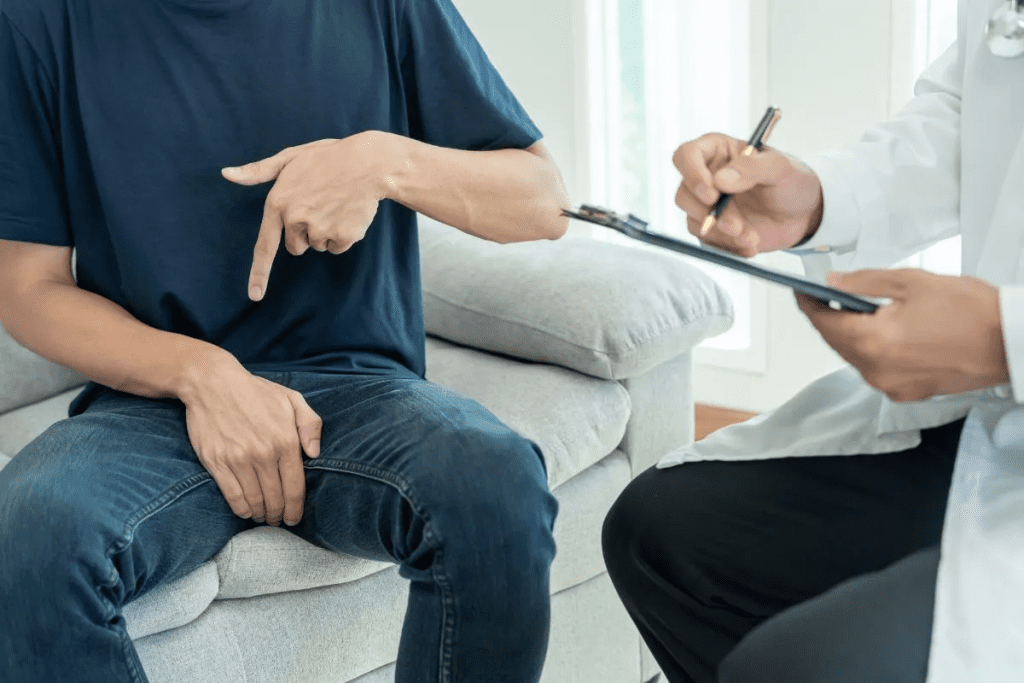
Prostate cancer spreading is a big problem worldwide. Nearly 30% of men see it come back after they’ve been treated. It’s very important to know the symptoms of advanced prostate cancer to get help quickly. Learn the key signs prostate cancer has spread to other organs or bones and how to detect them early for better care.
When prostate cancer spreads, it can show up in different parts of the body. This leads to many symptoms. Knowing these signs can help people and their families get medical help fast.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate cancer metastasis can occur in nearly 30% of men after initial treatment.
- Recognizing symptoms early is key for better treatment results.
- Advanced prostate cancer can show up in many parts of the body.
- Knowing the warning signs can lead to quick medical help.
- Early detection is essential for managing prostate cancer well.
Understanding Prostate Cancer and Its Progression
Prostate cancer starts when normal cells in the prostate gland change in a bad way. This leads to uncontrolled growth. The prostate is a small gland that helps with sperm health, producing fluids to nourish and protect them.
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is when cells in the prostate gland grow and multiply the wrong way. This can cause tumors, some of which are cancerous. Cancerous tumors can spread to other parts of the body.
Studies show prostate cancer cells take over the body’s energy, like other cancers. This lets them grow fast and a lot.
How Prostate Cancer Develops and Grows
Prostate cancer grows due to genetic and environmental factors. At first, it needs male hormones to grow. But as it gets worse, some cells may stop responding to hormone therapy, growing more aggressively.
Key factors influencing prostate cancer progression include:
- Genetic mutations that disrupt normal cell cycle regulation
- Hormonal influences, such as androgens
- Environmental factors, like diet and lifestyle
Knowing these factors helps in finding better treatments and managing the disease.
What Does It Mean When Prostate Cancer Spreads?
Knowing when prostate cancer spreads is key for patients to understand their diagnosis and treatment. When prostate cancer spreads, or metastasizes, it’s a serious step in the disease’s progression.
Defining Metastasis in Prostate Cancer
Metastasis in prostate cancer happens when cancer cells leave the prostate tumor and go to other parts of the body. This can include bones, lymph nodes, or other organs. It’s a complex process involving several steps.
Metastasis is a key sign of cancer getting worse. It changes how doctors treat prostate cancer. Spotting metastasis early is vital for effective treatment.
Common Pathways of Prostate Cancer Spread
Prostate cancer can spread in a few ways, mainly through the lymphatic system and bloodstream. The lymphatic spread means cancer cells go to nearby lymph nodes. These nodes can then send cells to other parts of the body. The hematogenous spread is when cancer cells enter the bloodstream and go to distant organs.
Common places for prostate cancer to spread include bones, lymph nodes, and sometimes the liver and lungs. Knowing these paths helps in spotting symptoms and managing the disease.
Common Sites Where Prostate Cancer Metastasizes

Prostate cancer can spread to different parts of the body. This leads to various symptoms and complications. Knowing where prostate cancer often spreads is key to managing it well.
Bone Metastasis
Bone metastasis is a common place for prostate cancer to spread. It can cause a lot of pain and increase the chance of fractures. The spine, pelvis, and ribs are often affected.
Symptoms of bone metastasis may include:
- Back pain
- Hip pain
- Rib pain
- Increased risk of fractures
Lymph Node Involvement
Lymph nodes are another common site for prostate cancer to spread. When cancer reaches the lymph nodes, they can swell. This swelling can be seen during a physical exam or through imaging tests.
Symptoms related to lymph node involvement may include:
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin
- Discomfort or pain in the affected area
Spread to Other Organs
Prostate cancer can also spread to other organs like the liver and lungs. The symptoms and complications vary based on the organ involved.
For example:
- Liver metastasis can cause abdominal pain and jaundice
- Lung metastasis can lead to coughing and difficulty breathing
Understanding where prostate cancer often spreads is vital. It helps both patients and healthcare providers manage the disease better. This improves the quality of life for those affected.
Signs Prostate Cancer Has Spread: An Overview
Prostate cancer that spreads can cause a variety of symptoms. These can range from mild to severe. It’s important for patients to know these signs to get the right medical care.
Early vs. Late Symptoms of Metastasis
Early signs of metastasis can be hard to spot. They might include:
- Mild bone pain
- General fatigue
- Minor changes in urinary habits
Late symptoms are more serious and can really affect your life. For example:
- Severe bone pain
- Difficulty walking or standing due to bone metastasis
- Significant weight loss
Symptom Patterns Based on Spread Location
The symptoms of prostate cancer metastasis depend on where the cancer spreads. For example:
- Bone Metastasis: Pain in the bones, like in the hips, back, or chest, is common.
- Lymph Node Involvement: Swelling in the legs or groin can happen if lymph nodes are affected.
- Other Organs: Symptoms can include neurological issues if the cancer spreads to the brain or spinal cord.
Bone-Related Signs of Prostate Cancer Metastasis
When prostate cancer spreads, it often goes to the bones. This can cause various symptoms that affect a patient’s life quality. It’s important to spot these signs early.
Back Pain and Prostate Cancer Metastasis
Back pain is a common symptom when prostate cancer spreads to the bones. This pain can feel like a dull ache or sharp stabbing. It’s key to tell this pain apart from other back pain causes, as it can lead to bone fractures or spinal cord issues.
Key characteristics of back pain related to prostate cancer metastasis include:
- Persistent pain that doesn’t improve with rest
- Pain that worsens at night or with certain movements
- Neurological symptoms such as numbness or weakness in the legs
Hip Pain as an Indicator of Spreading
Hip pain can also signal that prostate cancer has spread to the bones. This pain is often felt in the groin or thigh. It might be mistaken for arthritis or other hip issues. But, when linked to prostate cancer, it shows serious bone involvement.
It’s vital for patients with a history of prostate cancer to tell their healthcare provider about any new or worsening hip pain. Early detection can help manage the condition better.
Other Skeletal Pain Patterns
Prostate cancer metastasis can also cause pain in other bones, like the ribs, pelvis, or long bones. The pain’s intensity and type can vary. It often matches the bone’s location and how much cancer has spread.
Common features of skeletal pain due to prostate cancer spread include:
- Pain that is persistent and progressive
- Pain that is not necessarily related to movement or activity
- Pain that may be accompanied by other symptoms like fatigue or weight loss
Urinary Symptoms of Advanced Prostate Cancer
Advanced prostate cancer can cause many urinary symptoms. These symptoms affect a patient’s quality of life. They happen because the cancer grows in the prostate gland and nearby areas.
Difficulty Urinating
One common symptom is urinary retention, or trouble urinating. This is often due to the prostate gland getting bigger. It blocks the urine flow.
Symptoms include:
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Straining to urinate
- Frequent urination, often at night
- Feeling the bladder is not empty
Blood in Urine (Hematuria)
Blood in the urine, or hematuria, is another key symptom. It happens when cancer invades the urinary tract, causing bleeding.
Hematuria can show up as:
- Visible blood in the urine, making it look pink, red, or cola-colored
- Microscopic blood in the urine, seen only in lab tests
Changes in Bladder Function
Advanced prostate cancer can also change how the bladder works. This is due to the cancer’s effect on the bladder or treatments like surgery or radiation.
Changes include:
- Overactive bladder, causing urgency and frequency
- Underactive bladder, leading to incomplete emptying
| Symptom | Description | Possible Cause |
| Difficulty Urinating | Weak or interrupted urine flow, straining to urinate | Prostate enlargement obstructing urine flow |
| Blood in Urine (Hematuria) | Visible or microscopic blood in urine | Cancer invasion into the urinary tract |
| Changes in Bladder Function | Overactive or underactive bladder | Cancer impact on bladder or treatment effects |
Systemic Signs That Prostate Cancer Has Spread
Signs like unexplained weight loss and constant fatigue can mean prostate cancer has spread. When prostate cancer moves beyond the prostate, it can hit different parts of the body. This leads to various symptoms.
Unexplained Weight Loss
Weight loss without reason is a common sign of advanced prostate cancer. The cancer can make the body burn more energy, even if you eat more. This should make you see a doctor right away.
Persistent Fatigue and Weakness
Fatigue is a big problem for those with prostate cancer that has spread. The cancer can cause anemia, making you feel weak and tired. Also, the body uses more energy as the cancer grows, making you feel constantly tired.
Night Sweats and Fever
Night sweats and fever can happen when prostate cancer has spread. These signs often mean the cancer is getting worse. Night sweats can be due to hormonal changes or the body’s reaction to the cancer.
It’s important to notice these signs. They help both patients and doctors understand how the cancer is growing. This helps make better choices about treatment and care.
Lymphatic System Symptoms of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Metastatic prostate cancer often affects the lymphatic system. This system is key to our immune response. When cancer spreads here, it causes various symptoms.
Swollen Lymph Nodes
Swollen lymph nodes are a common symptom of prostate cancer spreading to the lymphatic system. Lymph nodes help fight infections and diseases. When cancer reaches them, the nodes swell.
Symptoms of swollen lymph nodes may include:
- Painless swelling in the neck, armpit, or groin
- Enlarged lymph nodes that are tender to the touch
- General feeling of illness or discomfort
Lymphedema and Related Issues
Lymphedema can occur when prostate cancer reaches the lymphatic system. It happens when fluid can’t drain properly, causing swelling. This usually affects the legs or genital area.
Common symptoms of lymphedema include:
| Symptom | Description |
| Swelling | Swelling in the affected limb or area, which can range from mild to severe |
| Heaviness or discomfort | A feeling of heaviness or discomfort in the affected limb |
| Skin changes | Thickening of the skin, or other skin changes in the affected area |
Managing lymphedema involves therapies like compression garments and exercises. Early treatment can help manage symptoms and improve life quality.
Neurological Signs of Prostate Cancer Spread
Prostate cancer spreading can lead to neurological symptoms that greatly affect a patient’s life. These symptoms happen when cancer reaches the spine or nervous system. This causes various problems.
Spinal Cord Compression Symptoms
Spinal cord compression is a serious issue from prostate cancer spreading. It happens when cancer in the spine presses on the spinal cord. Symptoms include:
- Severe back pain
- Numbness or tingling in the legs
- Weakness in the legs
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
This is a medical emergency that needs quick action to avoid lasting harm.
Nerve Pain and Weakness
Nerve pain, or neuropathic pain, is common in prostate cancer spread. It can be from cancer pressing on nerves or nerve damage from treatment. Symptoms include:
- Sharp, shooting, or burning pain
- Numbness or tingling sensations
- Muscle weakness
This pain and weakness can make daily life hard and affect well-being.
Cognitive Changes in Advanced Cases
In advanced prostate cancer, cognitive changes can happen. This is due to cancer reaching the brain or central nervous system. Symptoms include:
- Memory loss
- Confusion
- Difficulty concentrating
- Changes in mood or personality
These changes can be upsetting for patients and their families. It shows the need for full care in advanced prostate cancer.
Managing neurological symptoms is key to better life quality for patients with advanced prostate cancer. A team of specialists, including pain management and neurologists, work together. They aim to meet the complex needs of these patients.
Organ-Specific Symptoms When Prostate Cancer Spreads
When prostate cancer spreads, it can cause different symptoms. This is because it affects different parts of the body. Finding and treating it can be hard.
Liver Metastasis Signs
Liver metastasis from prostate cancer is rare but serious. It can lead to:
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Weight loss
Liver function tests are key to spotting liver metastasis. They check blood for signs of liver health.
Lung Metastasis Symptoms
Lung metastasis from prostate cancer can lead to breathing problems. Symptoms include:
- Coughing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
Imaging tests like CT scans and X-rays are vital. They show if and how much the lungs are affected.
Other Organ Involvement
Prostate cancer can also reach other organs. This includes the adrenal glands, brain, and kidneys. Symptoms can be:
| Organ | Possible Symptoms |
| Adrenal Glands | Fatigue, weight loss, hormonal imbalances |
| Brain | Headaches, seizures, confusion, weakness |
| Kidneys | Flank pain, hematuria (blood in urine), kidney failure symptoms |
Knowing these symptoms is key to managing prostate cancer that has spread. Early detection and treatment can greatly improve life quality.
How Doctors Diagnose Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Doctors use advanced imaging and lab tests to find metastatic prostate cancer. This method helps them see how far the cancer has spread. It’s key for making a good treatment plan.
Imaging Tests for Detecting Spread
Imaging tests are very important for finding metastatic prostate cancer. These include:
- Bone Scans: They spot cancer in bones, a common place for it to spread.
- CT Scans: Show detailed pictures of inside organs and find cancer in lymph nodes or other places.
- MRI: Gives clear images of the prostate and nearby areas to find cancer.
- PET Scans: Use a special tracer to find cancer cells, helping spot where it has spread.
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Blood tests are key for finding and watching prostate cancer. Important tests are:
- PSA Test: Checks the prostate-specific antigen in blood, which goes up in cancer.
- Other Biomarkers: New markers help see how fast cancer grows and how well it responds to treatment.
Biopsy Procedures
Biopsy takes tissue from the prostate or other cancer spots. It’s checked under a microscope to see if there are cancer cells.
- Prostate Biopsy: Finds prostate cancer and how aggressive it is.
- Biopsy of Metastatic Sites: Confirms cancer in other places, like lymph nodes or bones.
By using these tests together, doctors can accurately find metastatic prostate cancer. They then make a treatment plan that fits the patient’s needs.
Treatment Options for Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Men with metastatic prostate cancer now have more treatment choices than before. These choices aim to slow the disease’s spread, ease symptoms, and enhance life quality.
Hormone Therapy Approaches
Hormone therapy, or androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is key in treating metastatic prostate cancer. It lowers male hormones like testosterone, which prostate cancer cells need to grow. There are several hormone therapy types:
- Orchiectomy: This surgery removes the testicles to stop testosterone production.
- LHRH agonists: These medications lower testosterone by stopping luteinizing hormone production.
- LHRH antagonists: Drugs that quickly lower testosterone without the initial surge seen with LHRH agonists.
- Anti-androgens: Medications that block androgen action.
Chemotherapy for Advanced Disease
Chemotherapy is another option for metastatic prostate cancer, for those whose disease has grown despite hormone therapy. It can slow cancer growth, ease symptoms, and extend life. Common chemotherapy regimens include:
- Docetaxel: Often used with prednisone, it’s a standard first-line chemotherapy for metastatic prostate cancer.
- Cabazitaxel: Used for men whose cancer has progressed after docetaxel treatment.
Radiation and Other Targeted Treatments
Radiation therapy can treat metastatic prostate cancer, mainly for those with limited spread. It can manage symptoms and possibly extend life. Other targeted treatments include:
- Radium-223: A radioactive drug that targets bone metastases, improving pain and survival.
- PARP inhibitors: For men with certain genetic mutations (e.g., BRCA1 or BRCA2), these drugs can help stop cancer cells from repairing their DNA.
These treatments are often combined and tailored to each patient’s needs. Advances in treatment have greatly improved outcomes for men with metastatic prostate cancer.
Managing Symptoms of Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Managing symptoms of prostate cancer that has spread is key to a better life. Metastatic prostate cancer can cause many symptoms, depending on where it spreads. A good approach includes managing pain, improving life quality, and using supportive care.
Pain Management Strategies
Pain is a common symptom, often when cancer spreads to bones. Pain management strategies are vital for comfort. These may include:
- Medications such as opioids and non-opioid analgesics
- Radiation therapy to ease bone pain
- Other interventions like nerve blocks
Improving Quality of Life
Improving life quality for metastatic prostate cancer patients is important. It involves both physical and emotional needs. This includes:
- Physical therapy to keep mobility and strength
- Counseling or therapy for emotional support
- Nutritional support for good nutrition
Supportive Care Options
Supportive care is vital for managing metastatic prostate cancer. It offers a range of services for patients and families, including:
- Hospice care for advanced disease
- Palliative care teams for symptom management
- Support groups for patients and caregivers
By using these supportive care options, patients get the care they need.
Recognizing Prostate Cancer Recurrence and Progression
It’s key for patients to spot prostate cancer coming back early. This means getting medical help fast. Prostate cancer can return after treatment, showing signs and symptoms.
Rising PSA Levels After Treatment
A PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) level going up after treatment is a big warning sign. It means the cancer might be coming back.
After treatments, like surgery or radiation, patients get regular PSA tests. A steady increase in PSA levels can mean the cancer is back, even without symptoms.
New or Worsening Symptoms
New or getting worse symptoms can also point to prostate cancer coming back. These symptoms depend on where the cancer has spread.
For example, if the cancer goes to the bones, patients might feel bone pain or back pain. If it spreads to other places, symptoms like urinary problems or neurological issues can happen.
Timeline of Disease Progression
Knowing how fast prostate cancer grows is important. It helps set up treatment plans and manage what to expect.
How fast prostate cancer grows varies a lot. It depends on the cancer’s starting stage, how well the first treatment worked, and the patient’s overall health.
Conclusion: Living with Advanced Prostate Cancer
Advanced prostate cancer brings its own set of challenges. It’s important to know how to manage symptoms and deal with treatment side effects. Recognizing the signs that prostate cancer has spread is key.
End stage prostate cancer symptoms can really affect your life. It’s vital to work with your healthcare team to manage pain and other issues. This includes urinary problems and other complications.
Being informed and proactive can help you cope with advanced prostate cancer. This approach can improve your well-being and help you live better with the disease.
FAQ
What are the common signs that prostate cancer has spread?
Signs include bone pain, trouble urinating, and unexplained weight loss. Also, persistent fatigue and swollen lymph nodes are common.
How does prostate cancer metastasis affect the bones?
Metastasis to bones can cause back and hip pain. It also increases the risk of fractures.
What urinary symptoms are associated with advanced prostate cancer?
Symptoms include trouble urinating and blood in urine. Changes in bladder function also occur.
What systemic signs indicate that prostate cancer has spread?
Signs include unexplained weight loss and persistent fatigue. Night sweats and fever are also indicators.
How does prostate cancer affect the lymphatic system?
Metastasis can cause swollen lymph nodes and lymphedema. This affects the lymphatic system’s function.
What neurological symptoms can occur when prostate cancer spreads?
Symptoms include spinal cord compression and nerve pain. Weakness and cognitive changes can also occur.
What are the symptoms of prostate cancer metastasis to specific organs like the liver or lungs?
Liver metastasis can cause unique symptoms. Lung metastasis symptoms vary based on spread extent and location.
How is metastatic prostate cancer diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves imaging tests, blood tests, and biopsies. These help detect and manage metastatic disease.
What treatment options are available for metastatic prostate cancer?
Options include hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and radiation. Targeted treatments are also used, often together.
How can symptoms of metastatic prostate cancer be managed?
Pain management and supportive care improve quality of life. Other measures are also important.
What are the signs of prostate cancer recurrence and progression?
Signs include rising PSA levels and new symptoms. Changes in disease progression timeline are also indicators.
How can patients cope with advanced prostate cancer?
A holistic approach is needed. This includes managing symptoms and treatment side effects for overall well-being.
What is the significance of recognizing the signs of prostate cancer spread early?
Early recognition can greatly improve treatment outcomes. It allows for timely medical intervention.
Can difficulty urinating be a sign of prostate cancer spread?
Yes, it’s a common symptom of advanced prostate cancer.
Are there any specific symptoms associated with end-stage prostate cancer?
Symptoms include severe bone pain and significant weight loss. Neurological symptoms are also common.
How does prostate cancer metastasis affect the quality of life?
Metastasis can significantly impact quality of life. Managing symptoms and supportive care are key.
References
- Cancer Research UK. (2025, September 2). Symptoms of metastatic prostate cancer. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/prostate-cancer/metastatic-cancer/symptoms




































