What hurts when you have bladder cancer? Learn the negative reality of pain associated with bladder cancer symptoms. Crucial, powerful facts on discomfort.
Bladder cancer is a big health issue, hitting over 84,000 Americans every year. Painful urination and pelvic discomfort are early signs. We’ll look into the symptoms of urothelial carcinoma, a common bladder cancer type.
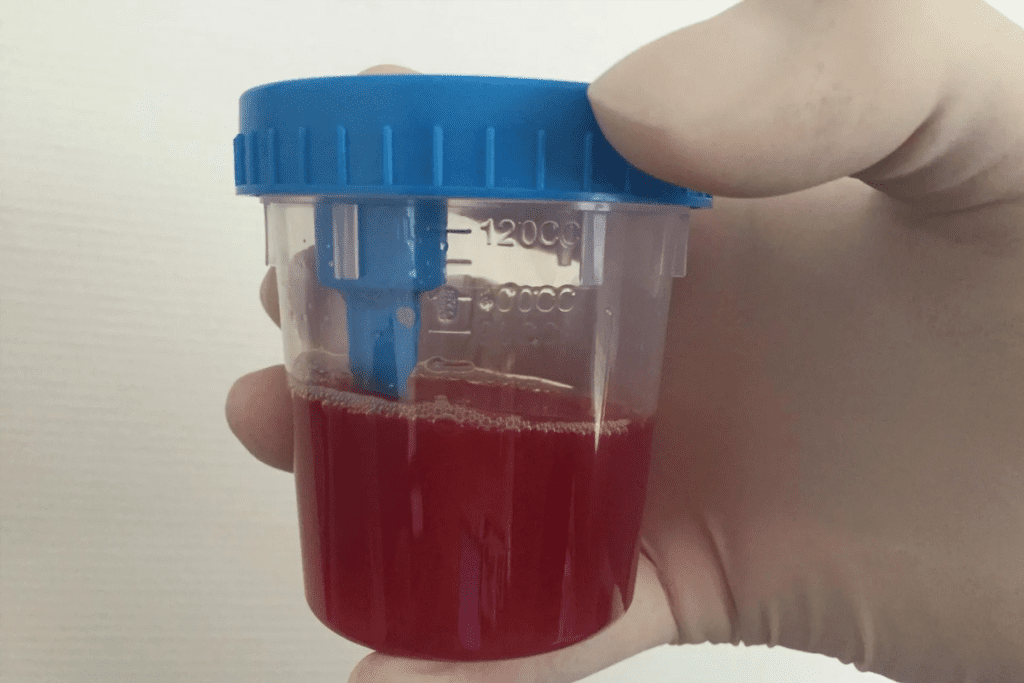
Knowing the symptoms and the need for early detection can lead to better results. Blood in urine is the most common sign, often with pelvic and back pain. We’ll cover what to watch for and how early detection boosts treatment success.
Key Takeaways
- Bladder cancer affects thousands of Americans each year.
- Painful urination and pelvic discomfort are early warning signs.
- Blood in urine is the most common symptom of bladder cancer.
- Early detection is key for effective treatment.
- Understanding survival rates offers valuable insights.
Common Pain Symptoms Associated with Bladder Cancer
Bladder cancer often shows through different pain symptoms. It’s important for patients to know these signs to get medical help quickly. We’ll look at the types of pain linked to bladder cancer and when to see a doctor.
The Nature of Bladder Cancer Pain
Bladder cancer pain is a key sign of the disease. This pain can feel like a dull ache or a sharp stab. Painful urination (dysuria) is common, feeling like a burning when you pee. Some people also feel pelvic pain, which can be mild or very severe.
When to Be Concerned About Bladder-Related Pain
It’s important to know the difference between normal discomfort and pain that might mean bladder cancer. If you have ongoing or severe pain in your pelvis or when peeing, see a doctor. Also, watch for pain that spreads to your lower back or comes with other signs like hematuria (blood in urine). Spotting these symptoms early can help a lot with treatment.
Stay alert to any changes in your body. If you’re not sure about your pain, get a doctor’s opinion. Knowing about bladder cancer pain and when to get help can help you stay healthy.
Blood in Urine: The Most Common Warning Sign
Blood in urine, known as hematuria, is common in bladder cancer patients. It happens in up to 85% of cases. Knowing about it is key for early detection and treatment.
Why Hematuria Occurs
Hematuria happens when bladder cancer cells or tumors bleed. This bleeding can come from the tumor damaging the bladder lining or by growing into blood vessels. We’ll dive deeper into why hematuria is linked to bladder cancer.
Blood in urine isn’t just about bladder cancer. But, it’s very common in bladder cancer patients. Spotting hematuria early can greatly improve treatment success and patient outcomes.
Visible vs. Microscopic Blood in Urine
Hematuria can be visible or microscopic. Visible hematuria makes urine look pink to dark red because of blood. Microscopic hematuria needs a microscope to see blood cells in the urine.
Both types of hematuria can point to bladder cancer. Neither should be ignored without a doctor’s check-up. Visible hematuria gets more attention, but microscopic hematuria can also signal cancer, even if urine looks normal.
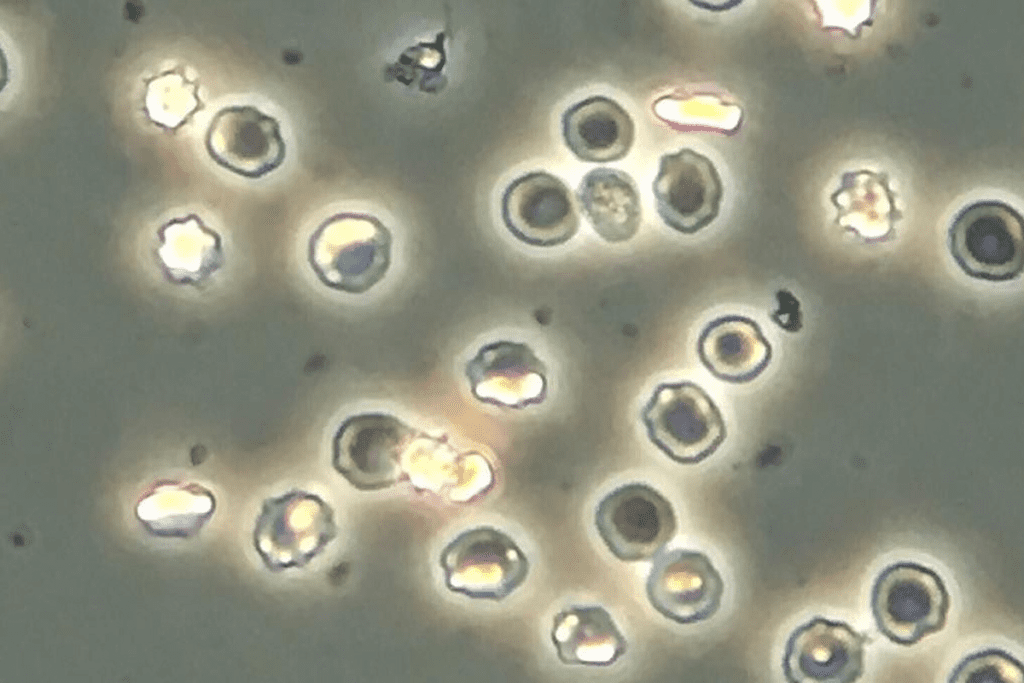
It’s important to know the difference between visible and microscopic hematuria for bladder cancer diagnosis. If you see either, see a healthcare professional for a detailed check-up.
Painful Urination (Dysuria) and Its Significance
Painful urination, or dysuria, is a key symptom that can point to several urinary tract problems, including bladder cancer. It can show up in different ways for different people. So, it’s important to know how it relates to bladder cancer.
How Dysuria Feels in Bladder Cancer Patients
In bladder cancer patients, dysuria can feel like a burning sensation or pain while urinating. This discomfort can vary from mild to severe and may stay the same or change. The pain is often sharp or feels like intense burning, mostly during or after urination.
Some key aspects of dysuria in bladder cancer patients include:
- A burning sensation while urinating
- Pain or discomfort in the bladder or urethra
- Increased frequency or urgency of urination
- Pain that persists or worsens over time
Distinguishing Cancer-Related Dysuria from Other Causes
Dysuria isn’t just for bladder cancer; it can also be caused by UTIs, kidney stones, or sexually transmitted infections. To tell if it’s related to cancer, look at the whole picture and other symptoms.
Some signs that suggest cancer-related dysuria include:
- Persistent or recurrent dysuria despite treatment for other issues
- Hematuria (blood in urine) along with dysuria
- Dysuria with other bladder cancer symptoms, like pelvic pain or frequent urination
It’s vital to understand dysuria’s nature and signs for early bladder cancer detection and treatment. If you have ongoing or severe dysuria, see a healthcare professional for a detailed check-up.
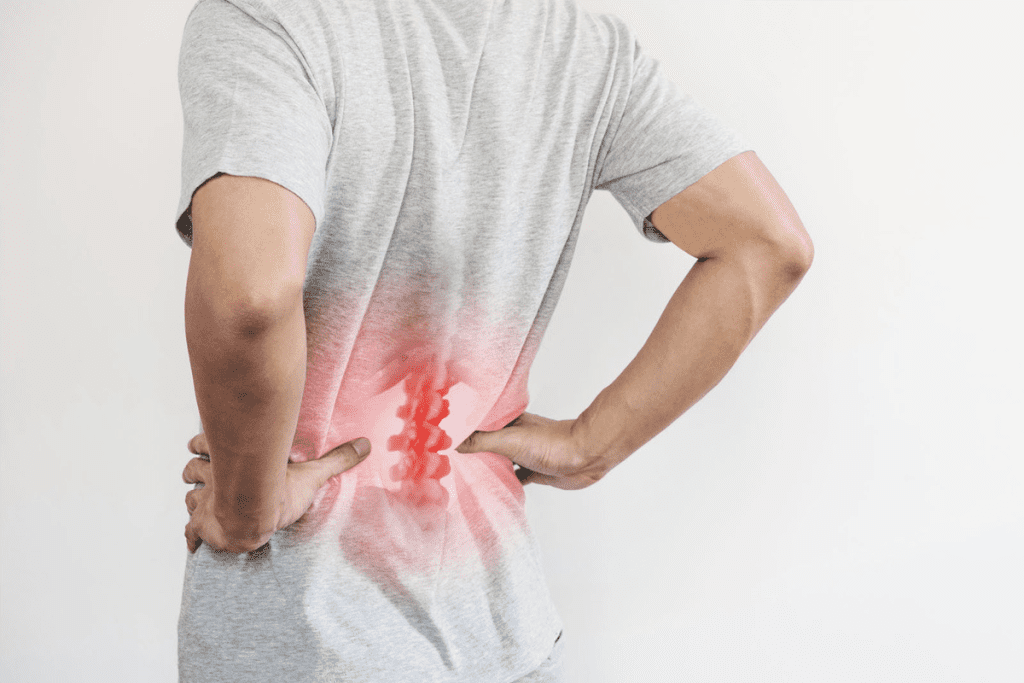
Pelvic Pain and Pressure Sensations
Pelvic pain is a common symptom of bladder cancer. It can feel like a dull ache or a sharp pain. The pain’s location and intensity can vary, depending on the tumor’s size and where it is.
Locations of Pelvic Discomfort
People with bladder cancer might feel pain in their lower abdomen, pelvis, or lower back. This pain can be constant or come and go. It often gets worse over time if not treated.
The location of pelvic pain can tell us about the cancer’s spread. Pain in the pelvic area might mean the cancer is touching nearby tissues or organs.
When Pelvic Pain Indicates Advanced Disease
Pelvic pain can also mean the cancer has spread. When cancer reaches nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body, it can cause a lot of pain. If you’re feeling persistent or severe pelvic pain, you should see a doctor right away.
Knowing about Pelvic Pain in Bladder cancer is key to managing it well.
Back Pain as a Symptom of Bladder Cancer
It’s important to know how back pain is linked to bladder cancer. Bladder cancer often shows symptoms like blood in the urine or painful urination. But, back pain can also be a warning sign, even if the cancer has grown.
Why Bladder Cancer Can Cause Back Pain
Back pain from bladder cancer happens in a few ways. As the cancer grows, it can hurt nearby nerves and tissues. In more serious cases, it can spread to the bones in the back, causing pain.
Key reasons for back pain in bladder cancer include:
- Cancer invasion into surrounding nerves and tissues
- Metastasis to the bones
- Hydronephrosis due to urinary tract obstruction
Differentiating Cancer-Related Back Pain from Other Causes
Telling if back pain is from bladder cancer or something else can be hard. But, some signs might point to a serious problem.
Characteristics of cancer-related back pain:
- Persistence and progression
- Association with other urinary symptoms
- Presence of systemic symptoms like weight loss
Understanding the link between bladder cancer and back pain is key. This is because the bladder is close to the lower back.
Seeing back pain as a bladder cancer symptom is critical. If you have back pain and other urinary issues, see a doctor. They can check if it’s related to bladder cancer.
Bladder Cancer Survival Rates by Age and Bladder Cancer Symptoms: What You Need to Know
Bladder cancer is a big health issue. Survival rates depend on many things. We need to look at age, stage at diagnosis, and catching symptoms early.
2025 Projections: 84,870 New Cases and 17,420 Deaths
In 2025, the U.S. will see about 84,870 new bladder cancer cases. Sadly, around 17,420 people will die from it. Knowing about survival rates and catching cancer early is key.
Urothelial carcinoma is the most common bladder cancer. It starts in the bladder’s lining. Finding epithelial cells in urine might mean something’s off, but it’s not always cancer.
Survival Statistics Based on Stage and Age
Survival rates for bladder cancer change a lot with stage and age. Early detection is linked to better survival. For example, a localized stage diagnosis has a 70% five-year survival rate. But, survival drops a lot for later stages.
Age also affects survival. Older people often have worse outcomes because of other health issues. We must think about this when looking at survival statistics.
How Early Symptom Recognition Impacts the 72% Survival Rate
Spotting symptoms early is key to better survival rates. Symptoms like blood in urine or painful urination help catch cancer sooner. This means better treatment and survival chances.
The five-year survival rate for bladder cancer is about 72% for those diagnosed between 2011 and 2017. But, this can change based on stage and age. Catching symptoms early can help improve survival chances.
In summary, knowing about bladder cancer survival rates and what affects them is vital. Recognizing symptoms early and understanding survival rates can help improve outcomes for bladder cancer patients.
Risk Factors and Prevention Strategies
Bladder cancer has risk factors that can be managed to lower its occurrence. Knowing these factors is key for prevention and early detection.
Smoking: A Major Risk Factor
Smoking causes nearly half of all new bladder cancer cases. Tobacco smoke’s chemicals get into the blood, then the kidneys, and end up in the urine. This damages the bladder lining and raises cancer risk.
Quitting smoking is a powerful way to lower bladder cancer risk. We urge smokers to find help and resources to quit.
Lifetime Risk
The chance of getting bladder cancer over a lifetime is about 2.1%. This risk comes from genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
Preventive Measures
There are steps you can take to lower bladder cancer risk. These include:
- Drinking plenty of water to dilute harmful substances in urine
- Avoiding chemicals used in manufacturing
- Eating lots of fruits and vegetables
By knowing the risks and taking action, you can greatly lower your chance of bladder cancer.
Conclusion: Modern Approaches to Bladder Cancer Treatment
Bladder cancer treatment has changed a lot, giving patients new hope. Now, we have surgery, chemotherapy, and more to fight urothelial carcinoma and squamous epithelial cell carcinoma. These methods are designed to help patients overcome their cancer.
Getting cancer early and treating it fast can make a big difference. If you see blood in your urine or feel pain when you pee, it might be cancer. It’s important to see a doctor right away.
Survival rates for bladder cancer depend on how old you are and when you’re diagnosed. Thanks to new treatments, more people are living longer. Doctors create a treatment plan just for you, based on your cancer and health.
Knowing the risks, like smoking, can help prevent bladder cancer. If you’re worried or notice symptoms, talk to a doctor. They can help you figure out the best way to take care of yourself.
FAQ
What are the common symptoms of bladder cancer?
Symptoms of bladder cancer include blood in urine (hematuria), painful urination (dysuria), and pelvic pain. Back pain can also occur. These signs may mean you have bladder cancer, if they don’t go away or get worse.
What is hematuria, and why is it a significant symptom of bladder cancer?
Hematuria is blood in the urine. It’s a key sign because it happens in about 85% of bladder cancer cases. This makes it a major warning sign.
How does bladder cancer cause painful urination?
Bladder cancer can irritate the bladder lining or block urine flow. This causes a burning or discomfort feeling when you pee.
What is the significance of pelvic pain in bladder cancer patients?
Pelvic pain in bladder cancer patients can mean the disease is getting worse. It might spread to nearby tissues or organs. This causes discomfort or pressure in the pelvic area.
Can bladder cancer cause back pain, and how can it be differentiated from other causes?
Yes, bladder cancer can cause back pain. This usually happens when the disease spreads to nearby tissues or organs. Back pain from cancer is different because it lasts longer, is more severe, and comes with other bladder cancer symptoms.
What are the survival rates for bladder cancer, and how do they vary by age?
Survival rates for bladder cancer depend on the stage and age of the patient. Early detection greatly improves survival chances. For example, the 5-year survival rate is about 72% for early-stage bladder cancer.
What are the risk factors for developing bladder cancer?
Risk factors for bladder cancer include smoking, which causes nearly half of new cases. Other factors are age, exposure to harmful chemicals, and genetics.
How can the risk of developing bladder cancer be reduced?
To lower bladder cancer risk, quit smoking, avoid harmful chemicals, and live a healthy lifestyle. Early detection and treatment also help improve outcomes.
What are the treatment options available for bladder cancer?
Treatments for bladder cancer vary based on the disease’s stage and severity. They include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or a mix of these. Modern treatments aim to increase survival rates and improve quality of life.
Why is early detection of bladder cancer so important?
Early detection of bladder cancer is key because it greatly improves treatment success and survival chances. Spotting symptoms early and getting medical help can lead to diagnosis at a treatable stage.
What is urothelial carcinoma, and how is it related to bladder cancer?
Urothelial carcinoma, or transitional cell carcinoma, is the most common bladder cancer type. It starts in the urothelial cells lining the bladder. Knowing this type is vital for diagnosis and treatment.
Can squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate bladder cancer?
Finding squamous epithelial cells in urine can be normal. But an abnormal amount or context might suggest bladder cancer, along with other symptoms.
References
American Cancer Society. (n.d.). Key Statistics for Bladder Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/bladder-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
Provides estimates for 2025: ~84,870 new bladder cancer cases and ~17,420 deaths in the U.S.
Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER). (n.d.). Cancer Stat Facts: Bladder Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/urinb.html
Reports age-adjusted incidence, mortality, and distribution by age groups for bladder cancer. S
Bladder Cancer Advocacy Network. (n.d.). 5 Bladder Cancer Warning Signs: Pain, Frequent Urination … https://bcan.org/facing-bladder-cancer/bladder-cancer-signs-symptoms/










