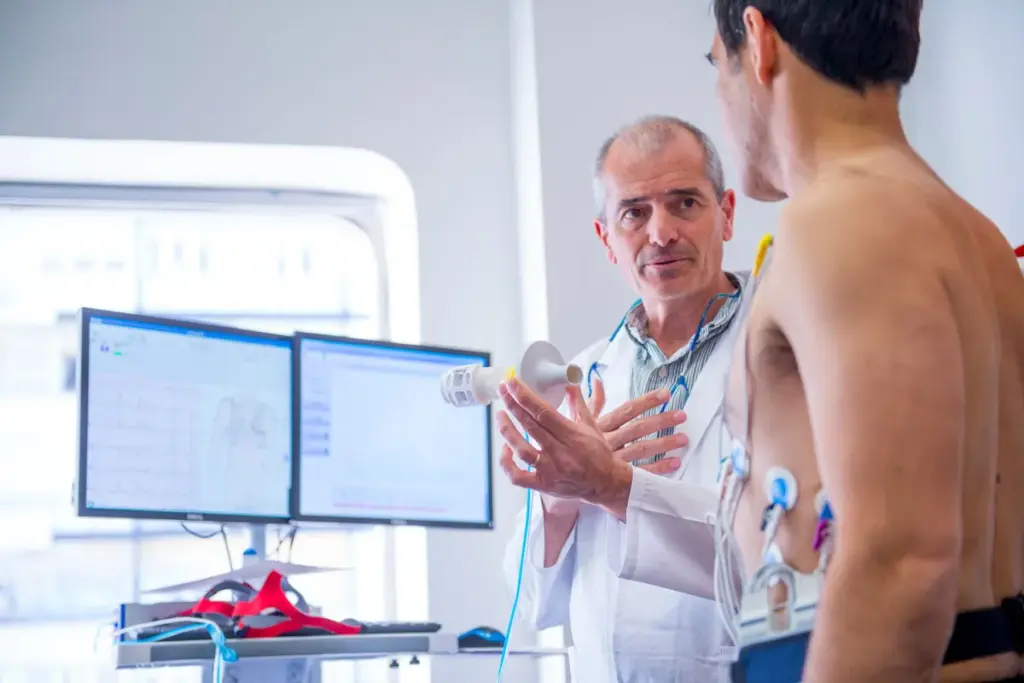

Every year, thousands of athletes push their bodies to the limit. The importance of sports cardiology has never been more pronounced. Athletes require specialized cardiac care to perform at their best while minimizing heart-related risks.
We explore the world of sports cardiology. Medical professionals work hard to keep athletes healthy. A sports cardiologist focuses on athletes’ heart health, providing care from routine check-ups to complex interventions.
Becoming a sports cardiologist requires rigorous education and training. They need to know how to handle athletes’ heart health. This includes cardiologist education requirements that prepare them for the unique demands.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the role of a sports cardiologist in athlete care.
- The importance of specialized cardiac care for athletes.
- Overview of the cardiology career path and education requirements.
- The unique demands of athletes’ heart health.
- The role of sports cardiologists in preventing heart-related issues.
The Role of a Sports Cardiologist
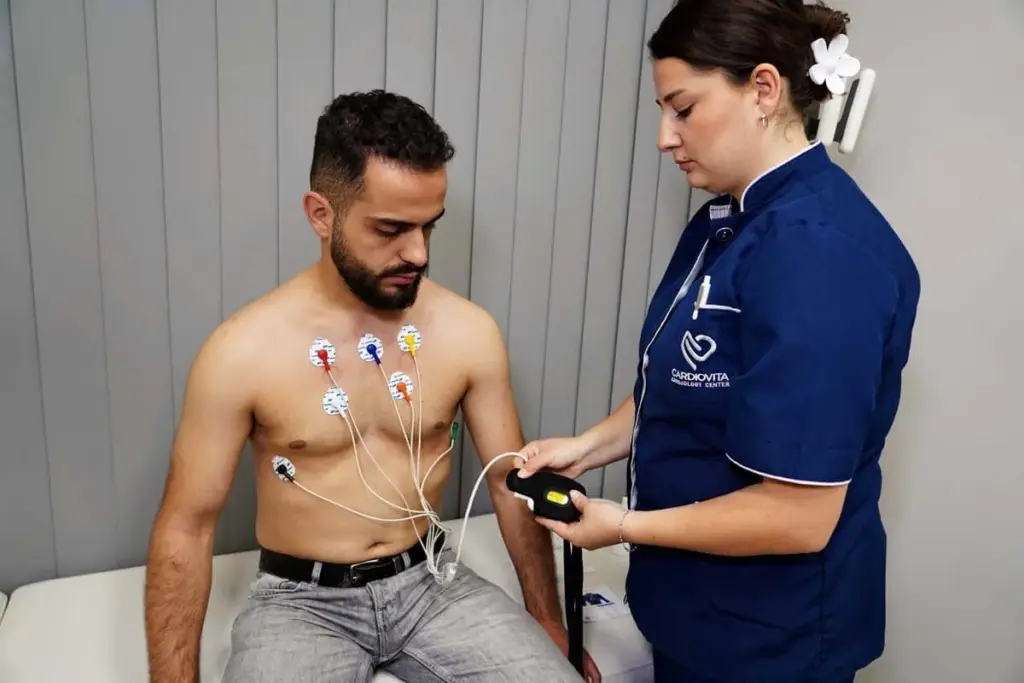
Sports cardiology is a new field that focuses on athletes’ heart health. It blends understanding heart health with physical performance. This area of cardiology deals with heart issues linked to exercise and sports.
Defining Sports Cardiology as a Specialty
Sports cardiology is all about athletes’ heart health. It looks at how an athlete’s heart changes and tells the difference between good changes and bad ones. It’s a mix of regular cardiology and knowing what athletes need.
Athletes have special heart needs because of their training. Sports cardiologists must know the difference between normal heart changes and serious problems. This is to prevent sudden cardiac death or other heart issues.
Key Responsibilities and Patient Population
Sports cardiologists diagnose and manage heart problems in athletes. They take medical histories, do physical checks, and use tests like ECGs and echocardiograms. They also help decide when athletes can go back to playing safely.
These doctors work with athletes, coaches, and other health experts. They help athletes stay healthy and perform well. Their patients are athletes of all ages and sports.
|
Key Responsibilities |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Diagnosis and Management |
Diagnosing and managing cardiovascular conditions in athletes, including the use of advanced diagnostic tests. |
|
Return-to-Play Guidance |
Providing guidance on when athletes can safely return to play after a cardiac event. |
|
Preventive Care |
Offering preventive care and advice on maintaining optimal cardiovascular health for athletes. |
Differences Between Sports Cardiologists and Other Cardiac Specialists
General cardiologists treat many heart conditions. Sports cardiologists focus on athletes’ heart health. They understand how exercise affects the heart.
Comparison with General Cardiologists
General cardiologists handle a wide range of heart diseases. Sports cardiologists focus on athletes’ heart health. They know how exercise affects the heart.
Sports cardiologists tailor care for athletes. They deal with athlete’s heart syndrome and arrhythmias caused by exercise. They also look at doping’s heart effects.
Sports cardiologists and general cardiologists differ in their care approach. Sports cardiologists consider how athletes’ bodies change with exercise. They look at heart rate and blood pressure changes.
Overlap with Sports Medicine Physicians
Sports cardiologists work with sports medicine physicians. Sports medicine doctors focus on athletes’ health and performance. They give advice on injuries and nutrition.
Sports cardiologists add to this care. They focus on athletes’ heart health. This team approach ensures athletes get all-around care.
Unique Focus Areas of Sports Cardiology
Sports cardiology has special areas of focus:
- Pre-participation screening for athletes to find heart risks
- Diagnosing and managing athlete-specific heart conditions
- Deciding when athletes can return to play after heart events
- Studying how exercise affects the heart
A top sports cardiologist, says, “Sports cardiology is growing fast. New tech and research help us understand exercise and heart health better.” This shows how sports cardiology keeps improving to help athletes.
“Athletes face unique heart challenges. Sports cardiologists lead in understanding and treating these issues.”
Sports Cardiologist
Why Sports Cardiology Has Become an Important Medical Field
Cardiac issues in athletes have made sports cardiology a key field. It’s vital for athletes’ health. This specialty is growing in importance.
The Rise of Cardiac Issues in Athletes
More athletes are facing heart problems. This calls for specialized care in sports cardiology. Factors like intense training and genetic risks are to blame.
Sports cardiology is key in addressing these issues. It helps athletes perform better and stay safe.
Preventing Sudden Cardiac Death in Sports
Sports cardiology is vital in stopping sudden cardiac death (SCD) in athletes. SCD can happen without warning, often due to hidden heart conditions. Sports cardiologists use screenings and tests to find at-risk athletes.
Early detection helps prevent such tragedies. It saves lives and gives peace of mind to athletes and their families.
Evolution of the Specialty in Modern Medicine
Sports cardiology has grown from a niche to a recognized specialty. New diagnostic tools and knowledge of athlete heart health have driven this growth. Today, it leads in medical innovation, using the latest research and techniques.
As we learn more about athlete heart health, sports cardiology’s role will grow. It will provide essential care and support to athletes worldwide.
Educational Background Required for Sports Cardiologists
To become a sports cardiologist, you need a deep educational journey. It starts with a solid undergraduate degree and goes through medical school and beyond. We’ll cover the essential steps and what makes you stand out in this field.
Undergraduate Education and Prerequisites
The journey to sports cardiology begins with an undergraduate degree. Most go for a bachelor’s in biology, chemistry, or physics. You’ll need to take courses like organic chemistry and biochemistry.
It’s important to have a good academic record. This boosts your chances of getting into medical school.
While in undergrad, try to get involved in research, volunteer, or internships. This experience is key for a strong medical school application.
Medical School Training
After undergrad, you’ll attend medical school. Here, you’ll earn an M.D. or D.O. degree. Medical school lasts four years, with both classroom learning and clinical rotations.
During clinical rotations, you’ll get real-world experience. This is your chance to see what being a doctor is like, including cardiology.
Competitive Factors for Cardiology Programs
After medical school, you’ll apply for internal medicine and cardiology programs. The competition is fierce. Your application will be judged on your grades, research, and letters of recommendation.
|
Competitive Factor |
Description |
Importance Level |
|---|---|---|
|
Academic Performance |
Strong grades and class rankings |
High |
|
Research Experience |
Publications, presentations, and research projects |
High |
|
Letters of Recommendation |
Endorsements from respected professionals |
Medium |
|
Personal Statement |
A compelling narrative outlining career goals |
Medium |
Knowing these factors can help you prepare a strong application for cardiology programs.
How to Become a Cardiologist: The Complete Pathway
Becoming a cardiologist is a long and challenging journey. It involves many stages of education and training. We will show you the path to cardiology certification, including the timeline and costs.
Step-by-Step Guide to Cardiology Certification
To become a cardiologist, you must follow several steps:
- Finish your undergraduate studies with a focus on sciences.
- Go to medical school to get an MD or DO degree.
- Complete a residency in internal medicine.
- Do a cardiology fellowship for specialized training.
- Get certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM).
Each step is important and builds on the last. This ensures cardiologists have the right knowledge and skills.
Timeline and Duration of Training
It takes over a decade to become a cardiologist after high school. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
|
Stage |
Duration |
|---|---|
|
Undergraduate Education |
4 years |
|
Medical School |
4 years |
|
Internal Medicine Residency |
3 years |
|
Cardiology Fellowship |
3 years |
|
Total Duration |
14 years |
The exact time may vary based on personal choices and extra training.
Costs and Financial Considerations
Getting a cardiologist degree is very expensive.
“The financial burden of medical education can be substantial, but it’s essential to consider the long-term benefits and earning capacity of a cardiology career.”
Cardiologist
Here are the estimated costs:
|
Educational Stage |
Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
|
Undergraduate Education (4 years) |
$100,000 – $200,000 |
|
Medical School (4 years) |
$200,000 – $400,000 |
|
Residency and Fellowship (6 years) |
Variable stipend; often minimal debt accumulation |
|
Total Estimated Cost |
$300,000 – $600,000 |
It’s important for those aiming to be cardiologists to plan for these costs. They should also look into financial aid options.
Specialized Training for Sports Cardiology
To specialize in sports cardiology, cardiologists need more than basic cardiology training. The field keeps growing, so staying current is key. It’s vital for sports cardiologists to know the newest research and best practices.
Additional Fellowships and Certifications
Cardiologists often get extra training in sports cardiology. They do fellowships that focus on athletes’ heart health. These programs teach about the special heart needs of athletes and common heart issues they face.
Getting certifications from groups like the American Board of Internal Medicine (ABIM) is also important. These certifications show cardiologists can handle athletes’ heart problems well.
Sports Medicine Integration
Working with sports medicine is a big part of sports cardiology training. Cardiologists team up with sports medicine doctors, trainers, and others. Together, they give athletes full care.
This teamwork helps create plans for athlete health checks, injury prevention, and managing heart issues. It’s all about keeping athletes safe and healthy.
Continuing Education Requirements
Staying up-to-date is essential for sports cardiologists. They must keep learning about new research, tech, and treatment methods. This includes going to conferences, workshops, and online courses focused on sports cardiology.
|
Continuing Education Activity |
Description |
Frequency |
|---|---|---|
|
Conferences and Symposia |
Attend events focused on sports cardiology to learn about the latest research and network with professionals. |
Annually |
|
Workshops and Hands-on Training |
Participate in practical training sessions to enhance skills in procedures and techniques relevant to sports cardiology. |
Bi-annually |
|
Online Courses and Webinars |
Engage in online educational programs to stay updated on the latest guidelines and research findings. |
Quarterly |
By getting more fellowships, working with sports medicine, and keeping up with education, sports cardiologists can give athletes the best care. This ensures athletes’ heart health and helps them perform at their best.
Daily Responsibilities of a Sports Cardiologist
A sports cardiologist’s day is filled with many tasks. They see patients, work with sports teams, and conduct research. This job requires a mix of clinical work, teamwork, and research.
Clinical Practice and Patient Consultations
We start by talking to athletes about their heart health. We look at their medical history, do physical checks, and run tests. Our goal is to help them stay safe and perform well.
Our job also includes:
- Doing electrocardiograms (ECGs) and understanding the results.
- Using echocardiograms to check the heart’s shape and how it works.
- Helping athletes plan their exercise and training based on their heart health.
Athletic Team Collaborations
Working with sports teams is key. We team up with coaches, trainers, and other doctors to care for athletes. This means:
- Checking if athletes are okay to play sports.
- Creating plans for emergencies during games.
- Going to team meetings to talk about athlete health and how to improve performance.
The American Heart Association says checking athletes before they play is very important. We follow the latest sports cardiology research and guidelines.
Research and Academic Responsibilities
Research and teaching are big parts of our job. They help us keep up with the latest in sports cardiology. We do:
- Studies on heart problems in athletes.
- Writing papers for scientific journals.
- Sharing our findings at conferences.
A leading researcher says new imaging and diagnostic tools are changing sports cardiology. They help us give better, more personal care to athletes. Our research aims to improve our understanding and treatment of heart health in athletes.
Diagnostic Tools Used by Sports Cardiologists
Sports cardiologists use many tools to check athletes’ heart health. These tools help find heart problems that could affect an athlete’s performance or safety.
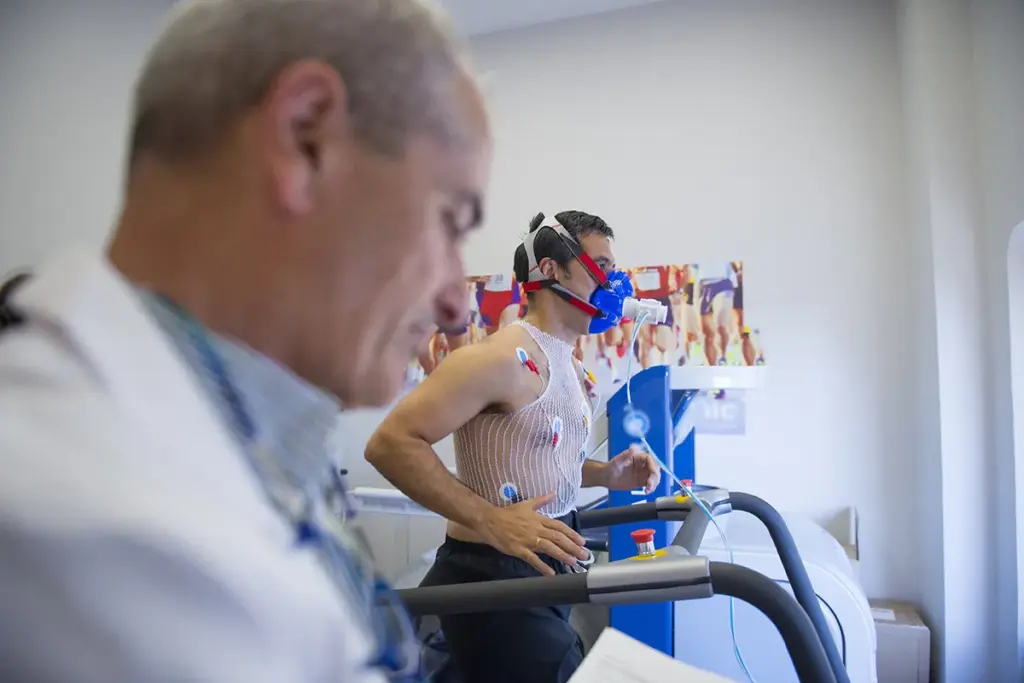
Electrocardiography (ECG) and Stress Testing
Electrocardiography (ECG) records the heart’s electrical activity. It spots arrhythmias and other heart issues. Stress testing, paired with ECG, checks how the heart works when stressed, usually through exercise or medicine.
Stress tests are key for spotting heart disease and seeing how the heart handles exercise. This is very important for athletes.
Echocardiography and Ultrasound
Echocardiography uses sound waves to make heart images. It’s a non-invasive way to check the heart’s shape and how it works. It’s great for looking at heart valves, finding birth defects, and measuring heart chambers.
Advanced Imaging Techniques
Cardiac MRI and CT scans give detailed heart pictures. They help find and treat complex heart problems.
|
Diagnostic Tool |
Purpose |
Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
|
Electrocardiography (ECG) |
Records heart’s electrical activity |
Detects arrhythmias and cardiac abnormalities |
|
Stress Testing |
Evaluates heart function under stress |
Identifies coronary artery disease, assesses heart’s response to exertion |
|
Echocardiography |
Creates images of the heart using ultrasound |
Assesses heart structure and function, detects congenital defects |
|
Advanced Imaging (MRI, CT) |
Provides detailed heart anatomy images |
Diagnoses complex cardiac conditions, aids in treatment planning |
Understanding Cardiac CT Scans in Sports Cardiology
Cardiac CT scans are a non-invasive way to check the heart’s structure and function. They are key in sports cardiology.
What is Computed Tomography in Cardiac Assessment
Computed Tomography (CT) scans use X-rays to make detailed images of the heart. In cardiac assessment, CT scans spot issues like coronary artery disease and cardiac structure problems. These can affect an athlete’s performance or health.
We use cardiac CT scans to fully understand the heart’s anatomy. This tool is very useful in sports cardiology. Here, accurate diagnoses are very important.
What a Cardiac CT Scan Shows
A cardiac CT scan shows detailed images of the heart’s structure. This includes the coronary arteries, chambers, and tissues around them. It can show conditions like coronary artery anomalies and cardiac hypertrophy.
The info from a cardiac CT scan is key for diagnosing and managing cardiac conditions in athletes. It helps us spot risks and plan treatments.
|
Condition |
What CT Scan Shows |
Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary Artery Disease |
Narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries |
Increased risk of heart attack |
|
Cardiac Hypertrophy |
Thickening of heart muscle |
Potential for arrhythmias and heart failure |
|
Coronary Artery Anomalies |
Abnormal origin or course of coronary arteries |
Increased risk of sudden cardiac death |
Preparation and Procedure for Cardiac CT
Before a cardiac CT scan, patients remove metal objects and wear a hospital gown. Sometimes, a contrast dye is used to make images clearer.
During the scan, the patient lies on a table that moves into a CT scanner. The scan takes just a few minutes. Then, a radiologist or cardiologist analyzes the images.
We make sure patients know what to expect. This helps reduce anxiety and makes the process smoother.
Interpreting Cardiac Imaging Results for Athletes
Understanding cardiac imaging results for athletes is complex. It’s important to know the difference between normal heart changes and serious issues. This helps keep athletes safe and healthy.
Normal vs. Abnormal Findings in Athletic Hearts
Athletes’ hearts often change in ways that might look bad on scans. For example, the heart muscle can get thicker. But, it’s key to tell if this is good or bad.
Good changes in the heart are balanced and healthy. Bad changes might look different and could mean the heart isn’t working right. MRI or CT scans can help figure this out.
Athlete’s Heart Syndrome vs. Pathological Conditions
Athlete’s heart syndrome is when an athlete’s heart changes in a good way because of exercise. It might be slower, thicker, and bigger. But, it’s important to know if this is just from exercise or if it’s a serious problem.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a serious issue that can cause sudden death in young athletes. It looks different on scans and needs a careful check-up to diagnose.
Using CT Scans to Detect Coronary Abnormalities
CT scans are great for finding problems in the heart’s arteries. They can spot issues that might cause sudden death in athletes. This is because they give clear pictures of the arteries.
When we look at CT scans, we’re looking for signs of trouble. Like if a heart artery starts in the wrong place. Modern CT scanners can show these details very clearly.
|
Imaging Modality |
Key Features |
Clinical Utility |
|---|---|---|
|
Coronary CT Angiography |
Detailed images of coronary arteries, detection of anomalies |
Highly effective in detecting coronary artery anomalies, risk stratification for sudden cardiac death |
|
Cardiac MRI |
Tissue characterization, assessment of cardiac function |
Useful in diagnosing cardiomyopathies, assessing myocardial fibrosis |
|
Echocardiography |
Assessment of cardiac structure and function, detection of hypertrophy |
Initial screening tool, useful for monitoring cardiac function |
In conclusion, understanding cardiac images in athletes is complex. We use advanced scans like CT and MRI to make sure athletes are healthy. This helps keep them safe and performing well.
Common Cardiac Conditions Treated by Sports Cardiologists
Sports cardiologists deal with many heart issues in athletes. These include structural heart problems and serious arrhythmias. They need special knowledge to keep athletes safe and healthy.
Structural Heart Abnormalities
Structural heart issues are a big worry in sports cardiology. These problems affect how the heart works. For example:
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) makes the heart muscle thick, blocking blood flow.
- Mitral valve prolapse means the valve between chambers doesn’t close right.
- Atrial septal defects (ASD) are holes in the upper heart chambers’ wall.
Doctors use advanced tests like echocardiography and cardiac MRI to find these problems.
Electrical Disorders and Arrhythmias
Electrical heart issues and arrhythmias are also key areas for sports cardiologists. These problems can make the heart beat irregularly. Examples include:
- Atrial fibrillation, a fast and irregular heart rhythm.
- Ventricular tachycardia, a fast heart rate from the lower chambers.
- Long QT syndrome, causing chaotic heartbeats.
Treatment might include medicine, lifestyle changes, or procedures like catheter ablation.
Coronary Artery Anomalies
Coronary artery anomalies are rare but serious. They can cause sudden death, often during hard exercise. Doctors use tests like coronary CT angiography to find these issues.
|
Condition |
Description |
Diagnostic Tools |
|---|---|---|
|
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy |
Thickening of the heart muscle |
Echocardiography, Cardiac MRI |
|
Atrial Fibrillation |
Irregular heart rhythm |
ECG, Holter Monitor |
|
Coronary Artery Anomalies |
Abnormal formation of coronary arteries |
Coronary CT Angiography |
It’s vital to understand and manage these heart conditions for athletes’ health and performance. Sports cardiologists are key in diagnosing and treating these issues. They help athletes stay safe while playing sports.
Pre-participation Screening and Evaluation
Sports cardiologists play a key role in checking athletes’ heart health before they start playing sports. This screening aims to find athletes at risk of heart problems during sports.
Protocols and Guidelines for Athletic Screening
Many guidelines exist for athlete screening. The American Heart Association (AHA) has a 14-element checklist. It includes a detailed medical history and physical exam. It looks for symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and fainting, and checks family history for sudden heart death.
There’s debate on using electrocardiography (ECG) in screening. Some say ECG should be part of it, mainly for high-risk athletes.
Risk Stratification for Athletes
Risk stratification is key in athlete screening. It sorts athletes by their risk of heart problems. Age, sport type, and medical history are considered. Those with heart issues or playing high-intensity sports are at higher risk.
This helps doctors suggest the right preventive steps and monitoring.
When to Recommend Advanced Cardiac Imaging
Not all athletes need advanced heart imaging like echocardiography or MRI for screening. It’s suggested when initial tests show issues or when there’s a strong heart disease suspicion. The choice for advanced imaging depends on the athlete’s risk factors and symptoms.
If an athlete shows signs of heart problems, more tests might be needed. This helps confirm the issue and plan the next steps.
Return-to-Play Decision Making
Deciding if an athlete can play sports again after a heart event is complex. Sports cardiologists like us are key in making this call. We check if it’s safe for them to play again.
Our evaluation looks at many factors. We consider how serious the heart event was, how well treatment worked, and the athlete’s heart health. This helps us decide if they’re ready to play.
Assessment Criteria After Cardiac Events
We look at several important things when checking if an athlete can play again. These include:
- Cardiac Function: We use tests like echocardiography and stress tests to check the heart.
- Risk Stratification: We look at the athlete’s past health, family history, and other factors to predict future risks.
- Symptoms and Clinical Presentation: We check for symptoms like chest pain, irregular heartbeats, or fainting.
Individualized Exercise Prescriptions
After a heart event, athletes need custom exercise plans. These plans are made just for them, based on their health and needs. They help balance exercise with heart safety.
|
Component |
Description |
Considerations |
|---|---|---|
|
Exercise Type |
Aerobic, resistance, or flexibility training |
Athlete’s sport, fitness level, and heart condition |
|
Intensity and Duration |
Gradual increase in intensity and time |
Watching heart rate, blood pressure, and symptoms |
|
Frequency |
How often to exercise per week |
Considering recovery time and heart risk |
Monitoring and Follow-up Protocols
Athletes need regular monitoring and check-ups after heart events. This ensures their safety and the success of their exercise plan. We adjust their plan as needed.
By following these steps, we lower the risk of heart problems. This helps athletes safely get back to their sports.
Career Outlook and Salary Expectations
The need for sports cardiologists is growing fast. This is because more people are focusing on heart health in athletes. This growth means good job chances for those who specialize in this field.
Job Market for Sports Cardiologists
The job market for sports cardiologists is booming. There’s a big push to prevent sudden heart deaths in sports and manage heart issues in athletes. This makes sports cardiologists very sought after by teams, universities, and private practices.
Key factors driving the demand include:
- More people are getting into sports and physical activities.
- There’s more awareness of heart health issues in athletes.
- New technologies are improving how we diagnose and treat heart problems.
Compensation Ranges and Factors
Sports cardiologists are among the top earners in medicine. How much they make depends on where they work, their experience, and who they work for. Those in high-demand places or with professional sports teams often earn more.
Typical factors influencing salary include:
- Years of experience and specialization
- Where they live and the cost of living
- The type of employer (academic, private practice, sports team)
Practice Settings and Opportunities
Sports cardiologists can work in many places. They can choose from private practices, universities, hospitals, and professional sports teams. This lets them pick the best fit for their career and personal life.
Opportunities in different settings include:
- Working directly with patients
- Doing research and teaching
- Working with sports teams and organizations
As the field grows, we’ll see even more chances for sports cardiologists. This will make their careers even more promising.
Conclusion
Sports cardiology is a key medical field that looks after athletes’ heart health. It’s about preventing, finding, and treating heart problems in athletes. These doctors need special skills and knowledge.
To become a sports cardiologist, you need a lot of education. This includes going to college and medical school. Then, you get special training and certifications. It’s all about understanding how to care for athletes’ hearts.
In short, sports cardiology is more than just treating heart issues. It’s about keeping athletes safe and healthy. As more athletes need heart care, sports cardiologists will play a bigger role. This shows how important and challenging this career path is.
FAQ
What is sports cardiology, and why is it important?
Sports cardiology is a medical field that focuses on athletes’ heart health. It helps prevent, diagnose, and treat heart issues. These issues can affect athletes’ performance and health.
What does a sports cardiologist do?
A sports cardiologist checks and manages athletes’ heart health. They give advice on exercise and decide when athletes can return to play after heart events.
How does one become a sports cardiologist?
To be a sports cardiologist, one must go to medical school and complete a cardiology residency. They also need specialized training in sports cardiology, like fellowships and certifications.
What is the difference between a sports cardiologist and a general cardiologist?
Sports cardiologists focus on athletes’ heart health. General cardiologists care for a wider range of patients.
What diagnostic tools do sports cardiologists use?
They use tools like electrocardiography, stress testing, and echocardiography. They also use advanced imaging, like cardiac CT scans.
What is a cardiac CT scan, and how is it used in sports cardiology?
A cardiac CT scan is a non-invasive test that shows the heart and blood vessels. It helps find heart problems and check overall heart health.
How do sports cardiologists interpret cardiac imaging results?
They look at imaging results to find normal and abnormal findings. They consider the athlete’s condition and medical history.
What are some common cardiac conditions treated by sports cardiologists?
They treat heart problems like structural issues, electrical disorders, and coronary artery anomalies.
What is pre-participation screening, and why is it important?
Pre-participation screening checks an athlete’s heart health before sports. It helps find heart risks and prevent sudden death.
How do sports cardiologists make return-to-play decisions?
They decide when athletes can play again by checking their heart health. They also consider the risk of more heart problems and create exercise plans.
What is the career outlook for sports cardiologists?
The job outlook for sports cardiologists is good, with more demand for their specialized care. They can work in hospitals, clinics, or private practices.
How much do sports cardiologists typically earn?
Their salaries vary based on location, experience, and where they work. Generally, they earn well, similar to other cardiology specialists.
References
National Center for Biotechnology Information. Evidence-Based Medical Insight. Retrieved from https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29167199/





