Comprehensive guide to all arthritis tests and diagnosis procedures, from initial consultation to definitive results.
Diagnosing arthritis can be tough because it looks like other common problems. At Liv Hospital, we know how key a detailed check-up is to get it right.
We help you through the testing steps. This includes checking you, blood tests, and scans to understand your health fully.
With over 350 million people worldwide dealing with arthritis, the right tests are key. Our aim is to help you manage your health. We explain the tools used to spot this condition.
Key Takeaways
- Comprehensive diagnosis involves clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging methods.
- Accurate diagnosis is key for managing arthritis well.
- Liv Hospital offers top-notch healthcare with full support.
- Early diagnosis can greatly help in managing arthritis.
- We take a personal approach to diagnose and treat each patient.
Understanding Arthritis: Types and Prevalence

Arthritis affects millions worldwide, with over 100 types identified. It’s important to understand each type for proper diagnosis and treatment. A thorough approach is needed to manage this condition effectively.
Common Types of Arthritis
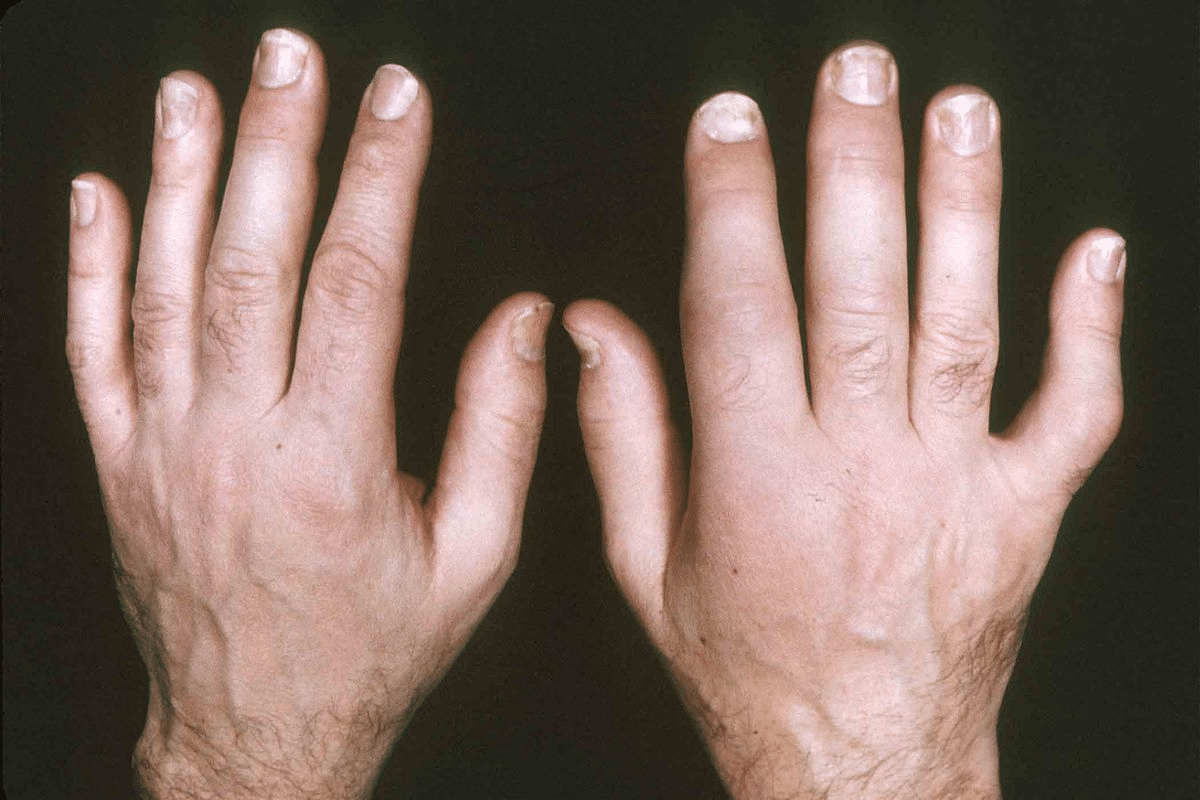
Osteoarthritis is the most common, caused by cartilage breakdown in joints. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder that leads to joint inflammation. Psoriatic arthritis and gout are also significant types.
Each type of arthritis has its own characteristics. A tailored approach is necessary for diagnosis and treatment. Knowing these differences helps in managing the condition better.
Global and National Prevalence Statistics
More than 350 million people worldwide suffer from arthritis. In the U.S., osteoarthritis affects over 32 million adults. Rheumatoid arthritis impacts about 0.5% to 1% of North America’s population.
|
Type of Arthritis |
Global Prevalence |
U.S. Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
|
Osteoarthritis |
237 million |
32 million |
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Varied, approximately 0.5-1% of global population |
1.3 million |
|
Psoriatic Arthritis |
Part of psoriatic disease spectrum |
Associated with 7.4 million adults with psoriasis |
Risk Factors for Developing Arthritis
Family history, age, and lifestyle are key risk factors for arthritis. Knowing these can help in early detection and prevention. For example, staying at a healthy weight can lower the risk of osteoarthritis.
Previous joint injuries, infections, and jobs that strain joints are also risk factors. Recognizing these can help in taking preventive steps and early intervention.
Recognizing Symptoms That Warrant Testing

Arthritis symptoms can be hard to spot at first. But catching them early is vital for managing them well. It’s important to know the common signs that might mean you have arthritis.
Early Warning Signs of Arthritis
The first signs of arthritis include persistent joint pain, stiffness in the morning, and swelling in the joints. You might also feel like moving less and get tired easily. Some people with arthritis also have a fever.
These symptoms can make everyday tasks harder. Spotting them early means you can get medical help sooner.
Differentiating Arthritis Pain from Other Joint Issues
Telling arthritis pain from other joint problems is key to getting the right diagnosis. Arthritis pain sticks around and comes with stiffness and swelling. It’s not like the pain you get from overdoing it or minor injuries, which usually goes away.
- Persistent pain and stiffness, mainly in the morning
- Swelling and redness around the joints
- Less ability to move your joints
- Feeling tired and not well overall
When to Seek Medical Attention
If your symptoms keep you from doing daily things or last a long time, you should see a doctor. Catching arthritis early and treating it can make a big difference. If you notice any odd or lasting joint symptoms, don’t wait to see a healthcare expert.
Keeping a journal of your symptoms can help a lot. Write down when they happen, how bad they are, and what makes them better or worse. This info is super helpful when you talk to your doctor.
The Arthritis Tests and Diagnosis Process: An Overview
Diagnosing arthritis takes a multifaceted approach. It includes clinical checks, lab tests, and imaging. This detailed process helps find the right treatment for each patient.
The Diagnostic Journey: What to Expect
Arthritis testing starts with a medical history assessment and physical examination. This first step helps doctors understand symptoms and possible causes. It sets the stage for more tests.
A leading rheumatologist says, “A thorough diagnosis is essential for managing arthritis.” This shows how important a detailed diagnostic journey is.
The Multidisciplinary Approach to Diagnosis
Getting an accurate arthritis diagnosis often needs a multidisciplinary approach. Doctors like rheumatologists, radiologists, and orthopedic specialists work together. Their teamwork ensures a complete understanding of the patient’s condition.
- Rheumatologists focus on arthritis and related issues.
- Radiologists are experts in imaging studies.
- Orthopedic specialists know about joint health and surgery.
Timeline for Complete Diagnosis
The timeline for diagnosis varies based on the case’s complexity and tests needed. It can take weeks to months. The time depends on extra tests, specialist availability, and the patient’s health.
Knowing what to expect in the diagnostic journey helps patients prepare. Working with their healthcare team makes the process smoother. This way, patients get an accurate diagnosis.
Clinical Evaluation: The First Step
A thorough clinical evaluation is key to spotting arthritis symptoms and finding the right treatment. We start by looking at the patient’s overall health. This helps us choose the best way to diagnose.
Medical History Assessment
Looking at a patient’s medical history is very important. We ask about their symptoms, when they started, and how bad they are. We also ask about their family’s history of arthritis and other health issues.
The Arthritis Foundation says, “A detailed medical history is key to diagnosing arthritis. It helps us tell different types of arthritis apart and rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.”
“Understanding a patient’s medical history is key to diagnosing arthritis accurately.”
Physical Examination Techniques
In the physical exam, we use different methods to check the joints. We look for signs like swelling, redness, and warmth. We also check reflexes and muscle strength to see if there’s nerve involvement.
Key parts of the physical exam include:
- Looking at joints for signs of inflammation or deformity
- Feeling joints for tenderness or swelling
- Checking how well joints move and function
- Testing muscle strength and reflexes
Joint Function and Mobility Tests
Tests for joint function and mobility are very important. They show how well joints move and how daily activities are affected. We use special tests to check the range of motion, stability, and function of joints.
|
Test |
Description |
Purpose |
|---|---|---|
|
Range of Motion Assessment |
Evaluating the degree to which a patient can move a joint |
To assess joint mobility and identify limitations |
|
Joint Stability Testing |
Checking for joint stability and ligament integrity |
To determine if there’s ligament damage or joint instability |
|
Functional Assessment |
Evaluating the patient’s ability to perform daily activities |
To understand the impact of arthritis on daily functioning |
By combining the info from the medical history, physical exam, and joint tests, we get a full picture of the patient’s condition. This helps us make a good plan for diagnosis and treatment.
Laboratory Tests for Arthritis Detection
Laboratory tests are key in diagnosing arthritis. They offer insights into the disease’s presence and progression. These tests help doctors identify important markers for an accurate diagnosis.
Blood Tests for Inflammatory Markers
Blood tests are vital in diagnosing arthritis. They measure inflammatory markers that show if arthritis or other conditions are present. Some important tests include:
- Rheumatoid factor (RF)
- Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies (anti-CCP)
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
These tests help identify arthritis types, like rheumatoid arthritis. They also track inflammation levels in the body.
Complete Blood Count (CBC) Interpretation
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) tests various blood components. It looks at red and white blood cell counts, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels. In arthritis, a CBC can show inflammation or infection signs.
An elevated white blood cell count means there’s an inflammatory response.
“A CBC provides a snapshot of the body’s inflammatory state, which is vital for diagnosing and managing arthritis.”
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Measurement
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) test shows how fast red blood cells settle. A high ESR means there’s inflammation, common in arthritis like rheumatoid arthritis. Though not specific to arthritis, a high ESR helps confirm the diagnosis with other findings.
By combining lab test results with clinical evaluations, doctors get a full picture of a patient’s condition. They can then create a detailed treatment plan.
Imaging Techniques in Arthritis Diagnosis
Imaging techniques are key in diagnosing arthritis. They show how joints are doing. This helps doctors decide on treatments.
X-Ray Examination: Revealing Joint Changes
X-rays are a basic tool for arthritis diagnosis. They show changes like joint space narrowing and bone spurs. X-ray imaging is great for tracking arthritis over time.
Ultrasound Imaging for Soft Tissue Visualization
Ultrasound gives a close look at soft tissues around joints. It spots inflammation and thickened synovial tissue. Ultrasound’s real-time imaging helps with injections or aspirations.
MRI Scanning for Detailed Joint Assessment
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) checks joints thoroughly. It spots early arthritis signs like bone marrow edema. MRI’s high sensitivity is key for tracking arthritis.
CT Scans and Their Diagnostic Value
Computed Tomography (CT) scans show joints in detail. They’re good for bone damage and deformities. While not as good for soft tissues, CT scans are useful.
|
Imaging Technique |
Primary Use in Arthritis Diagnosis |
Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
X-ray |
Assessing bone damage and joint space narrowing |
Widely available, cost-effective |
|
Ultrasound |
Visualizing soft tissue inflammation and joint effusion |
Real-time imaging, guides injections/aspirations |
|
MRI |
Detailed assessment of joint structures and soft tissues |
High sensitivity for early arthritis signs |
|
CT Scan |
Evaluating bone structure and joint alignment |
Detailed cross-sectional images |
These imaging methods help doctors understand arthritis better. They can then plan effective treatments.
Specialized Tests for Specific Arthritis Types
Different types of arthritis need special tests for accurate diagnosis and treatment. We know that each type of arthritis requires specific tests. These tests help guide treatment and improve patient care.
Diagnostic Approaches for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) diagnosis combines clinical evaluation and special tests. Blood tests check for rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (anti-CCP). These markers are often found in RA patients.
Even if these markers are not present, it doesn’t mean you don’t have RA. Imaging tests like ultrasound and MRI also help. They show joint damage and inflammation, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
Testing for Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) diagnosis mainly relies on clinical evaluation and imaging. X-rays show joint damage like cartilage loss and bone spurs, typical of OA. Sometimes, MRI or CT scans are used to check joint health and rule out other conditions.
Psoriatic Arthritis Diagnostic Methods
Diagnosing psoriatic arthritis (PsA) involves clinical assessment, medical history, and special tests. We look for signs of psoriasis and joint inflammation. Imaging tests like X-rays and MRI help identify joint damage and inflammation.
Blood tests may be used to rule out other forms of arthritis and assess inflammatory markers.
Gout and Pseudogout Testing Procedures
Gout and pseudogout diagnosis involves analyzing synovial fluid. We perform arthrocentesis to collect joint fluid. This fluid is then examined for monosodium urate crystals (in gout) or calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals (in pseudogout).
|
Arthritis Type |
Primary Diagnostic Tests |
Key Diagnostic Markers |
|---|---|---|
|
Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Blood tests, Ultrasound, MRI |
Rheumatoid Factor, Anti-CCP |
|
Osteoarthritis |
X-ray, MRI, CT scan |
Joint damage, cartilage loss |
|
Psoriatic Arthritis |
Clinical assessment, X-ray, MRI |
Psoriasis, joint inflammation |
|
Gout/Pseudogout |
Arthrocentesis, Synovial fluid analysis |
Monosodium urate crystals, Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals |
By using these specialized tests, we can accurately diagnose and manage various types of arthritis. This improves patient outcomes and quality of life.
Joint Fluid Analysis and Synovial Biopsy
To diagnose arthritis, doctors often use joint fluid analysis and synovial biopsy. These tools show joint inflammation and help find specific arthritis types.
Arthrocentesis Procedure Explained
Arthrocentesis, or joint aspiration, removes fluid for analysis. It’s done with a sterile needle and syringe under local anesthesia. This procedure can spot gout, pseudogout, or septic arthritis by looking at the fluid.
Key steps in the arthrocentesis procedure include:
- Preparation of the skin with antiseptic solution
- Administration of local anesthesia
- Insertion of a needle into the joint space
- Aspiration of joint fluid into a syringe
- Analysis of the aspirated fluid in a laboratory
What Joint Fluid Analysis Reveals
Joint fluid analysis is key for diagnosing arthritis. It can show:
- Crystals for gout or pseudogout
- Bacteria or fungi for infection
- Inflammatory cells or proteins for rheumatoid arthritis
The analysis looks at the fluid’s appearance, viscosity, and cells. For example, gouty fluid has monosodium urate crystals. Septic fluid has a high white blood cell count.
When Synovial Biopsy Is Necessary
A synovial biopsy takes a sample of the joint lining. It’s needed when:
- The diagnosis is unclear after fluid analysis
- There’s a suspicion of a specific condition like synovial sarcoma
- Evaluation of chronic synovitis is needed
The biopsy can be done arthroscopically or through open surgery. The tissue is then examined for abnormalities.
|
Diagnostic Feature |
Joint Fluid Analysis |
Synovial Biopsy |
|---|---|---|
|
Crystals |
Directly identifies crystals associated with gout or pseudogout |
May show crystal deposition in the synovium |
|
Infection |
Can diagnose septic arthritis by identifying bacteria or fungi |
Can confirm infection and identify the causative organism |
|
Inflammation |
Assesses inflammatory cell count and protein levels |
Provides detailed histological assessment of synovial inflammation |
Joint fluid analysis and synovial biopsy together help doctors understand arthritis. This guides the right treatment.
Age-Specific Considerations in Arthritis Testing
The way we test for arthritis changes with age. As we get older, the types of arthritis we get also change. This means we need to think about age-specific considerations when testing and diagnosing.
Juvenile Arthritis Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnosing juvenile arthritis is a detailed process. It involves looking at the child’s medical history, symptoms, and physical exam. This helps us accurately diagnose and treat the condition.
- Clinical evaluation of joint inflammation and damage
- Laboratory tests, including blood counts and inflammatory markers
- Imaging studies to assess joint damage and growth abnormalities
Testing Considerations for Adults (30-60)
For adults, arthritis diagnosis combines clinical assessment, lab tests, and imaging. We aim to identify the exact type of arthritis. This helps us choose the right treatment.
Key points include:
- Assessing symptom duration and severity
- Evaluating for other conditions that may mimic or coexist with arthritis
- Using imaging studies to assess joint damage
Diagnostic Challenges in Elderly Patients
Diagnosing arthritis in elderly patients is tricky. This is because of comorbidities, age-related changes, and medication side effects. We must carefully distinguish between different types of arthritis and other conditions.
Special considerations for elderly patients include:
|
Challenge |
Diagnostic Approach |
|---|---|
|
Comorbidities |
Comprehensive medical history and physical examination |
|
Age-related changes |
Careful interpretation of imaging studies |
|
Medication side effects |
Review of current medications and possible interactions |
Understanding these age-specific considerations helps us improve diagnosis accuracy. It also allows us to create effective treatment plans for each patient’s unique needs.
Conclusion: Moving Forward After Diagnosis
Getting an arthritis diagnosis can change your life, but it’s not the end. You can work with doctors to make a plan that helps you feel better. It’s key to keep moving forward after finding out you have arthritis.
Tests help figure out what kind of arthritis you have and how bad it is. This lets you get the right treatment early. Knowing about the tests and diagnosis is the first step to managing your arthritis.
Getting a diagnosis is just the start. We urge patients to stay informed and active in managing their condition. Work with your healthcare team to create a plan that might include medicine, lifestyle changes, and more. This way, you can control your arthritis and live a better life.
FAQ
How do you test for arthritis?
To test for arthritis, we use a few steps. First, we take a detailed medical history and do a physical exam. This helps us find symptoms and possible causes. Then, we do blood tests and imaging to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the common laboratory tests used to diagnose arthritis?
We use blood tests to check for inflammation. Tests like Complete Blood Count (CBC) and Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) are common. They help us see if you have inflammation and what type of arthritis it might be.
What imaging techniques are used in diagnosing arthritis?
We use X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and CT scans to look at joints. Each method gives us different views of joint health. They help us see inflammation, changes in structure, and bone damage.
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
For rheumatoid arthritis, we do specific blood tests. These include rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP tests. We also do clinical exams and imaging to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the role of joint fluid analysis in diagnosing arthritis?
Joint fluid analysis, or arthrocentesis, is key. It involves taking fluid from the joint. This helps us find crystals or infections, which is important for diagnosing gout or septic arthritis.
Are there age-specific considerations in diagnosing arthritis?
Yes, age matters when diagnosing arthritis. Kids with juvenile arthritis need a thorough check-up. For older adults, we must consider other health issues and age-related changes.
Can you be tested for arthritis?
Yes, there are tests for arthritis. These include blood tests and imaging studies. A doctor will help you through the testing process to find out if you have arthritis and what type.
How to detect arthritis early?
To catch arthritis early, watch for signs like joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Seeing a doctor quickly is important for early diagnosis and treatment.
What are the risk factors for developing arthritis?
Risk factors for arthritis include family history, age, and lifestyle. Knowing these can help in early detection and prevention.
Is there a single test for diagnosing arthritis?
No, there’s no one test for arthritis. We use a mix of clinical exams, blood tests, and imaging to find out if you have arthritis and what kind.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Guidance. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6681064/









