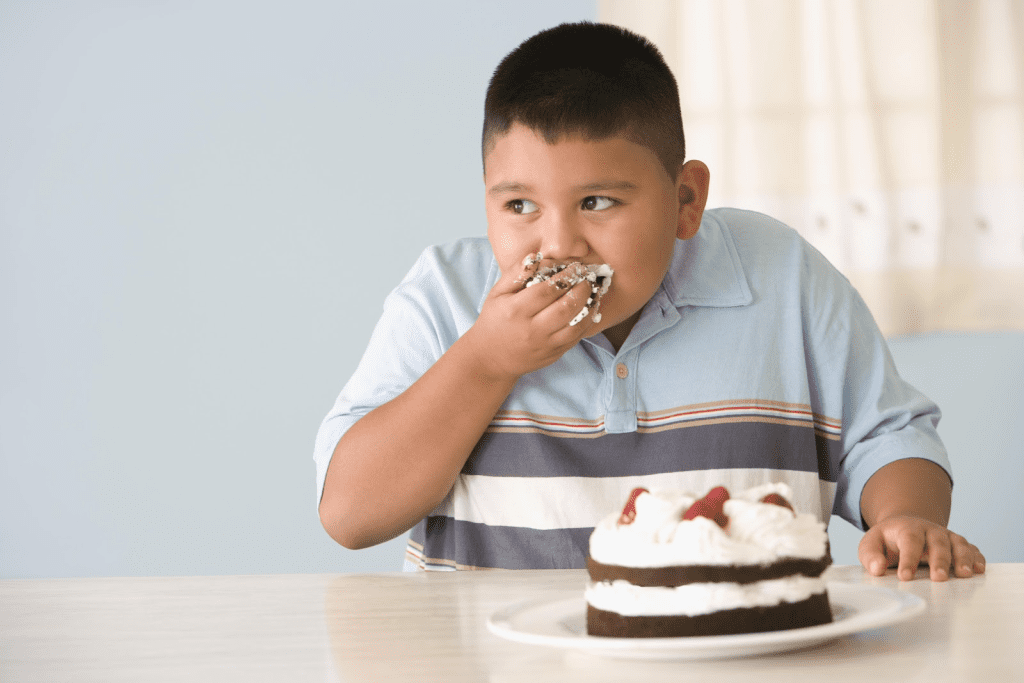
Childhood obesity is a big problem worldwide. It affects over 160 million kids aged 5-19. This issue is caused by many factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
When kids eat more calories than they need, they gain weight. This extra energy is stored as fat. This leads to obesity. Knowing why kids get obese is key to stopping it.
Key Takeaways
- Childhood obesity is a complex condition influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
- Over 160 million children aged 5-19 were living with obesity in 2022.
- Obesity occurs due to an imbalance between calorie intake and expenditure.
- Understanding the causes is critical for prevention and intervention.
- Lifestyle factors, including diet and physical activity, play a significant role.
The Alarming Rise of Obesity in Children
Obesity in children is a big problem worldwide. We see more kids getting obese, which affects their health and happiness.
Global Statistics: 160+ Million Children Affected
More than 160 million kids are dealing with obesity. This number shows how serious the issue is. It’s a big risk for health problems like diabetes and heart disease.
Obesity in kids can harm their health for a long time. It’s important to understand obesity meaning to help them.
Tripling Rates: UNICEF’s Perspective
UNICEF says obesity in kids has tripled in 20 years. It’s due to bad eating habits, less exercise, and money issues. About 188 million kids aged 5-19 are now obese.
We need to tackle this problem together. Governments, doctors, families, and communities must work to help kids live healthier.
United States: 19.3% of Children Ages 2-19 Are Obese
In the U.S., 19.3% of kids aged 2-19 are obese. That’s about 14.4 million kids. It’s a big worry because it means we need to act fast to help them.
We want to help families and doctors. Knowing the average weight for 12-year-olds can help spot weight problems early.
- Key factors contributing to childhood obesity include:
- Poor dietary habits and consumption of high-calorie foods
- Decreased physical activity and increased screen time
- Socioeconomic factors and limited access to healthy food options
By understanding these causes, we can fight childhood obesity. We aim to make kids’ lives healthier all over the world.
Poor Dietary Habits and Food Choices

Unhealthy eating habits are a big problem in kids worldwide. Eating too much junk food and sugary drinks is a major cause.
Consumption of Calorie-Rich, Nutrient-Poor Foods
Kids who eat a lot of junk food are more likely to get obese. Junk food has lots of calories but not enough good stuff like vitamins and fiber. Eating too much of it can make kids gain weight.
Research shows that eating too much processed and fast food can make kids more likely to get obese. These foods are full of unhealthy fats and sugars, which are bad for kids’ health.
Sugar-Sweetened Beverages and Processed Snacks
Drinks like soda and sweetened teas are full of sugar and calories. Drinking them a lot can make kids eat more without feeling full, leading to weight gain.
Snacks like chips and baked goods are also bad for kids. They have lots of unhealthy fats and sugars. Eating them too often can make kids eat less healthy foods and gain weight.
Increasing Portion Sizes and Frequent Eating
Food portions have gotten bigger, which means kids eat more calories. Eating bigger portions can make kids eat more than they need, leading to weight gain.
Snacking too much can also lead to eating too many calories. If snacks are high in calories and low in nutrients, they can make kids eat more than they should.
Replacement of Traditional Diets with Fast Food
Fast food is becoming more popular, which is bad for kids’ health. It’s full of calories, unhealthy fats, and sodium, but lacks essential nutrients. Eating fast food regularly can make kids’ diets unbalanced and lead to weight gain.
Studies show that kids who eat fast food a lot are more likely to gain weight and become obese. We need to teach kids to eat healthier and balanced foods. For more info on childhood obesity, visitthis resource.
Sedentary Lifestyle in Childhood
Sedentary behaviors are rising in kids, linked to more obesity. A sedentary lifestyle means little physical activity. When kids watch screens more, they burn less energy, which can cause weight gain.
Excessive Screen Time and Digital Entertainment
Digital entertainment is everywhere, making kids watch screens a lot. Watching TV, playing games, or using devices for hours cuts down on physical activity. It also exposes them to ads for junk food, raising obesity risks.
Declining Physical Activity and Outdoor Play
Less physical activity and outdoor play are big problems. Regular exercise is key to a healthy weight. But today’s kids do less because of screens and fewer chances to play outside.
Poor Sleep Patterns and Their Impact
Poor sleep is also linked to obesity in kids. Bad sleep or disrupted patterns can make kids hungrier and eat more. Plus, tired kids are less likely to move, making the problem worse.
Stress-Related and Emotional Eating Behaviors
Stress and emotional eating add to obesity in kids. Children might eat more when stressed or upset. If they choose high-calorie foods, it can lead to weight gain. It’s important to help kids manage these eating habits.
Early Life and Developmental Risk Factors
Understanding early life and developmental risk factors is key to tackling childhood obesity. These factors can greatly affect a child’s chance of becoming obese and facing health problems.
Maternal Health: Obesity and Gestational Diabetes
A mother’s health during pregnancy is very important for her child’s future health. Maternal obesity and gestational diabetes are big risks for childhood obesity. Research shows that kids born to mothers with these conditions are more likely to be obese and have metabolic disorders.
Studies show maternal health affects a child’s metabolism and weight control. For example, gestational diabetes can cause babies to be born larger than usual. This can lead to obesity later on.
Infant Feeding Practices
How a child is fed in early life is also important. Breastfeeding helps protect against obesity by regulating appetite and metabolism. On the other hand, formula feeding, which can be high in sugar and calories, can lead to obesity.
When and what solid foods are introduced to infants also matter. Starting with high-calorie foods too early can lead to eating too many calories and unhealthy eating habits.
Antibiotic Use During Infancy
Antibiotics in infancy can increase obesity risk. Antibiotics can mess with the gut microbiota, which is vital for metabolic health and immune system development. Changes in gut microbiota early on can lead to obesity later.
Adverse Childhood Experiences and Trauma
Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), like trauma, also raise obesity risk. Children who experience trauma may have different stress responses. This can lead to unhealthy eating habits and metabolic changes.
To lower these risks, parents and caregivers need to be aware. They should focus on a healthy pregnancy, proper infant feeding, less antibiotic use, and a supportive environment. This can help prevent childhood obesity.
By tackling these early-life developmental risks, we can prevent childhood obesity. This promotes healthier outcomes for kids.
Environmental and Genetic Influences
Childhood obesity is a complex issue. It’s influenced by many environmental and genetic factors. We see that obesity in kids isn’t just about personal choices. It’s also shaped by their surroundings and genes.
Food Environment and Accessibility Issues
The availability of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods is key. Places with few healthy food options, called “food deserts,” see more obesity.
Key factors include fast-food chains and easy access to processed snacks.
Socioeconomic Status and Health Disparities
Socioeconomic status greatly affects obesity rates in kids. Lower-income families face challenges like limited healthy food and safe places to play.
We must recognize health disparities and work to reduce them. This is vital for fighting childhood obesity.
Family Lifestyle and Parental Feeding Practices
A family’s lifestyle and how they feed their kids matters a lot. Families with obesity history are at higher risk. This is true if they eat too many calories and don’t encourage exercise.
- Feeding practices that lead to overeating or restrict certain foods can be harmful.
- It’s important to create a home environment that supports healthy eating and activity.
Genetic Predisposition and Hereditary Factors
Genetics also plays a part in childhood obesity. Kids with obesity in their family history are more likely to struggle with weight.
Genetics can’t be changed, but knowing its role helps in making better interventions.
Conclusion: Tackling the Multifaceted Causes of Childhood Obesity
Understanding childhood obesity is key to fighting it. We’ve looked at how bad eating, not moving enough, and early life risks play a part. Also, genetics and the environment matter too.
To stop childhood obesity, we need a big plan. It should cover how kids eat, move, and live at home. Eating right, being active, and sleeping well can help a lot.
The World Health Organization says we must tackle obesity from all sides. Working together, we can make a better world for kids to grow up in.
Our main goal is to give kids a healthy start. We want to help them develop good habits and avoid obesity.
FAQ
What is childhood obesity?
Childhood obesity is when kids have too much body fat. It’s caused by genetics, environment, and lifestyle.
What are the main causes of childhood obesity?
Main causes include bad eating habits and not being active. Early life factors and genetics also play a part.
How do dietary habits contribute to childhood obesity?
Eating too much junk food and sugary drinks leads to weight gain. This is because these foods have lots of calories but not much nutrition.
What is the impact of a sedentary lifestyle on childhood obesity?
Sitting too much and not moving enough increases obesity risk. This includes too much screen time and bad sleep habits.
How do early life risk factors influence childhood obesity?
Factors like mom’s health and how babies are fed can affect obesity risk. So can antibiotics and tough childhoods.
What is the role of environmental and genetic influences in childhood obesity?
Where kids live and their family’s lifestyle matter. So do their genes. These all impact obesity risk.
How can childhood obesity be prevented?
To prevent obesity, promote healthy habits. This means eating right, staying active, and living in a healthy environment. Also, address early life and environmental factors.
What is the average weight for a 12-year-old child?
A 12-year-old’s weight varies by height, sex, and body type. Healthy weights range from 76-125 pounds for girls and 85-135 pounds for boys.
How is obesity defined in children?
Obesity in kids is defined by BMI percentiles. Kids above the 95th percentile are considered obese.
What are the symptoms of obesity in children?
Signs include too much weight, less activity, and health issues like high blood pressure and breathing problems.
What is prepubescent?
Prepubescent means before puberty, usually between 8-12 years old.
How is BMI calculated for kids?
BMI for kids uses weight and height. It’s plotted on a growth chart to find the BMI percentile.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). Childhood Obesity Facts. Retrieved fromhttps://www.cdc.gov/obesity/data/childhood.html

































