The New Era of Cardiac Care: An Overview
Cardiovascular diseases are among the most prevalent chronic conditions in our country. robotic bypass surgery for bypass operations in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases provides significant benefits in terms of patient comfort and speedy recovery. A robotic bypass can be performed using three small incisions in the armpit and a 4 cm cut on the rib cage without using a scalpel directly on the heart or stopping it.
Liv Hospital Cardiovascular Surgery Specialist Prof. Dr. Ahmet Ozkara: “We perform robotic bypass surgery using the main vessel of the heart, the thoracic aorta. Unlike traditional bypass procedures, we are able to complete the operation without opening the thorax or stopping the heart.
Emphasizing that robotic bypass surgery allows patients to resume normal life faster, Liv Hospital Cardiovascular Surgery Specialist Prof. Dr. Ahmet Ozkara stated that this approach leads to significantly reduced infection and bleeding rates, and added: “It is also superior to conventional bypass surgery in terms of appearance. The patient can return to work within a few weeks and regain normal physical condition.
No scalpel is used
With advances over the past 15 years, minimally invasive techniques have become increasingly common alternatives to traditional cardiac surgery. In the US and across Europe, robotic heart surgeries have risen by 20 percent in recent years, and this trend is mirrored in our country. In robotic bypass surgery, the procedure is done without cutting the breastbone, or sternum. The robotic arm is inserted through small incisions on either side of the rib cage. A 3-dimensional camera inserted through an incision provides an image that is 8“10 times larger and clearer. One surgeon attaches the instruments to the robotic arm, while another operates them remotely from a console with a video screen.
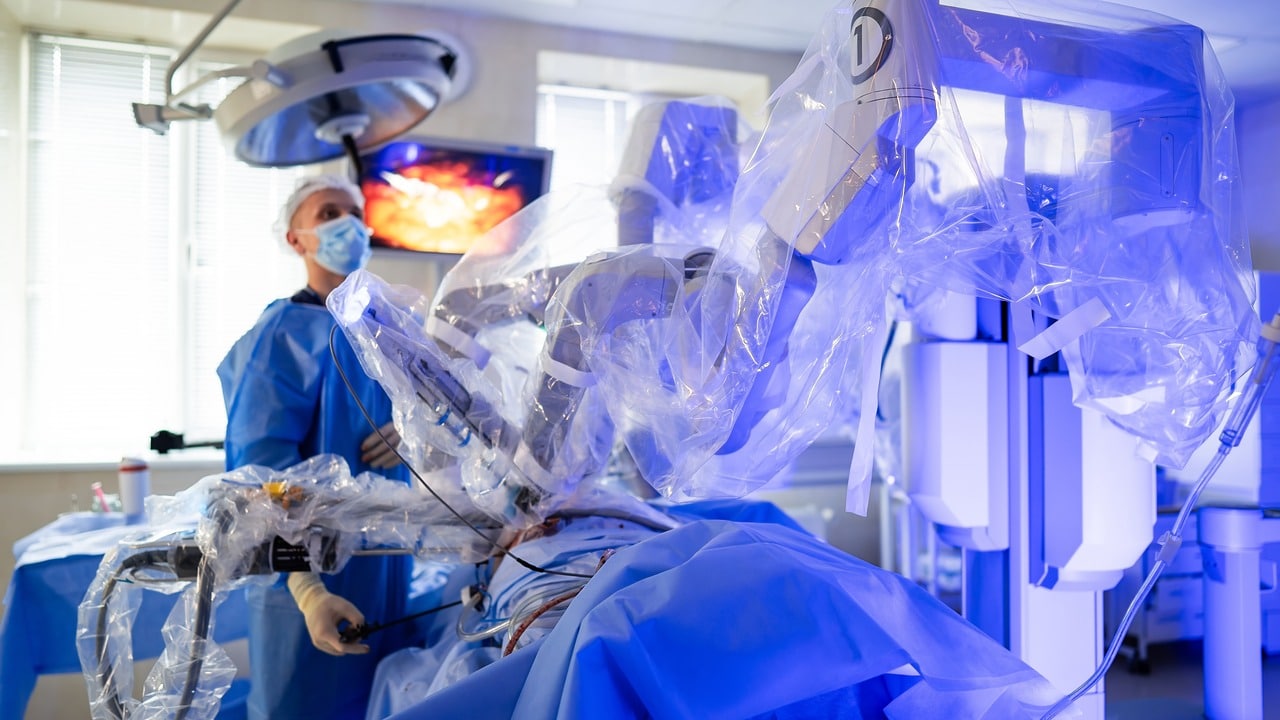
Comfortable For Both Patient And The Surgeon
The instruments used in robotic bypass surgery offer more safety compared to conventional or thoracoscopic methods. Controlled by the surgeon’s finger movements at the console, these robotic arms can perform motions that the wrist cannot. There is no tremor or fatigue, and reaching anatomically challenging areas becomes easier. This results in comfort for both the surgeon and the patient.
Less pain, less infection
Robotic bypass surgery is used for coronary artery bypass, mitral valve repair, congenital heart procedures, and arrhythmia surgery in suitable patients. Coronary artery bypass can be done with or without stopping the heart, sometimes using a cardiopulmonary pump. During mitral valve surgery, the heart is stopped with a special solution. Robotic heart surgery offers a significantly shorter recovery, and patients often return to work within 7“10 days. There is less bleeding, infection, pain, and need for blood transfusion. It also delivers better cosmetic outcomes.
Advantages of robotic surgery
Better results:
Pain and certain post-operative physical function issues are less frequent, resulting in higher patient satisfaction.
- Less damage: The procedure is carried out through small incisions with camera guidance; contrary to common belief, robotic bypass surgery offers a clearer, more detailed view than open surgery, enabling significantly less tissue trauma.
- Faster recovery: Recovery after surgery is much faster than with open procedures. This also leads to a shorter hospital stay and a quicker return to normal activities.
- Less pain: Since the surgery is performed through small cuts, patients experience less pain following the procedure.
- Lower infection risk: The risk of post-operative surgical site infection is reduced, thanks to the very small incisions.
- Better cosmetic result: As the operation is done through 1“1.5 cm incisions, cosmetic outcomes are improved compared to open surgery.
- Clearer field of view: With the assistance of optical systems, a more detailed and clearer field of view is obtained compared to open surgery.
- Reduced blood loss: Blood loss is minimized due to decreased tissue injury.
Clinical Benefits & Patient Outcomes
The shift to robotic surgery is not just about technology; it is about patient-centric outcomes. Below is a detailed breakdown of why this method is becoming the preferred standard for eligible patients.
Drastic Reduction in Trauma
Because the sternum is left intact, the structural integrity of the chest is preserved.
- Less Pain: Patients report significantly lower pain scores post-operation. The agony associated with coughing or moving after a broken sternum is virtually eliminated.
- Reduced Blood Loss: Smaller incisions mean less tissue damage, leading to minimal blood loss and a reduced need for blood transfusions.
Accelerated Recovery Timeline
In traditional surgery, patients often spend a week in the hospital and require months to feel “normal” again. Driving and heavy lifting are prohibited for weeks. In contrast, robotic surgery offers a much faster timeline.
- Hospital Stay: Often reduced to just a few days.
- Return to Work: As Prof. Dr. Ozkara notes, patients can often return to work and normal physical conditions within a week or two.
- Psychological Benefit: The quick return to autonomy boosts the patient’s morale and mental health.
Lower Infection Rates
Surgical Site Infections are a serious complication in cardiac surgery. Large incisions, especially in patients with diabetes or obesity, are prone to healing issues. The tiny ports used in robotic surgery drastically minimize the surface area exposed to potential bacteria, bringing infection rates down significantly.
Cosmetic Superiority
For many patients, the “zipper” scar down the center of the chest is a constant reminder of their trauma. Robotic surgery leaves only faint, small scars on the side of the chest, which are often hidden by the arm. This offers a vastly superior cosmetic result.
For more information about our academic and training initiatives, visit Liv Hospital Academy.
* Liv Hospital Editorial Board has contributed to the publication of this content .
* Contents of this page is for informational purposes only. Please consult your doctor for diagnosis and treatment. The content of this page does not include information on medicinal health care at Liv Hospital .
Frequently Asked Questions
Is every patient a candidate for robotic bypass surgery?
Not every patient is eligible. It depends on the number of vessels that need bypassing, the location of the blockages, and the patient’s overall lung and chest anatomy. While it is ideal for single or double vessel disease, complex multi-vessel cases may still require traditional approaches or a “hybrid” method (combining stents with robotic surgery).
Is the robot doing the surgery by itself?
Absolutely not. The robot is a tool, completely controlled by the surgeon at all times. It cannot make a move, cut, or suture without the surgeon’s direct command from the console. Think of it as a high-tech power steering system for the surgeon’s hands.
What happens if there is a complication during the robotic procedure?
Safety is the priority. In the rare event of a complication or if the anatomy proves too difficult to navigate robotically, the surgical team is always prepared to convert the procedure to a traditional open surgery immediately. This is a standard safety protocol.
Is robotic surgery more expensive?
Generally, the use of advanced technology can make the procedure itself more expensive than traditional surgery. However, when factoring in the shorter hospital stay, reduced need for blood transfusions, fewer complications, and faster return to the workforce, the overall economic cost can be comparable or even advantageous in the long run.
Can robotic surgery be used for other heart conditions?
Yes. Beyond coronary artery bypass, robotic systems are extensively used for Mitral Valve Repair, Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure, tumor removal, and arrhythmia surgery.
How long does the surgery take?
Robotic surgeries can sometimes take slightly longer than traditional surgeries due to the setup time of the robot and the meticulous nature of the microsurgery. However, the “operating time” is balanced by the significantly shorter “recovery time.”



































