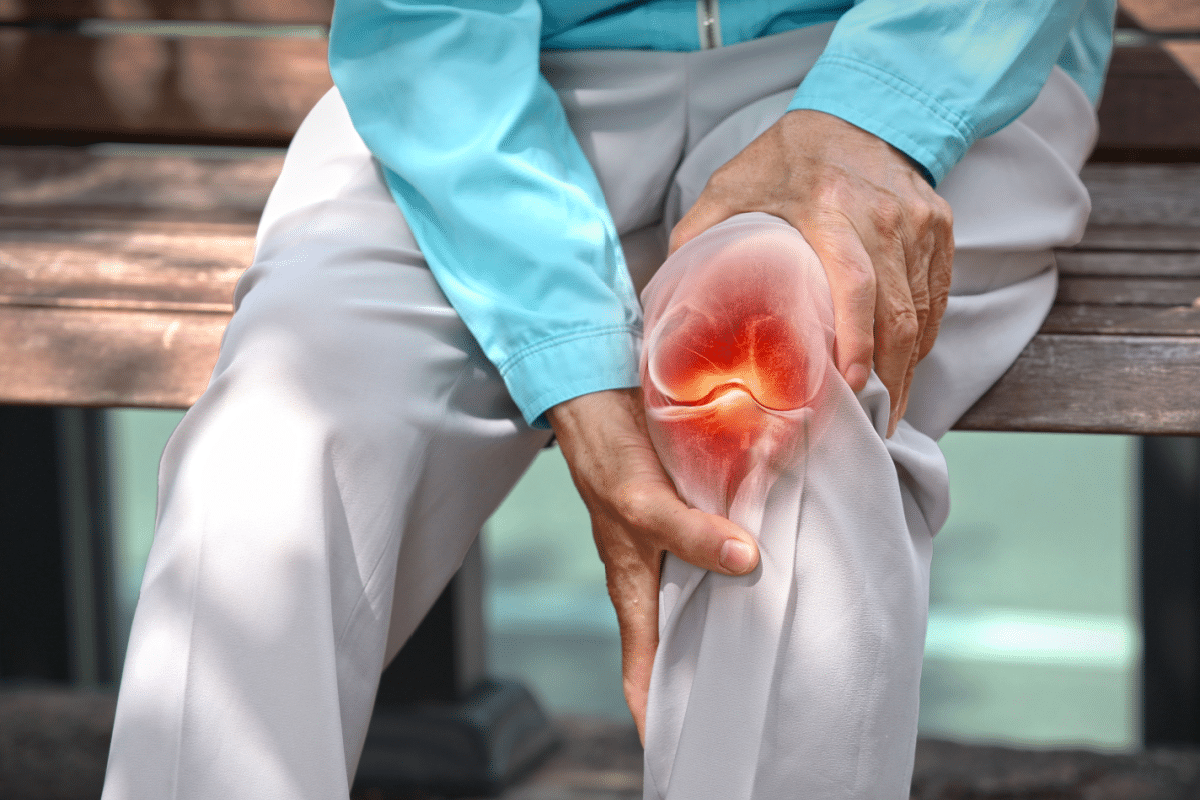
Osteoarthritis affects about 528 million people worldwide. It causes joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. But, effective management is possible with the right care and personalized self-care strategies. Listing seven effective osteoarthritis self care steps, focusing on exercise, weight management, and heat/cold therapy.
We believe in empowering patients with knowledge and support. This is key to managing arthritis well. Our 7 effective care steps aim to help people regain their independence and quality of life. We blend medical expertise with a focus on the patient.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding osteoarthritis is key to managing it well.
- Personalized self-care strategies are very important.
- Combining professional advice with self-care can greatly improve life quality.
- Our 7 effective care steps offer a complete care plan.
- Empowering patients with knowledge and support is essential for managing osteoarthritis.
The Global Impact of Osteoarthritis

Osteoarthritis is a big health problem worldwide, affecting hundreds of millions. It not only hurts people but also strains healthcare systems and economies.
528 Million People Affected Worldwide
By 2019, 528 million people were dealing with osteoarthritis globally. This huge number shows how common the disease is. It also shows we need better ways to manage it.
Who gets osteoarthritis can vary. Age, being overweight, and past injuries play a part. As more people get older, osteoarthritis will likely become even more common.
113% Increase In People Affected
More people are living with osteoarthritis than ever before. From 1990 to now, there’s been a 113% increase. This rise is due to more older people, more obesity, and living longer.
This trend makes it clear we need good ways to care for osteoarthritis. We must find ways to help people live better with the condition.
Knee Joints: The Most Vulnerable Target
The knee joints are often hit hard by osteoarthritis. Their complex design and weight-bearing role make them vulnerable.
Knowing which joints are most affected is key to good self-care. By focusing on the most at-risk areas, we can take steps to manage the condition and prevent more damage.
Why Osteoarthritis Self Care Is Essential
Managing osteoarthritis well means more than just medical treatments. Medical care is key, but it mainly helps with symptoms. Self-care is important because it lets people help themselves more.
The Limitations of Medical Interventions Alone
Medical treatments, like drugs and surgery, are vital for osteoarthritis. But, they have their limits. Drugs can have side effects and may not work as well over time. Surgery is usually for when the condition is very bad.
Medical care alone might not meet all the needs of those with osteoarthritis. That’s why self-care is so important. It helps with medical treatments and improves overall health.
Research Supporting Self-Management Effectiveness
Studies show that self-management can really help with osteoarthritis. A program that teaches patients, exercises them, and supports them can greatly improve pain and joint function. A recent study found that self-management can reduce pain and improve function.
This research highlights the value of self-care in treatment plans. It empowers people to manage their condition better. This leads to better health and a better life.
Building Patient Autonomy and Confidence
Self-care for osteoarthritis helps people feel more in control. It’s about taking charge of your health. A patient advocate said, “Self-care is not just about managing symptoms; it’s about taking charge of your health and well-being.”
When people feel confident in managing their osteoarthritis, they make better health choices. This leads to better outcomes and a better life.
Creating Your Personalized Self-Care Plan
Managing osteoarthritis starts with a plan made just for you. Everyone’s experience with osteoarthritis is different. So, you need a plan that fits your needs. By looking at what you need, talking to doctors, and setting goals, you can make a good self-care plan.
Assessing Your Specific Joint Needs
To make a good self-care plan, know which joints are hurt by osteoarthritis. Find out which joints hurt the most and how they move and feel. This info helps you plan your exercises, manage pain, and change your daily activities.
Joint Assessment Checklist:
- Identify the joints affected by osteoarthritis
- Evaluate the range of motion and strength
- Assess pain levels during different activities
When to Consult Healthcare Professionals
It’s important to talk to doctors when making your self-care plan. They can help make sure you’re doing the right things. You should talk to them if you’re not sure how bad your osteoarthritis is, if your symptoms change suddenly, or if you’re thinking about new treatments or supplements.
|
Situation |
Recommended Action |
|---|---|
|
Uncertain about osteoarthritis severity |
Consult a rheumatologist or primary care physician |
|
Sudden changes in symptoms |
Seek immediate medical attention |
|
Considering new treatments or supplements |
Discuss with your healthcare provider |
Setting Realistic Goals and Expectations
Setting goals that you can reach is key to staying motivated. Try to set goals that are specific, measurable, and achievable. For example, you might want to move your joints better, feel less pain, or do more every day. Check your goals often and change them if needed to keep moving forward.
Example of Goal Setting:
- Improve knee flexion by 20 degrees within 6 weeks
- Reduce daily pain score from 7 to 5 on the pain scale within 3 months
- Increase daily walking distance by 500 meters within 2 months
By following these steps and staying active, you can make a self-care plan that works for you. Our goal is to give you the tools and knowledge to manage your osteoarthritis and improve your life.
Step 1: Implementing Joint-Friendly Exercise Routines
For those with osteoarthritis, gentle exercises can greatly improve life quality. Regular activity is key in osteoarthritis self care. It keeps joints moving, reduces pain, and boosts well-being.
Exercise plans should fit your needs and abilities. The right exercises can manage symptoms and slow disease.
Low-Impact Aerobic Activities
Low-impact aerobic activities are great for osteoarthritis. They’re good for the heart without harming joints. Examples include:
- Swimming or water aerobics
- Cycling on a stationary bike
- Using an elliptical machine
- Brisk walking on flat surfaces
These activities improve heart health, keep weight in check, and lower chronic disease risk.
Strength Training for Joint Support
Strengthening muscles around joints offers extra support and less pain. Strength training should be done 2-3 times a week. It targets major muscle groups. Examples include:
- Resistance band exercises
- Light weightlifting
- Bodyweight exercises like squats and lunges (modified as needed)
The Arthritis Foundation says, “Strengthening muscles around joints can absorb stress and pressure. This reduces pain and improves function.”
“Exercise is a critical component of osteoarthritis management. It’s not just about reducing pain; it’s about improving function and enriching quality of life.”
Flexibility Exercises to Maintain Range of Motion
Flexibility exercises are vital for joint mobility and less stiffness. Activities like yoga and gentle stretching improve flexibility and range of motion. It’s important to:
- Hold stretches for 15-30 seconds
- Avoid bouncing or jerking movements
- Focus on major muscle groups and joints affected by osteoarthritis
By adding these exercises to your daily routine, you can improve joint health and life quality.
Step 2: Weight Management for Reduced Joint Pressure
Managing your weight is key to easing joint pressure. Keeping a healthy weight helps reduce stress on joints like knees and hips.
The Biomechanics of Weight and Joint Stress
Extra weight adds stress to joints that carry our body’s weight. For every pound, the knee joint feels 3-4 times that when walking. Losing weight can lessen this stress, helping slow osteoarthritis.
Key factors to consider:
- The relationship between body weight and joint stress
- How weight loss can alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms
- The importance of maintaining a healthy weight
Sustainable Approaches to Weight Loss
Crash diets and extreme weight loss are not good. Instead, aim for a balanced diet and regular exercise. Losing 1-2 pounds a week is safe and effective.
Nutritional tips:
- Eat whole, unprocessed foods like veggies, fruits, and lean proteins
- Reduce high-calorie, high-fat, and high-sugar foods
- Drink plenty of water
Tracking Progress and Adjusting Goals
It’s important to track your weight loss. Use a food diary or mobile app to monitor your eating and exercise. Regularly check your progress to adjust your plan as needed.
Tips for successful tracking:
- Set realistic and achievable goals
- Regularly review your progress
- Make adjustments as needed to stay on track
Step 3: Anti-Inflammatory Dietary Changes
Diet is key in managing osteoarthritis. Some foods can help reduce inflammation. Making smart food choices can ease symptoms.
Foods That Fight Joint Inflammation
Eating anti-inflammatory foods can help with osteoarthritis. Good choices include:
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
- Fruits and veggies rich in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens
- Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat
- Nuts and seeds, such as walnuts and chia seeds
- Olive oil, which has anti-inflammatory oleocanthal
The Mediterranean diet is great for osteoarthritis. It focuses on these foods.
Ingredients to Limit or Avoid
Some foods can make inflammation worse. It’s best to limit or avoid:
- Processed foods with AGE products that cause inflammation
- Sugary drinks and foods with refined sugars
- Foods high in saturated and trans fats, like red meat and processed snacks
- Nightshade veggies, like tomatoes and peppers, which can worsen symptoms for some
Practical Meal Planning for Joint Health
Planning an anti-inflammatory diet is doable. Here are some tips:
|
Meal |
Foods to Include |
Sample Meal |
|---|---|---|
|
Breakfast |
Oatmeal with fruits and nuts |
Steel-cut oats with berries and walnuts |
|
Lunch |
Grilled fish with vegetables |
Salmon with roasted veggies and quinoa |
|
Dinner |
Lean protein with whole grains and veggies |
Grilled chicken with brown rice and steamed broccoli |
Focus on whole, nutrient-rich foods. Limit processed and sugary foods. This helps support osteoarthritis self-care.
Step 4: Evidence-Based Supplements for Joint Health
Managing osteoarthritis requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes lifestyle changes, exercise, and nutritional supplements. Some supplements have shown promise in easing OA symptoms and supporting joint health.
Glucosamine and Chondroitin: What Research Shows
Glucosamine and chondroitin are popular supplements for osteoarthritis. Research has shown mixed results, but some studies suggest they may help. A 2018 meta-analysis in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research found they provided significant pain relief and improved function in knee OA patients.
The benefits of glucosamine and chondroitin include:
- Reduced pain and inflammation
- Improved joint function
- Potential slowing of OA progression
Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Turmeric Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids, like EPA and DHA, have anti-inflammatory properties. They may benefit individuals with osteoarthritis. Omega-3 supplements have been shown to reduce joint pain and stiffness in some studies. Turmeric, with curcumin, also has anti-inflammatory properties that may help alleviate OA symptoms.
The benefits of omega-3 fatty acids and turmeric include:
- Reduced inflammation
- Potential improvement in joint pain and function
- Antioxidant properties
Vitamin D and Calcium for Bone Support
Vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone health, which is linked to joint health. Research suggests that maintaining adequate levels of vitamin D may help reduce OA progression risk. Calcium is important for maintaining bone density, which can help alleviate joint pressure.
When considering supplements for osteoarthritis, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. They can help determine the best treatment for your needs. This ensures safe and effective use of supplements.
Step 5: Topical Treatments and Pain Relief
Topical treatments are a focused way to handle osteoarthritis pain. They are applied right on the skin over the joint. This method gives relief without the side effects of pills.
Over-the-Counter Analgesic Options
OTC topical analgesics are easy to find and work well for pain. Topical NSAIDs, like diclofenac gel, are favorites because they target the pain area. Other options include topical capsaicin creams and menthol-based products. These products create a sensation that can take your mind off the pain.
Natural Alternatives for Localized Pain
If you don’t want to use drugs or want something extra, natural options are available. Arnica gel and creams with CBD are popular for their pain and inflammation relief. Even though research is growing, many people find them helpful for their symptoms.
Application Techniques for Maximum Benefit
To get the best from topical treatments, apply them right. Clean and dry the skin first for better absorption. Use the amount suggested and massage it in until it’s fully absorbed. Some products need you to wash your hands afterward, while others stay on.
Adding topical treatments to your care plan can lead to better pain relief. This can greatly improve your life quality.
Step 6: Mastering Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are simple yet effective ways to ease arthritis pain and swelling. They have been used for years to help manage arthritis. They offer relief from pain and stiffness.
When to Apply Heat vs. Cold
Knowing when to use heat or cold is key to getting the most out of these therapies. Heat therapy helps relax muscles and reduce stiffness before you start moving. It also improves blood flow, aiding in healing and easing muscle spasms.
Cold therapy, on the other hand, is best for reducing swelling and numbing pain. It’s great to use after you’ve been active or during a flare-up.
Start your day with heat therapy to loosen up and move more easily. Use cold therapy after exercising or when you’re in pain.
Safe Application Methods and Duration
Applying heat or cold safely is important. For heat, use a warm towel or a low-setting heating pad. Never put heat directly on your skin to avoid burns. For cold, wrap an ice pack or cold gel pack in a towel. Don’t put ice straight on your skin.
Both heat and cold should be used for 15 to 20 minutes. Always check your skin before and after to avoid any bad reactions.
DIY Solutions for Home Treatment
Making your own heat or cold therapy at home is easy. For heat, wet a towel, microwave it briefly, and then wrap it in another towel. For cold, use a frozen bag of peas or make an ice pack in a sealable bag.
These DIY methods are handy for managing arthritis symptoms without expensive gear. Adding heat and cold therapy to your routine can help you use less medication. It can also make your life better overall.
Step 7: Assistive Devices and Home Modifications
As we move forward in treating ourselves, using assistive devices and changing our homes can really help. These steps help us stay independent and ease the pain in our joints.
Joint-Sparing Tools for Daily Activities
Joint-sparing tools make everyday tasks simpler and less painful. For example:
- Long-handled reachers for picking up items without bending
- Adaptive utensils with ergonomic handles for easier grip
- Buttonhooks and zipper pulls to simplify dressing
These tools help reduce stress on our joints. This makes daily activities easier for us.
Braces, Splints, and Supports
Braces, splints, and supports offer extra stability to our joints. They help reduce pain and improve how we move. Some common ones are:
- Knee braces for ligament support and stability
- Wrist splints to immobilize and protect the joint
- Ankle supports for added stability during movement
It’s important to talk to a healthcare professional to find the right one for you.
Creating an Arthritis-Friendly Living Space
Changing our living space can greatly help with managing osteoarthritis. Here are some ideas:
|
Modification |
Benefit |
|---|---|
|
Installing grab bars in strategic locations |
Enhanced balance and reduced fall risk |
|
Using non-slip mats in bathrooms and kitchens |
Prevention of slips and falls |
|
Rearranging furniture for clear pathways |
Easier navigation and reduced strain |
By making these changes, we can make our homes safer and more comfortable.
By using assistive devices and making home changes, we can better manage osteoarthritis. This helps us keep a good quality of life.
Managing Pain Flares and Setbacks
For those with osteoarthritis, learning to handle pain flares is key. It helps keep their quality of life high. Effective pain management is a big part of self-care, allowing for active and happy lives.
Identifying Triggers and Warning Signs
Knowing what causes pain flares is vital. Common causes include too much activity, weather changes, and repetitive strain. By knowing what triggers their pain, people can take steps to lessen its impact.
Keeping a pain diary is a great tool. It helps track when pain happens and what’s happening around that time. This way, patterns and triggers can be found.
Emergency Pain Relief Strategies
Having a plan for pain flares is essential. This might include:
- Using over-the-counter pain relief medications as directed
- Applying heat or cold therapy to affected joints
- Resting and avoiding activities that make the pain worse
- Using relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation
Knowing when to see a doctor is also important. If pain is severe, swelling, or redness doesn’t get better with rest and treatment, seek medical help.
Mental Health Aspects of Chronic Pain
Chronic pain can really affect mental health. It can lead to frustration, anxiety, and depression. It’s important to tackle these issues as part of self-care.
Supporting mental health can include:
|
Mental Health Strategy |
Description |
Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Mindfulness and Meditation |
Practices that help individuals stay present and focused |
Reduces stress, improves mood |
|
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) |
A form of therapy that helps change negative thought patterns |
Enhances coping skills, reduces pain perception |
|
Support Groups |
Groups where individuals can share experiences and support one another |
Provides community, reduces feelings of isolation |
By adding these strategies to their self-care, people with osteoarthritis can manage pain better. This improves their overall well-being.
Conclusion: Sustaining Your Self-Care Journey
As we wrap up our look at osteoarthritis self-care, it’s clear that keeping up with self-care is key. By adding the 7 effective care steps to your daily life, you can greatly enhance your quality of life. Remember, keep going on your self-care path, adjusting as you need to keep your joints healthy.
Good arthritis self-care means doing exercises that are easy on your joints, managing your weight, eating foods that fight inflammation, and using proven supplements. By treating osteoarthritis yourself with these methods, you can lessen pain and move better. Stick to your self-care plan, using tools like heat and cold therapy, assistive devices, and making your home easier to move around in.
By being proactive with your arthritis self-care, you can manage your osteoarthritis better. We believe that with determination and the right methods, you can find lasting relief and better joint health. Keep your self-care a priority, and you’ll be ready to face the challenges of osteoarthritis.
FAQ
What is osteoarthritis and how does it affect the body?
Osteoarthritis is a disease that wears down cartilage in joints. It causes pain and stiffness. It affects millions of people worldwide, making everyday tasks hard.
Why is self-care important for managing osteoarthritis?
Self-care is key for managing osteoarthritis. It lets people take charge of their health. This reduces the need for just medical help and boosts overall well-being.
How can I create a personalized self-care plan for osteoarthritis?
To make a self-care plan, first figure out what your joints need. Talk to doctors and set achievable goals. Use the 7 care steps from our guide to help.
What types of exercises are beneficial for osteoarthritis management?
Good exercises for osteoarthritis include low-impact aerobics, strength training, and flexibility exercises. They keep joints moving, reduce pain, and improve function.
How does weight management impact osteoarthritis?
Keeping a healthy weight eases joint stress and pain. It also slows down the disease. So, managing weight is very important for osteoarthritis care.
What dietary changes can help alleviate osteoarthritis symptoms?
Eating anti-inflammatory foods and avoiding pro-inflammatory ones can help. Planning meals that support joint health also helps ease symptoms.
Are there any supplements that can support osteoarthritis management?
Supplements like glucosamine, chondroitin, omega-3 fatty acids, and turmeric might help joint health. But, always talk to a doctor before taking any supplements.
How can I manage pain flares and setbacks?
To handle pain flares, know what triggers them and use quick pain relief methods. Also, take care of your mental health to deal with chronic pain.
What are some effective topical treatments for osteoarthritis pain relief?
Topical treatments like over-the-counter pain relievers and natural options can help. They work best when applied correctly.
How can I incorporate heat and cold therapy into my self-care routine?
Learn when to use heat or cold, how to apply them safely, and try DIY methods. This helps you use heat and cold therapy well for osteoarthritis care.
What assistive devices and home modifications can help with osteoarthritis management?
Using tools, braces, and supports that don’t strain joints helps a lot. Making your home arthritis-friendly also improves daily life and reduces joint strain.
Can osteoarthritis self-care be maintained over time?
Yes, by following the 7 care steps daily and sticking to your plan, you can manage osteoarthritis long-term. This improves your life quality over time.
References
https://www.modernedgeortho.com/blog/living-with-osteoarthritis-6-ways-to-improve-your-life





