could be watching it, surgery, or something else.
Getting advice from a retina specialist is very important. It helps make sure you get the best treatment for your situation.
Conservative Management Approaches
Managing epiretinal pucker, a retina condition, can be done with conservative methods. These are very effective, mainly for mild cases.
Observation for Mild Cases
For those with mild epiretinal pucker, observation is often the first step. Regular visits to an eye care professional are key to track the condition.
Observation helps doctors see if the condition is getting worse. It also helps decide when to take action if needed.
Vision Aids and Adaptive Techniques
Besides observation, vision aids and adaptive techniques can greatly improve life for those with epiretinal pucker. These include:
- Magnifying glasses or lenses to enhance visual clarity
- Adjusting lighting at home to reduce glare
- Using assistive technology, such as text-to-speech software
These tools help patients adjust to their condition and stay independent.
Managing Associated Conditions
It’s also important to manage associated conditions when treating epiretinal pucker. Conditions like diabetic retinopathy or retinal vein occlusion can make things worse. Treating these can prevent more problems.
By taking a holistic approach to eye care, doctors can create a better management plan for patients with epiretinal pucker.
Surgical Treatment of Epiretinal Pucker
When other treatments don’t work, surgery is an option for epiretinal pucker. It’s considered when the condition really affects a person’s life.
Vitrectomy Procedure
The main surgery for epiretinal pucker is pars plana vitrectomy (PPV) with membrane peeling. PPV removes the vitreous gel from the eye. Then, a saline solution or gas is used to help the retina heal.
Membrane Peeling Techniques
Membrane peeling is key in treating epiretinal pucker. It involves carefully removing the epiretinal membrane that causes vision problems. Intraoperative Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) helps surgeons see if they’ve removed all the membrane.
Intraoperative Considerations
Several things are thought about during surgery to get the best results. Using intraoperative OCT to check the retina is important. It’s also vital to avoid harming the retina during the procedure.
Post-Surgical Recovery and Care
Recovering from epiretinal pucker surgery needs careful care and watching. We’ll help you through each stage of recovery and managing any issues.
Immediate Post-Operative Period
The first days after surgery are key for a good recovery. Patients are usually told to rest for the rest of the day after surgery. They should avoid hard activities. It’s also good to have someone with you at home for the first night.
You might feel some pain, redness, or blurry vision. These feelings are usually short-lived. They can be helped with eye drops and pain medicine as prescribed. Always follow your doctor’s advice on medicine and check-ups.
Long-Term Recovery Timeline
The time it takes to fully recover from epiretinal pucker surgery varies. Visual improvement can take several months, with some seeing changes in weeks. It’s important to be patient and let your eye heal fully.
- Within the first week: Vision starts to get better, but it might be blurry.
- 1-3 months: Vision gets clearer and distortion lessens.
- 3-6 months: Vision keeps getting better, with some reaching their best vision.
Managing Complications
While rare, knowing about possible complications is important. Watch for signs of infection, retinal detachment, or high eye pressure. If you have severe pain, sudden vision loss, or more redness, call your doctor right away.
By following your doctor’s post-op instructions and going to all follow-up visits, we can lower the chance of problems. This helps ensure the best results.
Treatment Outcomes and Prognosis
Epiretinal pucker treatment results vary a lot. It’s key for patients to know this when choosing a treatment.
Visual Improvement Expectations
How much vision improves after surgery for epiretinal pucker differs for everyone. Some see big improvements, while others see smaller changes. Most patients notice a clear improvement in their sight.
What affects how much vision improves includes:
- How well you could see before surgery
- How long the epiretinal membrane was there
- If you have other eye problems
Preoperative Visual Acuity | Average Postoperative Improvement |
20/40 or better | 2-3 lines on the Snellen chart |
20/50 to 20/100 | 3-4 lines on the Snellen chart |
Worse than 20/100 | 4-5 lines on the Snellen chart |
Factors Affecting Surgical Success
Many things can affect how well surgery works for epiretinal pucker. Your eye’s overall health and any other eye issues are big factors. The skill of the surgeon and the method used also matter a lot.
Important factors for success include:
- The surgeon’s skill in removing membranes
- Any other eye problems you have
- How well you follow your doctor’s advice after surgery
Recurrence Rates and Management
It’s possible for the membrane to come back after surgery, but it’s rare. Research shows the rate of recurrence is low.
Dealing with a return of the membrane usually means:
- Going back for regular check-ups to watch for signs of it coming back
- Having surgery again if it affects your vision a lot
Dealing with epiretinal pucker can be tough. Knowing about treatment results helps patients make better choices for their care.
Living with Epiretinal Membrane
Living with epiretinal membrane (ERM) means we need to manage it well. It affects our daily life. Understanding ERM and its impact on our vision is key.
Adapting to Visual Changes
Adjusting to ERM’s visual effects can be tough. But, there are ways to help. Using vision aids and learning new techniques can improve our daily life a lot.
For example, magnifying glasses, better lighting, and assistive tech can help a lot. Making our living space simpler and using high-contrast colors can also help.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-up
Seeing an eye doctor regularly is very important for ERM patients. It helps catch any changes early. This way, we can manage the condition better and avoid problems.
Monitoring Aspect | Frequency | Purpose |
Visual Acuity Tests | Every 6 months | To assess changes in vision |
OCT Imaging | Annually or as needed | To monitor ERM progression |
Comprehensive Eye Exam | Annually | To evaluate overall eye health |
Support Resources and Communities
ERM can be tough emotionally, but there’s help out there. Support groups, online forums, and counseling offer advice and support. They help us manage ERM better.
Meeting others with ERM can be really helpful. It lets us share our stories, learn from others, and feel less alone.
By using these resources and being proactive, we can live better with ERM. We can adapt to its visual effects and improve our lives.
Conclusion
Understanding epiretinal pucker and its treatments is key for those affected. We’ve looked at causes, symptoms, and treatment methods. This includes both non-surgical and surgical options.
Treatment for epiretinal pucker can greatly improve life quality. It helps with visual distortions and better vision. Getting advice from a retina specialist is important for making the right care choices.
Regular check-ups and the right treatment can manage symptoms and maybe even improve vision. If you’re experiencing symptoms, see a healthcare professional. They can help find the best treatment for you.
FAQ
What is epiretinal pucker, and how does it affect vision?
Epiretinal pucker, or epiretinal membrane (ERM), is a condition. It forms a layer of fibrous tissue on the retina. This causes visual distortions and can lower your visual acuity.
It can really affect your daily life and how well you see things.
What are the common symptoms of epiretinal pucker?
Symptoms include seeing things differently (metamorphopsia) and blurry vision. They can get worse over time. These symptoms can make everyday tasks harder.
How is epiretinal pucker diagnosed?
Doctors use a detailed eye exam and tests like optical coherence tomography (OCT). They also do fluorescein angiography. These help see how bad the ERM is.
What are the treatment options for epiretinal pucker?
Treatment depends on how bad the symptoms are. For mild cases, watching it closely might be enough. For more severe cases, surgery might be needed.Surgery includes removing the vitreous gel and peeling the membrane. This can greatly improve your vision.
When should I seek medical attention for epiretinal pucker?
See a doctor if your symptoms are very bad or getting worse. If it’s affecting your daily life, get help. A retina specialist can give you the best advice.
What is the surgical procedure for treating epiretinal pucker?
Surgery removes the vitreous gel and peels the membrane. Intraoperative OCT helps make sure the surgery goes well.
What is the recovery process like after surgery for epiretinal pucker?
After surgery, you need to take care of your eyes right away. Recovery takes time. You might face some complications. Always follow up with your doctor to get the best results.
What are the expectations for visual improvement after treating epiretinal pucker?
How much your vision improves depends on the surgery’s success and your condition. Many people see a big improvement in their vision and symptoms.
Can epiretinal pucker recur after treatment?
Yes, it can come back. Talk to your doctor about the chances and how to manage it. They can help you plan for the long term.
How can I adapt to living with epiretinal membrane?
Get used to the changes in your vision by seeing your doctor regularly. Use support groups and resources for help and advice.
What is the relationship between epiretinal pucker and posterior vitreous detachment?
ERM often happens with posterior vitreous detachment (PVD). Knowing this can help doctors diagnose and treat ERM better.
Are there any secondary causes of epiretinal pucker?
Yes, things like diabetic retinopathy and retinal vein occlusion can cause it. Finding out what’s causing it is key to treating it right.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560703/