ASGS (Parotidectomy) – Diagnosis and Tests uses specialized imaging (Ultrasound, MRI), biopsy, and facial nerve testing to confirm tumors and plan surgery.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
The diagnosis of a lump in the parotid gland is a careful process. It starts with a doctor feeling the area and then confirming the lump’s nature using simple imaging tests.
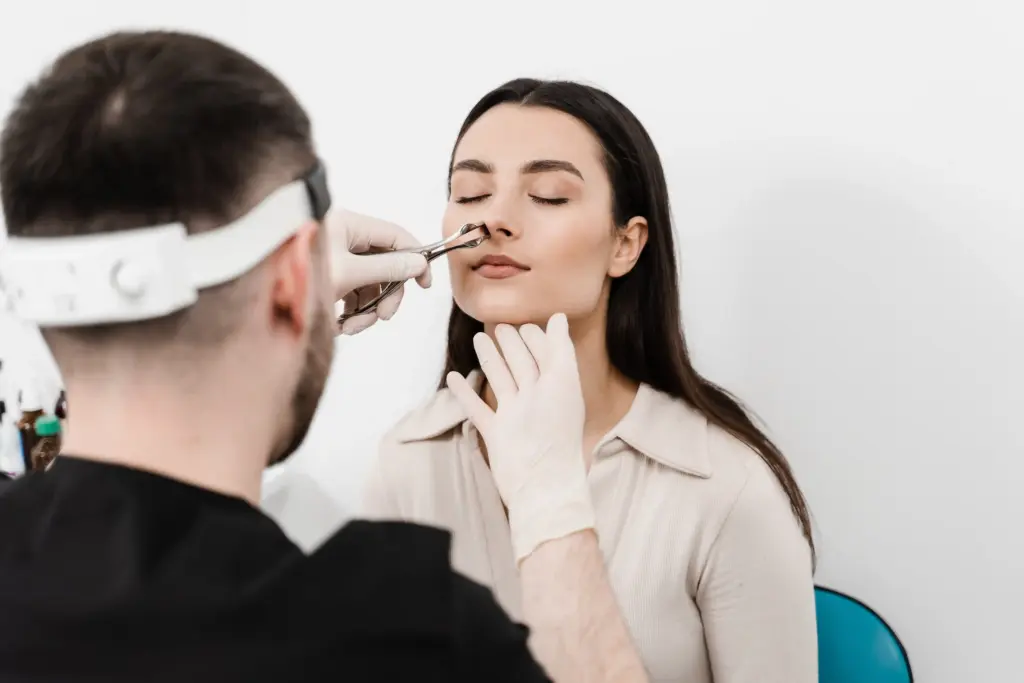
Advanced diagnostic methods are mandatory before Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy). These tests provide the detailed map needed to confirm the tumor type and plan the operation to protect the facial nerve.
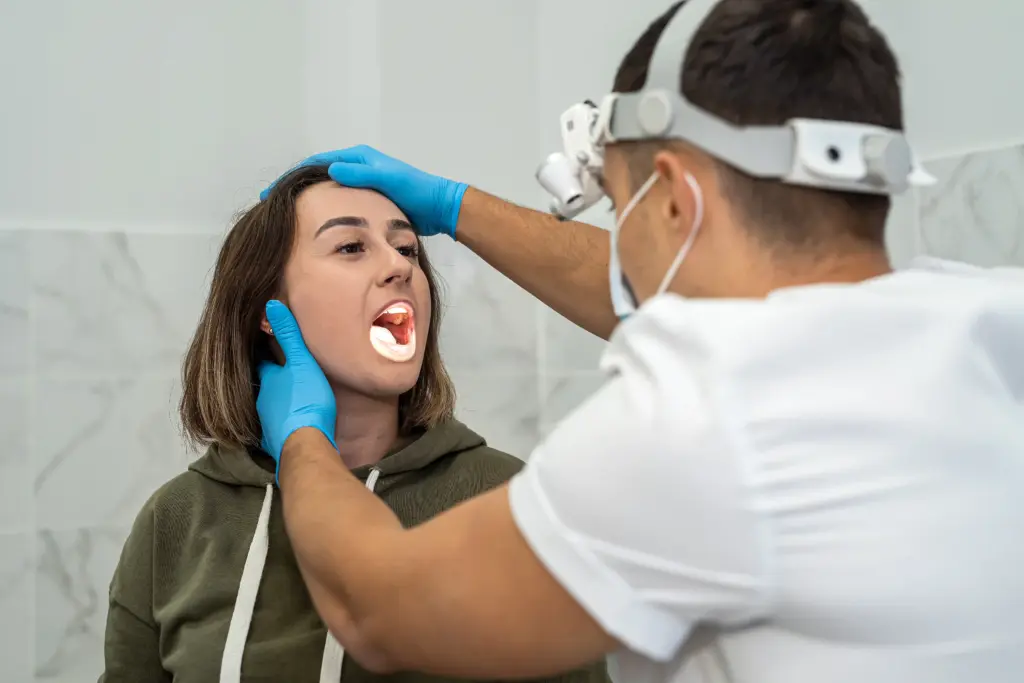
The Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy is a key step in diagnosing a parotid mass. It is a simple, quick procedure done in the doctor’s office or imaging clinic.
Doctors combine the results of the imaging scans (MRI/CT) and the FNA biopsy to form a complete picture. These results determine the final surgery type (e.g., superficial vs. total parotidectomy).
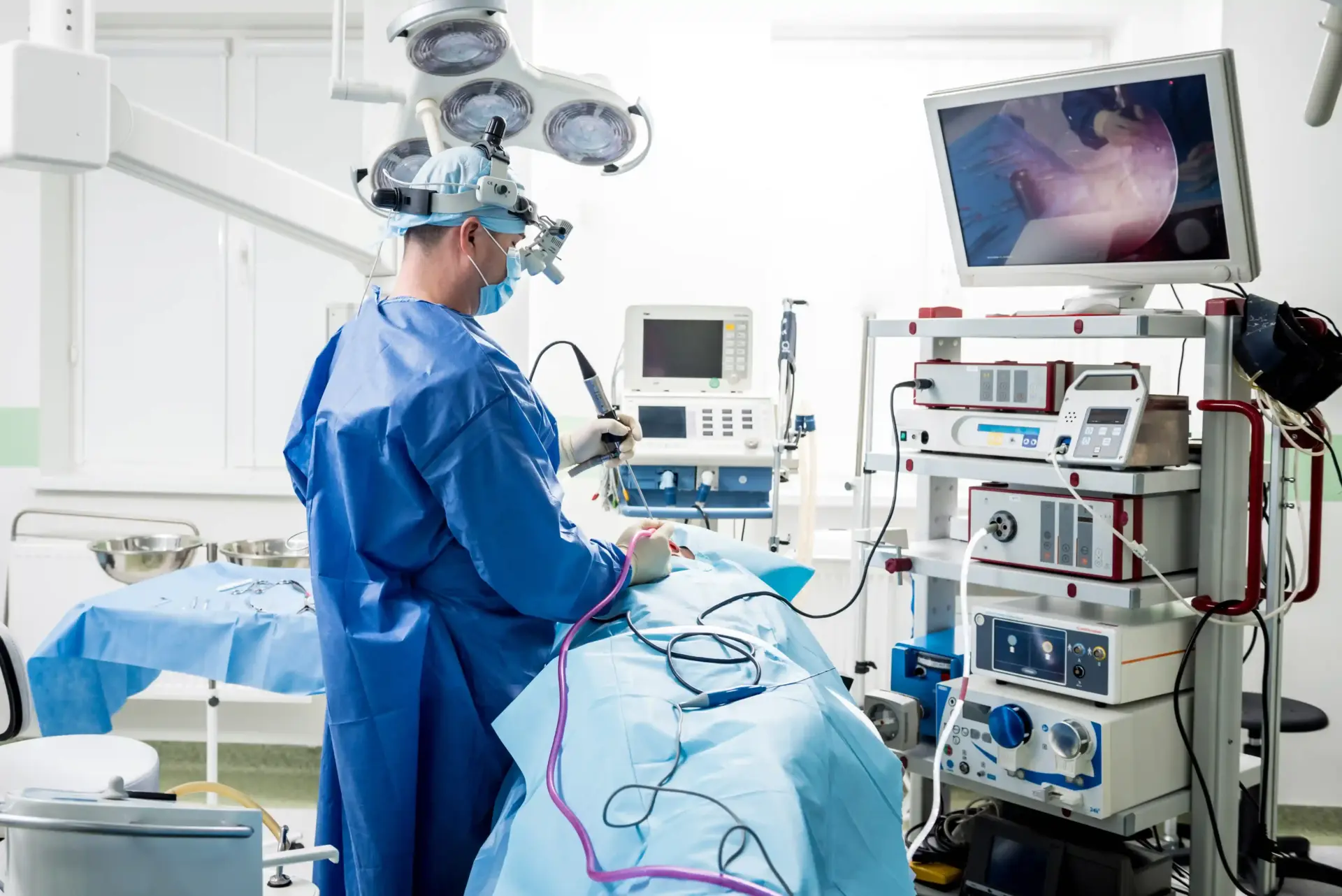
Preparation for advanced imaging and biopsy is generally simple. Following these steps helps ensure the clearest possible images and most accurate test results.
After completing your Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) biopsy and imaging tests, here is what you can expect regarding results and the next steps for finalizing your surgical plan:
You need advanced imaging immediately when a painless lump is confirmed by a physical exam or ultrasound. A complete diagnosis is required before any surgery.
Send us all your questions or requests, and our expert team will assist you.
Diagnosis requires a physical exam, imaging tests (Ultrasound/MRI), and a Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy to confirm the tumor type.
You will need to remove all metal objects for the MRI. If undergoing an FNA biopsy, you must tell the doctor about any blood-thinning medications.
No, the Auricular Salivary Gland Surgery (Parotidectomy) procedure for General diagnosis is usually not painful. The area is often numbed, and the procedure is quick.
The MRI is highly accurate for visualizing the nerve, and the FNA biopsy is highly accurate for confirming whether the lump is cancerous (malignant).
Yes, the parotid gland is the largest salivary gland. However, after its removal, the other glands usually increase their production to compensate, so overall saliva production remains mostly normal.


Why do you have a deviated septum? Learn easy ultimate cause facts and find effective ways to treat the pain and breathe better instantly. A

Millions of people worldwide suffer from allergic rhinitis. This condition can really affect their quality of life. Using an air purifier might help manage its

Allergic rhinitis affects millions worldwide, causing significant discomfort and impacting quality of life. Research has shown that certain nutrients can play a key role in

Did you know millions of people worldwide have a condition where their immune system attacks their own tissues? This leads to ongoing allergic reactions. Autoimmune

Listing common causes for extended hoarseness and addressing hoarseness timing concern (laryngitis, GERD, vocal abuse). hoarseness timing concern Having a hoarse voice for months can

Did you know that sinusitis sickness can make you feel really tired and exhausted? It’s not just the usual congestion and facial pressure. Many people

Leave your phone number and our medical team will call you back to discuss your healthcare needs and answer all your questions.
Your Comparison List (you must select at least 2 packages)