Many women feel anxious about medical imaging procedures. A transvaginal ultrasound is a tool used to see inside the female reproductive organs. It gives a clear view of the inside, helping doctors find and treat problems.
This internal ultrasound is great for checking the reproductive organs’ health. Doctors use it to understand symptoms and plan treatments.
In this article, we’ll talk about what a transvaginal ultrasound is and why it’s important. We’ll also cover what it can show and what to expect during the procedure.
Key Takeaways
- A transvaginal ultrasound is a diagnostic tool used to visualize the female reproductive organs.
- It provides a clear and detailed view of the internal structures.
- This type of internal ultrasound is useful in assessing reproductive health.
- The procedure helps healthcare providers diagnose and treat various conditions.
- It is an important tool in gynecological diagnostics.
What Is a Transvaginal Ultrasound?
Transvaginal ultrasound is a tool used to see the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic areas. It uses a special probe inserted into the vagina. This probe captures detailed images of the reproductive organs.
Definition and Basic Principles
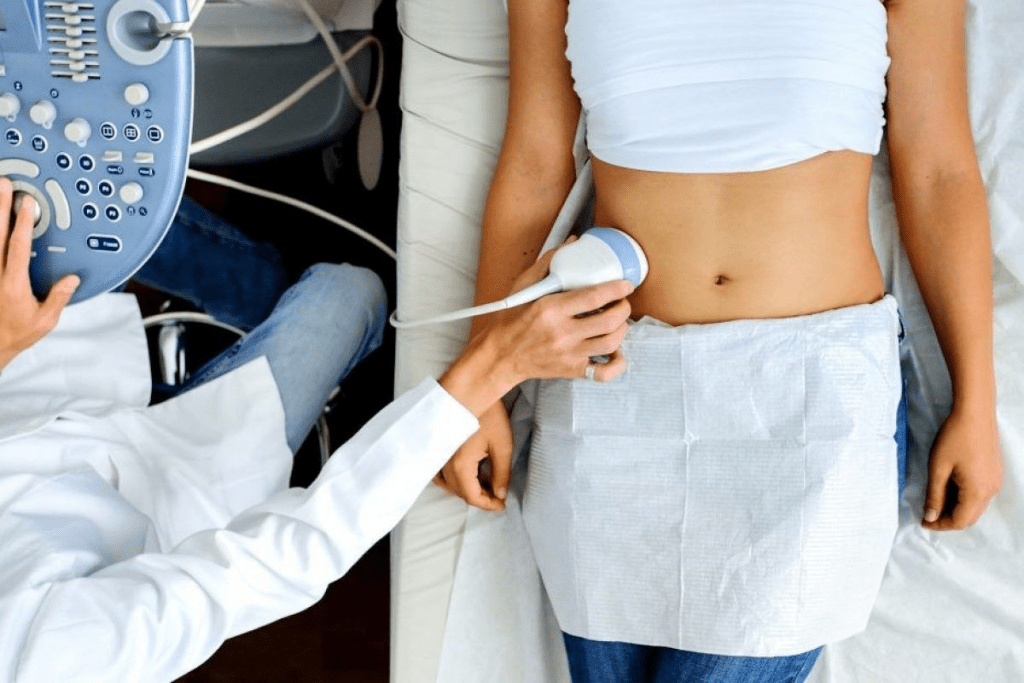

A transvaginal ultrasound is when a probe is inserted into the vagina to see the female reproductive organs. It works by sending high-frequency sound waves. These waves bounce off organs and return to the probe, creating images.
The transvaginal ultrasound definition includes the technique and the technology. It’s great for looking at the uterus, ovaries, cervix, and more in the pelvic area.
Comparison with Abdominal Ultrasound
Abdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound are different. An abdominal ultrasound uses a probe on the abdomen to see organs. It’s good for many things but not as detailed as a transvaginal ultrasound for deep pelvic areas.
Transvaginal ultrasounds give clearer images because the probe is closer. This means less distortion and better views of reproductive organs. It’s great for diagnosing issues related to these organs.
| Characteristics | Abdominal Ultrasound | Transvaginal Ultrasound |
| Probe Location | On the abdomen | Inserted into the vagina |
| Image Resolution | General, may be lower for deep pelvic structures | High, for reproductive organs |
| Diagnostic Use | Broad, including obstetric and abdominal conditions | Detailed for female reproductive organs |
In summary, both abdominal and transvaginal ultrasounds are useful. But, the choice depends on what you need to see and the detail required. For many gynecological issues, a transvaginal ultrasound is the best choice for clear images.
The Technology Behind the Ultrasound Wand
Understanding the ultrasound wand’s technology is key to seeing its importance in medicine. The transvaginal ultrasound probe has changed gynecology and obstetrics a lot.
Transvaginal Ultrasound Probe Design
The transvaginal ultrasound probe is made to get top-notch images. It has a high-frequency transducer at the tip for clear sonographic images of the reproductive organs. Its size and shape are designed for comfort and image quality.
The ultrasound wand comes with a sterile sheath and gel for easy use. This makes the exam less uncomfortable and works smoothly.
How Sonographic Images Are Generated
Creating sonographic images starts with high-frequency sound waves from the probe’s tip. These sound waves go through tissues and organs in the pelvic area. When they hit different densities, they bounce back as echoes.
The echoes are caught by the transducer and turned into electrical signals. The ultrasound machine then makes these signals into real-time images on the screen. This lets doctors see inside the body in detail.
The quality of the sonographic images depends on the transducer’s frequency and the ultrasound machine’s quality. New tech has made transvaginal ultrasound a must-have in today’s medicine.
Medical Reasons for a Transvaginal Ultrasound
Gynecologists use transvaginal ultrasounds for many reasons. This tool gives a detailed look at the female reproductive organs. It helps doctors diagnose and manage different conditions.
Diagnostic Indications
Transvaginal ultrasounds help check several gynecological symptoms and conditions. Some key uses include:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding
- Pelvic pain or cramping
- Suspected ectopic pregnancy
- Ovarian cysts or masses
- Uterine abnormalities such as fibroids or polyps
These uses show how important transvaginal ultrasounds are. They give clear images of the reproductive organs. This helps doctors make accurate diagnoses.
Screening and Monitoring Purposes
Transvaginal ultrasounds are also used for screening and monitoring. They help in:
- Monitoring fetal development during early pregnancy
- Assessing the thickness of the endometrium
- Evaluating the cervix for possible issues
- Guiding certain gynecological procedures
Healthcare providers use transvaginal ultrasounds for these tasks. This allows them to offer proactive care and timely interventions.
In conclusion, transvaginal ultrasounds are key in diagnosing and monitoring gynecological conditions. Their ability to provide detailed images makes them essential in modern gynecological care.
Preparing for Your Transvaginal Procedure
We guide you through the steps to prepare for your transvaginal ultrasound procedure, ensuring you’re well-informed.
A transvaginal ultrasound is a routine diagnostic procedure. It requires some preparation for a smooth and comfortable experience. Knowing what to expect can help reduce anxiety and make you feel more at ease.
Before the Appointment Instructions
To prepare for your transvaginal ultrasound, follow these guidelines:
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water before your appointment. This helps ensure a full bladder, improving ultrasound image quality.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable clothing that is easy to remove. You will be asked to undress from the waist down.
- Arrive Early: Plan to arrive 10-15 minutes before your scheduled appointment. This allows time to complete any necessary paperwork.
What to Expect Upon Arrival
Upon arrival, you will be greeted by our friendly staff. They will guide you through the check-in process. You will then be taken to a private examination room where the procedure will be explained in detail.
Our goal is to make you feel as comfortable and relaxed as possible throughout the process.
| Preparation Step | Description |
| Registration | Complete necessary paperwork and provide any required insurance information. |
| Pre-Procedure Explanation | Our medical staff will explain the transvaginal ultrasound procedure, answer any questions, and address any concerns. |
| Examination | The transvaginal ultrasound will be performed by a trained healthcare professional. |
By being prepared and understanding what to expect, you can make your transvaginal ultrasound experience as smooth and stress-free as possible.
The Transvaginal Ultrasound Procedure Step by Step
When you have a transvaginal ultrasound, you’ll go through a safe and helpful process. This test looks at the female reproductive organs. It helps doctors decide on the best treatment or care.
Who Performs the Examination
A trained healthcare professional does the ultrasound. This could be a sonographer or an obstetrician/gynecologist. They know how to use the equipment and understand the images. Their skill is key to getting accurate and useful results.
Positioning and Process Details
To start, you’ll lie on an exam table with your legs in stirrups. This is like a pelvic exam. Then, a small probe is gently put into your vagina.The probe is designed to maximize comfort while still providing clear diagnostic images.
The doctor will move the probe to get pictures from different angles. These images will show up on a screen for you to see. The whole thing is done carefully to make you as comfortable as possible.
How Long Does a Transvaginal Ultrasound Take?

A transvaginal ultrasound usually takes 15 to 30 minutes. The time can vary based on the exam’s purpose and the images needed. Most people find it quick and easy.
“The transvaginal ultrasound procedure is a valuable diagnostic tool that provides critical information about the female reproductive health. Its ability to offer detailed images of the organs makes it an indispensable resource in gynecological care.”
Knowing what happens in a transvaginal ultrasound helps you prepare. It can make you feel less anxious and make the experience smoother.
Does a Transvaginal Ultrasound Hurt?
Many people worry about pain or discomfort during a transvaginal ultrasound. But knowing what to expect can ease these fears. We’re here to explain what sensations and discomfort you might feel during the procedure.
Common Sensations and Discomfort Levels
Some women might feel a bit of discomfort during a transvaginal ultrasound. But for most, it’s not painful. How much discomfort you feel can depend on your anxiety and how sensitive you are to pain.
Common sensations include feeling a bit of pressure or slight discomfort when the probe is inserted or moved. This feeling is usually mild and short-lived. Also, the probe is smaller than a speculum used in a routine pelvic exam, which many find more comfortable.
Tips for Reducing Anxiety and Discomfort
To lessen discomfort and anxiety during a transvaginal ultrasound, try these steps:
- Breathing techniques: Deep, slow breaths can help relax your body and mind.
- Communication: Tell your healthcare provider about your anxiety or discomfort. They can offer reassurance and adjust their technique as needed.
- Relaxation: Trying to relax your pelvic muscles can make the procedure more comfortable.
By understanding the process and taking steps to relax, most women find the discomfort is minimal and short-lived. We’re committed to making your experience as comfortable as possible.
What Does a Transvaginal Ultrasound Show?
A transvaginal ultrasound gives a detailed look at the female reproductive organs. It’s key for checking the health of the pelvic area. We use it to see both normal and abnormal structures.
Normal Pelvic Anatomy Visualization
During a transvaginal ultrasound, we can see the pelvic organs clearly. This includes the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix. The ultrasound shows detailed images of these organs’ size, shape, and position.
For example, it can measure the uterus’s lining thickness. This is important for checking menstrual health and fertility. It also lets us count and size the ovaries’ follicles.
Common Abnormal Findings
Transvaginal ultrasounds also spot abnormalities. Common ones are cysts, fibroids, polyps, and other masses. These can cause symptoms like pelvic pain, heavy bleeding, or trouble getting pregnant.
Here are some common abnormal findings and their symptoms:
| Condition | Description | Typical Symptoms |
| Ovarian Cysts | Fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries | Pelvic pain, bloating |
| Uterine Fibroids | Non-cancerous growths in the uterus | Heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure |
| Endometrial Polyps | Growths on the lining of the uterus | Irregular bleeding, infertility |
Spotting these conditions helps doctors plan the right treatment. Transvaginal ultrasounds are key in gynecology. They help find and manage pelvic problems early.
Uterine Examination Through Internal Ultrasound
Internal ultrasound is a key tool for checking the uterus. It shows detailed images of the uterus. This helps doctors understand its health well.
We use it to see the uterus clearly. This is important for diagnosing and treating gynecological issues.
Normal Uterine Appearance and Measurements
The uterus looks like a pear on ultrasound. Its size and shape can differ. But, there are standard measurements.
The length of the uterus is usually 7 to 8 cm. It’s 4 to 5 cm wide and 2 to 3 cm thick in non-pregnant women.
The endometrium’s thickness changes with the menstrual cycle. It’s 1-2 mm early in the cycle and 7-16 mm later.
Detecting Uterine Abnormalities and Conditions
Internal ultrasound is great at finding uterine issues. It spots fibroids, polyps, and adhesions. Fibroids look like dark spots in the wall. Polyps are bright spots inside the endometrium.
It also finds birth defects like a unicornuate or bicornuate uterus. These can affect fertility and pregnancy. It checks the endometrium for endometrial hyperplasia or cancer.
Ovarian and Fallopian Tube Assessment
We use transvaginal ultrasounds to check the health of ovaries and fallopian tubes. This tool is key for spotting issues that might affect women’s reproductive health.
Normal Ovarian Structure and Function
The ovaries are key for making eggs and hormones. These hormones help control the menstrual cycle and support pregnancy. A normal ovary looks like an oval with many small follicles. Transvaginal ultrasound lets us see the ovaries’ size, shape, and follicle count. This gives us clues about how well the ovaries are working.
Identifying Cysts, Masses, and Tubal Conditions
Transvaginal ultrasound is great at finding ovarian cysts, masses, and fallopian tube issues. Cysts are fluid-filled sacs on the ovaries. Masses can be harmless or cancerous. The fallopian tubes might have problems like hydrosalpinx, where they fill with fluid, or tubal ectopic pregnancy.
| Condition | Ultrasound Characteristics | Clinical Significance |
| Ovarian Cyst | Anechoic or hypoechoic structure within the ovary | May cause pelvic pain or be asymptomatic |
| Tubal Ectopic Pregnancy | Adnexal mass separate from the ovary, with or without cardiac activity | Life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical attention |
| Hydrosalpinx | Dilated fallopian tube filled with anechoic fluid | Associated with infertility and increased risk of ectopic pregnancy |
By carefully checking ovaries and fallopian tubes, doctors can spot many conditions. This includes everything from harmless cysts to serious ectopic pregnancies. This helps doctors treat patients quickly and effectively.
Cervical Evaluation via Vaginal Ultrasound
Cervical evaluation via vaginal ultrasound is key in gynecology. It lets us see the cervix in detail. This gives us insights into its structure and any issues.
Cervical Length and Structure Measurement
Vaginal ultrasounds help measure cervical length accurately. Accurate cervical length measurement is key in spotting preterm labor and other pregnancy issues. We can also check the cervical structure, like the internal and external os, for any problems.
A study in a Journal found that cervical length by ultrasound predicts preterm birth well.
“The measurement of cervical length by transvaginal ultrasound has become an essential tool in the assessment of women at risk for preterm labor.”
Detecting Cervical Changes and Abnormalities
Vaginal ultrasounds are great at spotting cervical changes and issues, like shortening or lesions. Early detection means we can act fast, helping patients better. We can also find cervical insufficiency, which needs careful watching or treatment.
Using vaginal ultrasound for cervical checks has greatly improved our ability to diagnose and manage cervical problems. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists says, “Transvaginal ultrasound is a valuable tool in the evaluation of the cervix, mainly in pregnant women.”
With vaginal ultrasound, we can give our patients the best care for their cervical health. We do this with great precision and accuracy.
Transvaginal Ultrasound in Pregnancy
Transvaginal ultrasound is a key tool in early pregnancy. It gives clear images of the embryo. This is very important for checking the health and growth of the fetus in the first stages of pregnancy.
Early Pregnancy Visualization Timeline
One big plus of transvaginal ultrasound is seeing the embryo early. You can spot the gestational sac as early as 4.5 to 5 weeks. Then, the yolk sac and embryo become visible around 5.5 to 6 weeks.
As pregnancy goes on, this ultrasound keeps giving detailed pictures. It helps doctors watch how the fetus is growing and spot any problems early.
| Gestational Age | Visible Structures |
| 4.5-5 weeks | Gestational sac |
| 5.5-6 weeks | Yolk sac and embryo |
| 6-7 weeks | Fetal heartbeat |
Detecting Complications and Ectopic Pregnancies
Transvaginal ultrasound is also key in finding problems like ectopic pregnancies. These are when the embryo grows outside the uterus. Finding them early is very important for the mother’s health.
“The use of transvaginal ultrasound has significantly improved the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancies, allowing for timely intervention.” –
OB-GYN Specialist
With transvaginal ultrasound, doctors can spot issues early. This means they can give the right care and help to pregnant women.
Diagnosing Gynecological Conditions
Transvaginal ultrasounds have changed how we diagnose gynecological conditions. They give detailed views of women’s reproductive health. Accurate diagnosis is key for effective treatment.
These ultrasounds are clear and effective for diagnosing many conditions. They show the reproductive organs in high detail. This helps doctors spot problems and plan treatments.
Fibroids, Polyps, and Endometrial Issues
Fibroids, polyps, and endometrial issues can cause a lot of discomfort. Transvaginal ultrasounds are great for finding these problems.
- Fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or around the uterus. They can lead to heavy bleeding and pain.
- Polyps grow on the uterus lining and can cause irregular bleeding.
- Endometrial issues, like thickening or cancer, can also be found with these ultrasounds.
| Condition | Symptoms | Diagnostic Features on Transvaginal Ultrasound |
| Fibroids | Heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain | Hypoechoic or heterogeneous masses within the uterus |
| Polyps | Irregular menstrual bleeding | Pedunculated or sessile growths on the endometrial lining |
| Endometrial Hyperplasia/Cancer | Abnormal uterine bleeding | Thickened endometrium, irregular endometrial texture |
Endometriosis, Adenomyosis, and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Endometriosis, adenomyosis, and PID can also be checked with transvaginal ultrasounds.
Endometriosis is when endometrial tissue grows outside the uterus. It causes pain and infertility. Ultrasounds can spot endometriomas, related to endometriosis.
Adenomyosis is when endometrial tissue grows into the uterine wall. It leads to heavy bleeding and pain. Ultrasounds can show an enlarged uterus with mixed textures.
PID is an infection of the reproductive organs. It can cause infertility and chronic pain if not treated. Ultrasounds can spot signs like tubal damage or abscesses.
Using transvaginal ultrasounds, doctors can accurately diagnose these conditions. This helps them create effective treatment plans, improving patient outcomes.
Pelvic Ultrasound vs. Transvaginal Ultrasound
It’s important to know the differences between pelvic and transvaginal ultrasounds. Both are used in gynecological exams but serve different purposes. They offer unique benefits for patients and healthcare providers.
Key Differences in Approach and Imaging
Pelvic and transvaginal ultrasounds differ in how they are done and the images they give. A pelvic ultrasound scans the pelvic area from the outside. It uses a transducer that moves over the skin to see the internal organs.
A transvaginal ultrasound, on the other hand, uses a special transducer inserted into the vagina. This gives clearer images of the reproductive organs.
Pelvic Ultrasound: This method is easy and shows the whole pelvic area. It’s good for finding big problems or issues that don’t need detailed images.
Transvaginal Ultrasound: Because the transducer is closer, it gives sharper images. It’s better for spotting small problems or checking the uterine lining and ovarian follicles.
| Characteristics | Pelvic Ultrasound | Transvaginal Ultrasound |
| Approach | Abdominal | Vaginal |
| Image Clarity | General view | High-resolution |
| Usefulness | Detecting larger abnormalities | Assessing smaller structures and details |
When Each Method Is Preferred or Combined
Choosing between pelvic and transvaginal ultrasound depends on the situation. For early pregnancy, a transvaginal ultrasound is often better. It shows the embryo and gestational sac clearly. A pelvic ultrasound might be used first to check for big problems or to look at the whole pelvic area.
“The selection between pelvic and transvaginal ultrasound should be guided by the clinical context and the information required for patient care.” – Expert Opinion
Sometimes, both methods are used together. For example, a pelvic ultrasound might be done first. Then, a transvaginal ultrasound might be used for a closer look if needed.
Knowing the strengths and limits of each ultrasound helps doctors make the best choice. This ensures patients get the right care for their needs.
Understanding Transvaginal Ultrasound Results
Getting your transvaginal ultrasound results can feel both relieving and exciting. We’re here to help you understand what these results mean. We’ll explain what the images show and what might happen next.
Interpreting Your Ultrasound Report
Your ultrasound report is a detailed document. It shows what your transvaginal ultrasound found. It talks about the uterus, ovaries, and other pelvic areas. We’ll make it clear what these details mean for your health.
Look for parts of your report that describe your reproductive organs’ size, shape, and health. Any odd findings will be pointed out. We’ll tell you what these could mean for your overall health.
When Additional Testing Is Recommended
At times, your ultrasound results might suggest you need more tests. This could be more imaging, blood work, or a visit to a specialist. We’ll talk about why this is needed and what you can expect next.
Remember, more testing is often necessary for a correct diagnosis and care. We’re here to support you, giving you the info and reassurance you need.
By understanding your ultrasound results, you’re taking charge of your health. We’re dedicated to helping you through every step. From interpreting your results to any actions that follow.
Safety and Limitations of Transvaginal Sonography
Transvaginal ultrasound is mostly safe, but knowing its limits is key for good care. We’ll look at its safety and what it can’t do.
Safety Profile and Considerations
Transvaginal ultrasound is safe with little risk. It uses non-ionizing waves, not radiation. This makes it safe for many, including pregnant women. But, it’s an invasive procedure.
Some might find it uncomfortable or feel anxious. The probe goes into the vagina. This is usually okay, but not for everyone.
Key safety considerations include:
- Proper training and expertise of the healthcare provider performing the procedure
- Use of appropriate infection control measures
- Patient comfort and consent throughout the procedure
It’s also important to think about who can’t have it. Some vaginal or cervical conditions might make it not safe.
What Transvaginal Ultrasound Cannot Detect
Transvaginal ultrasound is very useful, but it’s not perfect. It can miss some things. For example, it can’t see what’s outside the pelvic area. Also, things like bowel gas or obesity can make images less clear.
Some limitations include:
- Detecting conditions outside the pelvic region
- Visualizing structures behind or within bony or gas-filled areas
- Diagnosing certain types of soft tissue abnormalities that require other imaging modalities like MRI
Knowing these limits helps doctors understand what they see. It helps them decide if more tests are needed.
Conclusion
We’ve looked into transvaginal ultrasounds, a key tool in gynecology. This method gives a clear view of the female reproductive system. It helps doctors spot and track different health issues.
A transvaginal ultrasound conclusion is key in diagnosis. It shows the health of the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes. This info helps doctors plan the best treatment.
Understanding transvaginal ultrasounds helps doctors diagnose issues like fibroids and endometriosis. It also helps in tracking pregnancies and spotting any problems early.
In short, transvaginal ultrasounds are essential for women’s health. They offer a safe way to diagnose and manage gynecological problems. As medical tech advances, their role will grow even more.
FAQ
What is a transvaginal ultrasound?
A transvaginal ultrasound is a medical imaging technique. It uses a special probe to show detailed images of the female reproductive organs from inside the vagina.
Is a transvaginal ultrasound painful?
Some discomfort might be felt, but it’s not usually painful. The amount of discomfort can differ from person to person.
How long does a transvaginal ultrasound take?
The time needed for a transvaginal ultrasound varies. It usually takes about 15 to 30 minutes.
What can a transvaginal ultrasound show?
It can show detailed images of the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, and cervix. This helps diagnose conditions like fibroids, cysts, and ectopic pregnancies.
How do I prepare for a transvaginal ultrasound?
You might need to arrive with a full bladder and wear comfortable clothes. You’ll need to undress from the waist down. Specific instructions may vary.
What is the difference between a pelvic ultrasound and a transvaginal ultrasound?
A pelvic ultrasound is done externally. A transvaginal ultrasound involves a probe inserted into the vagina for more detailed images.
Can a transvaginal ultrasound detect pregnancy complications?
Yes, it can detect early pregnancy complications like ectopic pregnancies and issues with the embryo’s development.
Are transvaginal ultrasounds safe?
When done by trained professionals, transvaginal ultrasounds are safe. They don’t use radiation and are a valuable diagnostic tool.
How do I understand my transvaginal ultrasound results?
Understanding your results involves looking at the images and report from the healthcare professional. They can explain the findings and what to do next.
Can a transvaginal ultrasound diagnose all gynecological conditions?
While it’s a powerful tool, it has its limits. Some conditions might need more tests or procedures for a full evaluation.
References
- Chiu, S., Staley, H., Jeevananthan, P., et al. (2025). Ovarian Cancer Screening: Recommendations and Future Prospects. Rofo. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-2589-5696

































