What is considered positive urinalysis? Learn the crucial, powerful indicators on a UTI test (leukocytes, nitrites) that confirm a urinary tract infection.
Urinalysis is a key tool for finding health issues, like urinary tract infections (UTIs). It helps us spot problems in the urine. A positive test means there might be bacteria, blood, or other issues in the urinary system.

Knowing what a positive urinalysis means is important for treating urinary problems right. Medical guidelines say a positive test shows things like bacteria or white blood cells in the urine.
Key Takeaways
- A positive urinalysis indicates the presence of abnormalities in the urine.
- Abnormal findings include positive leukocyte esterase, nitrites, or white blood cells above 5 per high-power field.
- Understanding urinalysis results is vital for diagnosing urinary tract conditions.
- A positive result can signal the presence of bacteria or other irregularities in the urinary tract.
- Accurate diagnosis relies on interpreting urinalysis results correctly.
The Fundamentals of Urinalysis Interpretation
Urinalysis is a key tool in diagnosing health issues. It gives us insights into a patient’s health. We use it to check for infections and kidney problems.
We look at several things when we interpret urinalysis results. These include leukocyte esterase, nitrites, protein, and blood in the urine.
What a Urinalysis Measures
A urinalysis checks many important parts of urine. This gives us a full picture of a patient’s health. We look at:
- Leukocyte Esterase: An enzyme that shows white blood cells, meaning a possible infection.
- Nitrites: Nitrites mean a bacterial infection, as many bacteria can change nitrate to nitrite.
- Protein: Too much protein in urine can mean kidney damage or disease.
- Blood: Red blood cells in urine can mean infections, kidney stones, or tumors.
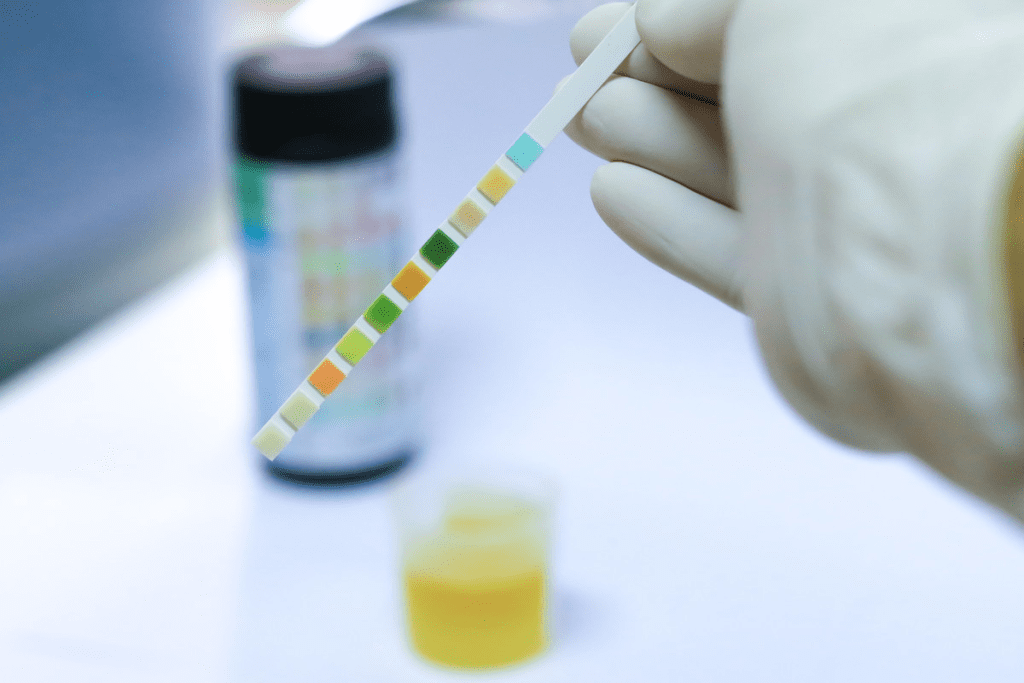
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings
It’s important to know the difference between normal and abnormal urinalysis results. Normal results usually show:
- Negative or trace amounts of protein
- No leukocyte esterase or nitrites
- Few or no red blood cells
Abnormal results can mean different health issues. For example, leukocyte esterase or nitrites might mean a urinary tract infection (UTI).
When Doctors Order Urinalysis Tests
Doctors order urinalysis tests for many reasons. These include:
- Diagnosing urinary tract infections
- Monitoring kidney function and detecting kidney disease
- Screening for diseases like diabetes
- Investigating symptoms like painful urination or blood in the urine
Understanding urinalysis helps doctors make better decisions for patient care. They can then create effective treatment plans.
5 Key Indicators That Signal a Positive UTI Test
Diagnosing urinary tract infections (UTIs) involves several important indicators in urinalysis results. These indicators are key for healthcare professionals to make accurate diagnoses and effective treatment plans.
Leukocyte Esterase: What Positive Results Mean
Leukocyte esterase is an enzyme made by white blood cells. Its presence in urine is a big sign of a possible UTI. A positive result for leukocyte esterase means the body is fighting an infection. This calls for further tests to confirm a UTI.
Nitrite in Urine: A Strong Sign of Bacteria
Nitrites in urine are another key sign of a UTI. Many bacteria, like Escherichia coli, can turn nitrate to nitrite. A positive nitrite test shows there are bacteria in the urine.
High WBC in Urine: When White Blood Cells Exceed 5 per HPF
White blood cells (WBCs) in urine show the body is fighting an infection or inflammation. If there are more than 5 WBCs per high power field (HPF), it’s abnormal and might mean a UTI. High WBC counts in urine are a key sign of infection, helping doctors diagnose.
Red Blood Cells: Significance When Above 3 per HPF
Red blood cells (RBCs) in urine can also point to a UTI, if there are more than 3 RBCs per HPF. While not only for UTIs, RBCs suggest irritation or infection in the urinary tract. More tests are needed to find out why.
Understanding these 5 key indicators”leukocyte esterase, nitrite, high WBC count, and red blood cells”helps healthcare professionals accurately diagnose and manage UTIs. Each indicator gives important information. Together, they help make a full assessment of the patient’s condition.
How to Interpret Combined Urinalysis Results
Understanding combined urinalysis results is key for diagnosing and treating urinary tract infections (UTIs). Analyzing these results together gives a full picture of a patient’s health.
Urinalysis looks at many things, like nitrites, leukocytes, and bacteria in urine. This helps doctors make better decisions for their patients.
image is to be corrected’
The Significance of Both Positive Nitrites and Leukocytes
A positive test for both nitrites and leukocytes means a UTI is likely. Nitrites in urine show bacteria are present, as many UTI-causing bacteria turn nitrate to nitrite. Leukocytes or white blood cells show the body is fighting an infection.
Seeing both means a bacterial UTI is likely. This helps doctors start the right antibiotics.
What UA Bacteria Levels Indicate
The amount of bacteria in urine, shown by urinalysis (UA bacteria), is very important for UTI diagnosis. More than 100,000 colony-forming units per milliliter is a clear sign of infection.
But, we must look at all urinalysis results and symptoms together. A urine sample from a bladder infection will show high bacteria levels and other infection signs.
When Urinalysis Results Suggest Bladder Infection
Urinalysis can show a bladder infection with signs like bacteria in urine, leukocytes, and sometimes red blood cells. These signs, along with symptoms like pain or needing to urinate often, point to cystitis or bladder infection.
Doctors use these results to plan a treatment. This might include antibiotics and care to help symptoms.
Common Pathogens Detected in Positive Urinalysis
Knowing the common pathogens in positive urinalysis is vital for diagnosis and treatment. We look for bacteria and understand infections’ causes. This helps us choose the right treatment for each pathogen.
Escherichia coli: The Predominant Cause of UTIs
Escherichia coli, or E. coli, is the main cause of urinary tract infections (UTIs). E. coli causes about 75-90% of uncomplicated UTIs. It’s common in the gut and sticks to the urinary tract. But, E. coli’s role is changing due to antibiotics and demographic shifts.
Shifting Patterns in Bacteriuria
E. coli is not the only cause of UTIs anymore. Other bacteria like Klebsiella pneumoniae, Proteus mirabilis, and Staphylococcus saprophyticus are becoming more common. This change is due to antibiotic resistance and an aging population. Knowing this helps us treat infections better.
Non-Bacterial Causes of Positive Results
Not all positive urinalysis results are from bacteria. Fungal and viral infections, and contamination, can also cause issues. Sometimes, nitrites in urine don’t mean bacteria. It’s important to consider these when looking at urinalysis results.
In summary, knowing about common pathogens in positive urinalysis is key for good patient care. By understanding E. coli and other pathogens, and non-bacterial causes, doctors can make better treatment choices.
Follow-Up Testing After Positive Urinalysis
After a positive urinalysis, we need to do more tests to make sure we treat the UTI right. A positive test means we might have a UTI, but we need more tests to be sure. These tests help us find out what’s causing the infection.
Confirming Infection with Urine Culture
A urine culture is a key test to confirm an infection and find the bacteria causing it. This test is important for choosing the right antibiotics. We take a urine sample and send it to a lab to check for bacteria.
Key aspects of urine culture include:
- Identifying the type of bacteria causing the infection
- Determining the antibiotic sensitivity of the bacteria
- Guiding targeted antibiotic therapy
Duration of Urine Culture Tests
Many people wonder, “how long does a urine culture take?” Results usually come in 24 to 48 hours. But, some labs might give preliminary results in just 24 hours. The time it takes can depend on the lab and the testing methods.
While we wait for the results, doctors might start treating with antibiotics. They do this based on symptoms and the first test results.
Advanced Diagnostic Approaches
New ways to diagnose UTIs are being developed. These include molecular tests that can quickly find the bacteria and its resistance to antibiotics.
Some of the benefits of advanced diagnostic approaches include:
- Rapid diagnosis, allowing for timely treatment
- Improved accuracy in identifying the causative organism
- Better guidance for antibiotic therapy, potentially reducing antibiotic resistance
As we keep improving UTI diagnosis, we’ll likely see even better tools. These tools will give us more detailed information about the infection.
In conclusion, after a positive urinalysis, more tests are needed to confirm a UTI and guide treatment. Understanding urine culture and other tests helps doctors give patients the best care.
Conclusion: Taking Action on Positive Urinalysis Results
Understanding urinalysis results is key for managing patients well, mainly when a UTI is suspected. We’ve looked at signs of a UTI, like leukocyte esterase, nitrite, and white blood cells and bacteria in urine.
It’s important to know how to read these results, including what combined findings mean. Also, follow-up tests like urine culture are vital for a correct diagnosis and treatment. This way, healthcare teams can give the best care to those with urinary issues.
When bacteria are found in urine, knowing the type and how severe it is is critical. This helps decide the right treatment. We stress the need for accurate reading and quick action to avoid problems and get the best results for patients.
FAQ
What is considered a positive urinalysis result?
A positive urinalysis result shows an infection or inflammation in the urinary tract. This includes bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
What does a positive nitrite test mean in urinalysis?
A positive nitrite test in urinalysis means bacteria are likely in the urine. This is because some bacteria can change nitrate to nitrite.
What is the significance of high WBC in urine?
High WBC (white blood cells) in urine means there’s an infection or inflammation. This is often seen in urinary tract infections (UTIs).
How long does a urine culture take to provide results?
A urine culture usually takes 24 to 48 hours for results. But, it can take longer depending on the lab and the bacteria type.
What is bacteriuria, and how is it related to UTIs?
Bacteriuria is when bacteria are found in the urine. It’s a sign of a UTI. It’s detected by urinalysis and confirmed with a culture.
What is the role of urinalysis in diagnosing UTIs?
Urinalysis is key in diagnosing UTIs. It finds bacteria, white blood cells, and other signs of infection. This helps doctors spot infections early.
How do healthcare professionals interpret combined urinalysis results?
Healthcare professionals look at many factors in urinalysis. They check nitrite, leukocyte esterase, and WBC count. This helps them understand the patient’s condition and plan treatment.
What are the common pathogens detected in positive urinalysis results?
The most common pathogens in positive urinalysis results are bacteria. Escherichia coli (E. coli) is the main cause of UTIs.
What is the significance of both positive nitrites and leukocytes in urinalysis?
Both positive nitrites and leukocytes in urinalysis show a bacterial infection. It means there are bacteria and an inflammatory response, like in a UTI.
Reference
Lee, J.-H., et al. (2021). Deconstructing the urinalysis: A novel approach to diagnostic and prognostic utility.https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8486290/
- A modern review of urinalysis interpretation including pyuria, microscopic findings, and combined metrics.
American Academy of Family Physicians. (2022). Office-based urinalysis: A comprehensive review.https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2022/0700/office-based-urinalysis.html
- This review explains how dipstick findings like leukocyte esterase, nitrites, and microscopic findings correlate with urinary tract infection (UTI) and inflammation.
Medscape. (n.d.). Urinalysis (interpretation and abnormalities).https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2074001-overview
- Comprehensive medical-reference article describing how combined positive findings (nitrite, leukocyte esterase, bacteria) are interpreted.


































