Did you know that 1 in 8 men will face prostate issues at some point? These problems can really affect a man’s life, causing pain and worry. Knowing what causes them is key to managing and treating them. Identify the primary drivers behind prostate problems, with a focus on prostate cancer as a significant underlying cause.
At our medical institution, we take prostate health very seriously. Things like age, family history, and lifestyle play a big role in prostate problems. By looking into these causes, we can tailor care and support for those dealing with them.
Our team is here to help men deal with prostate cancer symptoms and other issues. We aim to give care that meets each patient’s specific needs.
Key Takeaways
- Prostate problems are a common health issue affecting many men worldwide.
- Age, genetics, and lifestyle are significant factors contributing to prostate issues.
- Understanding the causes of prostate problems is essential for effective treatment.
- Personalized care and support are key for managing prostate health.
- Our medical team is committed to providing complete care for prostate-related issues.
Understanding the Prostate Gland
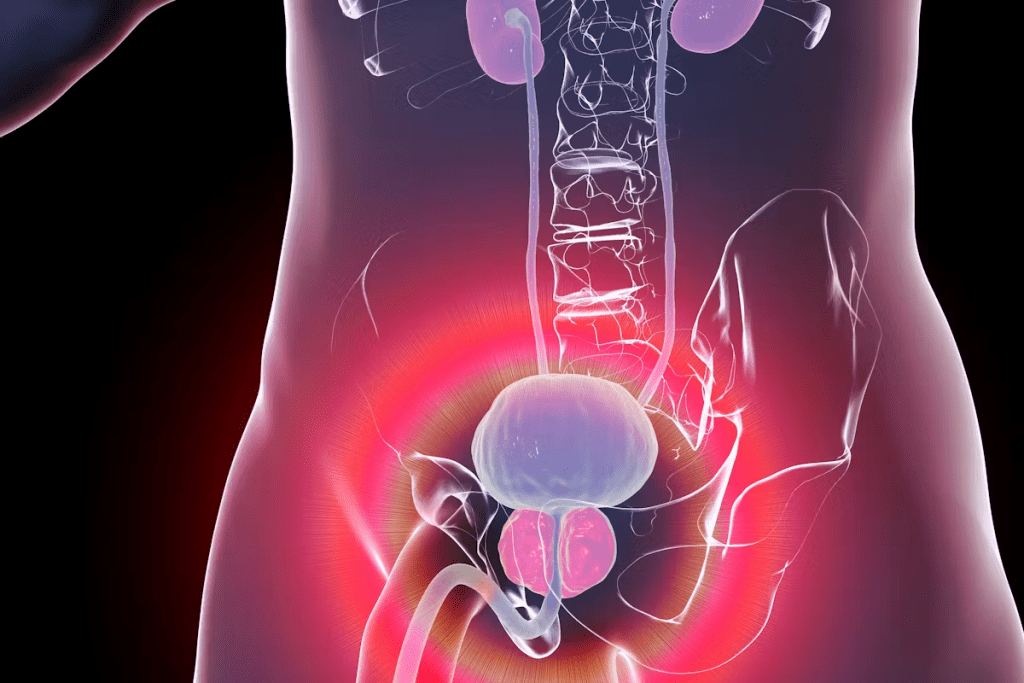
The prostate gland is a key part of the male body. It’s important for both urine and reproductive health. Knowing about its anatomy and function is essential for men’s health.
Anatomy and Location of the Prostate
The prostate gland is small, like a walnut. It’s found below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It wraps around the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder to the penis. Knowing where it is helps doctors diagnose and treat prostate problems.
Function and Importance
The prostate gland makes seminal fluid. This fluid nourishes and protects sperm during ejaculation. It’s key for male fertility. The prostate also helps urine flow smoothly by surrounding the urethra.
Prostate health is linked to overall men’s health. Problems with the prostate can cause a lot of discomfort and health issues. So, regular check-ups are very important.
Normal Changes Throughout Life
The prostate gland changes throughout a man’s life. During puberty, it grows as hormone levels rise. In older age, it often grows again, a condition called benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
| Life Stage | Prostate Changes | Health Implications |
| Puberty | Enlargement due to hormonal changes | Generally no significant health issues |
| Adulthood | Stable size, possible prostatitis or other issues | Possible urinary or reproductive problems |
| Older Age | Enlargement (BPH), possible cancer | Urinary symptoms, serious health issues |
Knowing about these changes helps men spot problems early. This makes it easier to get medical help on time.
Overview of Common Prostate Problems

Many men face prostate issues like BPH, prostatitis, and prostate cancer as they get older. These problems can really affect their quality of life. It’s important to know about their symptoms, how to find out if you have them, and what treatments are available.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH, or an enlarged prostate, is a common issue for older men. It can make it hard to pee, make the pee weak, and you might need to pee a lot.
To find out if you have BPH, doctors might do a digital rectal exam (DRE) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing. The treatment depends on how bad your symptoms are. It could be medicine or surgery.
Prostatitis
Prostatitis is when the prostate gland gets inflamed, often because of a bacterial infection. You might feel pain in your pelvic area, have trouble peeing, and feel feverish.
Doctors use urinalysis, a prostate exam, and sometimes check the prostate fluid to diagnose prostatitis. For bacterial prostatitis, they usually prescribe antibiotics. For non-bacterial prostatitis, they might give anti-inflammatory medications.
Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a common cancer in men. In the early stages, it often doesn’t show any symptoms. That’s why regular check-ups are so important.
Doctors use PSA testing, DRE, and biopsy to diagnose prostate cancer. The treatment depends on how advanced the cancer is. It could be watching it closely, surgery, or radiation therapy.
Other Prostate Conditions
There are other prostate issues like prostatodynia (painful prostate) and prostate cysts. These can be very uncomfortable and need to be checked by a doctor.
| Condition | Common Symptoms | Diagnostic Methods | Typical Treatments |
| BPH | Difficulty urinating, weak urine flow | DRE, PSA testing | Medications, surgery |
| Prostatitis | Pelvic pain, urinary issues, fever | Urinalysis, prostate examination | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Prostate Cancer | Often asymptomatic in early stages | PSA testing, DRE, biopsy | Active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy |
Age-Related Factors in Prostate Health
Age plays a big role in prostate health for men. As men age, their prostate goes through changes. Knowing these changes helps keep the prostate healthy and lowers the risk of problems.
Hormonal Changes with Aging
Hormone levels change with age, affecting the prostate. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a strong form of testosterone, is key. It’s linked to prostate growth.
Hormonal shifts can raise DHT levels, causing prostate enlargement. This is known as Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH). It’s common in older men and can lead to urinary issues.
Cellular Changes in Older Men
Cell changes with age also impact prostate health. Older men’s prostate cells grow and divide more. This can lead to abnormal cells and even cancer.
The table below shows some key cell changes and their effects on prostate health:
| Cellular Change | Potential Implication |
| Increased cell growth | Prostate enlargement (BPH) |
| Abnormal cell division | Prostate cancer |
| Cellular inflammation | Prostatitis |
Why Age Increases Risk
Age raises the risk of prostate issues due to hormonal and cell changes. As men age, these changes become more likely. This makes age a big risk factor for prostate health problems.
Knowing how age affects the prostate helps men take action. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and being aware of symptoms can help catch and manage problems early.
Hormonal Influences on Prostate Problems
It’s key to know how hormones affect prostate health. Hormonal changes, like the balance between hormones, are important. They play a big role in prostate problems.
Testosterone and DHT Effects
Testosterone is a major hormone for men and impacts prostate health. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), made from testosterone, is very important for prostate issues. DHT helps prostate cells grow, which can cause Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH).
The change of testosterone to DHT is key for prostate health. This change is helped by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. Stopping this enzyme can lower DHT levels and help with prostate problems.
Estrogen Balance in Men
Estrogen is important for men’s health, including the prostate. Keeping estrogen balanced is key. It works with testosterone and DHT to affect prostate cell growth.
Studies show that an estrogen and testosterone imbalance can cause prostate issues. Keeping these hormones balanced is vital to avoid prostate problems.
Hormonal Imbalances and Prostate Growth
Hormonal imbalances can cause prostate growth, common in older men. The mix of testosterone, DHT, and estrogen affects how fast and how much the prostate grows.
| Hormone | Effect on Prostate |
| Testosterone | Promotes prostate cell growth |
| DHT | Enhances prostate cell growth, contributing to BPH |
| Estrogen | Interacts with testosterone and DHT to influence prostate growth |
Knowing how hormones affect the prostate is vital for good treatment plans. By fixing hormonal imbalances, we can manage prostate health better. This helps lower the risk of prostate-related issues.
Genetic and Hereditary Causes
A man’s genetic makeup and family history can greatly impact his likelihood of experiencing prostate problems. We recognize that genetic and hereditary factors play a key role in determining the risk of prostate issues.
Family History Patterns
Men with a family history of prostate cancer are at a higher risk of developing prostate problems. The risk increases with the number of affected relatives and is significant if these relatives were diagnosed at a younger age. We are learning more about how family history patterns can help identify men who may benefit from earlier screening and preventive measures.
Specific Genetic Mutations
Certain genetic mutations have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer and other prostate problems. For instance, mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, known for their association with breast and ovarian cancer, also elevate the risk of prostate cancer. Understanding these specific genetic mutations can help in assessing individual risk more accurately.
Hereditary Prostate Conditions
Some prostate conditions have a clear hereditary component. Men with a family history of prostate issues are not only at risk of prostate cancer but may also be more likely to experience other prostate conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). We are working to understand how hereditary factors contribute to these conditions.
Genetic Testing Considerations
Genetic testing can provide valuable information about a man’s risk of developing prostate problems. The decision to undergo genetic testing is complex and involves considering family history, ethnic background, and other risk factors. We advise men to discuss the implications and benefits of genetic testing with their healthcare provider to make an informed decision.
Prostate Cancer: Primary Causes and Risk Factors
Prostate cancer is caused by genetics, environment, and lifestyle. Knowing these factors helps us understand risk and how to prevent it.
Cellular Mutations and Cancer Development
Prostate cancer starts with cell mutations that cause cells to grow out of control. These changes can come from genes and the environment. We’ll look into how these mutations happen and their part in cancer.
Key Factors in Cellular Mutations:
- Genetic errors during cell division
- Environmental exposures to carcinogens
- Hormonal influences, like testosterone and DHT
High-Risk Genetic Factors
Some men are at higher risk due to their genes. Mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes, for example, raise prostate cancer risk. We’ll talk about why genetic testing is key for men with a family history of prostate cancer.
| Genetic Mutation | Risk Increase |
| BRCA1 | Moderate to High |
| BRCA2 | High |
| HOXB13 | Moderate |
Race and Ethnicity Considerations
Prostate cancer rates differ by race and ethnicity. African men, for instance, face higher rates and death rates. We’ll explore why this is and what it means for screening and treatment.
Geographic and Environmental Influences
Where you live and your environment play big roles in prostate cancer risk. Men in certain areas face unique environmental risks. We’ll look at how moving and environmental changes affect cancer rates.
Environmental Factors to Consider:
- Exposure to pesticides and other chemicals
- Urban vs. rural living conditions
- Dietary patterns influenced by local culture
Inflammatory Causes of Prostate Problems
It’s key to know the inflammatory causes of prostate issues for effective treatment. Inflammation is a big part of many prostate problems. It affects men’s health all over the world.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections often cause prostatitis, which is inflammation of the prostate gland. These infections can be either acute or chronic. They are usually caused by Escherichia coli bacteria.
We find out if someone has bacterial prostatitis through urine tests and prostate fluid analysis. Treatment often includes antibiotics. In severe cases, hospital care might be needed.
Non-Bacterial Inflammation
Non-bacterial prostatitis, or chronic pelvic pain syndrome, is when men have prostate pain and urinary symptoms without a bacterial infection. The exact cause is often unknown.
It’s thought that factors like past infections, nerve damage, and stress might play a role. This makes it hard to pinpoint the exact cause.
Chronic Inflammation Effects
Long-term inflammation of the prostate can cause lasting damage. It also raises the risk of prostate cancer. Chronic prostatitis leads to ongoing pain, discomfort, and urinary problems.
We treat chronic inflammation with medicines, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies.
Autoimmune Factors
Autoimmune responses, where the body attacks its own tissues, can cause prostate inflammation. Research shows that autoimmune factors might be involved in some cases of prostatitis.
| Cause | Description | Common Symptoms |
| Bacterial Infections | Acute or chronic infections caused by bacteria | Urinary pain, fever, chills |
| Non-Bacterial Inflammation | Chronic pelvic pain syndrome without bacterial infection | Prostate pain, urinary symptoms |
| Chronic Inflammation | Long-term inflammation leading to possible prostate damage | Persistent pain, urinary issues |
| Autoimmune Factors | Immune system attacking prostate tissue | Varying symptoms, often similar to other inflammatory causes |
Understanding these causes helps us diagnose and treat prostate problems better. This improves the lives of those affected.
Dietary Factors Affecting Prostate Health
Diet is key to keeping the prostate healthy. Some foods can raise or lower the risk of prostate issues. It’s important to know how different foods affect the prostate gland.
Impacts of High-Fat Diets
Eating too much fat can harm the prostate. Studies show that high-fat diets, mainly saturated fats, cause inflammation. This can make prostate problems worse.
Key findings on high-fat diets include:
- Increased risk of prostate cancer
- Potential for worsening BPH symptoms
- Link to chronic inflammation
Effects of Red Meat Consumption
Red meat and prostate health have been closely studied. Eating moderate amounts of red meat is usually okay. But, eating a lot of red meat, and processed meat in particular, can increase risks.
“A diet rich in red meat, mainly processed meat, may lead to prostate cancer. This is because of its high fat and sodium.” –
A Research Journal
Dairy Products and Calcium
Dairy and calcium have a mixed effect on the prostate. Calcium is good for bones, but too much can raise cancer risk.
| Dairy Product | Calcium Content | Prostate Health Impact |
| Milk | 300 mg per cup | Potential increased risk with high consumption |
| Cheese | 200-400 mg per ounce | Variable impact based on type and amount |
Nutrients and Foods Protecting Prostate Health
Some foods and nutrients help protect the prostate. These include:
- Tomatoes and lycopene
- Green tea and antioxidants
- Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli
- Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish
In conclusion, diet greatly affects prostate health. Knowing which foods are good or bad can help support prostate health.
Lifestyle Contributors to Prostate Problems
Our daily habits and choices greatly affect our prostate health. What we eat, how much we exercise, and whether we smoke or drink alcohol are key factors. These choices can increase the risk of prostate problems.
Sedentary Behavior Effects
A sedentary lifestyle, marked by long periods of sitting, is linked to health issues like prostate problems. Regular physical activity is vital for our health and lowers the risk of prostate issues.
Obesity and Weight Issues
Obesity is a major lifestyle factor affecting prostate health. Being overweight or obese raises the risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can lower this risk.
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and drinking too much alcohol are known risks for many health problems, including prostate issues. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol intake can greatly improve health and lower prostate problem risks.
Stress and Prostate Health
Chronic stress negatively impacts prostate health. Stress management techniques, like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing, can help reduce stress. This promotes overall well-being.
By making smart lifestyle choices, we can actively work towards good prostate health. This reduces the risk of prostate problems.
Environmental and Occupational Risk Factors
Environmental and occupational exposures are key in prostate health issues. Certain chemicals, radiation, and workplace hazards can harm the prostate. It’s important to know these risks.
Chemical Exposures
Some chemicals increase the risk of prostate problems. Pesticides, heavy metals, and industrial pollutants can harm prostate health. For example, Agent Orange exposure during the Vietnam War raises prostate cancer risk.
| Chemical | Source | Potential Risk |
| Pesticides | Agricultural use | Increased risk of prostate cancer |
| Heavy Metals | Industrial exposure | Potential for prostate damage |
| Agent Orange | Military use | Higher risk of prostate cancer |
Radiation Effects
Radiation exposure can harm prostate health. Ionizing radiation increases prostate cancer risk. This radiation comes from medical treatments and industrial sources.
“Radiation exposure, mainly ionizing radiation, is a prostate cancer risk factor. It’s important to monitor and protect against it.”
Source: An Institute
Workplace Hazards
Some workplaces increase prostate problem risks. Men in chemical-exposed industries, like manufacturing or agriculture, face higher risks.
Environmental Pollutants
Environmental pollutants affect prostate health. Air and water pollution, with pollutants like particulate matter and VOCs, can cause health issues, including prostate problems.
To reduce these risks, men can take steps like wearing protective gear, avoiding smoking, and living healthily. Knowing these risks helps prevent prostate problems and promotes health.
Recognizing Symptoms of Prostate Problems
Knowing the signs of prostate issues is key to managing them well. These problems can show up in many ways, affecting a man’s health in different areas.
Urinary Symptoms and Changes
Changes in how you pee can be a sign of prostate trouble. You might notice:
- Weak or interrupted urine flow
- Frequent urination, even at night
- Hard time starting or stopping pee
- Pain or burning when you pee
These signs can really disrupt your daily life and health.
Pain and Discomfort Signs
Pain or discomfort can point to prostate issues. You might feel:
- Pain in your lower back, hips, or pelvis
- Discomfort or pain during ejaculation
- Pain in the rectal area
Seeing a doctor is important to figure out why you’re feeling this way.
Sexual Function Effects
Prostate problems can also mess with your sex life. You might notice:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Painful ejaculation
- Changes in how much you want sex
These issues can also affect your mind, so it’s important to tackle them fully.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Get help right away if you have:
- Severe pain or trouble peeing
- Blood in your pee or semen
- Keep getting the same symptoms
Seeing a doctor early can really help your situation.
| Symptom | Description | Possible Cause |
| Weak urine flow | Less force or flow when you pee | Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) |
| Pain during ejaculation | Discomfort or pain when you ejaculate | Prostatitis |
| Frequent urination | Need to pee a lot, often at night | Prostate getting bigger or infected |
Knowing these symptoms can help you get medical help on time. This can really improve your life quality.
Prevention Strategies for Prostate Health
Keeping your prostate healthy starts with making smart choices. Eating right, staying active, and getting regular check-ups are key. These steps can help lower your risk of prostate problems.
Dietary Recommendations
Eating a balanced diet is key for your prostate. Focus on foods like fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Some foods are extra good for your prostate, such as:
- Tomatoes and tomato products, which are high in lycopene, an antioxidant that may help reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines, which are rich in omega-3 fatty acids that support overall health.
- Green tea, which contains catechins that may have anti-cancer properties.
- Cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli and cauliflower, which contain sulforaphane that may help prevent cancer cell growth.
Also, cut down on:
- Red meat and processed meats, which have been linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer.
- Dairy products are high in calcium, as excessive calcium intake may increase prostate cancer risk.
- Foods high in saturated fats, which can contribute to overall health issues.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Exercise is a big part of keeping your prostate healthy. It helps you stay at a healthy weight and boosts your overall health. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week.
Good exercises include:
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Cycling
- Resistance training to build muscle and improve bone density
Regular Screening Guidelines
Regular check-ups are important for catching prostate problems early. The American Cancer Society says men should talk to their doctor about screening at age 50. If you have a family history of prostate cancer, start the conversation sooner.
Screening tests might include:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) test
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
Supplements and Preventive Medications
While diet and exercise are key, some supplements and medications can also help. For example:
- Saw palmetto may help alleviate symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
- Zinc supplements may support prostate health, though excessive intake should be avoided.
- Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may have a protective effect against prostate cancer, though their use should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Always talk to your doctor before taking any supplements or medications. They can help you choose what’s best for your health.
By following these steps, men can keep their prostate healthy. This includes eating right, staying active, getting regular check-ups, and using supplements and medications wisely. This approach can help lower the risk of prostate problems.
| Prevention Strategy | Description | Benefits |
| Dietary Changes | Incorporate fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and beneficial foods like tomatoes and fatty fish. | Reduces risk of prostate cancer, supports overall health |
| Regular Exercise | Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week. | Maintains healthy weight, reduces inflammation |
| Regular Screenings | Discuss screening options with a healthcare provider, starting at age 50 or earlier for high-risk individuals. | Early detection of prostate problems |
| Supplements and Medications | Consider saw palmetto, zinc supplements, and aspirin after consulting with a healthcare provider. | May alleviate BPH symptoms, support prostate health |
Conclusion
Prostate health is key for men’s well-being. It needs a full approach that includes knowing risks, spotting symptoms, and using prevention. This article has covered the causes of prostate issues, like age, hormones, genes, and lifestyle.
Men can lower their risk of prostate problems by understanding these causes and symptoms. They can take steps to prevent issues like BPH, prostatitis, and cancer. Eating right, exercising, and getting screenings are important for keeping the prostate healthy.
We stress the need for men to be proactive about their prostate health. Talking openly with doctors about risks and prevention is vital. This way, men can improve their health and life quality, cutting down on cancer and other prostate issues.
FAQ
What are the primary causes of prostate problems?
Prostate issues can stem from age, genetics, lifestyle, and environment. Knowing these causes helps men prevent problems and seek medical help when needed.
Where is the prostate gland located and what is its function?
The prostate gland is below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra. It makes seminal fluid, which helps sperm during ejaculation.
What are the common symptoms of prostate problems?
Symptoms include trouble starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, and frequent need to urinate. Pain in the pelvic area or lower back can also occur. Sexual function may be affected.
How does age affect prostate health?
Age increases the risk of prostate issues. Hormonal and cellular changes with age can lead to BPH, prostatitis, and cancer. Understanding these changes helps men protect their prostate health.
What is the role of genetics in prostate problems?
Genetics are key in prostate health. Certain genetic mutations and hereditary conditions raise the risk. Family history can also indicate a higher risk, making genetic testing important for some.
How can lifestyle factors impact prostate health?
Lifestyle choices like a sedentary lifestyle, obesity, smoking, and too much alcohol can harm the prostate. A balanced lifestyle, including a healthy diet and exercise, is vital for prostate health.
What dietary factors can affect prostate health?
A diet high in fat, red meat, and dairy can harm the prostate. Eating protective foods and nutrients can help maintain health and reduce risk.
How can men reduce their risk of prostate problems?
Men can lower their risk by eating well, exercising, and getting regular check-ups. Supplements and preventive medications can also help, under a doctor’s guidance.
When should men seek medical attention for prostate symptoms?
Men should see a doctor for persistent or severe urinary symptoms, pelvic pain, or sexual function issues. Early detection and care are key to managing prostate problems.
What is the importance of regular screening for prostate health?
Regular screening helps catch prostate problems early, when they’re easier to treat. Screening guidelines vary based on age, risk factors, and individual needs. It’s important to discuss screening with a healthcare provider.
Can prostate cancer be prevented or detected early?
While prostate cancer can’t be prevented, early detection through screening can improve treatment outcomes. Understanding risk factors helps men take steps to reduce their risk.
References
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. (2025, August 10). Prostate problems. https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/prostate-problems









