Urological emergencies are serious medical issues with the urinary tract or male genital organs. They need quick action to avoid serious harm or death. These emergencies are scary and need fast help from a urologist or emergency room doctor, especially in rare but critical cases like Water Under The Bridge Iliac Vessels: Emergency.

Examples of urological emergencies include acute urinary retention, severe urinary tract infections, testicular torsion, and priapism. Our team is dedicated to top-notch healthcare. We offer full support and guidance to international patients.
Key Takeaways
- Urological emergencies require immediate medical attention.
- Examples include acute urinary retention and testicular torsion.
- Prompt intervention is key to avoid long-term damage.
- Our institution provides full support for international patients.
- Urological emergencies can be life-threatening if not treated quickly.
Understanding Urological Emergencies
It’s key for healthcare teams to know about urological emergencies. These are urgent medical issues with the urinary tract or male genital areas. They need quick action to avoid serious problems or loss of organ function.
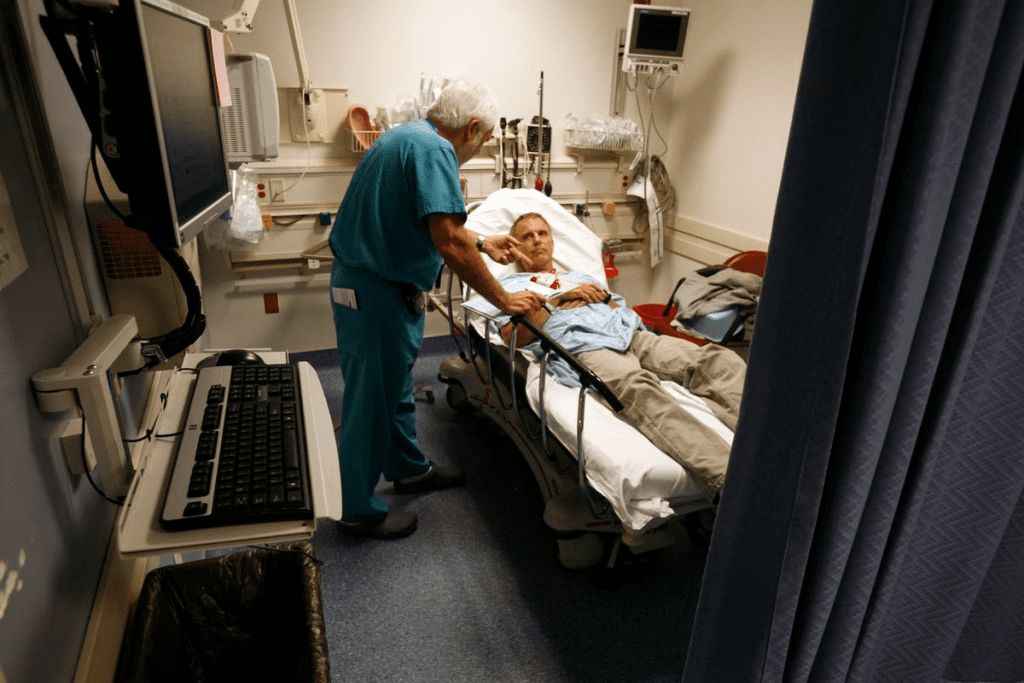
Definition and Clinical Significance
Urological emergencies include acute urinary retention, severe urinary tract infections, and issues like testicular torsion and priapism. These conditions are very serious and need fast treatment. For example, acute urinary retention is very painful and can be life-threatening. It needs quick catheterization to avoid kidney damage.
Quickly diagnosing and treating urological emergencies is vital. It helps prevent long-term harm and improves patient results. The American Urological Association says knowing these conditions well is key for doctors.
Prevalence and Hospital Resource Utilization
Urological emergencies like acute urinary retention are common. They use a lot of hospital resources. This shows the need for quick and effective management.
These emergencies need fast care and often lead to longer hospital stays and higher costs. Understanding cbi medical and uro medical term helps grasp the full impact. It shows why specialized care and patient education are so important.
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute urinary retention is when the bladder can’t empty. It’s a common reason for urgent urological care. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is key.
Causes and Risk Factors
Obstruction in the bladder or urethra, and issues with bladder signals are common causes. Age is a big risk factor, with 10% of men aged 70-79 and 30% of men aged 80-89 experiencing at least one episode. Other risks include BPH, urethral stricture, and some neurological disorders.
- Obstruction due to BPH or urethral stricture
- Neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis
- Medications that affect bladder muscle tone
Clinical Presentation
Patients with AUR have severe lower abdominal pain and a palpable bladder. They can’t urinate despite feeling the need to. We look at their medical history to find causes and risk factors.
Clinical evaluation includes a detailed history, physical exam, and sometimes imaging. This helps find the cause of AUR.
Emergency Management and Catheterization
The first step is catheterization to decompress the bladder. This relieves pain and prevents complications like bladder rupture. It’s both a diagnostic and therapeutic tool.
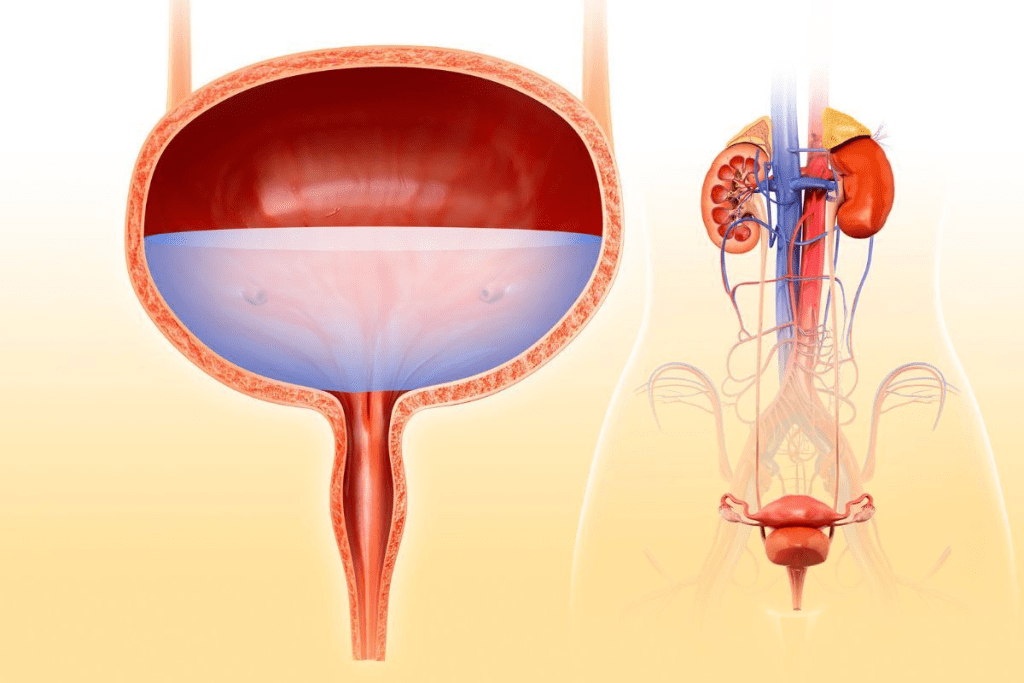
image is to be corrected’
After decompression, we do more tests to find the cause of AUR. CBI urology specialists manage these cases, from catheterization to treating the cause.
- Initial assessment and catheterization
- Diagnostic tests to identify the cause
- Treatment of the underlying condition
Severe Urinary Tract Infections and Urosepsis
Severe urinary tract infections (UTIs) can turn into urosepsis, a serious condition that needs quick medical help. UTIs are common, hitting nearly half of all people at least once. If not treated right, they can cause severe infections and urosepsis.
From UTI to Systemic Infection
A UTI can spread to the kidneys and into the blood, leading to urosepsis. This serious condition causes a big inflammatory response that can harm organs. Quick action and treatment are key to avoid lasting damage and death.
Things like delayed treatment, diabetes, and urinary blockages can make UTIs worse. Patients with a stent might see clots or tissue in the urine, showing a complicated UTI.
High-Risk Populations
Some groups face a higher risk of severe UTIs and urosepsis. These include the elderly, people with diabetes, those with weak immune systems, and those with urinary issues. It’s vital to spot and treat UTIs early in these groups to stop urosepsis.
Emergency Antibiotic Therapy and Supportive Care
Managing severe UTIs and urosepsis means starting antibiotics fast and giving supportive care. The American Urological Association (AUA) offers guidelines for managing related issues, like hematuria. Choosing the right antibiotic depends on local resistance and the patient’s risk factors. Supportive care might include fluids, managing sepsis, and fixing urinary blockages.
In summary, severe UTIs and urosepsis are big urological emergencies needing fast action and treatment. Knowing the risks and using the right management can lower the harm and death rates from these conditions.
Water Under the Bridge Iliac Vessels: Vascular Complications in Urology
Vascular problems in urology often come from the close link between urology and blood vessels. The urinary and blood systems work together closely. This can lead to serious issues during urology procedures.
Anatomical Relationship Between Urological and Vascular Structures
In the pelvic area, the urology and blood systems are very close. The iliac vessels are near the urinary tract. This makes them at risk during surgeries. Knowing this is key for urologists to avoid blood vessel problems.
image is to be corrected’
Iatrogenic Vascular Injuries During Urological Procedures
During urology procedures, blood vessel injuries can happen. These can be from direct damage, misplaced tools, or unseen anatomical differences. Such injuries can cause serious bleeding, hematomas, or long-term damage.
To lower these risks, urologists need to know about possible blood vessel problems. Planning before surgery, with detailed images, helps spot risks. This way, they can plan to avoid them.
Management of Urological-Vascular Emergencies
Handling urology and blood vessel emergencies needs a team effort. Urologists and vascular experts work together. If there’s a big injury, quick action is needed to stop bleeding. This might mean emergency surgery or using endovascular methods.
With a ruptured bladder, blood tests are very important. A big drop in hemoglobin means there’s a lot of bleeding. This calls for fast action, like blood transfusions and surgery. Knowing how to read these blood test results is vital for quick and right treatment.
It’s important to fully understand the risks in urology to avoid and handle blood vessel problems well. This helps improve patient results and lowers the risk of serious issues.
Obstructive Uropathy and Renal Colic
Ureteral obstruction, often due to stones, leads to obstructive uropathy and renal colic. This is a serious urological emergency that needs quick action. We will cover the causes, symptoms, and how to manage it.
Ureteral Stones and Pathophysiology
Ureteral stones are a main cause of obstructive uropathy. They block urine flow, causing high pressure in the kidney. This can lead to pain and kidney damage. Intrinsic causes, like stones, and extrinsic causes, such as tumors, can block the ureter.
Clinical Presentation and Differential Diagnosis
People with obstructive uropathy have severe flank pain, known as renal colic. This pain can spread to the groin. They may also feel nauseous, vomit, and have blood in their urine. To find the cause, doctors use imaging studies, like CT scans.
Emergency Management Strategies
Handling obstructive uropathy in emergencies involves fixing the blockage and easing pain. Ureteral stenting or percutaneous nephrostomy help restore urine flow. Pain relief is also key, often needing strong pain medicines. Quick action is vital to avoid infections or kidney damage, which is important in urology cbi and understanding medical term uro.
Genital Emergencies
The genital area is prone to emergencies like infections, injuries, and issues with reproductive organs. These problems need quick medical help to avoid serious issues and long-term harm.
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency where the spermatic cord twists, cutting off blood to the testicle. It causes severe pain and swelling. If not treated fast, it can lead to losing the testicle.
It’s vital to act quickly if you think someone has testicular torsion. The signs include sudden pain, and doctors use exams and images to diagnose.
Priapism
Priapism is a long-lasting erection without sexual arousal. It can cause ischemic damage if not treated quickly. It’s a urological emergency, and treatments aim to stop the erection and restore blood flow.
Priapism can happen due to some medicines or health issues. Treatment might include draining, flushing, or medicines to stop the erection.
Fournier’s Gangrene
Fournier’s gangrene is a severe infection of the genital and perineal areas. It can spread fast and be deadly. It needs aggressive surgical debridement and antibiotics.
It’s key to spot and treat Fournier’s gangrene early. Look for severe pain, swelling, and crepitus, along with signs of infection.
Gross Hematuria
Gross hematuria means a lot of blood in the urine. It can signal serious urological issues, like cancer or trauma. While not always urgent, it’s a sign to check for serious problems.
Managing gross hematuria involves finding the cause. A detailed diagnostic process is needed. Treatment targets the root cause of the bleeding.
Conclusion: Recognizing and Responding to Urological Emergencies
It’s key to spot and handle urological emergencies fast to avoid lasting harm. Quick action can greatly help patients, cutting down on serious problems and death risks.
We’ve talked about urgent urological issues like sudden urinary blockage, severe infections, and genital emergencies. Knowing what causes these, their signs, and how to act quickly is vital for doctors. Our team is dedicated to top-notch care for these urgent cases, using the newest methods and guidelines.
By knowing how to tackle urological emergencies well, we can make patient care better. The term CBI medical term, linked to continuous bladder irrigation, is one way we manage these urgent cases.
FAQ
What is considered a urological emergency?
Urological emergencies include acute urinary retention, severe urinary tract infections, testicular torsion, priapism, and obstructive uropathy. These conditions need quick treatment to avoid serious problems.
What are the symptoms of acute urinary retention?
Symptoms include severe lower abdominal pain, a palpable bladder, and not being able to urinate. Emergency treatment involves catheterization to relieve the bladder.
How is a urinary tract infection (UTI) managed in an emergency setting?
UTIs in emergencies are treated with antibiotics and supportive care. The elderly and diabetics need fast treatment to avoid urosepsis.
What is the role of catheterization in managing acute urinary retention?
Catheterization helps in cases of acute urinary retention. It relieves severe discomfort and prevents complications.
What are the complications of delayed treatment for testicular torsion?
Delayed treatment can cause loss of the affected testicle due to poor blood flow. Quick surgery is needed to restore blood flow and prevent damage.
How is priapism treated in an emergency setting?
Priapism is treated with emergency measures to end the prolonged erection and restore normal blood flow to prevent tissue damage.
What is Fournier’s gangrene, and how is it managed?
Fournier’s gangrene is a severe infection of the genital and perineal areas. It is treated with aggressive surgery and supportive care to prevent further issues.
What does gross hematuria indicate, and how is it evaluated?
Gross hematuria means significant blood in the urine. It can signal various conditions, including emergencies. Tests are used to find the cause and guide treatment.
How are ureteral stones managed in an emergency setting?
Ureteral stones causing blockage are treated with emergency methods. This includes placing a ureteral stent or percutaneous nephrostomy to relieve pain and prevent complications.
What are the implications of a ruptured bladder on bloodwork?
A ruptured bladder can cause abnormal bloodwork, showing signs of infection or inflammation. Quick diagnosis and treatment are key to prevent further issues.
What are the AUA guidelines for managing hematuria?
The American Urological Association (AUA) has guidelines for managing hematuria. These outline the right evaluation and treatment for patients with blood in their urine.
What is CBI in the context of urology?
Continuous Bladder Irrigation (CBI) in urology means flushing the bladder with saline solution continuously. It’s often used after certain procedures to prevent clots and aid healing.
References
Kazımoğlu, H., & Dokur, M. (2017). The top 100 cited articles on urological emergencies: A bibliometric analysis. Turkish Journal of Urology, 44(3), 239“250. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5937644/
Epidemiology and management of urological emergencies in a tertiary care setting. (2025). International Journal of Emergency Medicine. https://intjem.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12245-025-00882-8
Non-Traumatic Urologic Emergencies in Men: A Clinical Review. (n.d.). eScholarship. https://escholarship.org/uc/item/2cj981j1



































