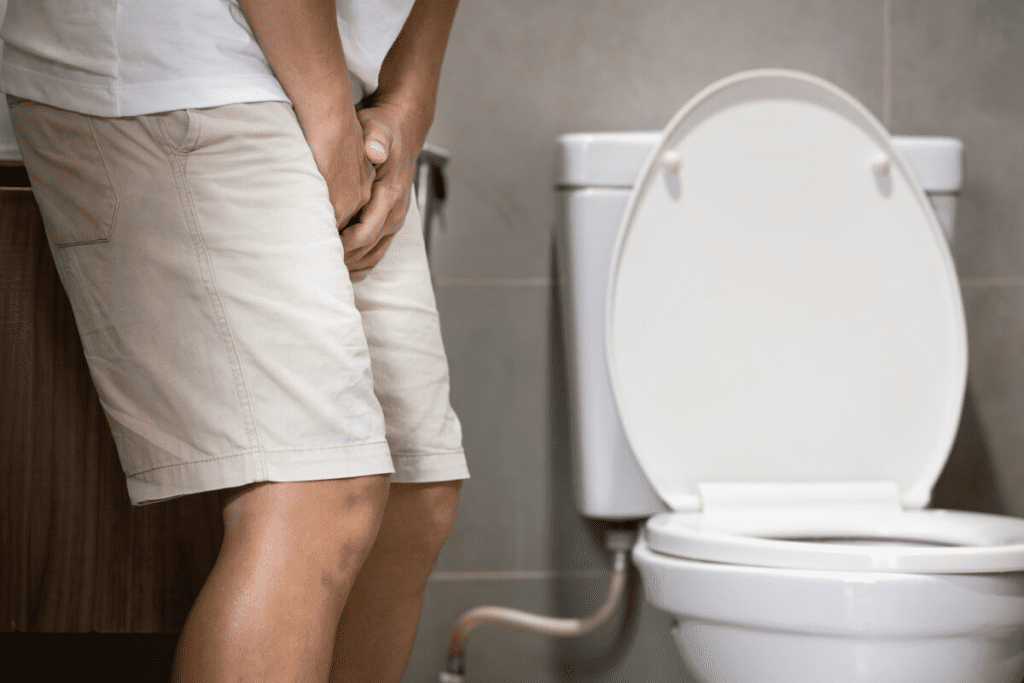
The term for needing to get up many times at night to pee is nocturia, a form of Frequent urination that disrupts sleep and daytime energy.
Nocturia is common, affecting up to 40% of adults and more than 70% of people over age 70, making it one of the most frequent urination concerns in older adults.
Waking repeatedly to urinate fragments sleep, and Frequent urination at night may signal bladder irritation, fluid timing issues, or other treatable causes.
Anyone experiencing persistent nocturia or Frequent urination should discuss triggers, fluid habits, and medications with a clinician to personalize management and improve sleep quality.
Key Takeaways
- Nocturia is the medical term for waking up at night to urinate.
- It affects up to 40% of adults and over 70% of those older than 70.
- Nocturia can significantly disrupt sleep and impact quality of life.
- Understanding nocturia is crucial for addressing its underlying causes.
- Recognizing nocturia as a medical condition can lead to better outcomes.
Understanding Nocturia: The Medical Term for Nighttime Urination
Nocturia is when you wake up at night to use the bathroom. It affects many adults, especially as they get older. Up to 40% of adults and over 70% of those over 70 experience it.
Definition and Clinical Significance
Nocturia is not just a sign of aging. It can really change how you live your life. It’s linked to health problems like diabetes and heart disease. Knowing about nocturia helps doctors find and treat the real cause.
“Nocturia is a symptom, not a disease,” doctors say. It means there’s something else going on that needs to be checked. If not treated, it can make you tired during the day and lower your quality of life.
How Nocturia Differs from Other Urinary Conditions
Nocturia is often mixed up with other issues, like making too much urine or an overactive bladder. But nocturia is about needing to go at night. It’s all about how often you go at night.
- Nocturia: Nighttime urination
- Polyuria: Excessive urine production overall
- Overactive Bladder Syndrome: Frequent urination throughout the day
The Normal vs. Abnormal Frequency of Nighttime Urination
It’s okay to wake up once at night to use the bathroom, especially as you get older. But waking up more than that is not normal. It might mean you have nocturia.
Doctors look at how often you go at night to figure out if you have nocturia. They want to find the cause and help you feel better. Knowing what’s normal helps them spot when you might have nocturia.
The Prevalence of Nocturia Across Age Groups and Genders
It’s important for doctors to know how common nocturia is in different groups. Nocturia is when you wake up many times at night to use the bathroom. It’s more common in some people than others, depending on their age and gender.
Statistics on Nocturia in the General Population
Research shows that many people deal with nocturia. It’s more common in women under 50 and in both men and women over 70. This is because of hormonal changes and aging.
“Nocturia is a complex issue,” says a top urology expert. “It needs a detailed approach to understand its impact on different groups.”
Nocturia in Women: Hormonal Influences and Age Factors
In women, hormonal changes during different stages of life affect nocturia. For example, lower estrogen levels during menopause can cause more trips to the bathroom at night.
- Hormonal changes during menstrual cycles and menopause
- Impact of pregnancy on bladder control
- Age-related changes in the urinary system
Nocturia in Men: Prostate Issues and Age-Related Changes
In men, prostate issues are a big reason for nocturia. As men get older, their prostate gland can grow, making it hard to urinate. This, along with other age-related changes, can lead to more nighttime bathroom trips.
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and its impact on urination
- Age-related decline in bladder function
- Increased risk of nocturia with comorbid conditions
Elderly Population: Why Nighttime Urination Increases with Age
The elderly face a higher risk of nocturia. This is due to decreased bladder capacity, increased urine production at night, and higher rates of comorbid medical conditions. Knowing these factors helps in managing nocturia in older adults.
By understanding nocturia’s prevalence in different age groups and genders, doctors can better treat their patients. This ensures each person gets the care they need.
7 Common Causes of Frequent Urination During the Night
Understanding why we wake up to use the bathroom at night is key. Nocturia, or waking up to pee, affects many people. It can ruin their sleep and daily life. There are many reasons why this happens, which we will explore.
Nocturnal Polyuria: Excessive Nighttime Urine Production
Nocturnal polyuria means peeing too much at night. It’s a big reason for nocturia. It can be caused by drinking too much before bed, sleep issues, or health problems like diabetes insipidus or heart failure.
Global Polyuria: Increased 24-Hour Urine Output
Global polyuria means peeing more in a day. It can also lead to waking up at night. It’s often due to drinking too much, diabetes mellitus, or diuretics. Knowing the difference between these types is important for treatment.
Reduced Bladder Capacity and Overactive Bladder Syndrome
Having a small bladder or overactive bladder can cause frequent nighttime trips to the bathroom. This can be due to bladder infections, bladder stones, or neurological disorders. Treatment may include fixing the cause or using medications and behavioral modifications.
Sleep Disorders and Their Impact on Urination Patterns
Sleep disorders, like sleep apnea, can mess with our pee schedule. Sleep and pee problems can feed into each other. Treating sleep issues is crucial for managing nocturia, showing we need a full approach to solve it.
How Nocturia Impacts Quality of Life and Health
Nocturia is more than a small problem; it deeply affects patients’ lives and health. It has wide-ranging effects that go beyond just the symptoms. It impacts many areas of health and daily life.

Sleep Disruption and Daytime Fatigue
Nocturia messes up the normal sleep pattern, causing poor sleep. This leads to daytime fatigue. It makes it hard to do daily tasks and stay productive.
Also, not getting enough sleep hurts thinking, memory, and decision-making. It makes everyday activities tough.
Increased Risk of Falls and Injuries in the Elderly
The elderly face big risks from nocturia. They wake up often to use the bathroom. This raises the risk of falls and injuries. Getting up in the dark is dangerous, especially for those who move slowly or have balance problems.
Research shows nocturia increases fall risk. Falls can cause serious injuries, like broken bones, and even death.
Psychological Effects: Depression, Anxiety, and Social Isolation
Nocturia also affects the mind. The sleep disruptions and discomfort can cause depression and anxiety. This harms mental health and overall well-being.
Also, the tiredness and poor quality of life from nocturia can make people stay away from social events. This leads to social isolation. It makes people feel lonely and depressed.
Long-term Health Consequences and Mortality Risk
Ignoring nocturia can harm health long-term. Chronic sleep problems and related health issues raise the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and other metabolic problems.
Also, poor health and increased fall risk can raise mortality risk. This shows why treating nocturia is crucial.
In summary, nocturia’s impact on life and health is wide and serious. To improve well-being, we need to tackle it fully. This means looking at both physical and mental effects.
Diagnosing Nocturia: Tests and Evaluations
Diagnosing nocturia requires a detailed approach. We use a thorough process to find the cause. This ensures we check all possible factors.
Initial Assessment and Medical History
The first step is an initial assessment and medical history. We collect information on symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle. This helps us find the root cause of nocturia.
Bladder Diary: Tracking Urination Patterns
A bladder diary is key in diagnosing nocturia. Patients record fluid intake, urination, and nocturia episodes. This diary helps us understand their urinary habits and find patterns that may cause their condition. For more on using a bladder diary, checktrusted medical literature.
Laboratory Tests and Urinalysis
Laboratory tests and urinalysis are vital. We test for diabetes, urinary tract infections, and other issues. Urinalysis checks for kidney problems like hematuria or proteinuria.
Advanced Diagnostic Procedures
In some cases, advanced diagnostic procedures are needed. These include urodynamic tests, imaging studies, or other tests based on symptoms and history. This helps us find the exact cause of nocturia.
By combining these methods, we can accurately diagnose nocturia. Then, we create a treatment plan that meets the patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Managing Night time Urination
Managing night timeurination requires a mix of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and new therapies. We create treatment plans that fit each patient’s needs. This ensures they get the best care possible.
Behavioral Modifications and Lifestyle Changes
First, we focus on behavioral modifications and lifestyle changes. This includes managing how much fluid you drink and avoiding caffeine and alcohol at night. We also suggest a timed voiding schedule.
Another key tip is to elevate your legs during the day to reduce swelling. Also, try not to drink too much water before bedtime. These steps can help a lot with nighttime urination.
Medications for Different Types of Nocturia
For some, medications are needed to handle nocturia. The right medicine depends on the cause, like diuretics for fluid retention or drugs for bladder control.
We also look at meds for conditions that lead to nocturia, like desmopressin for too much urine at night.
Treating Underlying Medical Conditions
It’s key to treat the medical issues causing nocturia. This might mean managing diabetes, treating sleep apnea, or fixing urinary tract infections.
For men, prostate problems often lead to nocturia. Treatments could include drugs to shrink the prostate or ease symptoms.
Innovative Therapies and Emerging Treatments
We’re always exploring innovative therapies and new treatments for nocturia. This includes looking at new meds and procedures that can help symptoms and improve life quality.
Our goal is to offer the latest and most effective treatments. This way, our patients get the best care out there.
Practical Tips to Reduce Nighttime Bathroom Trips
To cut down on nighttime bathroom trips, try these tips. They are based on solid evidence. Making lifestyle and behavior changes can help manage nighttime urination well.
Evening Fluid Management Strategies
It’s key to manage fluids in the evening. We advise cutting down on fluids two hours before bed. Watching your fluid intake can really help reduce nighttime trips to the bathroom.
Dietary Adjustments to Minimize Nocturia
Changing what you eat can also help. Stay away from caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime. Also, eating less salt can make you pee less at night.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol before bedtime.
- Reduce salt intake to minimize urine production.
- Limit fluids at least two hours before bed.
Sleep Environment Optimization
Making your bedroom sleep-friendly is important. Make sure it’s dark, quiet, and comfy. Improving your sleep space can cut down on nighttime bathroom trips.
Bladder Training Techniques
Bladder training helps you go longer without needing to pee. It builds up your bladder’s capacity. Start with small steps and gradually increase the time between bathroom visits.
By using these tips, you can greatly reduce nighttime bathroom trips. This can improve your life quality a lot.
Conclusion: When to Seek Medical Help for Nocturia
Knowing when to get medical help is key to managing nocturia well. If you keep waking up to pee or have other symptoms, see a doctor. Our healthcare team focuses on you, offering top care and support for nocturia.
Spotting the signs that mean you need a doctor is the first step to better health. We’re here to help you find the best ways to deal with nocturia. If you’re dealing with it, don’t wait to get help. Our team is ready to guide you in making the right choices for your health.
FAQ
What is nocturia, and how is it defined?
Nocturia is when you need to get up to pee a lot at night. It means you wake up to use the bathroom.
How common is nocturia, and which age groups are most affected?
Nocturia is common, affecting up to 40% of adults. It’s even more common in people over 70, hitting over 70% of them.
What are the main causes of nocturia?
Nocturia can be caused by several things. These include too much pee at night, more pee overall, a small bladder, an overactive bladder, and sleep issues.
How does nocturia impact quality of life?
Nocturia messes with your sleep, making you tired during the day. It also raises the risk of falls, depression, anxiety, and feeling lonely. It affects your health and happiness.
What diagnostic tests are used to evaluate nocturia?
Doctors use several tests to figure out nocturia. These include checking your medical history, a bladder diary, lab tests, and sometimes more advanced tests.
What treatment options are available for managing nocturia?
There are many ways to manage nocturia. You can try changing your habits, taking medicine, treating other health issues, or trying new therapies.
How can I reduce nighttime bathroom trips?
To cut down on nighttime trips, try drinking less water in the evening. Make smart food choices, create a comfy sleep space, and practice bladder training.
Is nocturia related to diabetes or hormonal changes?
Yes, diabetes and hormonal changes can cause nocturia. They can make you pee more and affect your bladder.
Can nocturia be a sign of an underlying serious health condition?
Yes, if you have persistent or severe nocturia, it could mean a serious health issue. It’s important to see a doctor to find out and get treatment.
How does age affect the likelihood of experiencing nocturia?
As you get older, especially over 70, you’re more likely to have nocturia. This is because of age-related changes and health issues.
Are there any differences in how nocturia affects men and women?
Yes, men and women are affected differently by nocturia. Women under 50 and both men and women over 70 are more likely to have it. Hormones, prostate issues, and aging play a role.
References
- Leslie, S. W. (2024). Nocturia. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.



































